SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 1073-1084.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.05.003
• Special topic on the Yunnan Yangbi MS6.4 and Qinghai Maduo MS7.4 earthquakes • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Jing-wei1,2)( ), CHEN Chang-yun1),*(
), CHEN Chang-yun1),*( ), ZHAN Wei1), WU Yan-qiang1)
), ZHAN Wei1), WU Yan-qiang1)
Received:2021-05-31
Revised:2021-08-11
Online:2021-10-20
Published:2021-12-06
Contact:
CHEN Chang-yun
李经纬1,2)( ), 陈长云1),*(
), 陈长云1),*( ), 占伟1), 武艳强1)
), 占伟1), 武艳强1)
通讯作者:
陈长云
作者简介:李经纬, 男, 1989年生, 2016年于中国地质大学(武汉)获测绘科学与技术硕士学位, 工程师, 主要从事GPS数据处理与地壳形变分析研究, E-mail: li-jingwei@cug.edu.cn。
基金资助:CLC Number:
LI Jing-wei, CHEN Chang-yun, ZHAN Wei, WU Yan-qiang. RESEARCH ON FAST ACQUISITION OF GNSS COSEISMIC HORIZONTAL DISPLACEMENT OF MADUO MS7.4 EARTHQUAKE IN QINGHAI PROVINCE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2021, 43(5): 1073-1084.
李经纬, 陈长云, 占伟, 武艳强. 青海玛多7.4级地震GNSS同震水平位移的快速获取[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1073-1084.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.dzdz.ac.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.05.003
| 测站名称 | UTC 00:00—09:00 | UTC 09:00—18:00 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | E | N | E | |
| DLHA | -0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
| GSJT | 0.3 | -0.1 | -0.3 | -0.3 |
| GSLZ | -0.7 | -1.2 | 1.4 | 0.3 |
| GSMA | -0.1 | -0.6 | -0.5 | 1.0 |
| GSMX | 1.0 | -0.2 | -0.4 | 0.8 |
| QHBM | -1.8 | -1.1 | 1.4 | 1.0 |
| QHDL | -0.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| QHGE | 0.1 | -1.6 | -0.2 | 0.4 |
| QHMD | -1.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 | -0.8 |
| QHME | -0.7 | -0.5 | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| QHMQ | 0.6 | 0.1 | -0.5 | 0.7 |
| QHYS | 4.6 | -0.4 | 2.1 | -1.6 |
| SCGZ | 0.4 | -1.9 | -1.5 | 2.5 |
| SCLH | 1.9 | -1.7 | -0.2 | 0.7 |
| SCMX | 0.7 | 0.7 | -0.8 | -1.0 |
| SCSP | 0.4 | -1.0 | -0.4 | 1.2 |
| SCXJ | -0.2 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| XNIN | -1.0 | -0.7 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| XZCD | 2.3 | -0.5 | -2.5 | -0.2 |
Table1 The difference of coordinate values obtained from data of different time periods (UTC 00:00—18:00 as the benchmark)(unit: mm)
| 测站名称 | UTC 00:00—09:00 | UTC 09:00—18:00 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | E | N | E | |
| DLHA | -0.1 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.0 |
| GSJT | 0.3 | -0.1 | -0.3 | -0.3 |
| GSLZ | -0.7 | -1.2 | 1.4 | 0.3 |
| GSMA | -0.1 | -0.6 | -0.5 | 1.0 |
| GSMX | 1.0 | -0.2 | -0.4 | 0.8 |
| QHBM | -1.8 | -1.1 | 1.4 | 1.0 |
| QHDL | -0.6 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 0.3 |
| QHGE | 0.1 | -1.6 | -0.2 | 0.4 |
| QHMD | -1.2 | 2.2 | 2.2 | -0.8 |
| QHME | -0.7 | -0.5 | 1.1 | 0.4 |
| QHMQ | 0.6 | 0.1 | -0.5 | 0.7 |
| QHYS | 4.6 | -0.4 | 2.1 | -1.6 |
| SCGZ | 0.4 | -1.9 | -1.5 | 2.5 |
| SCLH | 1.9 | -1.7 | -0.2 | 0.7 |
| SCMX | 0.7 | 0.7 | -0.8 | -1.0 |
| SCSP | 0.4 | -1.0 | -0.4 | 1.2 |
| SCXJ | -0.2 | 0.7 | 0.2 | 0.0 |
| XNIN | -1.0 | -0.7 | 0.8 | 0.5 |
| XZCD | 2.3 | -0.5 | -2.5 | -0.2 |
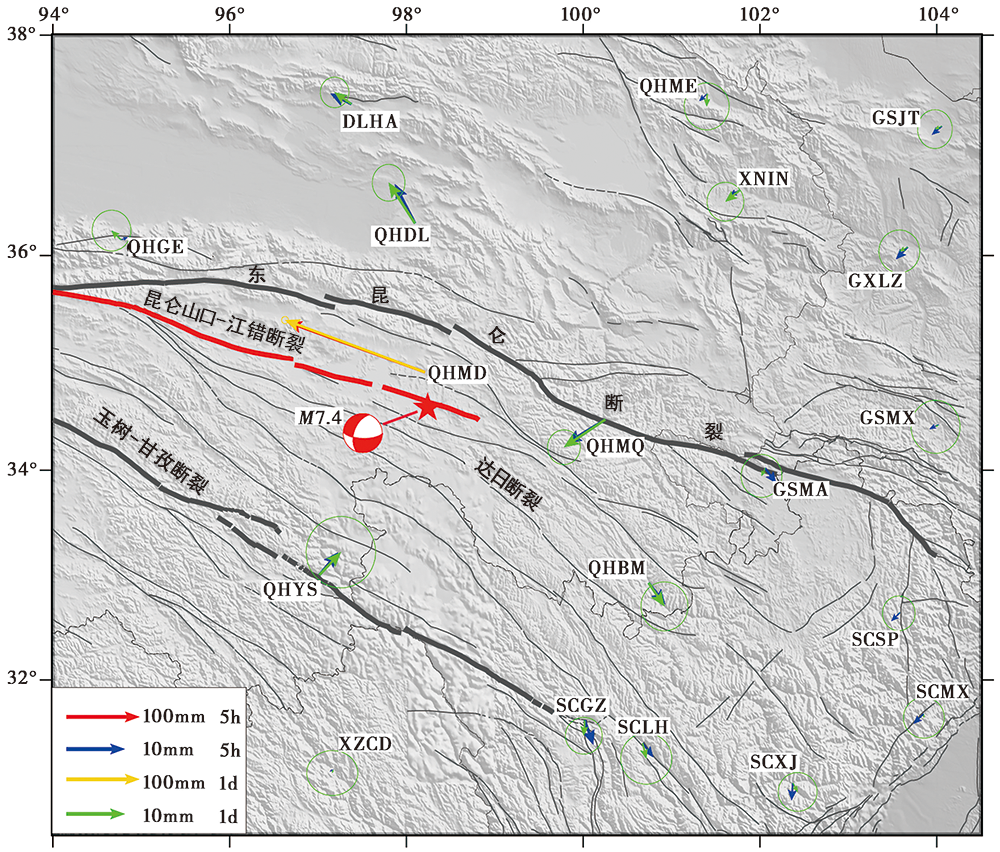
Fig. 3 Coseismic displacement obtained respectively from the GNSS station’s five-hour and multi-day solutions of the MS7.4 Maduo earthquake in Qinghai Province.
| 测站名称 | 震后5h | 多天 | 差值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | E | N | E | N | E | |
| DLHA | 2.9 | -5.7 | 3.2 | -4.6 | -0.3 | -1.1 |
| GSJT | -2.3 | -2.7 | -0.8 | -1.9 | -1.5 | -0.8 |
| GSLZ | -3.3 | -3.2 | -1.2 | -2.3 | -2.0 | -0.9 |
| GSMA | -4.1 | 3.0 | -2.1 | -1.0 | -2.0 | 4.0 |
| GSMX | -1.2 | -2.5 | -0.6 | -0.9 | -0.6 | -1.6 |
| QHBM | -5.8 | 4.5 | -6.4 | 4.3 | 0.7 | 0.1 |
| QHDL | 10.7 | -5.5 | 11.1 | -7.2 | -0.4 | 1.8 |
| QHGE | 0.6 | 1.8 | 2.5 | -2.6 | -1.9 | 4.5 |
| QHMD | 85.8 | -235.3 | 89.1 | -239.0 | -3.3 | 3.7 |
| QHME | -1.9 | -2.1 | -3.4 | -0.1 | 1.5 | -1.9 |
| QHMQ | -6.5 | -10.5 | -7.6 | -11.3 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| QHYS | 6.1 | 5.1 | 6.2 | 5.9 | 0.0 | -0.8 |
| SCGZ | -6.7 | 2.3 | -4.2 | -0.3 | -2.6 | 2.6 |
| SCLH | -3.8 | 2.9 | -4.2 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 1.9 |
| SCMX | -2.6 | -2.7 | -1.0 | 0.1 | -1.5 | -2.8 |
| SCSP | -2.3 | -2.3 | -0.2 | -0.3 | -2.1 | -2.0 |
| SCXJ | -4.7 | -0.4 | -2.4 | 1.3 | -2.3 | -1.7 |
| XNIN | -1.6 | -3.0 | -3.2 | -4.0 | 1.6 | 1.0 |
| XZCD | -0.6 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -0.3 | 0.4 | -0.7 |
Table2 Coseismic displacement and difference obtained by postseismic 5-hour and multi-day static solutions, respectively(unit: mm)
| 测站名称 | 震后5h | 多天 | 差值 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | E | N | E | N | E | |
| DLHA | 2.9 | -5.7 | 3.2 | -4.6 | -0.3 | -1.1 |
| GSJT | -2.3 | -2.7 | -0.8 | -1.9 | -1.5 | -0.8 |
| GSLZ | -3.3 | -3.2 | -1.2 | -2.3 | -2.0 | -0.9 |
| GSMA | -4.1 | 3.0 | -2.1 | -1.0 | -2.0 | 4.0 |
| GSMX | -1.2 | -2.5 | -0.6 | -0.9 | -0.6 | -1.6 |
| QHBM | -5.8 | 4.5 | -6.4 | 4.3 | 0.7 | 0.1 |
| QHDL | 10.7 | -5.5 | 11.1 | -7.2 | -0.4 | 1.8 |
| QHGE | 0.6 | 1.8 | 2.5 | -2.6 | -1.9 | 4.5 |
| QHMD | 85.8 | -235.3 | 89.1 | -239.0 | -3.3 | 3.7 |
| QHME | -1.9 | -2.1 | -3.4 | -0.1 | 1.5 | -1.9 |
| QHMQ | -6.5 | -10.5 | -7.6 | -11.3 | 1.2 | 0.8 |
| QHYS | 6.1 | 5.1 | 6.2 | 5.9 | 0.0 | -0.8 |
| SCGZ | -6.7 | 2.3 | -4.2 | -0.3 | -2.6 | 2.6 |
| SCLH | -3.8 | 2.9 | -4.2 | 1.0 | 0.4 | 1.9 |
| SCMX | -2.6 | -2.7 | -1.0 | 0.1 | -1.5 | -2.8 |
| SCSP | -2.3 | -2.3 | -0.2 | -0.3 | -2.1 | -2.0 |
| SCXJ | -4.7 | -0.4 | -2.4 | 1.3 | -2.3 | -1.7 |
| XNIN | -1.6 | -3.0 | -3.2 | -4.0 | 1.6 | 1.0 |
| XZCD | -0.6 | -1.0 | -1.0 | -0.3 | 0.4 | -0.7 |
| [1] | 邓起东, 冉勇康, 杨晓平, 等. 2007. 中国活动构造图[CM]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| DENG Qi-dong, RAN Yong-kang, YANG Xiao-ping, et al. 2007. Active Tectonic Map of China[CM]. Seismological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 范士杰, 刘焱雄, 张健, 等. 2013. PPP与GAMIT/TRACK在地震监测中的应用[J]. 测绘科学, 38(2): 184-186. |
| FAN Shi-jie, LIU Yan-xiong, ZHANG Jian, et al. 2013. Application of PPP and GAMIT/TRACK module in earthquake monitoring[J]. Science of Surveying and Mapping, 38(2): 184-186. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 高翔, 邓起东. 2013. 巴颜喀喇断块边界断裂强震活动分析[J]. 地质学报, 87(1): 9-19. |
| GAO Xiang, DENG Qi-dong. 2013. Analysis of large earthquakes in boundary faults around Bayankala fault-block[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(1): 9-19. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] |
华俊, 赵德政, 单新建, 等. 2021. 2021年青海玛多 MW7.3 地震InSAR的同震形变场、 断层滑动分布及其对周边区域的应力扰动[J]. 地震地质, 43(3): 677-691. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.03.013.
DOI |
| HUA Jun, ZHAO De-zheng, SHAN Xin-jian, et al. 2021. Coseismic deformation field, slip distribution and Coulomb stress disturbance of the 2021 MW7.3 Maduo earthquake using Sentinel-1 InSAR observations[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(3): 677-691. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] |
李智敏, 李文巧, 李涛, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震的发震构造和地表破裂初步调查[J]. 地震地质, 43(3): 722-737. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.03.16.
DOI |
| LI Zhi-min, LI Wen-qiao, LI Tao, et al. 2021. Seismogenic fault and coseismic surface deformation of the Maduo MS7.4 earthquake in Qinghai, China: A quick report[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(3): 722-737. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] |
梁明剑, 杨耀, 杜方, 等. 2020. 青海达日断裂中段晚第四纪活动性与1947年M7¾地震地表破裂带再研究[J]. 地震地质, 42(3): 703-714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.03.011.
DOI |
| LIANG Ming-jian, YANG Yao, DU Fang, et al. 2020. Late Quaternary activity of the central segment of the Dari Fault and restudy of the surface rupture zone of the 1947 M7¾ Dari earthquake. Qinghai Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(3): 703-714. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 潘家伟, 白明坤, 李超, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震地表破裂带及发震构造[J]. 地质学报, 95(6): 1655-1670. |
| PAN Jia-wei, BAI Ming-kun, LI Chao, et al. 2021. Coseismic surface rupture and seismogenic structure of the 2021-05-22 Maduo(Qinghai) MS7.4 earthquake[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(6): 1655-1670. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 王未来, 房立华, 吴建平, 等. 2021. 2021年青海玛多 MS7.4 地震序列精定位研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 51(7): 1-10. |
| WANG Wei-lai, FANG Li-hua, WU Jian-ping, et al. 2021. Aftershock sequence relocation of the 2021 MS7.4 Maduo earthquake, Qinghai, China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 51(7): 1-10. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 徐锡伟, 韩竹军, 杨晓平, 等. 2016. 中国及邻近地区地震构造图[CM]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| XU Xi-wei, HAN Zhu-jun, YANG Xiao-ping, et al. 2016. Seismotectonic Map of China and Adjacent Areas[CM]. Seismological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 殷海涛, 肖根如, 张磊, 等. 2012. TRACK高频GPS定位中震时参考站的选取方法[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 32(4): 15-19. |
| YIN Hai-tao, XIAO Gen-ru, ZHANG Lei, et al. 2012. Study on method for selecting reference station in high rate GPS positioning using track during earthquake[J]. Journal of Geodesy an Geodynamics, 32(4): 15-19. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等. 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12-20. |
| ZHANG Pei-zhen, DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Guo-min, et al. 2003. Strong earthquake activity and active blocks in mainland China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 33(S1): 12-20. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 中国地震局震害防御司. 1999. 中国近代地震目录(公元1912-1990年MS≥4.7)[Z]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社. |
| Department of Earthquake Disaster Prevention, China Earthquake Administration. 1999. Catalogue of Recent Chinese Earthquakes(1912-1990AD, MS≥4.7)[Z]. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 周命端, 覃发超, 杨玉忠, 等. 2015. 利用CGO分析处理GPS工程控制网的研究与实践[J]. 测绘通报, (S1): 84-87. |
| ZHOU Ming-duan, QIN Fa-chao, YANG Yu-zhong, et al. 2015. Research on using CGO to analyze and process the GPS engineering control network[J]. Bulletin of Surveying and Mapping, (S1): 84-87. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] |
Banerjee P, Pollitz F, Bürgmann R. 2005. The size and duration of the Sumatra-Andaman earthquake from far-field static offsets[J]. Science, 308(5729): 1769-1772.
PMID |
| [15] | Gan W J, Zhang P Z, Shen Z K, et al. 2007. Present-day crustal motion within the Tibetan plateau inferred from GPS measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 112(B8): B08416. |
| [16] |
Guo B F, Zhang X H, Ren X, et al. 2015. High-precision coseismic displacement estimation with a single-frequency GPS receiver[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 202(1): 612-623.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Li J W, Zhan W, Guo B F, et al. 2021. Combination of the Levenberg-Marquardt and differential evolution algorithms for the fitting of postseismic GPS time series[J]. Acta Geophysica, 69(2): 405-414.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Liu-Zeng J, Zhang Z, Rollins C, et al. 2020. Postseismic deformation following the 2015 MW7.8 Gorkha(Nepal)earthquake: New GPS data, kinematic and dynamic models, and the roles of afterslip and viscoelastic relaxation[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 125(9): e2020JB019852. |
| [19] | Psimoulis P, Houlié N, Michel C, et al. 2016. Analysis of 1-Hz GPS data for the estimation of long-period surface motion of Tohoku-Oki MW9.0 2011 earthquake [C]. 3rd Joint International Symposium on Deformation Monitoring, Vienna, Austria. |
| [20] |
Su K, Jin S G. 2020. Real-time seismic waveforms estimation of the 2019 MW=6.4 and MW=7.1 California earthquakes with high-rate multi-GNSS observations[J]. IEEE Access, 8(1): 85411-85420.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Tiryakioglu I, Yigit C O, Yavasoglu H, et al. 2017. The determination of interseismic, coseismic and postseismic deformations caused by the Gökçeada-Samothraki earthquake(2014, MW6.9 )based on GNSS data[J]. Journal of African Earth Sciences, 133:86-94.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Wang M, Shen Z K. 2020. Present-day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 125(2): e2019JB018774. |
| [23] |
Wu Y Q, Jiang Z S, Liang H B, et al. 2016. Coseismic deformations of the 2015 MW7.8 Gorkha earthquake and interseismic strain accumulation in the Himalayan tectonic belt and Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 670:144-154.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Zhu Y G, Diao F Q, Fu Y C, et al. 2021. Slip rate of the seismogenic fault of the 2021 Maduo earthquake in western China inferred from GPS observations[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 64(8): 1363-1370.
DOI URL |
| [1] | ZHU Zhi-guo, ZHU Yi-qing, WANG Dong-zhen, HUSAN Irxat. COMPREHENSIVE ANALYSIS OF GRAVITY AND CRUSTAL DEFORMATION OF JIASHI MS6.4 EARTHQUAKE IN 2020 [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(1): 269-285. |
| [2] | SHAO Yan-xiu, LIU-ZENG Jing, GAO Yun-peng, WANG Wen-xin, YAO Wen-qian, HAN Long-fei, LIU Zhi-jun, ZOU Xiao-bo, WANG Yan, LI Yun-shuai, LIU Lu. COSEISMIC DISPLACEMENT MEASUREMENT AND DISTRIBUTED DEFORMATION CHARACTERIZATION: A CASE OF 2021 MW7.4 MADOI EARTHQUAKE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(2): 506-523. |
| [3] | HAO Ming, WANG Qing-liang. PROGRESS IN APPLICATION OF GNSS TO DIVISION OF ACTIVE TECTONIC BLOCKS IN CONTINENTAL CHINA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2020, 42(2): 283-296. |
| [4] | YIN De-yu, LIU Qi-fang, LIU Chang, JI Xin-yang. ESTIMATING THE WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE RUPTURE PROCESS USING NEAR FIELD STRONG MOTION RECORDS AND COSEISMIC DISPLACEMENTS [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2018, 40(3): 698-717. |
| [5] | ZUO Rong-hu, QU Chun-yan, ZHANG Guo-hong, SHAN Xin-jian, SONG Xiao-gang, WEN Shao-yan, XU Xiao-bo. COSEISMIC DISPLACEMENT AND FAULT SLIP OF THE MW6.1 NAPA EARTHQUAKE IN AMERICA REVEALED BY SENTINEL-1A INSAR DATA [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2016, 38(2): 278-289. |
| [6] | WEI Wen-xin, JIANG Zai-sen, ZOU Zhen-yu, YANG Yong-lin, ZHANG Long, WU Yan-qiang. VERIFICATION RESEARCH ON THE COSEISMIC DISPLACEMENT OF THE APRIL 20, 2013, M7.0 LUSHAN EARTHQUAKE AND PRIMARY EXPLORATION OF SURFACE DEFORMATION MODE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2014, 36(2): 333-343. |
| [7] | LI Chuan-you, WEI Zhan-yu. DEFORMATION STYLES OF THE NORTHERNMOST SURFACE RUPTURE ZONE OF THE MS 8.0 WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2009, 31(1): 1-8. |
| [8] | LI Chuan-you, YE Jian-qing, XIE Fu-ren, ZHENG Wen-jun, HAN Yong-bing, LIU Yu-fa, WANG Wei-tao, WEI Zhan-yu, ZHAO Dong, MA Bao-qi, REN Jun-jie. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE SURFACE RUPTURE ZONE OF THE MS8.0 WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE, CHINA ALONG THE SEGMENT NORTH TO BEICHUAN [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2008, 30(3): 683-696. |
| [9] | WANG Hui, ZHANG Guo-min, ZHANG Huai, SHI Yao-lin, LIU Jie, SHEN Xu-hui. THE NUMERICAL SIMULATION ON COSEISMIC EFFECT OF THE 14 NOVEMBER 2001 GREAT KUNLUN EARTHQUAKE,NORTHERN TIBET,China [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2007, 29(3): 637-647. |
| [10] | SHI Ya-qin, LI Jin, FENG Xi-jie, DAI Wang-qiang, REN Jun, LI Xiao-ni, DOU Ma-li. THE STUDY OF PALEOEARTHQUAKE ON THE WEIHE FAULT ZONE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2007, 29(3): 607-616. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||