SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 625-648.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.03.005
• Research paper • Previous Articles Next Articles
LI Meng-yuan1)( ), JIANG Hai-kun2),*(
), JIANG Hai-kun2),*( ), SONG Jin2), WANG Jin-hong1)
), SONG Jin2), WANG Jin-hong1)
Received:2021-05-06
Revised:2021-07-10
Online:2022-06-20
Published:2022-08-02
Contact:
JIANG Hai-kun
李梦圆1)( ), 蒋海昆2),*(
), 蒋海昆2),*( ), 宋金2), 王锦红1)
), 宋金2), 王锦红1)
通讯作者:
蒋海昆
作者简介:李梦圆, 女, 1995年生, 2021年于中国地震局地震预测研究所获固体地球物理专业硕士学位, 助理工程师, 主要研究方向为地震活动及相关影响因素研究, E-mail: 2994020855@qq.com。
基金资助:CLC Number:
LI Meng-yuan, JIANG Hai-kun, SONG Jin, WANG Jin-hong. SEISMICITY TRIGGERED BY SEASONAL RAINFALL: A CASE STUDY IN BOMI, TIBET[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(3): 625-648.
李梦圆, 蒋海昆, 宋金, 王锦红. 西藏波密的地震活动及季节性降雨的触发作用[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 625-648.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
URL: https://www.dzdz.ac.cn/EN/10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.03.005
| 序 号 | 月-日 | 时:分:秒 (BTC) | 北纬 /(°) | 东经 /(°) | ML | 深度 /km (CENC) | 深度 /km (CAP) | 节面Ⅰ | 节面Ⅱ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| φs | δ | λ | φs | δ | λ | ||||||||
| 0 | 07-19 | 18:15:45 | 30.37 | 94.87 | 4.9 | 8 | 3 | 135° | 75° | 70° | 10° | 25° | 142° |
| 1 | 07-20 | 07:36:36 | 30.34 | 94.87 | 4.5 | 8 | 4 | 250° | 80° | -87° | 55° | 10° | -105° |
| 2 | 07-21 | 03:21:36 | 30.38 | 94.91 | 4.6 | 9 | 3 | 120° | 85° | 60° | 21° | 30° | 170° |
| 07-21 | 10:15:18 | 30.30 | 94.87 | 4.0 | 8 | ||||||||
| 3 | 07-21 | 14:18:46 | 30.34 | 94.83 | 4.6 | 7 | 2 | 112° | 74° | 102° | 255° | 20° | 55° |
| 4 | 07-21 | 21:26:14 | 30.33 | 94.90 | 4.3 | 10 | 0 | 95° | 76° | 94° | 260° | 15° | 75° |
| 5 | 07-23 | 08:47:42 | 30.35 | 94.85 | 4.4 | 10 | 3 | 135° | 75° | 65° | 16° | 29° | 148° |
| 6 | 07-24 | 21:34:22 | 30.35 | 94.86 | 4.4 | 7 | 3 | 275° | 80° | -60° | 22° | 31° | 161° |
| 7 | 07-25 | 23:58:34 | 30.37 | 94.85 | 4.3 | 8 | 0° | 90° | -25° | 90° | 55° | -180° | |
| 8 | 07-26 | 17:58:55 | 30.39 | 94.84 | 4.8 | 8 | 3 | 300° | 85° | -60° | 39° | 30° | -170° |
| 07-27 | 13:50:18 | 30.43 | 94.83 | 4.0 | 10 | ||||||||
| 07-28 | 11:32:27 | 30.35 | 94.89 | 4.4 | 10 | ||||||||
| 9 | 07-29 | 19:07:10 | 30.36 | 94.82 | 4.4 | 9 | 5 | 268° | 45° | -95° | 95° | 45° | -85° |
| 10 | 07-30 | 01:27:51 | 30.30 | 94.80 | 4.4 | 8 | 5 | 105° | 60° | -80° | 266° | 31° | -107° |
| 07-31 | 02:38:36 | 30.39 | 94.85 | 4.0 | 9 | ||||||||
| 11 | 08-01 | 00:45:07 | 30.37 | 94.86 | 4.6 | 6 | 5 | 101° | 55° | -87° | 275° | 35° | -95° |
| 12 | 08-08 | 16:43:58 | 30.33 | 94.93 | 4.8 | 7 | 3 | 105° | 80° | 60° | 358° | 31° | 161° |
| 13 | 08-09 | 16:50:11 | 30.32 | 94.92 | 4.8 | 10 | 5 | 65° | 50° | -80° | 230° | 41° | -102° |
| 14 | 08-10 | 01:13:30 | 30.34 | 94.85 | 4.4 | 7 | 4 | 90° | 65° | -85° | 258° | 25° | -101° |
| 15 | 08-12 | 02:14:14 | 30.35 | 94.87 | 4.6 | 10 | 4 | 95° | 75° | -80° | 241° | 18° | -123° |
| 16 | 08-12 | 05:27:26 | 30.35 | 94.89 | 4.3 | 10 | 4 | 95° | 75° | -85° | 256° | 16° | -108° |
| 17 | 08-13 | 12:27:57 | 30.31 | 94.89 | 4.3 | 10 | 4 | 100° | 70° | -90° | 280° | 20° | -90° |
| 08-14 | 20:58:38 | 30.36 | 94.80 | 4.4 | 8 | ||||||||
| 18 | 08-17 | 00:40:38 | 30.36 | 94.90 | 4.4 | 10 | 3 | 115° | 65° | 65° | 243° | 35° | 132° |
| 19 | 08-18 | 00:31:51 | 30.39 | 94.83 | 4.4 | 9 | 4 | 85° | 75° | -80° | 231° | 18° | -123° |
Table 1 The focal mechanism solutions of the 2020 Bomi swarm(ML≥4.0)
| 序 号 | 月-日 | 时:分:秒 (BTC) | 北纬 /(°) | 东经 /(°) | ML | 深度 /km (CENC) | 深度 /km (CAP) | 节面Ⅰ | 节面Ⅱ | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| φs | δ | λ | φs | δ | λ | ||||||||
| 0 | 07-19 | 18:15:45 | 30.37 | 94.87 | 4.9 | 8 | 3 | 135° | 75° | 70° | 10° | 25° | 142° |
| 1 | 07-20 | 07:36:36 | 30.34 | 94.87 | 4.5 | 8 | 4 | 250° | 80° | -87° | 55° | 10° | -105° |
| 2 | 07-21 | 03:21:36 | 30.38 | 94.91 | 4.6 | 9 | 3 | 120° | 85° | 60° | 21° | 30° | 170° |
| 07-21 | 10:15:18 | 30.30 | 94.87 | 4.0 | 8 | ||||||||
| 3 | 07-21 | 14:18:46 | 30.34 | 94.83 | 4.6 | 7 | 2 | 112° | 74° | 102° | 255° | 20° | 55° |
| 4 | 07-21 | 21:26:14 | 30.33 | 94.90 | 4.3 | 10 | 0 | 95° | 76° | 94° | 260° | 15° | 75° |
| 5 | 07-23 | 08:47:42 | 30.35 | 94.85 | 4.4 | 10 | 3 | 135° | 75° | 65° | 16° | 29° | 148° |
| 6 | 07-24 | 21:34:22 | 30.35 | 94.86 | 4.4 | 7 | 3 | 275° | 80° | -60° | 22° | 31° | 161° |
| 7 | 07-25 | 23:58:34 | 30.37 | 94.85 | 4.3 | 8 | 0° | 90° | -25° | 90° | 55° | -180° | |
| 8 | 07-26 | 17:58:55 | 30.39 | 94.84 | 4.8 | 8 | 3 | 300° | 85° | -60° | 39° | 30° | -170° |
| 07-27 | 13:50:18 | 30.43 | 94.83 | 4.0 | 10 | ||||||||
| 07-28 | 11:32:27 | 30.35 | 94.89 | 4.4 | 10 | ||||||||
| 9 | 07-29 | 19:07:10 | 30.36 | 94.82 | 4.4 | 9 | 5 | 268° | 45° | -95° | 95° | 45° | -85° |
| 10 | 07-30 | 01:27:51 | 30.30 | 94.80 | 4.4 | 8 | 5 | 105° | 60° | -80° | 266° | 31° | -107° |
| 07-31 | 02:38:36 | 30.39 | 94.85 | 4.0 | 9 | ||||||||
| 11 | 08-01 | 00:45:07 | 30.37 | 94.86 | 4.6 | 6 | 5 | 101° | 55° | -87° | 275° | 35° | -95° |
| 12 | 08-08 | 16:43:58 | 30.33 | 94.93 | 4.8 | 7 | 3 | 105° | 80° | 60° | 358° | 31° | 161° |
| 13 | 08-09 | 16:50:11 | 30.32 | 94.92 | 4.8 | 10 | 5 | 65° | 50° | -80° | 230° | 41° | -102° |
| 14 | 08-10 | 01:13:30 | 30.34 | 94.85 | 4.4 | 7 | 4 | 90° | 65° | -85° | 258° | 25° | -101° |
| 15 | 08-12 | 02:14:14 | 30.35 | 94.87 | 4.6 | 10 | 4 | 95° | 75° | -80° | 241° | 18° | -123° |
| 16 | 08-12 | 05:27:26 | 30.35 | 94.89 | 4.3 | 10 | 4 | 95° | 75° | -85° | 256° | 16° | -108° |
| 17 | 08-13 | 12:27:57 | 30.31 | 94.89 | 4.3 | 10 | 4 | 100° | 70° | -90° | 280° | 20° | -90° |
| 08-14 | 20:58:38 | 30.36 | 94.80 | 4.4 | 8 | ||||||||
| 18 | 08-17 | 00:40:38 | 30.36 | 94.90 | 4.4 | 10 | 3 | 115° | 65° | 65° | 243° | 35° | 132° |
| 19 | 08-18 | 00:31:51 | 30.39 | 94.83 | 4.4 | 9 | 4 | 85° | 75° | -80° | 231° | 18° | -123° |
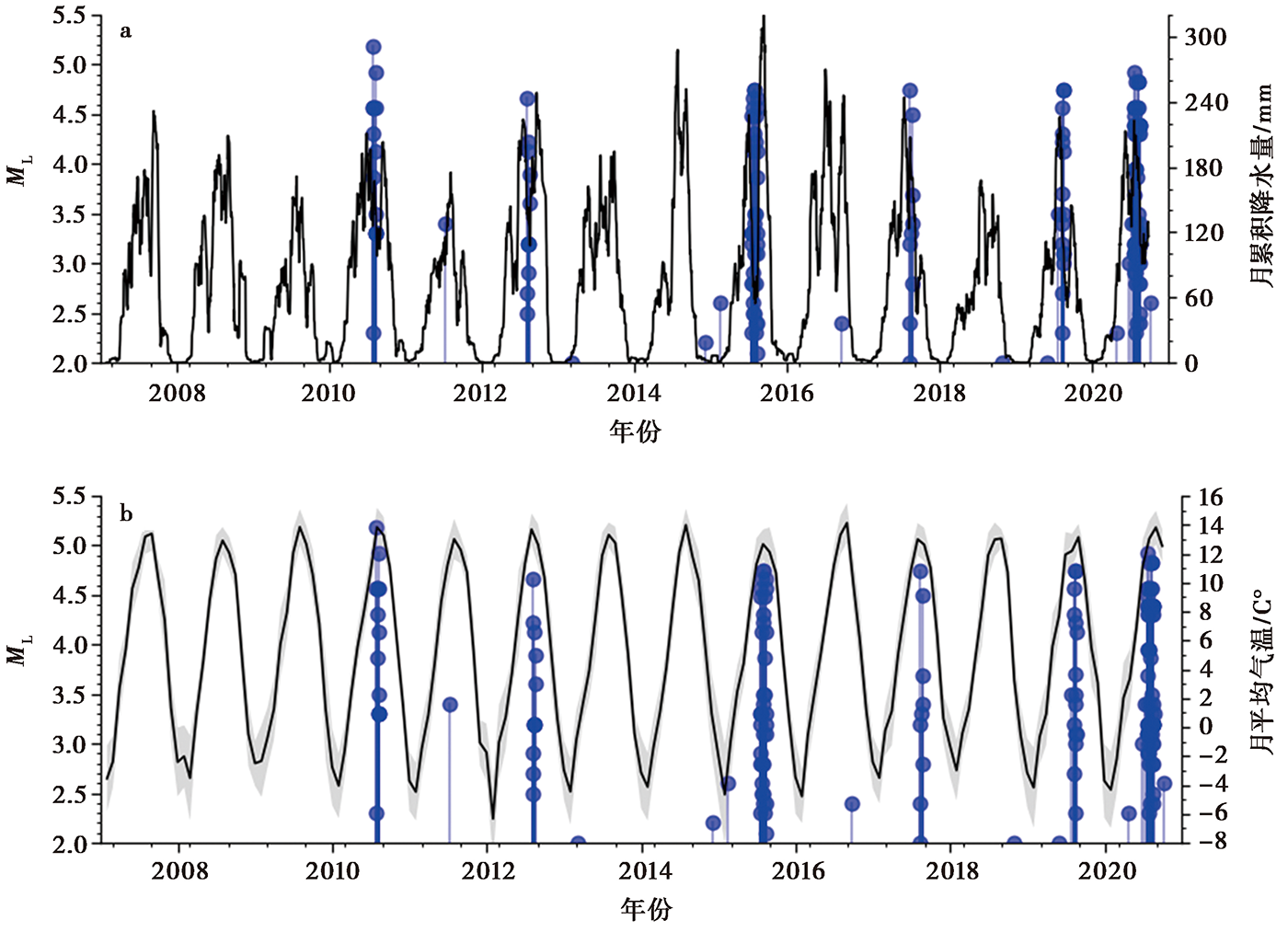
Fig. 7 Moving averages with 30 days window and 1 day step for precipitation(a), monthly mean temperature(b) and the M-t diagram of earthquakes with ML≥2.0 in Bomi swarm region(blue).
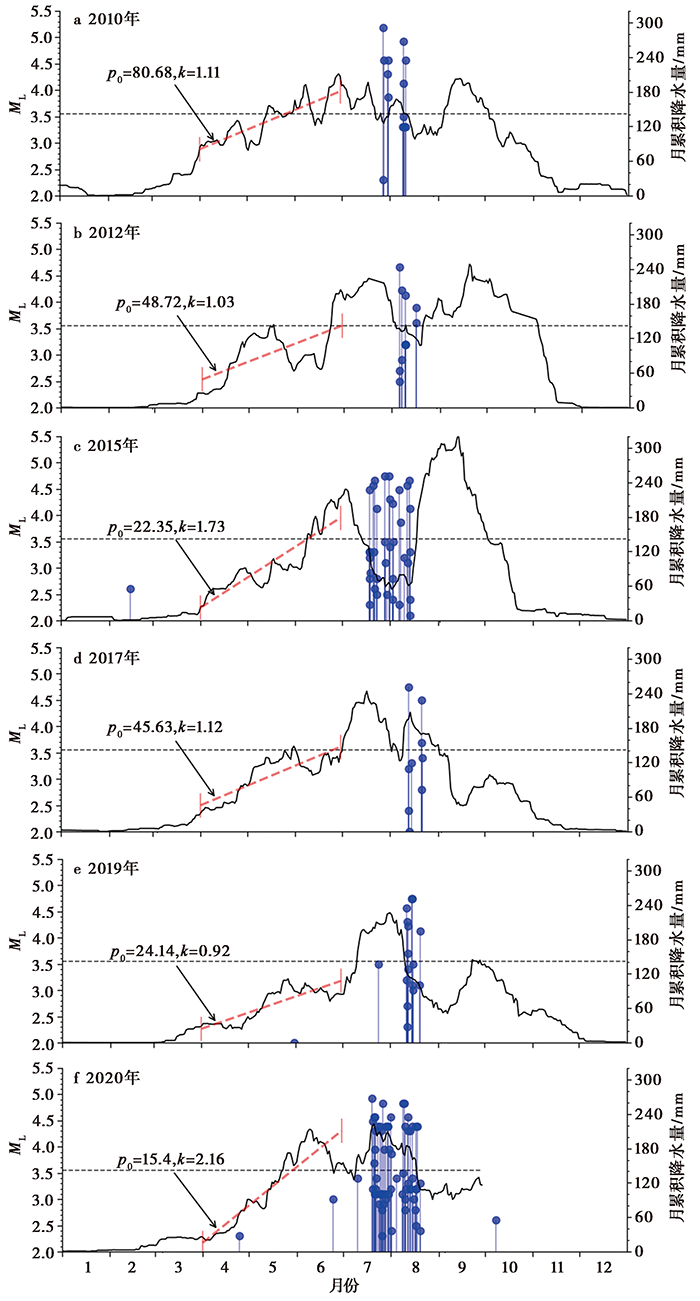
Fig. 8 Variations of monthly precipitation in years with earthquake activity since 2007(black) and the M-t diagram of earthquakes with ML≥2.0 in Bomi swarm region(blue).
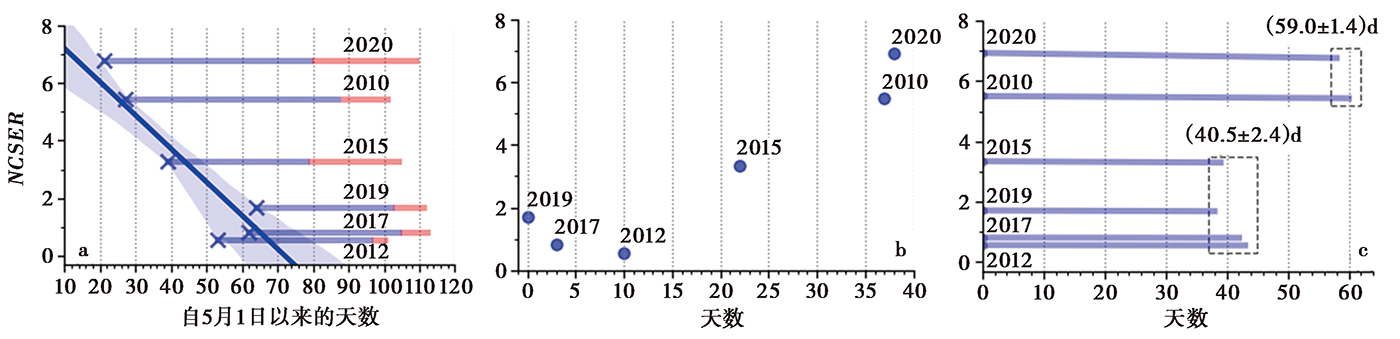
Fig. 9 The relationships between NCSER in years with earthquake activity and the starting time of precipitation above designated scale(a), the days of precipitation above designated scale in the first half year(b), and the time interval from the starting time of precipitation above designated scale to the first earthquake with ML≥4.0(c).
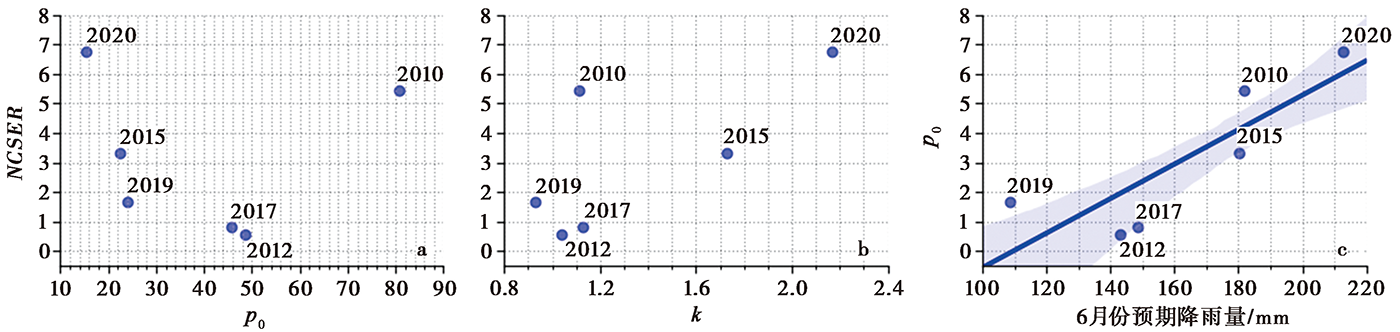
Fig. 10 The relationships between NCSER in years with earthquake activity and the cumulative precipitation in March p0(a), the average increasing rate k of precipitation from April to June(b), and the expected precipitation p in June(c).
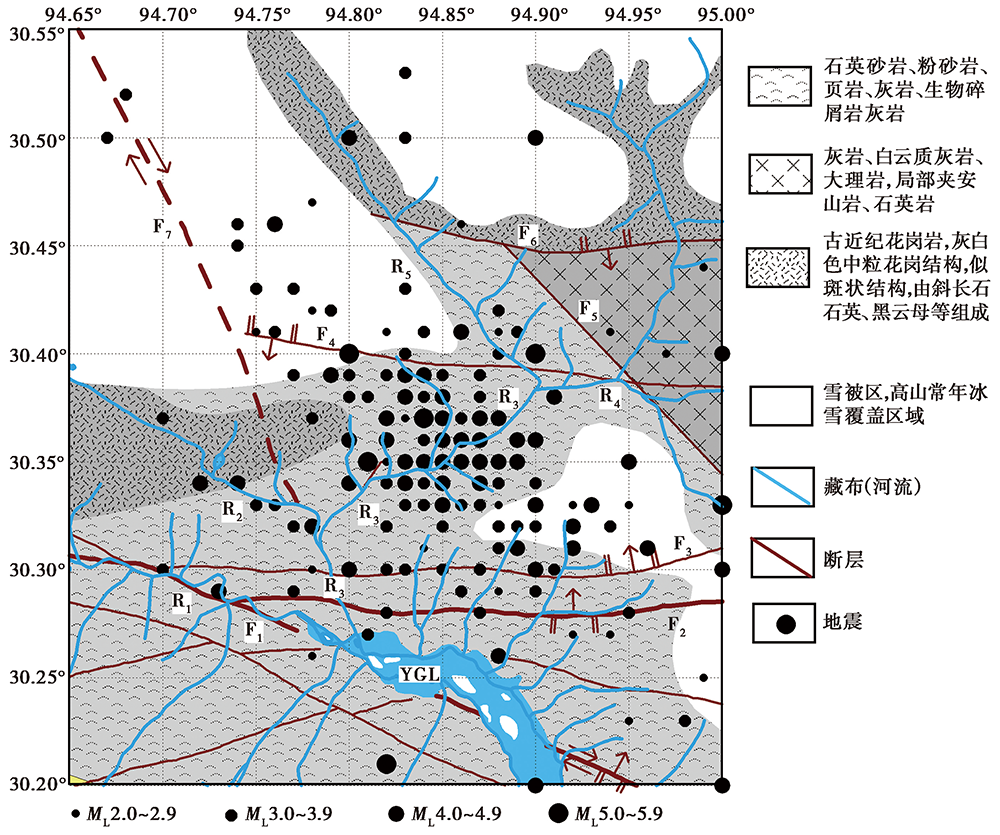
Fig. 11 Regional fault structures, lithology, river systems and distribution of earthquakes with ML≥2.0 since 1970 in Bomi swarm region and surrounding area.
| [1] | 白玲, 李国辉, 宋博文. 2017. 2017年西藏米林6.9级地震震源参数及其构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(12): 4956—4963. |
| BAI Ling, LI Guo-hui, SONG Bo-wen. 2017. The source parameters of M6.9 Mainling, Tibet earthquake and its tectonic implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(12): 4956—4963 (in Chinese). | |
| [2] | 陈颙, 黄庭芳, 刘恩儒. 2009. 岩石物理学[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社. |
| CHEN Yong, HUANG Ting-fang, LIU En-ru. 2009. Rock Physics[M]. University of Science and Technology of China Press, Hefei (in Chinese). | |
| [3] | 刁守中, 蒋海昆, 徐学炎. 1990. 山东胜利油田角07井注水地震序列的演化及其机制[J]. 地震学报, 12(4): 399—406. |
| DIAO Shou-zhong, JIANG Hai-kun, XU Xue-yan. 1990. The evolution and mechanism of earthquake sequences induced by water injection in Jiao 7 Oil Well of Shengli Oil Field, Shandong Province[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 12(4): 399—406 (in Chinese). | |
| [4] | 韩佳东, 杨建思, 刘莎, 等. 2019. 2017米林M6.9地震序列监测及南迦巴瓦地震活动性研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 62(6): 2059—2069. |
| HAN Jia-dong, YANG Jian-si, LIU Sha, et al. 2019. The 2017 Mainling M6.9 earthquake sequences monitoring and Namche Barwa seismicity analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 62(6): 2059—2069 (in Chinese). | |
| [5] | 冀琴, 杨太保, 李霞. 2014. 念青唐古拉山东段八盖乡地区近40年冰川与气候变化研究[J]. 水土保持研究, 21(2): 306—310. |
| JI Qin, YANG Tai-bao, LI Xia. 2014. Study on relationship between glacier retreat and climate change in the eastern Nyainqentanglha in the past 40 years[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 21(2): 306—310 (in Chinese). | |
| [6] | 蒋海昆, 杨马陵, 孙学军, 等. 2011. 暴雨触发局部地震活动的一个典型例子: 2010年6月广西凌云-凤山交界3级震群活动[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(10): 2606—2619. |
| JIANG Hai-kun, YANG Ma-ling, SUN Xue-jun, et al. 2011. A typical example of locally triggered seismicity in the boundary area of Lingyun and Fengshan following the large rainfall event of June 2010[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(10): 2606—2619 (in Chinese). | |
| [7] | 李鸿儒, 白玲, 詹慧丽. 2021. 嘉黎断裂带活动性研究进展[J]. 地球与行星物理论评, 52(2): 182—193. |
| LI Hong-ru, BAI Lin, ZHAN Hui-li. 2021. Research progress of Jiali fault activity[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 52(2): 182—193 (in Chinese). | |
| [8] | 任金卫, 单新建, 沈军, 等. 2001. 西藏易贡崩塌-滑坡-泥石流的地质地貌与运动学特征[J]. 地质论评, 47(6): 642—647. |
| REN Jin-wei, SHAN Xin-jian, SHEN Jun, et al. 2001. Geological characteristics and kinematies of the rock fall-landsilde in Yi’ong, southeastern Tibet[J]. Geological Review, 47(6): 642—647 (in Chinese). | |
| [9] | 沈大军, 陈传友. 1996. 青藏高原水资源及其开发利用[J]. 自然资源学报, 11(1): 8—14. |
| SHEN Da-jun, CHEN Chuan-you. 1996. Water resources of the Qing Hai-Xizang plateau and its exploitation[J]. Journal of Natural Resources, 11(1): 8—14 (in Chinese). | |
| [10] | 宋键, 唐方头, 邓志辉, 等. 2011. 喜马拉雅东构造结周边地区主要断裂现今运动特征与数值模拟研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(6): 1536—1548. |
| SONG Jian, TANG Fang-tou, DENG Zhi-hui, et al. 2011. Study on the characteristics and numerical simulation of the current movement of main faults in the area around the eastern Himalayan tectonic junction[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(6): 1536—1548 (in Chinese). | |
| [11] | 王晨旭, 熊永良, 张鲁鹏, 等. 2020. 尼泊尔地区季节性水文负荷对地震活动性的调制作用[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 40(6): 596—600. |
| WANG Chen-xu, XIONG Yong-liang, ZHANG Lu-peng, et al. 2020. Modulation of seismic activity by seasonal hydrological load in Nepal[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 40(6): 596—600 (in Chinese). | |
| [12] | 王大纯, 张人权, 史毅宏等(编著). 1995. 水文地质学基础[M]. 北京: 地质出版社: 129. |
| WANG Da-chun, ZHANG Ren-quan, SHI Yi-hong, et al(eds). 1995. Fundamentals of Hydrogeology [M]. Geological Publishing House, Beijing: 129(in Chinese). | |
| [13] | 王志伟. 2020. 流体对断层带地震活动性的影响: 川滇地区若干实例研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所: 32. |
| WANG Zhi-wei. 2020. The influence of fluid on the seismicity of fault zones: Some case studies in Sichuan-Yunnan region[D]. Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing: 32 (in Chinese). | |
| [14] | 杨锡金. 1985. 西藏南部山区河流的冰雪融水补给作用[J]. 冰川冻土, 7(3): 233—238. |
| YANG Xi-jin. 1985. The role of meltwater supply to the rivers in some mountains of south Tibet[J]. Journal of Glaciology and Geocryology, 7(3): 233—238 (in Chinese). | |
| [15] | 张捷, 况文欢, 张雄, 等. 2021. 全球油气开采诱发地震的研究现状与对策[J]. 地球与行星物理论评, 52(3): 239—265. |
| ZHANG Jie, KUANG Wen-huan, ZHANG Xiong, et al. 2021. Global review of induced earthquakes in oil and gas production fields[J]. Reviews of Geophysics and Planetary Physics, 52(3): 239—265 (in Chinese). | |
| [16] | Aki K, Fehler M, Aamodt R L, et al. 1982. Interpretation of seismic data from hydraulic fracturing experiments at the Fenton-hill, New-Mexico, hot dry rock geothermal site[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 87(B2): 936—944. |
| [17] |
Andajani R D, Tsuji T, Snieder R, et al. 2020. Spatial and temporal influence of rainfall oncrustal pore pressure based on seismic velocity monitoring[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 72: 1—17.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Beck J L. 1976. Weight-induced stresses and the recent seismicity at Lake Oroville, California[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 66(4): 1121—1131. |
| [19] |
Bell M L, Nur A. 1978. Strength changes due to reservoir-induced pore prossure and application to Lake Oroville[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 83: 4469—4483.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Bettinelli P, Avouac J, Flouzat M, et al. 2008. Seasonal variations of seismicity and geodetic strain in the Himalaya induced by surface hydrology[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 266(3-4): 332—344. |
| [21] | Bollinger L, Perrier F, Avouac J P, et al. 2007. Seasonal modulation of seismicity in the Himalaya of Nepal[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 34(8): L08304. |
| [22] |
Brace W F. 1984. Permeability of crystalline rocks: New in situ measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 89: 4327—4330.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Brace W F, Kohlstedt D L. 1980. Limits on lithospheric stress imposed by laboratory experiments[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 85: 6248—6252.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Godano C, Lippielloand E, de Arcangelis L. 2014. Variability of the b value in the Gutenberg-Richter distribution[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 199(3): 1765—1771.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Chen L, Talwani P. 2001. Mechanism of initial seismicity following impoundment of the Monticello Reservoir, South Carolina[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 91(6): 1582—1594.
DOI URL |
| [26] | Gough D I, Gough W I. 1970a. Stress and deflection in the lithosphere near Lake Kariba-I[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 21(1): 65—78. |
| [27] | Gough D I, Gough W I. 1970b. Load-induced earthquakes at Lake Kariba-II[J]. Geophysical Journal of the Royal Astronomical Society, 21(1): 79—101. |
| [28] | Gough D I, Gough W I. 1976. Time dependence and trigger mechanisms for the Kariba(Rhodesian)earthquakes[J]. Engineering Geology, 10(2-4): 211—217. |
| [29] | Gupta H K. 2002. A review of recent studies of triggered earthquakes by artificial water reservoirs with special emphasis on earthquakes in Koyna, India[J]. Earth-Science Reviews, 58(3-4): 279—310. |
| [30] | Hainazl S, Kraft T, Wassermann J, et al. 2006. Evidence for rainfall-triggered earthquakes acticity[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 33(19): L19303.https://doi.grg/10/1029/2006GL027642. |
| [31] | Hardebeck J L, Nazarech J J, Hauksson E. 1998. The static stress changes triggering model: Constraints from two southern California aftershock sequences[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 103(B10): 24427—24437. |
| [32] | Harris R A, Simpson R W. 1998. Suppression of large earthquakes by stress shadows: A comparison of Coulomb and rate-and-state failure[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 103(B10): 24439—24451. |
| [33] |
Heki K. 2013. Snow load and seasonal variation of earthquake occurrence in Japan[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 207(1-4): 159—164.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Hsu Y J, Kao H, Bürgmann R, et al. 2021. Synchronized and asynchronous modulation of seismicity by hydrological loading: A case study in Taiwan[J]. Science Advances, 7(16): 1—12. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.abf7282.
DOI |
| [35] |
Husen S, Bachmann C, Giardini D. 2007. Locally triggered seismicity in the central Swiss Alps following the large rainfall event of Augest 2005[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 171(3): 1126—1134.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Jiménez M J, Garcı'a-Fernández M. 2000. Occurrence of shallow earthquakes following periods of intense rainfall in Tenerife, Canary Islands[J]. Journal of Volcanology and Geothermal Research, 103(1-4): 463—468.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Johnson C W, Fu Y N, Burgmann R. 2017. Seasonal water storage, stress modulation, and California seismicity[J]. Science, 356(6343): 1161—1164.
DOI URL |
| [38] | King G C P, Stein R S, Lin J. 1994. Static stress changes and the triggering of earthquakes[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 84(3): 935—953. |
| [39] | Kisslinger C. 1991. Properties of aftershock sequences in southern California[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 96(B7): 11947—11958. |
| [40] | Kraft T, Wassermann J, Schmedes E, et al. 2006. Meteorological triggering of earthquake swarms at Mt. Hochstaufen, SE-Germany[J]. Tectonophysics, 424(3-4): 245—258. |
| [41] |
Lei X L, Su J R, Wang Z W. 2020. Growing seismicity in the Sichuan Basin and its association with industrial activities[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 63(11): 1633—1660. doi: 10.1007/s11430-020-9646-x.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Matsumura K. 1986. On regional characteristics of seasonal variation of shallow earthquake activity in the world[J]. Bulletin of the Disaster Prevention Reaearch Institute, 36(2): 43—98. |
| [43] |
Mukhopadhyay B, Asgupta S. 2015. Earthquake swarms near eastern Himalayan Syntaxis along Jiali Fault in Tibet: A seismotectonic appraisal[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 6(5): 715—722.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Phillips W S. 2000. Precise microearthquake locations and fluid flow in the geothermal reservoir at Soultz-sous-Forets, France[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 90(1): 212—228.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Pradeep T, Steve A. 1984. Pore press diffusion and the mechanism of reservoir-induced seismicity[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 85(122): 947—965. |
| [46] |
Rajendran K, Talwani P. 1992. The role of elastic, undrained, and drained responses in triggering earthquakes at Monticello Reservoir, South Carolina[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 82(4): 1867—1888.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Reasenberg P A, Simpson R W. 1992. Response of regional seismicity to the static stress change produced by the Loma Prieta earthquake[J]. Science, 255(5052): 1687—1690.
PMID |
| [48] | Roeloffs E A. 1988. Fault stability changes induced beneath a reservoir with cyclic variations in water level[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 93(B3): 2107—2124. |
| [49] |
Roth P, Pavoni N, Deichmann N. 1992. Seismotectonics of the eastern Swiss Alps and evidence for precipitation-induced variations of seismic activity[J]. Tectonophysics, 207(1-2): 183—197.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Saar M O, Manga M. 2003. Seismicity induced by seasonal groundwater recharge at Mt. Hood, Oregon[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 214(3-4): 605—618. |
| [51] | Stein R S. 1999. The role of stress transfer in earthquake occurrence[J]. Nature, 42: 605—609. |
| [52] | Talwani P, Chen L, Gahalaut K. 2007. Seismogenic permeability, ks[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 112(B7309): 1—18. |
| [53] |
Talwani P. 1997. On the nature of reservoir-induced seismicity[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 150: 473—492.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Townend J, Zoback M D. 2000. How faulting keeps the crust strong[J]. Geology, 28(5): 399—402.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Ueda T, Kato A. 2019. Seasonal variations in crustal seismicity in San-in district, southwest Japan[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 46(6): 3172—3179.
DOI |
| [56] | Utsu T. 2002. Statistical features of seismicity[M]// Lee W H K( ed). InternationalHandbook of Earthquake and EngineeringSeismology, PartA. Amsterdam, Elservier, Academic Press: 719—732. |
| [57] |
Withers R J, Nyland E. 1978. Time evolution of stress under an artificial lake and its implication for induced seismicity[J]. Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences, 15(9): 1526—1534.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
Witherspoon P A, Gale J E. 1977. Mechanical and hydraulic properties of rocks related to induced seismicity[J]. Engineering Geology, 11(1): 23—55.
DOI URL |
| [59] | Zoback M D, Harjes H P. 1997. Injection-induced earthquakes and crustal stress at 9km depth at the KTB deep drilling site, Germany[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 102(B8): 18477—18491. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||