SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 944-960.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.04.008
• Research paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
LIN Xu1,2)( ), LIU Hai-jin3), LIU-ZENG Jing4), WU Zhong-hai5), LI Zhao-ning6), CHEN Ji-xin1), LI Ling-ling1), HU Cheng-wei1)
), LIU Hai-jin3), LIU-ZENG Jing4), WU Zhong-hai5), LI Zhao-ning6), CHEN Ji-xin1), LI Ling-ling1), HU Cheng-wei1)
Received:2021-06-20
Revised:2021-12-01
Online:2022-08-20
Published:2022-09-23
林旭1,2)( ), 刘海金3), 刘静4), 吴中海5), 李兆宁6), 陈济鑫1), 李玲玲1), 胡程伟1)
), 刘海金3), 刘静4), 吴中海5), 李兆宁6), 陈济鑫1), 李玲玲1), 胡程伟1)
作者简介:林旭, 男, 1984年生, 2016年于中国科学院大学地质与地球物理研究所获第四纪地质学专业理学博士学位, 主要研究方向为青藏高原新生代构造演化, 黄河和长江的形成与发育过程, E-mail: hanwuji-life@163.com。
基金资助:CLC Number:
LIN Xu, LIU Hai-jin, LIU-ZENG Jing, WU Zhong-hai, LI Zhao-ning, CHEN Ji-xin, LI Ling-ling, HU Cheng-wei. PROVENANCE TRACING OF PB ISOTOPES OF FLUVIAL DETRITAL K-feldspar FROM THE YELLOW RIVER BASIN[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(4): 944-960.
林旭, 刘海金, 刘静, 吴中海, 李兆宁, 陈济鑫, 李玲玲, 胡程伟. 黄河流域碎屑钾长石Pb同位素物源示踪[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 944-960.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.dzdz.ac.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.04.008
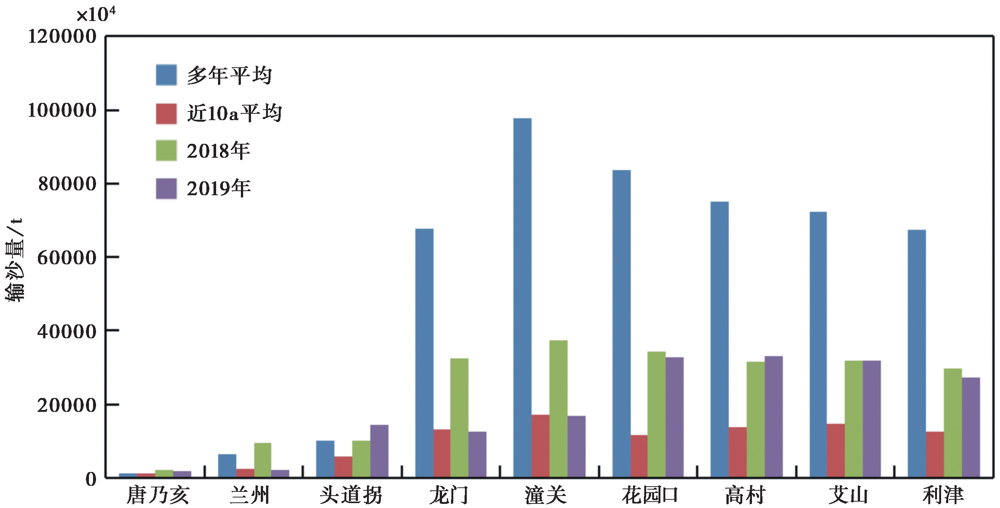
Fig. 2 Histogram of sediment transport at major hydrological stations in the Yellow River trunk stream (Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China, 2019).
| 样品性质 | 采样点 | 东经 | 北纬 | 样品分析数量/颗 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 河砂 | 玛多(黄河) | 98°10'17″ | 34°53'16″ | 69 | 本研究 |
| 河砂 | 玛曲(黄河) | 102°4'48″ | 33°57'28″ | 63 | |
| 河砂 | 同德(黄河) | 100°12'42″ | 35°21'24″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 临夏(大夏河) | 103°15'28″ | 35°37'25″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 河嘴(湟水) | 103°20'49″ | 36°7'12″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 兰州(黄河) | 103°36'32″ | 36°8'24″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 巴彦(黄河) | 107°22'8″ | 40°40'15″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 河曲(黄河) | 111°10'58″ | 39°20'2″ | 63 | |
| 河砂 | 韩城(黄河) | 110°35'52″ | 35°39'25″ | 63 | |
| 河砂 | 河津(汾河) | 110°51'57″ | 35°33'25″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 渭南(渭河) | 109°57'28″ | 34°37'51″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 巩义(伊洛河) | 112°55'18″ | 34°42'3″ | 62 | |
| 河砂 | 开封(黄河) | 114°15'21″ | 34°53'45″ | 62 | |
| 河砂 | 利津(黄河) | 118°3'21″ | 37°20'38″ | 65 | |
| 砂岩 | 河曲 | 111°24'28″ | 40°1'55″ | 65 | |
| 沙漠砂 | 腾格里沙漠 | 104°58'12″ | 37°27'39″ | 65 | 林旭未发表数据 |
| 沙漠砂 | 毛乌素沙漠 | 109°41'45″ | 38°23'6″ | 65 | |
| 基岩 | 秦岭(B2-2) | 48 | 张理刚, | ||
| 基岩 | 华北(A1-2) | 27 | |||
| 基岩 | 华北(A2) | 35 | |||
| 基岩 | 华北(A3-2) | 23 |
Table 1 Collected samples information
| 样品性质 | 采样点 | 东经 | 北纬 | 样品分析数量/颗 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 河砂 | 玛多(黄河) | 98°10'17″ | 34°53'16″ | 69 | 本研究 |
| 河砂 | 玛曲(黄河) | 102°4'48″ | 33°57'28″ | 63 | |
| 河砂 | 同德(黄河) | 100°12'42″ | 35°21'24″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 临夏(大夏河) | 103°15'28″ | 35°37'25″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 河嘴(湟水) | 103°20'49″ | 36°7'12″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 兰州(黄河) | 103°36'32″ | 36°8'24″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 巴彦(黄河) | 107°22'8″ | 40°40'15″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 河曲(黄河) | 111°10'58″ | 39°20'2″ | 63 | |
| 河砂 | 韩城(黄河) | 110°35'52″ | 35°39'25″ | 63 | |
| 河砂 | 河津(汾河) | 110°51'57″ | 35°33'25″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 渭南(渭河) | 109°57'28″ | 34°37'51″ | 65 | |
| 河砂 | 巩义(伊洛河) | 112°55'18″ | 34°42'3″ | 62 | |
| 河砂 | 开封(黄河) | 114°15'21″ | 34°53'45″ | 62 | |
| 河砂 | 利津(黄河) | 118°3'21″ | 37°20'38″ | 65 | |
| 砂岩 | 河曲 | 111°24'28″ | 40°1'55″ | 65 | |
| 沙漠砂 | 腾格里沙漠 | 104°58'12″ | 37°27'39″ | 65 | 林旭未发表数据 |
| 沙漠砂 | 毛乌素沙漠 | 109°41'45″ | 38°23'6″ | 65 | |
| 基岩 | 秦岭(B2-2) | 48 | 张理刚, | ||
| 基岩 | 华北(A1-2) | 27 | |||
| 基岩 | 华北(A2) | 35 | |||
| 基岩 | 华北(A3-2) | 23 |
| [1] | 陈垚. 2020. 黄河泥沙沉积物演化特征及物源示踪[D]. 西安: 长安大学. |
| CHEN Yao. 2020. Spatial evolution characteristics of the Yellow River sediments and the significance of provenance tracing[D]. Chang 'an University, Xi 'an. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 李维东, 赵希涛, 杨艳, 等. 2020. 黄河河套盆地段阶地砾石层的形成时代和物源分析[J]. 地球学报, 41(4): 515-524. |
| LI Wei-dong, ZHAO Xi-tao, YANG Yan, et al. 2020. Formation age and provenance analysis of the gravel layer in the Yellow River terraces of the Hetao Basin[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 41(4): 515-524. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 李智佩. 2006. 中国北方荒漠化形成发展的地质环境研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学. |
| LI Zhi-pei. 2006. Researches on geological environment of the formation and development of desertification in northern China[D]. Northwestern University, Xi'an. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 林晓彤, 李巍然, 时振波. 2003. 黄河物源碎屑沉积物的重矿物特征[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 23(3): 17-21. |
| LIN Xiao-tong, LI Wei-ran, SHI Zhen-bo. 2003. Characteristics of mineralogy in the clastic sediments from the Yellow River provenance, China[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 23(3): 17-21. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 林旭. 2011. 利用碎屑钾长石普通Pb同位素重建古嘉陵江、 古长江自中新世以来的流向[D]. 武汉: 中国地质大学. |
| LIN Xu. 2011. Reconstructing the flow direction of the ancient Jialing River and Yangtze River since Miocene using common Pb isotopes of detrital K-feldspar[D]. China University of Geosciences, Wuhan. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 林旭, 李玲玲, 刘海金, 等. 2022. 黄河上游物质在新近纪未流入晋陕峡谷[J]. 古地理学报, 24(3): 568-582. |
| LIN Xu, LI Ling-ling, LIU Hai-jin, et al. 2022. Sediments from the upper reaches of Yellow River did not enter into Shanxi-Shaanxi Gorge in the Neogene[J]. Journal of Palaeogeography, 24(3): 568-582. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 林旭, 刘静, 吴中海, 等. 2020a. 中国北部陆架海碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄和钾长石主微量元素物源示踪研究[J]. 地质学报, 94(10): 3024-3035. |
| LIN Xu, LIU Jing, WU Zhong-hai, et al. 2020a. Detrital zircon U-Pb ages and K-feldspar main and trace elements provenance studying from fluvial to marine sediments in northern China[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(10): 3024-3035. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 林旭, 刘静, 吴中海, 等. 2021a. 渤海钻孔物源示踪和河流沉积物扩散研究: 碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄和磷灰石原位地球化学元素双重约束[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 304-316. |
| LIN Xu, LIU Jing, WU Zhong-hai, et al. 2021a. Study on borehole provenance tracing and fluvial sediment diffusion in the Bohai Sea: Double constraints from detrital zircon U-Pb age and in-situ geochemical element of apatite grains[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 304-316. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 林旭, 刘静, 吴中海, 等. 2021b. 环渤海湾盆地主要河流碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄特征及其物源示踪意义[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 41(2): 136-145. |
| LIN Xu, LIU Jing, WU Zhong-hai, et al. 2021b. U-Pb age characteristics of major fluvial detrital zircons in the Bohai Bay Basin and their provenance implications[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 41(2): 136-145. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 林旭, 赵希涛, 吴中海, 等. 2020b. 渤海湾周缘主要河流钾长石物源示踪指标研究[J]. 地质科技通报, 39(6): 10-18. |
| LIN Xu, ZHAO Xi-tao, WU Zhong-hai, et al. 2020b. Source tracing elements of K-feldspar of main rivers around Bohai Bay Basin[J]. Bulletin of Geological Science and Technology, 39(6): 10-18. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 刘昌明. 2014. 中国水文地理[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| LIU Chang-ming. 2014. Hydrogeography of China[M]. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 王兆印, 王文龙, 田世民. 2007. 黄河流域泥沙矿物成分与分布规律[J]. 泥沙研究, 10(5): 1-8. |
| WANG Zhao-yin, WANG Wen-long, TIAN Shi-min. 2007. Mineral composition and distribution of the sediment in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 10(5): 1-8. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 王中波, 杨守业, 李日辉, 等. 2010. 黄河水系沉积物碎屑矿物组成及沉积动力环境约束[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 30(4): 73-85. |
|
WANG Zhong-bo, YANG Shou-ye, LI Ri-hui, et al. 2010. Detrital mineral composition of the sediments from Huanghe and its hydrodynamic environmental constraints[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 30(4): 73-85. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [14] | 岳保静, 廖晶. 2016. 黄河流域现代沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄物源探讨[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 36(5): 109-119. |
| YUE Bao-jing, LIAO Jing. 2016. Provenance study of Yellow River sediments by U-Pb dating of the detrital zircons[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 36(5): 109-119. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 张理刚. 1995. 东亚岩石圈块体地质[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| ZHANG Li-gang. 1995. Lithospheric Block Geology in East Asia[M]. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 张笑宇, 何梦颖, 王斌, 等. 2018. 渭河流域沉积物碎屑锆石U-Pb年龄物源示踪[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 38(1): 202-211. |
| ZHANG Xiao-yu, HE Meng-ying, WANG Bin, et al. 2018. Provenance study of the sediments in Wei River using the detrital zircon U-Pb dating[J]. Marine Geology and Quaternary Geology, 38(1): 202-211. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 中华人民共和国水利部. 2019. 中国河流泥沙公报[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社. |
| Ministry of Water Resources of the People’s Republic of China. 2019. Bulletin of River Sediment in China[M]. China Water and Power Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
Alizai A, Clift P D, Giosan L, et al. 2011. Pb isotopic variability in the modern-Pleistocene Indus River system measured by ion microprobe in detrital K-feldspar grains[J]. Geochimica et Cosmochimica Acta, 75(17): 4771-4795.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Barham M, Kirkland C L, Hovikoski J, et al. 2021. Reduce or recycle?Revealing source to sink links through integrated zircon-feldspar provenance fingerprinting[J]. Sedimentology, 68(2): 531-556.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Blowick A, Haughton P, Tyrrell S, et al. 2019. All mixed up: Pb isotopic constraints on the transit of sands through the Mississippi-Missouri River drainage basin, North America[J]. Geological Socitey of America Bulletin, 131(9-10): 1501-1518. |
| [21] |
Bodet F, Schärer U. 2001. Pb isotope systematics and time-integrated Th/U of SE-Asian continental crust recorded by single K-feldspar grains in large rivers[J]. Chemical Geology, 177(3-4): 265-285.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
Fan Y, Mou X, Wang Y, et al. 2018. Quaternary paleoenvironmental evolution of the Tengger Desert and its implications for the provenance of the loess of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 197: 21-34.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Garzanti E, Andò S. 2007. Heavy mineral concentration in modern sands: Implications for provenance interpretation[J]. Developments in Sedimentology, 58: 517-545. |
| [24] | Guo B, Liu S, Peng T, et al. 2018. Late Pliocene establishment of exorheic drainage in the northeastern Tibetan plateau as evidenced by the Wuquan Formation in the Lanzhou Basin[J]. Geomorphology, 33: 271-283. |
| [25] | Guo B, Peng T, Yu H, et al. 2020. Magnetostratigraphy and palaeoclimatic significance of the Late Pliocene red clay-Quaternary loess sequence in the Lanzhou Basin, western Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 47(3): 1-10. |
| [26] |
Hu B, Li G, Li J, et al. 2012. Provenance and climate change inferred from Sr-Nd-Pb isotopes of late Quaternary sediments in the Huanghe(Yellow River)Delta, China[J]. Quaternary Research, 78(3): 561-571.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Hu Z, Li M, Dong Z, et al. 2019. Fluvial entrenchment and integration of the Sanmen Gorge, the Lower Yellow River[J]. Global and Planetary Change, 178: 129-138.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Hu Z, Pan B, Bridgland D, et al. 2017. The linking of the upper-middle and lower reaches of the Yellow River as a result of fluvial entrenchment[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 166: 324-338.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Huang X, Mei X, Yang S, et al. 2021. Disentangling combined effects of sediment sorting, provenance, and chemical weathering from a Pliocene-Pleistocene sedimentary core(CSDP-1)in the South Yellow Sea[J]. Geochemistry, Geophysics, Geosystems, 22(5): 1-21. |
| [30] |
Jia X, Wang H. 2011. Mineral compositions and sources of the riverbed sediment in the desert channel of Yellow River[J]. Environmental Monitoring and Assessment, 173(1): 969-983.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Johnson S P, Kirkland C L, Evans N J, et al. 2018. The complexity of sediment recycling as revealed by common Pb isotopes in K-feldspar[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 9(5): 1515-1527.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Li B, Sun D, Xu W, et al. 2017. Paleomagnetic chronology and paleoenvironmental records from drill cores from the Hetao Basin and their implications for the formation of the Hobq Desert and the Yellow River[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 156: 69-89.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Lin X, Jolivet M, Liu-Zeng J, et al. 2022. The formation of the North Qilian Shan through time: Clues from detrital zircon fission-track data from modern river sediments[J]. Geosciences, 12(4), 166: 1-20.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Lin X, Tian Y, Donelick R A, et al. 2019. Mesozoic and Cenozoic tectonics of the northeastern edge of the Tibetan plateau: Evidence from modern river detrital apatite fission-track age constraints[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 170: 84-95.
DOI |
| [35] |
Liu J, Chen X, Shi W, et al. 2019. Tectonically controlled evolution of the Yellow River drainage system in the Weihe region, North China: Constraints from sedimentation, mineralogy and geochemistry[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 179: 350-364.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Liu Y, Song H, An Z, et al. 2020. Recent anthropogenic curtailing of Yellow River runoff and sediment load is unprecedented over the past 500y[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 117(31): 18251-18257.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Munnikhuis J. 2016. Variation of Sr and Pb isotopes in megacrystic K-feldspar from the Cathedral Peak Granodiorite, California[D]. University of North Carolina, Raleigh. |
| [38] | Nie J, Stevens T, Rittner M, et al. 2015. Loess plateau storage of northeastern Tibetan plateau-derived Yellow River sediment[J]. Nature Communications, 6(1): 1-10. |
| [39] |
Pan B, Pang H, Gao H, et al. 2016. Heavy-mineral analysis and provenance of Yellow River sediments around the China Loess Plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 127: 1-11.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Pan B, Su H, Hu Z, et al. 2009. Evaluating the role of climate and tectonics during non-steady incision of the Yellow River: Evidence from a 1.24Ma terrace record near Lanzhou, China[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 28(27-28): 3281-3290.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Pan B T, Li Q Y, Hu X F, et al. 2013. Cretaceous and Cenozoic cooling history of the eastern Qilian Shan, north-eastern margin of the Tibetan plateau: Evidence from apatite fission-track analysis[J]. Terra Nova, 25(6): 431-438.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Pang H, Pan B, Garzanti E, et al. 2018. Mineralogy and geochemistry of modern Yellow River sediments: Implications for weathering and provenance[J]. Chemical Geology, 488: 76-86.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
Qiao S, Shi X, Wang G, et al. 2017. Sediment accumulation and budget in the Bohai Sea, Yellow Sea and East China Sea[J]. Marine Geology, 390: 270-281.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Sun Y, Yan Y, Nie J, et al. 2020. Source-to-sink fluctuations of Asian aeolian deposits since the late Oligocene[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 200:102963. |
| [45] |
Ta W, Xiao H, Dong Z. 2008. Long-term morphodynamic changes of a desert reach of the Yellow River following upstream large reservoirs’ operation[J]. Geomorphology, 97(3-4): 249-259.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Tyrrell S, Haughton P D W, Daly J S, et al. 2006. The use of the common Pb isotope composition of detrital K-feldspar grains as a provenance tool and its application to Upper Carboniferous paleodrainage, northern England[J]. Journal of Sedimentary Research, 76(2): 324-345.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Vermeesch P, Resentini A, Garzanti E. 2016. An R package for statistical provenance analysis[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 336: 14-25.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Wang C, Liang X, Foster D A, et al. 2019. Provenance and drainage evolution of the Red River revealed by Pb isotopic analysis of detrital K-feldspar[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(12): 6415-6424.
DOI |
| [49] |
Wang Z Y, Wu Y Q, Tan L H, et al. 2019. Provenance studies of aeolian sand in Mu Us Desert based on heavy-mineral analysis[J]. Aeolian Research, 40: 15-22.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Wang Z, Zhang H, Garzanti E, et al. 2019. Evolution of the Upper Yellow River as revealed by changes in heavy-mineral and geochemical (REE) signatures of fluvial terraces(Lanzhou, China)[J]. Minerals, 9(10): 1-13.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Woodhead J D, Hergt J M. 2007. Strontium, neodymium and lead isotope analyses of NIST glass certified reference materials: SRM 610, 612, 614[J]. Geostandards Newsletter, 25: 261-266.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Xiao G, Pan Q, Zhao Q, et al. 2021. Early Pleistocene integration of the Yellow River Ⅱ: Evidence from the Plio-Pleistocene sedimentary record of the Fenwei Basin[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 577:110550. |
| [53] |
Xu Q, Yuan G, Ding J, et al. 2019. Cenozoic tectonic and paleoenvironmental evolution of northwestern China: Evidence from two deep boreholes in the Jartai Basin[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 173: 98-112.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Xu Y M, Jiang S Y. 2017. In-situ analysis of trace elements and Sr-Pb isotopes of K-feldspars from Tongshankou Cu-Mo deposit, SE Hubei Province, China: Insights into early potassic alteration of the porphyry mineralization system[J]. Terra Nova, 29(6): 343-355.
DOI URL |
| [55] | Yang J, Yuan H, Hu Y, et al. 2022. Significance of sedimentary provenance reconstruction based on borehole records of the North China Plain for the evolution of the Yellow River[J]. Geomorphology, 401:108077. |
| [56] |
Yang S, Jung H S, Li C. 2004. Two unique weathering regimes in the Changjiang and Huanghe drainage basins: Geochemical evidence from river sediments[J]. Sedimentary Geology, 164(1-2): 19-34.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Yin A. 2010. Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Asia: A preliminary synthesis[J]. Tectonophysics, 488(1-4): 293-325.
DOI URL |
| [58] | Zhang H, Nie J, Liu X, et al. 2021. Spatially variable provenance of the Chinese Loess Plateau[J]. Geology, 49(10): 1-5. |
| [59] | Zhang H Z, Lu H Y, Zhou Y L, et al. 2021. Heavy mineral assemblages and U-Pb detrital zircon geochronology of sediments from the Weihe and Sanmen Basins: New insights into the Pliocene-Pleistocene evolution of the Yellow River[J]. Palaeogeography, Palaeoclimatology, Palaeoecology, 562: 110072. |
| [60] |
Zhang J, Huang W W, Shi M C. 1990. Huanghe(Yellow River)and its estuary: Sediment origin, transport and deposition[J]. Journal of Hydrology, 120(1-4): 203-223.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
Zhang J, Wan S, Clift P D, et al. 2019. History of Yellow River and Yangtze River delivering sediment to the Yellow Sea since 3.5Ma: Tectonic or climate forcing?[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 216: 74-88.
DOI |
| [62] | Zhang X, Zhang G, Zhu G, et al. 1996. Elemental tracers for Chinese source dust[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 39(5): 512-521. |
| [1] | GUO Ru-jun, WEI Chuan-yi, LI Chang-an, ZHANG Yu-fen, LI Ya-wei, SUN Xi-lin, ZHANG Zeng-jie, LENG Yong-hui, SU Jian-chao, LI Guo-nai, LÜ Ling-yun, CHEN Xu, DING Zhi-qiang. A CENTENNIAL PUZZLE OF THE EVOLUTION OF THE YANGTZE RIVER: RETROSPECTION AND PROGRESSES [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(1): 1-28. |
| [2] | DANG Jia-xiang, ZHOU Yong-sheng. DEFORMATION MECHANISM OF GRANITIC ROCKS IN BRITTLE-PLASTIC TRANSITION ZONE [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2020, 42(1): 198-211. |
| [3] | LI Ya-wei, LI Chang-an, ZHANG Yu-fen, LIN Xu, WANG Jie-tao, SUN Xi-lin, WEI Chuan-yi, GUO Ru-jun, LENG Yong-hui. PROGRESS OF DETRITAL ZIRCON CHRONOLOGY IN SEDIMENT PROVENANCE STUDIES IN THE YANGTZE RIVER BASIN [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2019, 41(2): 521-544. |
| [4] | YAO Wen-qian, LIU-ZENG Jing, Michael Oskin, HAN Long-fei, LI Xue, WANG Heng, XU Xin-yue, LI Zhan-fei, ZHANG Jin-yu. APPLICATION OF SEMIAUTOMATIC EXTRACTION OF FLUVIAL TERRACES BASED ON R LANGUAGE-AN EXAMPLE FROM THE YELLOW RIVER TERRACES AT MIJIA SHAN [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2019, 41(2): 363-376. |
| [5] | LEI Qi-yun, CHAI Chi-zhang, ZHENG Wen-jun, DU Peng, XIE Xiao-feng, WANG Yin, CUI Jin, MENG Guang-kui. ACTIVITY AND SLIP RATE OF THE NORTHERN SECTION OF YELLOW RIVER FAULT REVEALED BY DRILLING [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2014, 36(2): 464-477. |
| [6] | WAN Jing-lin, ZHENG De-wen, ZHENG Wen-jun, WANG Wei-tao. MODELING THERMAL HISTORY DURING LOW TEMPERATURE BY K-FELDSPAR MDD AND FISSION TRACK:EXAMPLE FROM MESO-CENOZOIC TECTONIC EVOLUTION IN SAISHITENGSHAN IN THE NORTHERN MARGIN OF QAIDAM BASIN [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2011, 33(2): 369-382. |
| [7] | LIU Bai-chi, LIU Xiao-feng, YUAN Dao-yang, ZHENG Wen-jun, GUO Hua, CAO Juan-juan. QUATERNARY TECTONIC ACTIVITY IN NORTHEASTERN QINGHAI-XIZANG PLATEAU AS REFLECTED BY RIVER TERRACES ALONG THE MIDDLE-UPPER REACH OF THE YELLOW RIVER [J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2003, 25(1): 133-145. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||