SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 1127-1139.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.05.006
• Special topic on the Yunnan Yangbi MS6.4 and Qinghai Maduo MS7.4 earthquakes • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZHANG Bin1)( ), LI Xiao-jun1),*(
), LI Xiao-jun1),*( ), RONG Mian-shui1), YU Yan-xiang2), WANG Yu-shi1), WANG Ji-xin1)
), RONG Mian-shui1), YU Yan-xiang2), WANG Yu-shi1), WANG Ji-xin1)
Received:2021-06-15
Revised:2021-07-25
Online:2021-10-20
Published:2021-12-06
Contact:
LI Xiao-jun
张斌1)( ), 李小军1),*(
), 李小军1),*( ), 荣棉水1), 俞言祥2), 王玉石1), 王继鑫1)
), 荣棉水1), 俞言祥2), 王玉石1), 王继鑫1)
通讯作者:
李小军
作者简介:张斌, 男, 1989年生, 2019年于中国地震局地球物理研究所获固体地球物理学专业博士学位, 助理研究员, 主要研究方向为地震动衰减关系和地震动特性, E-mail: vincent_zhang0322@163.com。
基金资助:CLC Number:
ZHANG Bin, LI Xiao-jun, RONG Mian-shui, YU Yan-xiang, WANG Yu-shi, WANG Ji-xin. ANALYSIS OF STRONG GROUND MOTION CHARACTERISTICS AND EARTHQUAKE DAMAGE FOR THE YANGBI MS6.4 EARTHQUAKE, YUNNAN[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2021, 43(5): 1127-1139.
张斌, 李小军, 荣棉水, 俞言祥, 王玉石, 王继鑫. 云南漾濞 MS6.4地震强震动特征和震害分析[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1127-1139.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.dzdz.ac.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.05.006
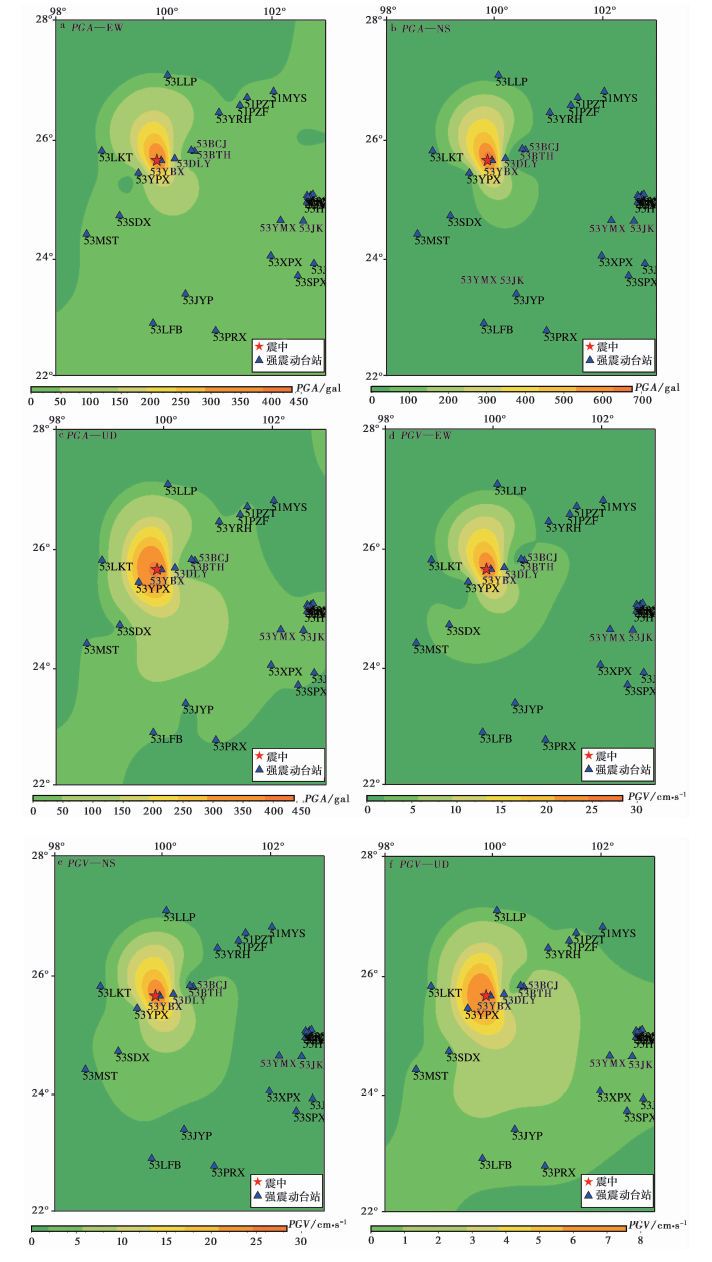
Fig. 2 Contours of peak ground acceleration(PGA)and peak ground velocity(PGV)of the Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake recorded by strong motion stations with epicenter distance less than 360km.
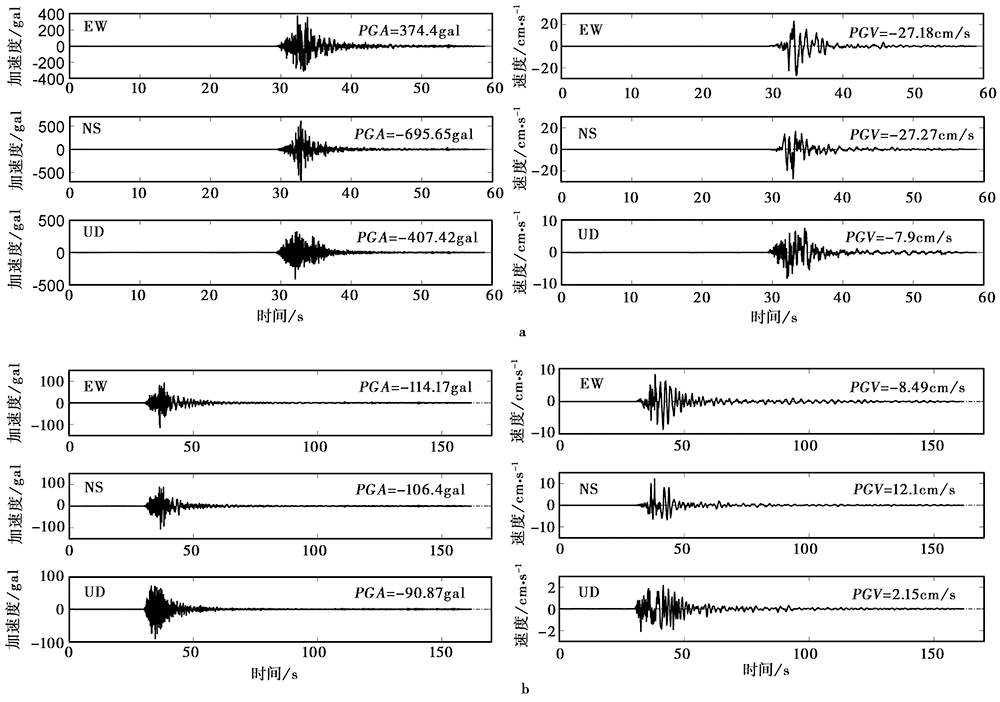
Fig. 3 Acceleration and velocity time histories during the Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake recorded by station 53YBX(Repi=8.03km)(a)and 53DLY(Repi=33.18km)(b).
| 台站名称 | 台站 代码 | 场地 类型 | 震中距 /km | PGA/gal | PGV/cm·s-1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EW | NS | UD | EW | NS | UD | ||||
| 漾濞台 | 53YBX | 土层 | 8.03 | 374.40 | -695.65 | -407.42 | -27.18 | -27.27 | -7.90 |
| 月溪井台 | 53DLY | 土层 | 33.18 | -114.17 | -106.40 | -90.87 | -8.49 | 12.10 | 2.15 |
| 永平台 | 53YPX | 土层 | 41.31 | -44.43 | -66.98 | 3.31 | -6.70 | ||
| 太和台 | 53BTH | 基岩 | 66.88 | -7.58 | -6.64 | 6.36 | -0.50 | 0.66 | -0.51 |
| 宾川县地震局台 | 53BCJ | 土层 | 72.13 | -22.96 | -25.19 | -17.48 | -2.74 | -2.71 | 1.46 |
Table1 Ground motion parameters of strong-motion recording at epicenter distances less than 100km observed in the Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake
| 台站名称 | 台站 代码 | 场地 类型 | 震中距 /km | PGA/gal | PGV/cm·s-1 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EW | NS | UD | EW | NS | UD | ||||
| 漾濞台 | 53YBX | 土层 | 8.03 | 374.40 | -695.65 | -407.42 | -27.18 | -27.27 | -7.90 |
| 月溪井台 | 53DLY | 土层 | 33.18 | -114.17 | -106.40 | -90.87 | -8.49 | 12.10 | 2.15 |
| 永平台 | 53YPX | 土层 | 41.31 | -44.43 | -66.98 | 3.31 | -6.70 | ||
| 太和台 | 53BTH | 基岩 | 66.88 | -7.58 | -6.64 | 6.36 | -0.50 | 0.66 | -0.51 |
| 宾川县地震局台 | 53BCJ | 土层 | 72.13 | -22.96 | -25.19 | -17.48 | -2.74 | -2.71 | 1.46 |
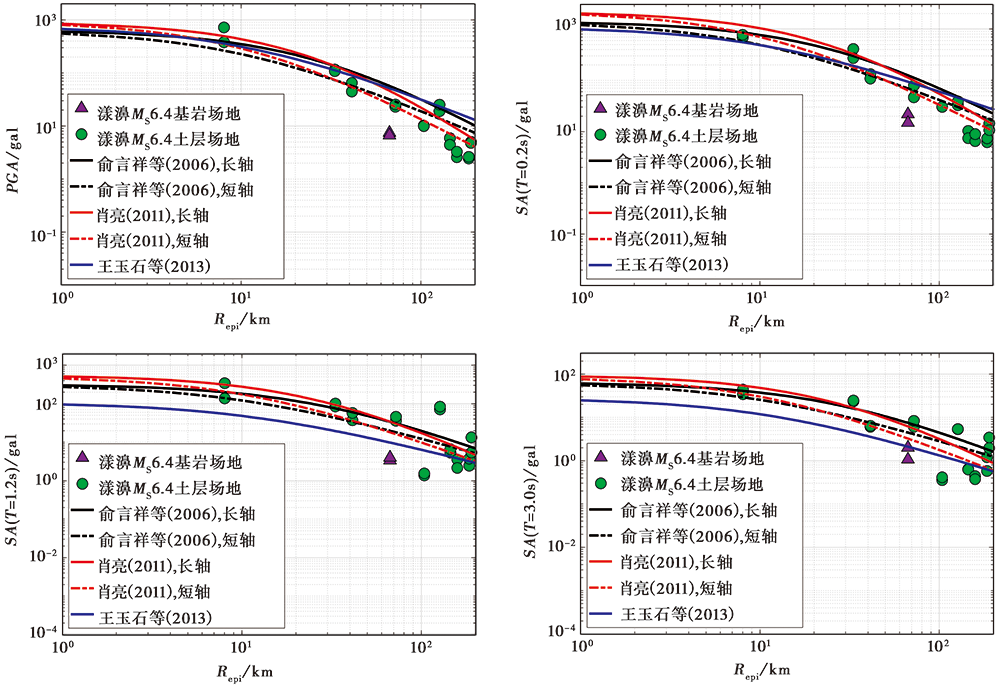
Fig. 4 Comparison of observed horizontal PGA and SA(T=0.2s, 1.2s, 3.0 s)of the Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake with the horizontal ground motion attenuation relation curves commonly used in China.
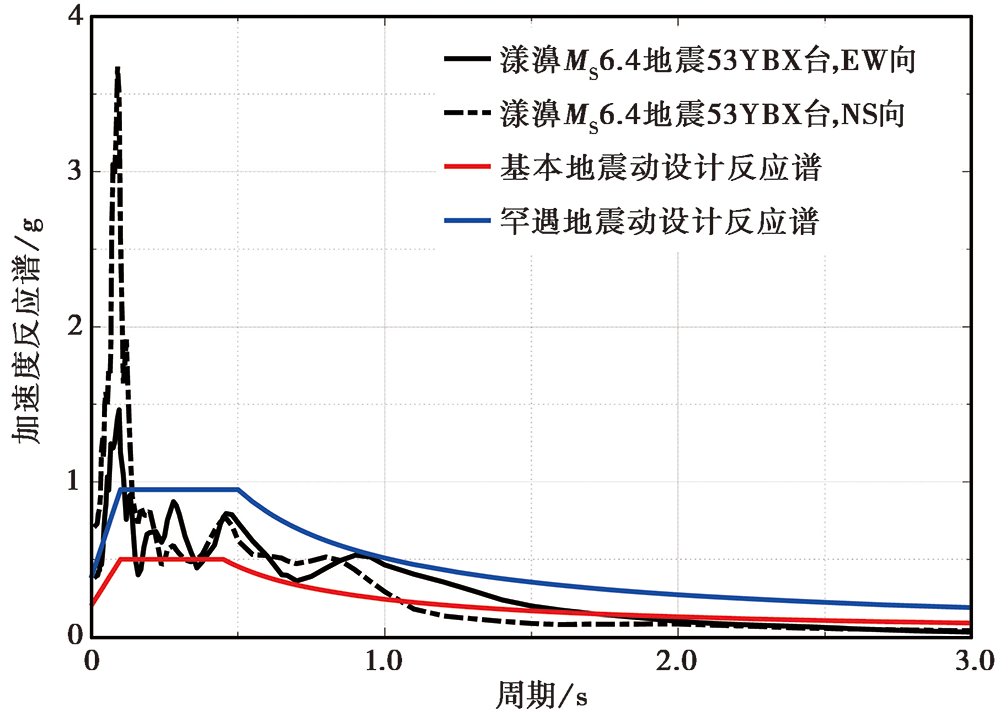
Fig. 6 Comparison of 5% damping acceleration response spectra in the EW and NS components of station 53YBX for the Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake with code design spectra.
| [1] | 胡聿贤, 周克森, 闫秀杰. 1996. 缺乏地震动加速度记录地区地震动估计的映射法[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 16(3): 1-10. |
|
HU Yu-xian, ZHOU Ke-sen, YAN Xiu-jie. 1996. A method for evaluation of ground motion in regions with few acceleration observation data[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 16(3): 1-10. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [2] | 王玉石, 李小军, 周正华. 2013. 川滇地区水平向强地震动衰减关系研究[J]. 地震学报, 35(2): 238-249. |
| WANG Yu-shi, LI Xiao-jun, ZHOU Zheng-hua. 2013. Research on attenuation relationships for horizontal strong ground motions in Sichuan-Yunnan region[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 35(2): 238-249. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 温瑞智, 任叶飞, 齐文浩, 等. 2013. 2013年4月20日芦山地震最大加速度记录分析[J]. 西南交通大学学报, 48(5): 783-791. |
| WEN Rui-zhi, REN Ye-fei, QI Wen-hao, et al. 2013. Maximum acceleration recordings from Lushan earthquake on April 20, 2013[J]. Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University, 48(5): 783-791. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 肖亮. 2011. 水平向基岩强地面运动参数衰减关系研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所: 153-154. |
| XIAO Liang. 2011. Study on the attenuation relationships of horizontal ground motion parameters near the source of rock site[D]. Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing: 153-154. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 俞言祥, 汪素云. 2006. 中国东部和西部地区水平向基岩加速度反应谱衰减关系[J]. 震灾防御技术, 1(3): 206-217. |
| YU Yan-xiang, WANG Su-yun. 2006. Attenuation relations for horizontal peak ground acceleration and response spectrum in eastern and western China[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 1(3): 206-217. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 张斌, 李小军, 俞言祥, 等. 2020. 鲁甸地震强震动记录与地震动衰减模型的对比研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(8): 2999-3014. |
| ZHANG Bin, LI Xiao-jun, YU Yan-xiang, et al. 2020. Comparison of strong ground motion records from Ludian, China, earthquake with ground-motion attenuation models[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(8): 2999-3014. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 中国地震局地球物理研究所. 2021. 2021年5月21日云南大理州漾濞县6.4级地震应急科技支撑简报[EB/OL].[2021-06-16]. www.cea-igp.ac.cn/kydt/278248.html. |
| Institute of Geophysics, China Earthquake Administration. 2021. Report on emergency measures taken in MS6.4 earthquake in Yangbi County, Dali Prefecture, Yunnan Province on May 21, 2021 [EB/OL].www.cea-igp.ac.cn/kydt/278248.html (in Chinese). | |
| [8] | 中华人民共和国城乡建设部. 2010. 建筑抗震设计规范(GB 50011-2010)[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社. |
| Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People’s Republic of China. 2010. Code for Seismic Design of Buildings(GB50011-2011)[S]. China Architecture & Building Press, Beijing (in Chinese). | |
| [9] | 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 2015. 中国地震动参数区划图(GB 18306-2015)[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社. |
| General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. 2015. Seismic Ground Motion Parameters Zonation Map of China(GB 18306-2015)[S]. China Standards Press, Beijing (in Chinese). | |
| [10] |
Ancheta T D, Darragh R B, Stewart J P, et al. 2014. NGA-West 2 database[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 30(3): 989-1005.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Atkinson G M, Silva W J. 2000. Stochastic modeling of California ground motions[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 90(2): 255-274.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Boore D M, Bommer J J. 2005. Processing of strong-motion accelerograms: Needs, options and consequences[J]. Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering, 25(2): 93-115.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Boore D M, Sisi A A, Akkar S. 2012. Using pad-stripped acausally filtered strong-motion data[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 102(2): 751-760.
DOI URL |
| [14] | Joyner W B, Boore D M. 1988. Measurement, characterization, and prediction of strong ground motion[C]. Earthquake Engineering and Soil Dynamics Ⅱ. Proceedings American Society Civil Engineering Geotechnical Engineering Division Specialty Conference, Park City, Utah: 43-102. |
| [15] |
Li X J, Zhou Z H, Huang M, et al. 2008a. Preliminary analysis of strong-motion recordings from the magnitude 8.0 Wenchuan, China, earthquake of 12 May 2008 [J]. Seismological Research Letters, 79(6): 844-854.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Li X J, Zhou Z H, Yu H Y, et al. 2008b. Strong motion observations and recordings from the great Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Earthquake Engineering and Engineering Vibration, 7(3): 235-246.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Trifunac M D, Brady A G. 1975. A study on the duration of strong earthquake ground motion[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 65(3): 581-626. |
| [18] |
Walling M, Silva W, Abrahamson N. 2008. Nonlinear site amplification factors for constraining the NGA models[J]. Earthquake Spectra, 24(1): 243-255.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Wessel P, Smith W H F. 1991. Free software helps map and display data[J]. Eos, Transactions American Geophysical Union, 72(41): 441-446. |
| [20] |
Xie J J, Li X J, Wen Z P, et al. 2014. Near-source vertical and horizontal strong ground motion from the 20 April 2013 MW68 Lushan earthquake in China[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 85(1): 23-33.
DOI URL |
| [1] | GOU Jia-ning, LIU Zi-wei, JIANG Ying, ZHANG Xiao-tong. GRAVITY PERTURBATION AND CHARACTERISTICS OF TEM-PORAL AND SPATIAL CHANGES OF BACKGROUND NOISE BE-FORE EARTHQUAKE: THE EXAMPLE OF MADUO MS7.4 AND YANGBI MS6.4 EARTHQUAKES [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(1): 252-268. |
| [2] | ZHANG Ke, WANG Xin, YANG Hong-ying, WANG Yue, XU Yan, LI Jing. THE CHARACTERISTICS AND SEISMOGENIC STRUCTURE ANALYSIS OF THE 2021 YANGBI MS6.4 EARTHQUAKE SEQUENCE, YUNNAN [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(1): 231-251. |
| [3] | FAN Wen-jie. CHARACTERISTICS OF TECTONIC STRESS FIELD AROUND THE YANGBI MS6.4 EARTHQUAKE AND ITS SURROUNDING AREAS ON MAY 21, 2021 AND ITS GEODYNAMIC IMPLICATION [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(1): 208-230. |
| [4] | YANG Jian-wen, JIN Ming-pei, YE Beng, GAO Qiong, CHEN Jia, ZHANG Hua-ying, DENG Jia-mei. A STUDY ON THE REGIONAL WAVE VELOCITY CHANGES BEFORE THE MS6.4 YANGBI EARTHQUAKE USING AMBIENT NOISE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2021, 43(5): 1171-1187. |
| [5] | LIU Dong, HAO Hong-tao, WANG Qing-hua, ZHENG Qiu-yue, HUANG Jiang-pei. GRAVITY FIELD CHANGE BEFORE THE 2021 YANGBI MS6.4 EARTHQUAKE, YUNNAN [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2021, 43(5): 1157-1170. |
| [6] | SONG Cheng-ke, CHEN Zheng-yu, ZHOU Si-yuan, XU Yu-jian, CHEN Bin. GEOMAGNETIC FIELD CHANGE BEFORE AND AFTER 2021 YANGBI MS6.4 EARTHQUAKE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2021, 43(4): 958-971. |
| [7] | LIANG Shan-shan, XU Zhi-guo, ZHANG Guang-wei, ZOU Li-ye, LIU Yan-qiong, GUO Tie-long. GEOMETRIC COMPLEXITY OF FAULT SYSTEM IN THE SOURCE REGION OF THE 2021 YANGBI, YUNNAN, MS6.4 EARTHQUAKE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2021, 43(4): 827-846. |
| [8] | QI Yu-ping, LONG Feng, LIN Sheng-jie, XIAO Ben-fu, ZHAO Xiao-yan, WANG Pei-ling, FENG Jian-gang. A STUDY ON THE EARTHQUAKE SEQUENCE TYPE IN THE MIDDLE SECTION OF THE NORTH-SOUTH SEISMIC BELT AND ITS SURROUNDING REGIONS [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2021, 43(1): 177-196. |
| [9] | YANG Yu, YANG Xiao-song, DUAN Qing-bao. NUMERICAL SIMULATION OF TEMPORAL-SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION OF PORE-FLUID PRESSURE INDUCED BY ZIPINGPU RESERVOIR IMPOUNDMENT [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2015, 37(2): 510-523. |
| [10] | TIAN Ying-ying, XU Chong, XU Xi-wei, WU Sai-er, CHEN Jian. SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION ANALYSIS OF COSEISMIC AND PRE-EARTHQUAKE LANDSLIDES TRIGGERED BY THE 2014 LUDIAN MS6.5 EARTHQUAKE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2015, 37(1): 291-306. |
| [11] | YI Gui-xi, WEN Xue-ze, ZHANG Zhi-wei, LONG Feng, RUAN Xiang, DU Fang. STUDY ON POTENTIAL STRONG EARTHQUAKE RISK IN MABIAN AREA,SOUTHERN SICHUAN [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2010, 32(2): 282-293. |
| [12] | Xiang Hongfa, Guo Shunmin, Zhang Wanxia, Zhang Bingliang. RIVER OFFSET AND SLIP RATE OF THE EAST SEGMENT OF ALTUN TAGH FAULT ZONE SINCE QUATERNARY [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2000, 22(2): 129-138. |
| [13] | Ma Jin, Liu Liqiang, Ma Shengli, Deng Zhihui. A DISCUSSION ON THE DISTURBANT STRESS FIELD IN COMPLEX FAULT SYSTEM AND IDENTIFICATION OF SEISMOGENIC FAULT [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 1995, 17(4): 372-382. |
| [14] | Ma Jin, Ma Shengli, Liu Liqiang. THE STAGES OF ANOMALIES BEFORE AN EARTHQUAKE AND THE CHARACTERISTICS OF THEIR SPATIAL DISTRIBUTION [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 1995, 17(4): 363-371. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||