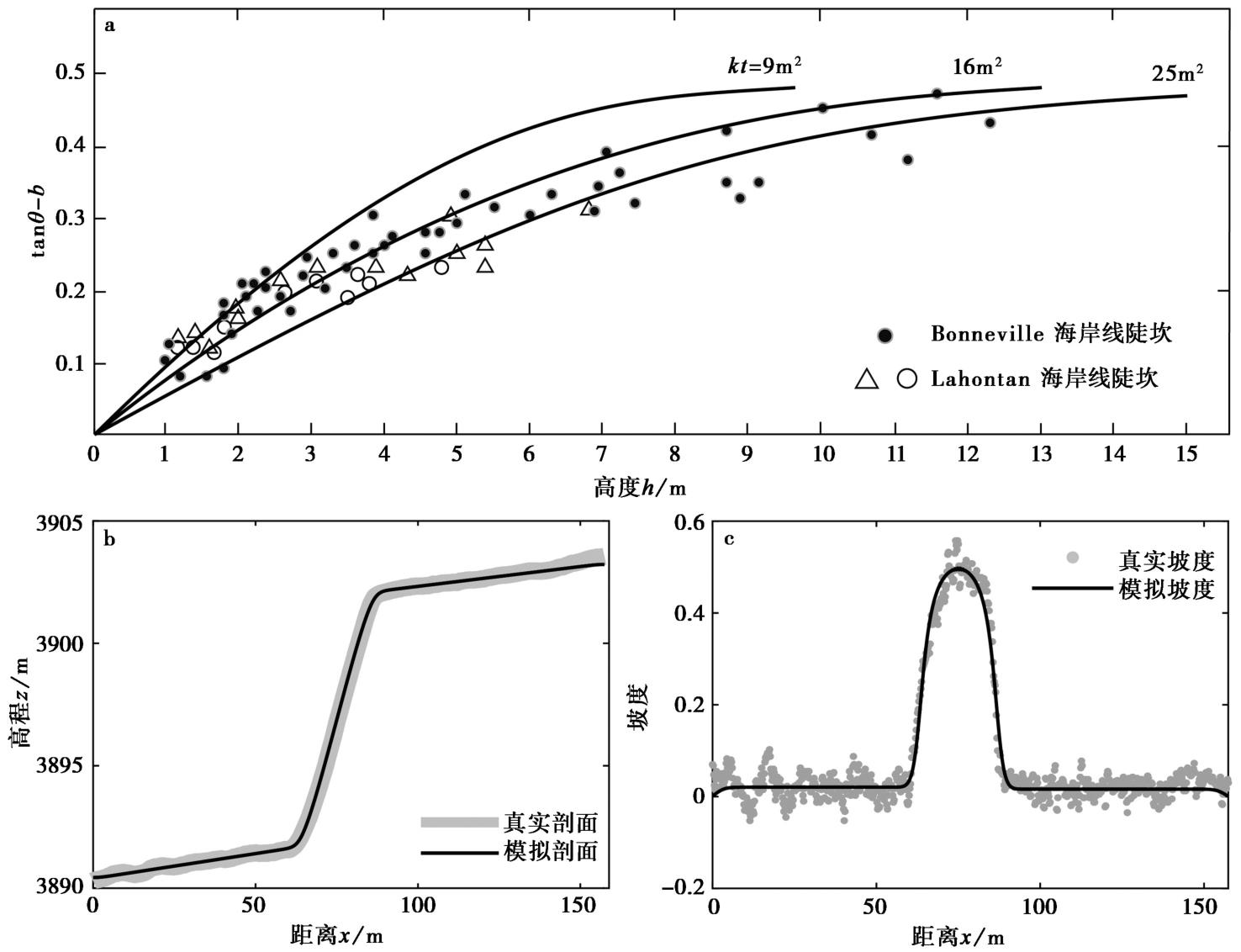
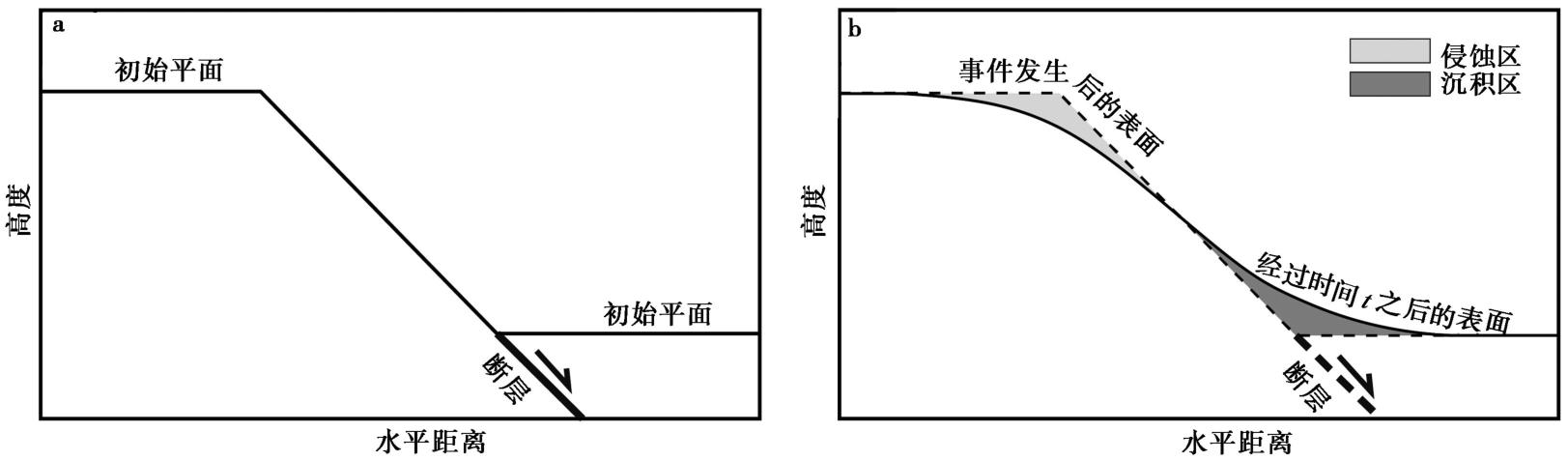
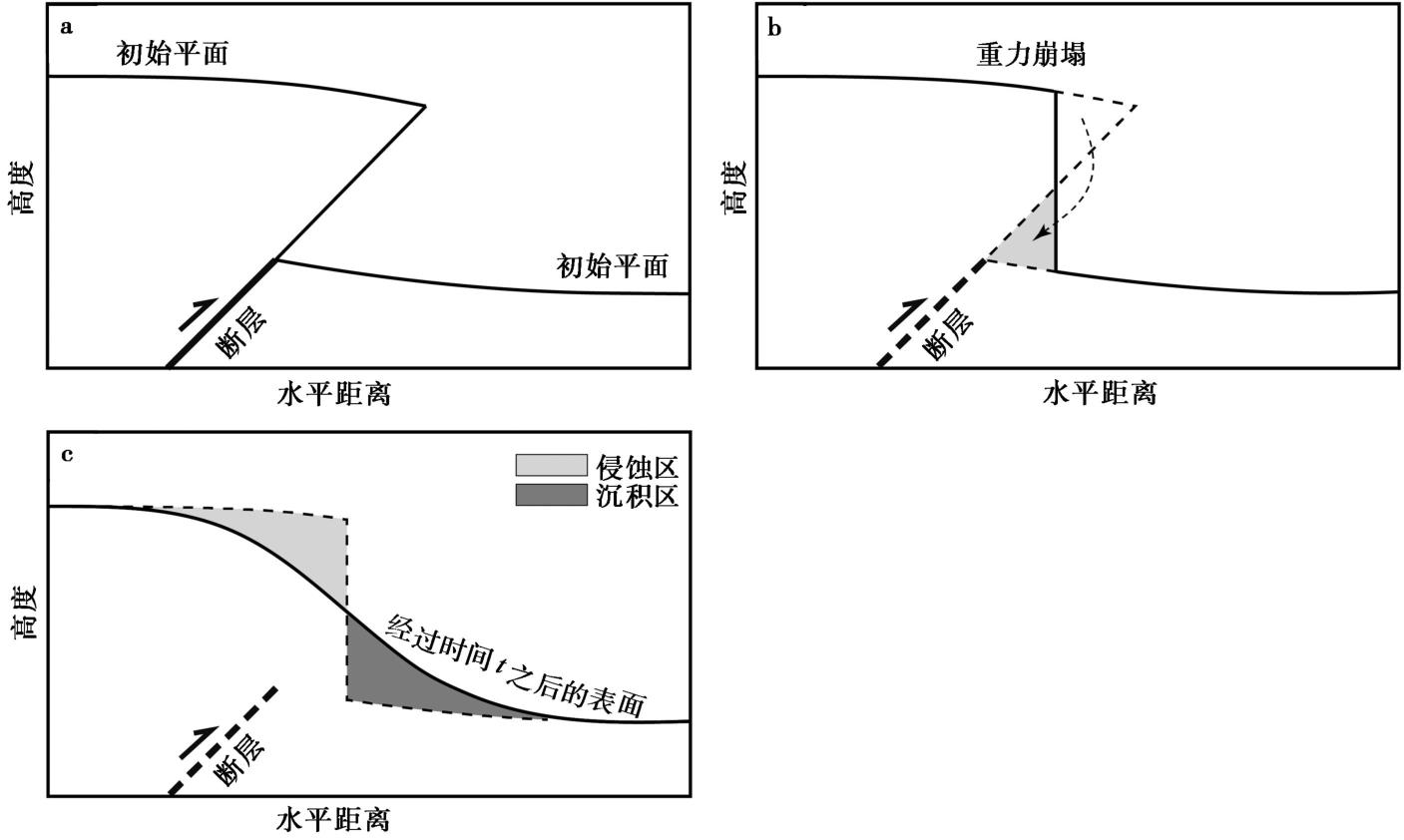
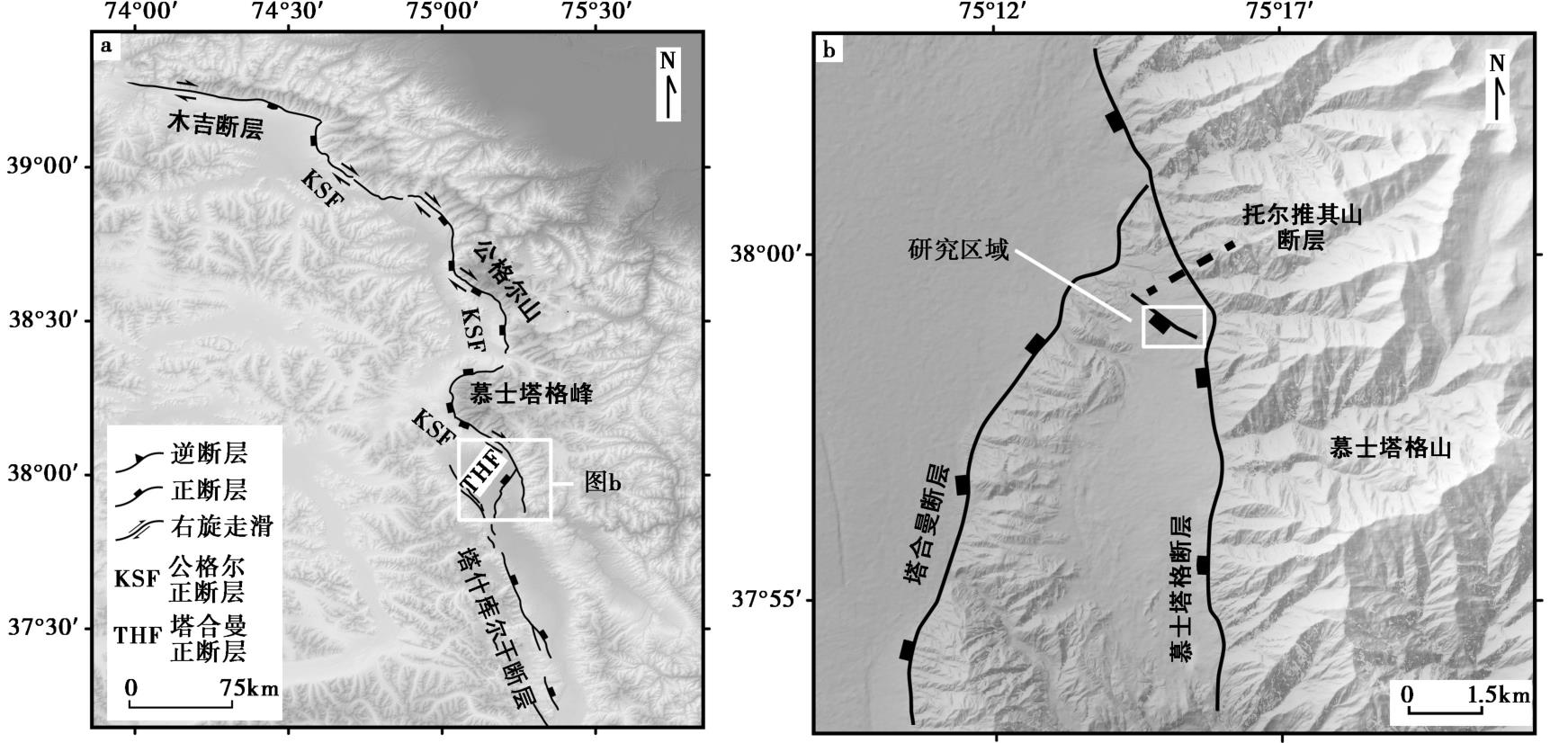
| [1] |
陈汉林, 陈沈强, 林秀斌. 2014. 帕米尔弧形构造带新生代构造演化研究进展[J]. 地球科学进展, 29(8): 890—902.
DOI
|
|
CHEN Han-lin, CHEN Shen-qiang, LIN Xiu-bin. 2014. A review of the Cenozoic tectonic evolution of Pamir Syntax[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 29(8): 890—902(in Chinese).
DOI
|
| [2] |
|
|
CHEN Jie, LI Tao, LI Wen-qiao, et al. 2011. Late Cenozoic and present tectonic deformation in the Pamir Salient, Northwestern China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 33(2): 241—259. (in Chinese).
DOI
|
| [3] |
葛进, 石许华, 陈汉林, 等. 2022. 帕米尔弧形构造带晚第四纪以来的不对称径向逆冲: 多时空尺度变形速率的启示[J]. 第四纪研究, 42(3): 673—691.
|
|
GE Jin, SHI Xu-hua, CHEN Han-lin, et al. 2022. Asymmetric radial thrusting of the Pamir Salient since the Late Quaternary: Implications from the spatio-temporal varations in deformation rates[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 42(3): 673—691. (in Chinese).
|
| [4] |
侯康明, 韩有珍, 张守杰. 1995. 断层崖形成年代的数学模拟计算[J]. 西北地震学报, 17(2): 68—75.
|
|
HOU Kang-ming, HAN You-zhen, ZHANG Shou-jie. 1995. Mathematical model calculation of fault scarp age[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 17(2): 68—75. (in Chinese).
|
| [5] |
李文巧. 2014. 帕米尔高原东北部塔什库尔干谷地活动构造与强震[J]. 国际地震动态, (8): 35—41.
|
|
LI Wen-qiao. 2014. Tectonic activity and strong earthquakes in the Tashkurgan Valley in the northeastern Pamir Plateau[J]. Recent Developments in World Seismology, (8): 35—41(in Chinese).
|
| [6] |
李文巧, 陈杰, 袁兆德, 等. 2011. 帕米尔高原 1895 年塔什库尔干地震地表多段同震破裂与发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 33(2): 260—276.
DOI
|
|
LI Wen-qiao, CHEN Jie, YUAN Zhao-de, et al. 2011. Coseismic surface ruptures of multi segments and seismogenic fault of the Tashkorgan earthquake in Pamir, 1895[J]. Seismology and Geology, 33(2): 260—276(in Chinese).
DOI
|
| [7] |
马金保, 张波, 王洋, 等. 2019. 基于低空遥感地貌观测的逆断层陡坎研究: 以张流沟滩断层陡坎为例[J]. 地学前缘, 26(2): 92—103.
DOI
|
|
MA Jin-bao, ZHANG Bo, WANG Yang, et al. 2019. A study on the scarp of reverse fault based on geomorphological observation by low-altitude remote sensing: taking the fault scarp of Zhangliugou beach as an example[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 26(2): 92—103(in Chinese).
DOI
|
| [8] |
冉勇康, 陈立春, 陈文山, 等. 2012. 中国大陆古地震研究的关键技术与案例解析(2): 汶川地震地表变形特征与褶皱逆断层古地震识别[J]. 地震地质, 34(3): 385—400.
|
|
RAN Yong-kang, CHEN Li-chun, CHEN Wen-shan, et al. 2012. Key techniques and several cases analysis in paleoseismic studies in China’s mainland(2): surface deformation characteristics of Wenchuan earthquake and paleoseismic indicators on fold-reverse fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 34(3): 385—400(in Chinese).
|
| [9] |
沈玉昌. 1986. 河流地貌学概论[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
SHEN Yu-chang. 1986. An Introduction to Fluvial Geomorphology[M]. Science Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
|
| [10] |
张裕明. 1986. 可可托海-二台断层陡坎的坡角变化、 年龄和大地震重复时间间隔[J]. 中国地震, 2(1): 61—68.
|
|
ZHANG Yu-ming. 1986. Slope variation and ages of scarps and recurrence intervals of great earthquakes on Koktohai-Ertai Fault[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 2(1): 61—68(in Chinese).
|
| [11] |
Ahnert F. 1976. Brief description of a comprehensive three-dimensional process-response model for landform development[J]. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie, NF, Supplementband, 25: 29—49.
|
| [12] |
Ahnert F. 1988. Modelling landform change[G]// Anderson M G. Modelling Geomorphological Systems. John Wiley & Sons, Chichester: 375—400.
|
| [13] |
Anderson R S, Humphrey N F. 1989. Interaction of weathering and transport processes in the evolution of arid landscape[G]// Cross T. Quantitative Dynamic Stratigraphy. Prentice Hall, New Jersey: 349—361.
|
| [14] |
Anderson R S. 1994. Evolution of the Santa-Cruz Mountains, California, through tectonic growth and geomorphic decay[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 99(B10): 2016120179.
|
| [15] |
Anderson R S. 2002. Modeling the tor-dotted crests, bedrock edges, and parabolic profiles of high alpine surfaces of the Wind River Range, Wyoming[J]. Geomorphology, 46(1-2): 35—58.
|
| [16] |
Andrews D J, Bucknam R C. 1987. Fitting degradation of shoreline scarps by a nonlinear diffusion-model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth and Planets, 92(B12): 12857—12867.
|
| [17] |
Andrews D J, Hanks T C. 1985. Scarp degraded by linear diffusion: Inverse solution for age[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth and Planets, 90(Nb12): 193—208.
|
| [18] |
Arnaud N, Brunel M, Cantagrel J, et al. 1993. High cooling and denudation rates at Kongur Shan, eastern Pamir(Xinjiang, China)revealed by 40Ar/39Ar alkali feldspar thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 12(6): 1335—1346.
|
| [19] |
Arrowsmith J R, Pollard D D, Rhodes D D. 1996. Hillslope development in areas of active tectonics[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 101(B3): 6255—6275.
|
| [20] |
Arrowsmith J R, Rhodes D D, Pollard D D. 1998. Morphologic dating of scarps formed by repeated slip events along the San Andreas Fault, Carrizo Plain, California[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 103(B5): 10141—10160.
|
| [21] |
Avouac J P. 1993. Analysis of scarp profiles: evaluation of errors in morphologic dating[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 98(B4): 6745—6754.
|
| [22] |
Avouac J P, Peltzer G. 1993. Active tectonics in southern Xinjiang, China: Analysis of terrace riser and normal fault scarp degradation along the Hotan-Qira fault system[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 98(B12): 21773—21807.
|
| [23] |
Banks M E, Watters T R, Robinson M S, et al. 2012. Morphometric analysis of small-scale lobate scarps on the Moon using data from the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 117(E12): E00H11.
|
| [24] |
Braun J, Sambridge M. 1997. Modelling landscape evolution on geological time scales: A new method based on irregular spatial discretization[J]. Basin Research, 9(1): 27—52.
|
| [25] |
Brunel M, Arnaud N, Tapponnier P, et al. 1994. Kongur Shan normal fault: Type example of mountain building assisted by extension(Karakoram fault, eastern Pamir)[J]. Geology, 22(8): 707—710.
|
| [26] |
Bucknam R, Anderson R. 1979. Estimation of fault-scarp ages from a scarp-height-slope-angle relationship[J]. Geology, 7(1): 11—14.
|
| [27] |
Burbank D W, Anderson R S. 2011. Tectonic Geomorphology[M]. John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, NJ.
|
| [28] |
Carretier S, Ritz J, Jackson J, et al. 2002. Morphological dating of cumulative reverse fault scarps: Examples from the Gurvan Bogd fault system, Mongolia[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 148(2): 256—277.
|
| [29] |
Carson M A, Petley D J. 1970. The existence of threshold hillslopes in the denudation of the landscape[J]. Transactions of the Institute of British Geographers, 49: 71—95.
|
| [30] |
Chevalier M L, Li H, Pan J, et al. 2011. Fast slip-rate along the northern end of the Karakorum fault system, western Tibet[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 38(22): L22309.
|
| [31] |
Chevalier M L, Pan J, Li H, et al. 2015. Quantification of both normal and right-lateral late Quaternary activity along the Kongur Shan extensional system, Chinese Pamir[J]. Terra Nova, 27(5): 379—391.
|
| [32] |
Clarke B A, Burbank D W. 2010. Bedrock fracturing, threshold hillslopes, and limits to the magnitude of bedrock landslides[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 297(3-4): 577—586.
|
| [33] |
Clifford S M. 1993. A model for the hydrologic and climatic behavior of water on Mars[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 98(E6): 10973—11016.
|
| [34] |
Colman S M, Watson K. 1983. Ages estimated from a diffusion equation model for scarp degradation[J]. Science, 221(4607): 263—265.
PMID
|
| [35] |
Craddock R A, Maxwell T A. 1993. Geomorphic evolution of the Martian highlands through ancient fluvial processes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 98(E2): 3453—3468.
|
| [36] |
Culling W E H. 1960. Analytical theory of erosion[J]. Journal of Geology, 68(3): 336—344.
|
| [37] |
Culling W E H. 1963. Soil creep and the development of hillside slopes[J]. Journal of Geology, 71(2): 127—161.
|
| [38] |
David A V, Spagnuolo M G, Silvestro S. 2014. Morphometric and geometric characterization of normal faults on Mars[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 41: 83—94.
|
| [39] |
Davis W M. 1892. The convex profile of bad-land divides[J]. Science, 20(508): 245.
|
| [40] |
de’ Michieli Vitturi M, Arrowsmith J R. 2013. Two-dimensional nonlinear diffusive numerical simulation of geomorphic modifications to cinder cones[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 38(12): 1432—1443.
|
| [41] |
De Chant L J, Pease P, Tchakerian V P. 1999. Modelling alluvial fan morphology[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 24(7): 641—652.
|
| [42] |
DeChant L J, Pease P, Tchakerian V P. 2021. Alluvial fan morphology: A self-similar free boundary problem description[J]. Geomorphology, 375(2): 107532.
|
| [43] |
Dietrich W E, Bellugi D G, Sklar L S, et al. 2003. Geomorphic transport laws for predicting landscape form and dynamics[G]//Wilcock P R, Iverson R M. Prediction in Geomorphology. Blackwell Publishing Limited, Oxford, UK: 103—132.
|
| [44] |
Dietrich W E, Perron J T. 2006. The search for a topographic signature of life[J]. Nature, 439(7075): 411—418.
|
| [45] |
Dietrich W E, Reiss R, Hsu M L, et al. 1995. A process-based model for colluvial soil depth and shallow landsliding using digital elevation data[J]. Hydrological Processes, 9(3-4): 383—400.
|
| [46] |
Doane T H. 2018. Theory and application of nonlocal hillslope sediment transport[D]. Vanderbilt University, Nashville, Tennessee.
|
| [47] |
Dunne T, Malmon D V, Dunne K B J. 2016. Limits on the morphogenetic role of rain splash transport in hillslope evolution[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research-Earth Surface, 121(3): 609—622.
|
| [48] |
Dunne T, Malmon D V, Mudd S M. 2010. A rain splash transport equation assimilating field and laboratory measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 115(F1): F01001.
|
| [49] |
Fagherazzi S, Howard A D, Wiberg P L. 2002. An implicit finite difference method for drainage basin evolution[J]. Water Resources Research, 38(7): 21—25.
|
| [50] |
Fernandes N F, Dietrich W E. 1997. Hillslope evolution by diffusive processes: The timescale for equilibrium adjustments[J]. Water Resources Research, 33(6): 1307—1318.
|
| [51] |
Fleming R W, Johnson A M. 1975. Rates of seasonal creep of silty clay soil[J]. Quarterly Journal of Engineering Geology, 8(1): 1—29.
|
| [52] |
Forman S L, Nelson A R, Mccalpin J P. 1991. Thermoluminescence dating of fault-scarp-derived colluvium: Deciphering the timing of paleoearthquakes on the Weber Segment of the Wasatch fault zone, north central Utah[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 96(B1): 595—605.
|
| [53] |
Foufoula-Georgiou E, Ganti V, Dietrich W. 2010. A nonlocal theory of sediment transport on hillslopes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 115(F2): F00A16.
|
| [54] |
Furbish D, Dietrich W. 2000. The diffusion-like coefficient in hillslope evolution models described in terms of the frequency and magnitude of soil particle motions associated with biological activity[J]. Geological Society of America Abstracts with Programs, 32(7): A-117.
|
| [55] |
Furbish D J, Fathel S L, Schmeeckle M W, et al. 2017. The elements and richness of particle diffusion during sediment transport at small timescales[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 42(1): 214—237.
|
| [56] |
Furbish D J, Haff P K. 2010. From divots to swales: Hillslope sediment transport across divers length scales[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 115(F3): F03001.
|
| [57] |
Furbish D J, Hamner K K, Schmeeckle M, et al. 2007. Rain splash of dry sand revealed by high-speed imaging and sticky paper splash targets[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 112(F1): F01001.
|
| [58] |
Furbish D J, Roering J J. 2013. Sediment disentrainment and the concept of local versus nonlocal transport on hillslopes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 118(2): 937—952.
|
| [59] |
Gabet E J. 2000. Gopher bioturbation: Field evidence for non-linear hillslope diffusion[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 25(13): 1419—1428.
|
| [60] |
Gabet E J. 2003. Sediment transport by dry ravel[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 108(B1): 2049.
|
| [61] |
Ganti V, Passalacqua P, Foufoula-Georgiou E. 2012. A sub-grid scale closure for nonlinear hillslope sediment transport models[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 117(F2): F02012.
|
| [62] |
Ge J, Shi X, Chen H, et al. 2022. Two kinematic transformations of the Pamir salient since the Mid-Cenozoic: Constraints from multi-timescale deformation analysis[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 10: 967529.
|
| [63] |
Gilbert G K. 1877. Report on the Geology of the Henry Mountains[M]. US Government Printing Office, Washington.
|
| [64] |
Gilbert G K. 1909. The convexity of hilltops[J]. Journal of Geology, 17(4): 344—350.
|
| [65] |
Golombek M, Bridges N. 2000. Erosion rates on Mars and implications for climate change: Constraints from the Pathfinder landing site[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Planets, 105(E1): 1841—1853.
|
| [66] |
Gosse J C, Phillips F M. 2001. Terrestrial in situ cosmogenic nuclides: theory and application[J]. Quaternary Science Reviews, 20(14): 1475—1560.
|
| [67] |
Guerit L, Métivier F, Devauchelle O, et al. 2014. Laboratory alluvial fans in one dimension[J]. Physical Review E, 90(2): 022203.
|
| [68] |
Hanks T C. 2000. The age of scarplike landforms from diffusion-equation analysis [G]// Noller J S, Sowers J M, Lettis W R. Quaternary Geochronology: Methods and Applications. John Wiley & Sons, Washington: 313—338.
|
| [69] |
Hanks T C, Andrews D J. 1989. Effect of far-field slope on morphologic dating of scarplike landforms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth and Planets, 94(B1): 565—573.
|
| [70] |
Hanks T C, Bucknam R C, Lajoie K R, et al. 1984. Modification of wave-cut and faulting-controlled landforms[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 89(Nb7): 5771—5790.
|
| [71] |
Hanks T C, Wallace R E. 1985. Morphological analysis of the Lake Lahontan shoreline and beachfront fault scarps, Pershing County, Nevada[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 75(3): 835—846.
|
| [72] |
Harkins N, Kirby E. 2008. Fluvial terrace riser degradation and determination of slip rates on strike-slip faults: An example from the Kunlun fault, China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 35(5): L05406.
|
| [73] |
Hecker S. 1985. Timing of Holocene faulting in part of a seismic belt, west-central Nevada, M.S[D]. University of Arizona, Tucson.
|
| [74] |
Heimsath A M, Dietrich W E, Nishiizumi K, et al. 1997. The soil production function and landscape equilibrium[J]. Nature, 388(6640): 358—361.
|
| [75] |
Hodge M, Biggs J, Fagereng Å, et al. 2020. Evidence from high-resolution topography for multiple earthquakes on high slip-to-length fault scarps: The Bilila-Mtakataka fault, Malawi[J]. Tectonics, 39(2): e2019TC005933.
|
| [76] |
Howard A D. 1994. A detachment-limited model of drainage basin evolution[J]. Water Resources Research, 30(7): 2261—2285.
|
| [77] |
Howard A D. 1997. Badland morphology and evolution: Interpretation using a simulation model[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 22(3): 211—227.
|
| [78] |
Hsu L, Pelletier J D. 2004. Correlation and dating of Quaternary alluvial-fan surfaces using scarp diffusion[J]. Geomorphology, 60(3-4): 319—335.
|
| [79] |
James M R, Robson S. 2012. Straightforward reconstruction of 3D surfaces and topography with a camera: Accuracy and geoscience application[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 117(F3): F03017.
|
| [80] |
Johnson K, Nissen E, Saripalli S, et al. 2014. Rapid mapping of ultrafine fault zone topography with structure from motion[J]. Geosphere, 10(5): 969—986.
|
| [81] |
Kirkby M. 1971. Hillslope process-response models based on the continuity equation[J]. Special Publication Institute of British Geographers, 3(1): 15—30.
|
| [82] |
Kirkby M J. 1967. Measurement and theory of soil creep[J]. Journal of Geology, 75(4): 359—378.
|
| [83] |
Kirkby M J. 1984. Modeling cliff development in South-Wales-Savigear Re-Viewed[J]. Zeitschrift Fur Geomorphologie, 28(4): 405—426.
|
| [84] |
Kirkby M J. 1985. A basis for soil-profile modeling in a geomorphic context[J]. Journal of Soil Science, 36(1): 97—121.
|
| [85] |
Kooi H, Beaumont C. 1994. Escarpment evolution on high-elevation rifted margins-Insights derived from a surface processes model that combines diffusion, advection, and reaction[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 99(B6): 12191—12209.
|
| [86] |
Lu L, Zhou Y, Zhang P, et al. 2022. Modelling fault scarp degradation to determine earthquake history on the Muztagh Ata and Tahman faults in the Chinese Pamir[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science. 10: 342.
|
| [87] |
Machette M, Personius S, Nelson A. 1987. Quaternary geology along the Wasatch fault zone: segmentation, recent investigations, and preliminary conclusions[R]// Gori P L, Hays W W. Assessment of Regional Earthquake Hazards and Risk Along the Wasatch Front, Utah: US Geological Survey: 87-585(A1—A72).
|
| [88] |
Martin Y. 2000. Modelling hillslope evolution: linear and nonlinear transport relations[J]. Geomorphology, 34(1-2): 1—21.
|
| [89] |
Martin Y, Church M. 1997. Diffusion in landscape development models: On the nature of basic transport relations[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 22(3): 273—279.
|
| [90] |
Mattson A, Bruhn R L. 2001. Fault slip rates and initiation age based on diffusion equation modeling: Wasatch fault zone and eastern Great Basin[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 106(B7): 13739—13750.
|
| [91] |
Mayer L. 1984. Dating Quaternary fault scarps formed in alluvium using morphologic parameters[J]. Quaternary Research, 22(3): 300—313.
|
| [92] |
Mckean J A, Dietrich W E, Finkel R C, et al. 1993. Quantification of soil production and downslope creep rates from cosmogenic 10Be accumulations on a hillslope profile[J]. Geology, 21(4): 343—346.
|
| [93] |
Mitchell N C. 1995. Diffusion transport model for pelagic sediments on the Mid-Atlantic Ridge[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 100(B10): 19991—20009.
|
| [94] |
Mitchell N C. 1996. Creep in pelagic sediments and potential for morphologic dating of marine fault scarps[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 23(5): 483—486.
|
| [95] |
Mitchell S G, Matmon A, Bierman P R, et al. 2001. Displacement history of a limestone normal fault scarp, northern Israel, from cosmogenic 36Cl[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 106(B3): 4247—4264.
|
| [96] |
Nash D B. 1980a. Forms of bluffs degraded for different lengths of time in Emmet-County, Michigan, USA[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 5(4): 331—345.
|
| [97] |
Nash D B. 1980b. Morphologic dating of degraded normal-fault scarps[J]. The Journal of Geology, 88(3): 353—360.
|
| [98] |
Nash D B. 1984. Morphologic dating of fluvial terrace scarps and fault scarps near West Yellowstone, Montana[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 95(12): 1413—1424.
|
| [99] |
Newman W I. 1983. Nonlinear diffusion: Self-similarity and traveling-waves[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 121(3): 417—441.
|
| [100] |
Pelletier J D, Cline M L. 2007. Nonlinear slope-dependent sediment transport in cinder cone evolution[J]. Geology, 35(12): 1067—1070.
|
| [101] |
Pelletier J D. 2008. Quantitative Modeling of Earth Surface Processes[M]. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
|
| [102] |
Pelletier J D, Delong S B, AI Suwaidi A H, et al. 2006. Evolution of the Bonneville shoreline scarp in west-central Utah: Comparison of scarp-analysis methods and implications for the diffusion model of hillslope evolution[J]. Geomorphology, 74(1-4): 257—270.
|
| [103] |
Perron J T. 2011. Numerical methods for nonlinear hillslope transport laws[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 116(F2): F02021.
|
| [104] |
Perron J T, Dietrich W E, Howard A D, et al. 2003. Ice-driven creep on Martian debris slopes[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 30(14): 1747.
|
| [105] |
Petit C, Mouthereau F. 2012. Steep topographic slope preservation by anisotropic diffusion: An example from the Neogene Têt fault scarp, eastern Pyrenees[J]. Geomorphology, 171: 173—179.
|
| [106] |
Pierce K L, Colman S M. 1986. Effect of height and orientation(microclimate)on geomorphic degradation rates and processes, late-glacial terrace scarps in central Idaho[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 97(7): 869—885.
|
| [107] |
Press W H, Teukolsky S A, Vetterling W T, et al. 1992. Numerical recipes in C: The Art of Scientific Computing, Second Edition[M]. Cambrige University Press, Cambrige.
|
| [108] |
Rhodes E J. 2011. Optically stimulated luminescence dating of sediments over the past 200, 000 years[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 39: 461—488.
|
| [109] |
Ritter J B, Miller J R, Enzel Y, et al. 1995. Reconciling the roles of tectonism and climate in Quaternary alluvial fan evolution[J]. Geology, 23(3): 245—248.
|
| [110] |
Ritz J F, Bourles D, Brown E, et al. 2003. Late Pleistocene to Holocene slip rates for the Gurvan Bulag thrust fault(Gobi-Altay, Mongolia)estimated with 10Be dates[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 108(B3): 2162.
|
| [111] |
Robinson A C, Yin A, Manning C E, et al. 2004. Tectonic evolution of the northeastern Pamir: Constraints from the northern portion of the Cenozoic Kongur Shan extensional system, western China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 116(7-8): 953—973.
|
| [112] |
Robinson A C, Yin A, Manning C E, et al. 2007. Cenozoic evolution of the eastern Pamir: Implications for strain-accommodation mechanisms at the western end of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 119(7-8): 882—896.
|
| [113] |
Roering J J. 2004. Soil creep and convex-upward velocity profiles: Theoretical and experimental investigation of disturbance-driven sediment transport on hillslopes[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 29(13): 1597—1612.
|
| [114] |
Roering J J, Kirchner J W, Dietrich W E. 1999. Evidence for nonlinear, diffusive sediment transport on hillslopes and implications for landscape morphology[J]. Water Resources Research, 35(3): 853—870.
|
| [115] |
Roering J J, Kirchner J W, Dietrich W E. 2001a. Hillslope evolution by nonlinear, slope-dependent transport: Steady state morphology and equilibrium adjustment timescales[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 106(B8): 16499—16513.
|
| [116] |
Roering J J, Kirchner J W, Sklar L S, et al. 2001b. Hillslope evolution by nonlinear creep and landsliding: An experimental study[J]. Geology, 29(2): 143—146.
|
| [117] |
Ruj T, Komatsu G, Pondrelli M, et al. 2018. Morphometric analysis of a Hesperian-aged Martian lobate scarp using high-resolution data[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 113: 1—9.
|
| [118] |
Schultz R A, Okubo C H, Wilkins S J. 2006. Displacement-length scaling relations for faults on the terrestrial planets[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 28(12): 2182—2193.
|
| [119] |
Schumer R, Meerschaert M M, Baeumer B. 2009. Fractional advection-dispersion equations for modeling transport at the Earth’s surface[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 114(F4): F00A07.
|
| [120] |
Selby M J, Hodder A P W. 1993. Hillslope Materials and Processes[M]. Oxford University Press, Oxford.
|
| [121] |
Shean D. 2017. High Mountain Asia 8-meter DEM Mosaics Derived from Optical Imagery, Version 1[DB/OL]. Boulder, Colorado USA: NASA National Snow and Ice Data Center Distributed Active Archive Center.
|
| [122] |
Strahler A N. 1950. Davis’ concepts of slope development viewed in the light of recent quantitative investigations[J]. Annals of the Association of American Geographers, 40(3): 209—213.
|
| [123] |
Tucker G E, Bradley D N. 2010a. Trouble with diffusion: Reassessing hillslope erosion laws with a particle-based model[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 115(F1): F00A10.
|
| [124] |
Tucker G E, Bras R L. 1998. Hillslope processes, drainage density, and landscape morphology[J]. Water Resources Research, 34(10): 2751—2764.
|
| [125] |
Tucker G E, Hancock G R. 2010b. Modelling landscape evolution[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 35(1): 28—50.
|
| [126] |
Tucker G E, Slingerland R L. 1994. Erosional dynamics, flexural isostasy, and long-lived escarpments: A numerical modeling study[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 99(B6): 12229—12243.
|
| [127] |
Van Der Beek P, Braun J. 1998. Numerical modelling of landscape evolution on geological time-scales: A parameter analysis and comparison with the south-eastern highlands of Australia[J]. Basin Research, 10(1): 49—68.
|
| [128] |
Wallace R E. 1977. Profiles and ages of young fault scarps, north-central Nevada[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 88(9): 1267—1281.
|
| [129] |
Wallace R E. 1986. Active Tectonics: Impact on Society[M]. The National Academy Press, Washington.
|
| [130] |
Webb H F, Jordan T H. 1993. Quantifying the distribution and transport of pelagic sediments on young abyssal hills[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 20(20): 2203—2206.
|
| [131] |
Westoby M J, Brasington J, Glasser N F, et al. 2012. ‘Structure-from-Motion ’photogrammetry: A low-cost, effective tool for geoscience applications[J]. Geomorphology, 179: 300—314.
|
| [132] |
Willgoose G, Bras R L, Rodriguez-Iturbe I. 1991. A coupled channel network growth and hillslope evolution model.1. Theory[J]. Water Resources Research, 27(7): 1671—1684.
|
| [133] |
Xu J H, Arrowsmith J R, Chen J, et al. 2021. Evaluating young fluvial terrace riser degradation using a nonlinear transport model: Application to the Kongur Normal Fault in the Pamir, northwest China[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 46(1): 280—295.
|
| [134] |
Yoo K, Amundson R, Heimsath A M, et al. 2005. Process-based model linking pocket gopher(Thomomys bottae)activity to sediment transport and soil thickness[J]. Geology, 33(11): 917—920.
|
| [135] |
Young A. 1960. Soil movement by denudational processes on slopes[J]. Nature, 188(4745): 120—122.
|
 ), 徐皓婷1)(
), 徐皓婷1)( ), 石许华1,2,3),*(
), 石许华1,2,3),*( ), 葛进1,2), 李丰1,2)
), 葛进1,2), 李丰1,2)
 ), XU Hao-ting1)(
), XU Hao-ting1)( ), SHI Xu-hua1,2,3),*(
), SHI Xu-hua1,2,3),*( ), GE Jin1,2), LI Feng1,2)
), GE Jin1,2), LI Feng1,2)