地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 772-794.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.03.010
王博1,2)( ), 崔凤珍3), 刘静1,3),*(
), 崔凤珍3), 刘静1,3),*( ), 周永胜1), 徐胜3), 邵延秀3)
), 周永胜1), 徐胜3), 邵延秀3)
收稿日期:2022-05-25
修回日期:2022-12-15
出版日期:2023-06-20
发布日期:2023-07-18
通讯作者:
* 刘静, 女, 1969年生, 教授, 主要从事活动构造、 地震地质、 古地震和地貌学等方面的研究, E-mail: 作者简介:王博, 男, 1984年生, 2023年于中国地震局地质研究所获构造地质专业博士学位, 主要研究方向为构造物理实验及流体动力学, E-mail: wangbo313@163.com。
基金资助:
WANG Bo1,2)( ), CUI Feng-zhen3), LIU-ZENG Jing1,3),*(
), CUI Feng-zhen3), LIU-ZENG Jing1,3),*( ), ZHOU Yong-sheng1), XU Sheng3), SHAO Yan-xiu3)
), ZHOU Yong-sheng1), XU Sheng3), SHAO Yan-xiu3)
Received:2022-05-25
Revised:2022-12-15
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-07-18
摘要:
2021年5月22日2时4分, 青海省果洛藏族自治州玛多县发生 MS7.4 地震。震后一个月, 在对地震地表破裂带的展布和同震位移进行详细勘察后, 有针对性地沿地表破裂带不同部位(西段、 中西段、 中东段、 东段)布设了7条800~3 000m的跨断裂测线, 对土壤气Rn、 H2、 Hg和CO2进行浓度测量和气体采集, 并对采集样品进行了碳同位素和氦同位素分析。测量结果表明, 地表各破裂段土壤气浓度的最大值差别较大, 破裂带东、 西两端的气体浓度较高而中段气体浓度较低, 可能与断层不同分段的破裂方式和应力分量不一致有关。土壤气中H2和Hg的浓度特征具有较好的一致性, 在地表破裂带内或紧邻处浓度较高。玛多 MS7.4 地震的发震断层东端出现多条分支, 破裂具有复杂性。从土壤气浓度测量结果来看, 南支和北支断层的活动都较强, 但北支断裂土壤气逸出浓度的曲线形态特征和断层产状不一致, 可能与北支断裂地表破裂范围大且存在多条次级断裂有关。3He/4He测定结果表明, 研究区土壤气中的稀有气体主要为大气来源, 但δ13C测值和CO2/3He计算结果显示玛多地震断层土壤气具有大气组分与地壳组分的混合特征。
王博, 崔凤珍, 刘静, 周永胜, 徐胜, 邵延秀. 玛多 MS7.4地震断层土壤气特征与地表破裂的相关性[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 772-794.
WANG Bo, CUI Feng-zhen, LIU-ZENG Jing, ZHOU Yong-sheng, XU Sheng, SHAO Yan-xiu. FAULT GAS OBSERVATION AND SURFACE RUPTURE FEATURE INTERPRETATION OF THE MS7.4 MADOI EARTHQUAKE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(3): 772-794.
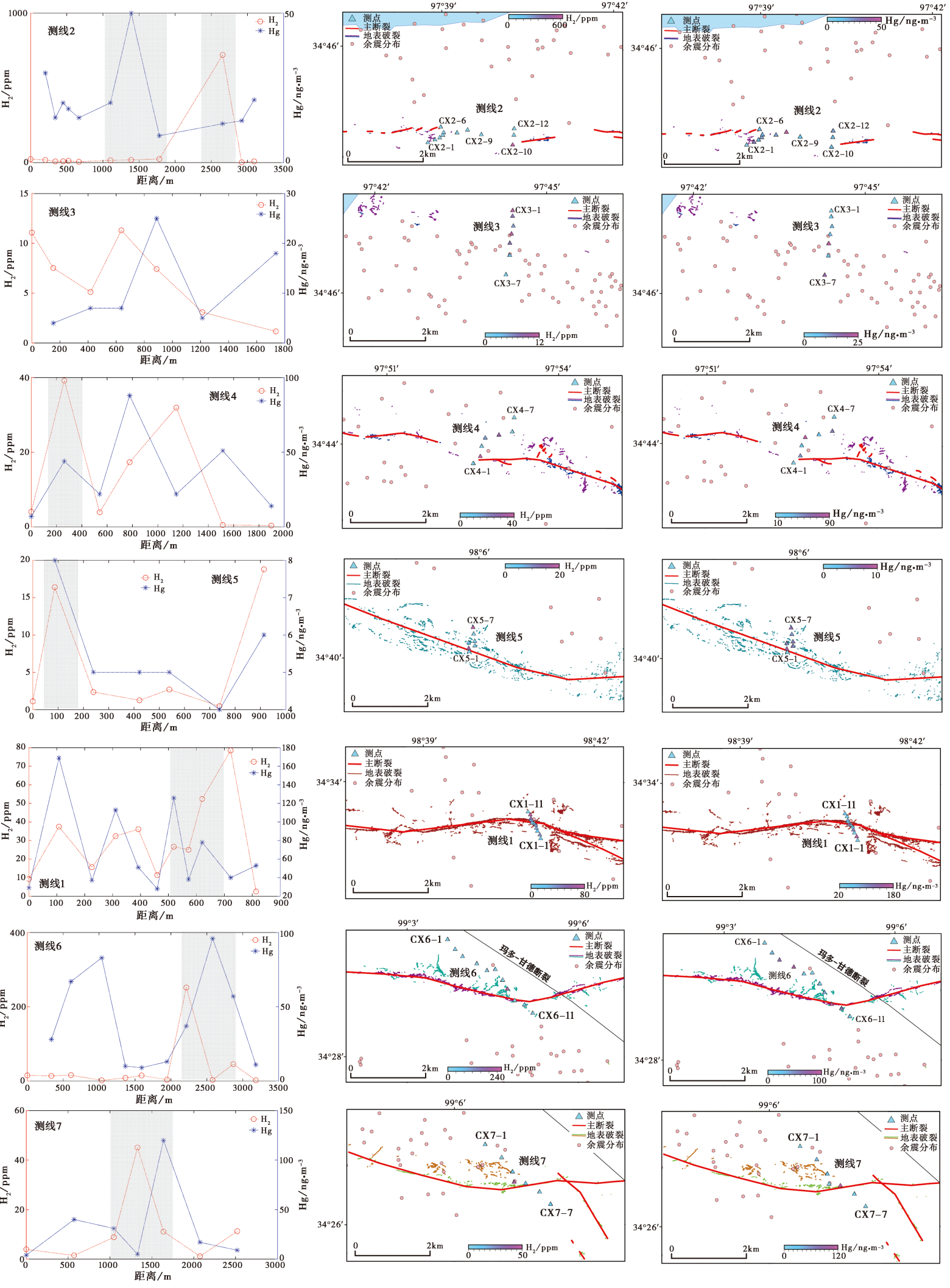
图 3 断层破裂带土壤气H2和Hg的浓度曲线和测点分布 自上而下, 测线依次沿地表破裂自西向东排列, 灰色阴影区域表示断层地表主破裂带
Fig. 3 H2 and Hg concentration curves of the soil gas in the fault rupture zone and the distribution of sampling points.
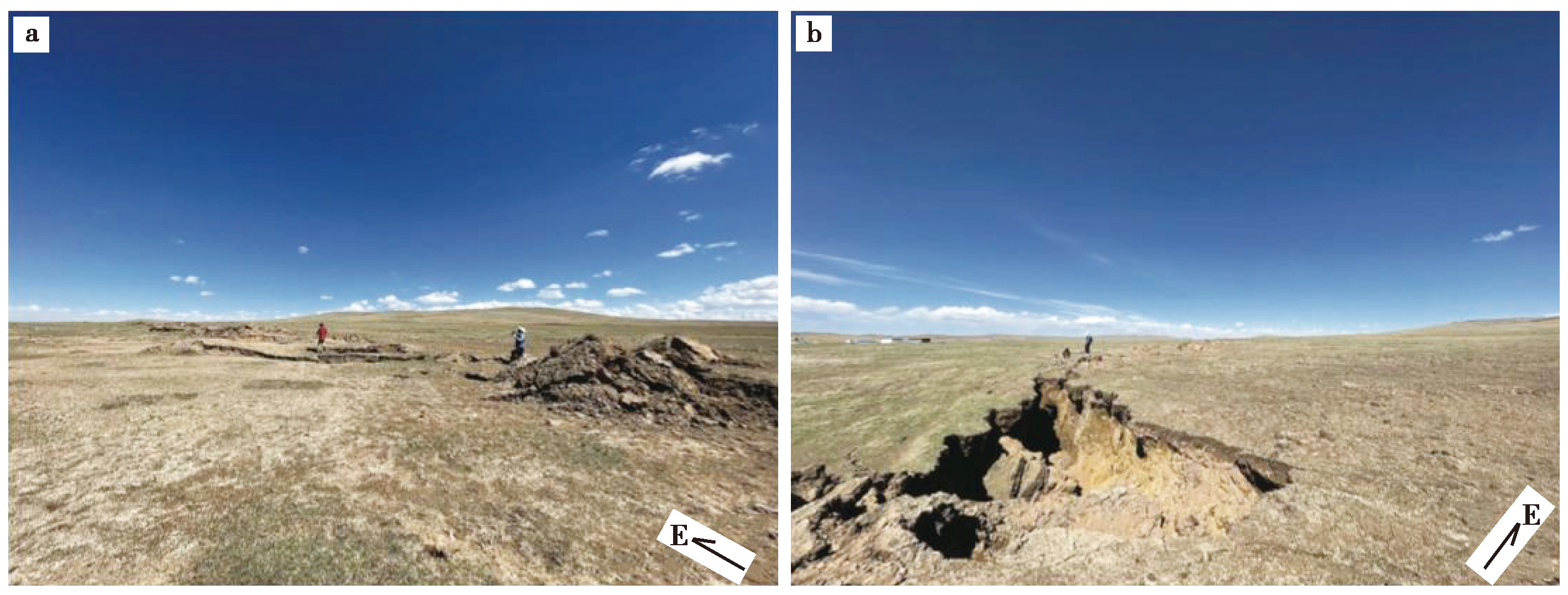
图 4 玛多地震西段鄂陵湖南侧雁列排列的剪切裂缝和鼓包
Fig. 4 Surface rupture(shearing fracture sand bulges)at the south of the Eling Lake on the western section of the Madoi earthquake.
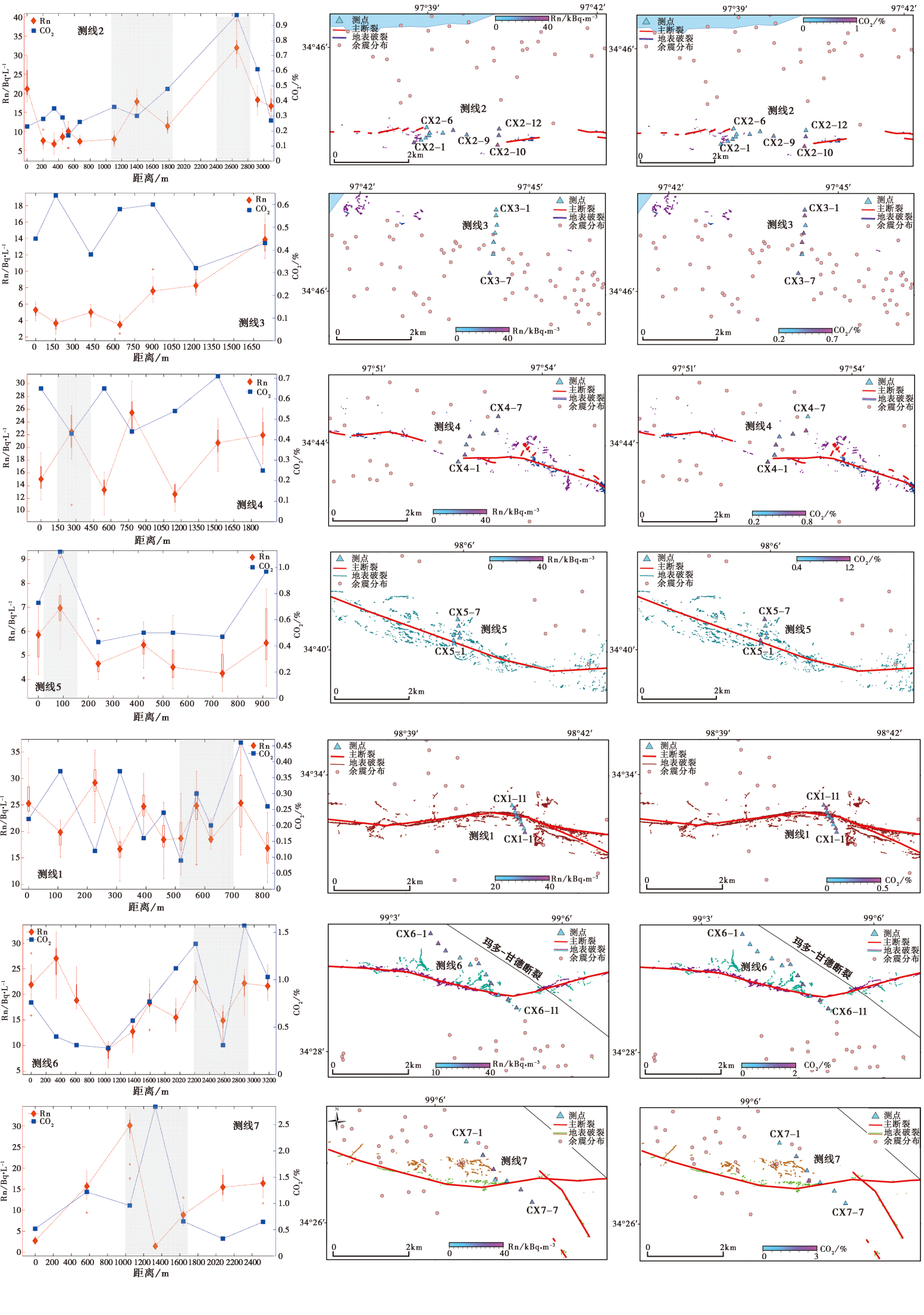
图 5 断层破裂带土壤气Rn和CO2的浓度曲线和测点分布 自上而下, 测线依次沿地表破裂自西向东排列, 灰色阴影区域表示断层地表主破裂带
Fig. 5 Rn and CO2 concentration curves of the soil gas in fault rupture zone and the distribution of sampling points.
| 序号 | 测点编号 | 采样时间 | δ13C/‰ | CO2/% | 采样方式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CX1-6(1) | 2021-06-23 | -19.7 | 0.24 | 气袋 |
| 2 | CX1-6(3) | 2021-06-23 | -19.6 | 0.24 | 气袋 |
| 3 | CX1-7(1) | 2021-06-23 | -13.6 | 0.09 | 瓶样 |
| 4 | CX1-8(1) | 2021-06-23 | -14.2 | 0.30 | 瓶样 |
| 5 | CX1-8(2) | 2021-06-23 | -22.2 | 0.30 | 气袋 |
| 6 | CX1-8(4) | 2021-06-23 | -20.1 | 0.30 | 气袋 |
| 7 | CX1-10(1) | 2021-06-23 | -14.0 | 0.46 | 瓶样 |
| 8 | CX2-5(1) | 2021-06-25 | -17.2 | 0.17 | 气袋 |
| 9 | CX2-5(2) | 2021-06-25 | -13.0 | 0.17 | 瓶样 |
| 10 | CX2-5(3) | 2021-06-25 | -17.2 | 0.17 | 气袋 |
| 11 | CX2-11(1) | 2021-06-25 | -14.3 | 0.61 | 瓶样 |
| 12 | CX2-11(2) | 2021-06-25 | -21.3 | 0.61 | 气袋 |
| 13 | CX2-11(4) | 2021-06-25 | -21.0 | 0.61 | 气袋 |
| 14 | CX3-4(1) | 2021-06-26 | -13.9 | 0.58 | 瓶样 |
| 15 | CX3-5(1) | 2021-06-26 | -20.2 | 0.60 | 气袋 |
| 16 | CX4-4(1) | 2021-06-26 | -13.6 | 0.44 | 瓶样 |
| 17 | CX4-4(1) | 2021-06-26 | -19.2 | 0.44 | 气袋 |
| 18 | CX4-4(2) | 2021-06-26 | -13.6 | 0.44 | 瓶样 |
| 19 | CX4-4(3) | 2021-06-26 | -19.2 | 0.44 | 气袋 |
| 20 | CX5-3(1) | 2021-06-27 | -14.0 | 0.43 | 瓶样 |
| 21 | CX5-4(2) | 2021-06-27 | -21.3 | 0.50 | 气袋 |
| 22 | CX5-4(4) | 2021-06-27 | -21.8 | 0.50 | 气袋 |
| 23 | CX6-6(1) | 2021-06-28 | -20.8 | 0.77 | 气袋 |
| 24 | CX6-6(3) | 2021-06-28 | -20.8 | 0.77 | 气袋 |
| 25 | CX6-7(1) | 2021-06-28 | -17.9 | 1.12 | 瓶样 |
| 26 | CX6-7(2) | 2021-06-28 | -15.9 | 1.12 | 瓶样 |
| 27 | CX6-7(2) | 2021-06-28 | -22.1 | 1.12 | 气袋 |
| 28 | CX6-7(4) | 2021-06-28 | -22.3 | 1.12 | 气袋 |
| 29 | CX6-8(3) | 2021-06-28 | -21.7 | 1.38 | 气袋 |
| 30 | CX7-4(1) | 2021-06-29 | -12.5 | 2.84 | 瓶样 |
| 31 | CX7-4(2) | 2021-06-29 | -12.5 | 2.84 | 瓶样 |
| 32 | CX7-5(1) | 2021-06-29 | -14.4 | 0.66 | 瓶样 |
表 2 土壤气中CO2的同位素组成
Table 2 Isotopic composition of CO2 in soil gases
| 序号 | 测点编号 | 采样时间 | δ13C/‰ | CO2/% | 采样方式 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CX1-6(1) | 2021-06-23 | -19.7 | 0.24 | 气袋 |
| 2 | CX1-6(3) | 2021-06-23 | -19.6 | 0.24 | 气袋 |
| 3 | CX1-7(1) | 2021-06-23 | -13.6 | 0.09 | 瓶样 |
| 4 | CX1-8(1) | 2021-06-23 | -14.2 | 0.30 | 瓶样 |
| 5 | CX1-8(2) | 2021-06-23 | -22.2 | 0.30 | 气袋 |
| 6 | CX1-8(4) | 2021-06-23 | -20.1 | 0.30 | 气袋 |
| 7 | CX1-10(1) | 2021-06-23 | -14.0 | 0.46 | 瓶样 |
| 8 | CX2-5(1) | 2021-06-25 | -17.2 | 0.17 | 气袋 |
| 9 | CX2-5(2) | 2021-06-25 | -13.0 | 0.17 | 瓶样 |
| 10 | CX2-5(3) | 2021-06-25 | -17.2 | 0.17 | 气袋 |
| 11 | CX2-11(1) | 2021-06-25 | -14.3 | 0.61 | 瓶样 |
| 12 | CX2-11(2) | 2021-06-25 | -21.3 | 0.61 | 气袋 |
| 13 | CX2-11(4) | 2021-06-25 | -21.0 | 0.61 | 气袋 |
| 14 | CX3-4(1) | 2021-06-26 | -13.9 | 0.58 | 瓶样 |
| 15 | CX3-5(1) | 2021-06-26 | -20.2 | 0.60 | 气袋 |
| 16 | CX4-4(1) | 2021-06-26 | -13.6 | 0.44 | 瓶样 |
| 17 | CX4-4(1) | 2021-06-26 | -19.2 | 0.44 | 气袋 |
| 18 | CX4-4(2) | 2021-06-26 | -13.6 | 0.44 | 瓶样 |
| 19 | CX4-4(3) | 2021-06-26 | -19.2 | 0.44 | 气袋 |
| 20 | CX5-3(1) | 2021-06-27 | -14.0 | 0.43 | 瓶样 |
| 21 | CX5-4(2) | 2021-06-27 | -21.3 | 0.50 | 气袋 |
| 22 | CX5-4(4) | 2021-06-27 | -21.8 | 0.50 | 气袋 |
| 23 | CX6-6(1) | 2021-06-28 | -20.8 | 0.77 | 气袋 |
| 24 | CX6-6(3) | 2021-06-28 | -20.8 | 0.77 | 气袋 |
| 25 | CX6-7(1) | 2021-06-28 | -17.9 | 1.12 | 瓶样 |
| 26 | CX6-7(2) | 2021-06-28 | -15.9 | 1.12 | 瓶样 |
| 27 | CX6-7(2) | 2021-06-28 | -22.1 | 1.12 | 气袋 |
| 28 | CX6-7(4) | 2021-06-28 | -22.3 | 1.12 | 气袋 |
| 29 | CX6-8(3) | 2021-06-28 | -21.7 | 1.38 | 气袋 |
| 30 | CX7-4(1) | 2021-06-29 | -12.5 | 2.84 | 瓶样 |
| 31 | CX7-4(2) | 2021-06-29 | -12.5 | 2.84 | 瓶样 |
| 32 | CX7-5(1) | 2021-06-29 | -14.4 | 0.66 | 瓶样 |
| 序号 | 测点编号 | 采样时间 | He /ppm | Ne /ppm | 4He/20Ne | 3He/4He | 20Ne/22Ne | Ne/22Ne | δ13C /‰ | CO2 /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CX1-8(1) | 2021-06-23 | 4.7 | 15.6 | 0.32 | 1.1×10-6±4.6×10-8 | 10.20±0.02 | 0.0290±0.0008 | -14.2 | 0.30 |
| 2 | CX6-7(1) | 2021-06-28 | 4.4 | 15.6 | 0.30 | 1.3×10-6±6.5×10-8 | 9.80±0.02 | 0.0280±0.0004 | -17.9 | 1.12 |
| 3 | CX7-4(1) | 2021-06-29 | 4.6 | 15.2 | 0.32 | 1.4×10-6±9.4×10-8 | 9.80±0.02 | 0.0280±0.0002 | -12.5 | 2.84 |
| 4 | 大气 | 5.4 | 18.2 | 0.30 | 1.4×10-6 | 9.80 | 0.0290 | -8.0 | 0.04 |
表 3 土壤气中氦同位素的组成
Table 3 Isotopic composition of He in soil gas
| 序号 | 测点编号 | 采样时间 | He /ppm | Ne /ppm | 4He/20Ne | 3He/4He | 20Ne/22Ne | Ne/22Ne | δ13C /‰ | CO2 /% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | CX1-8(1) | 2021-06-23 | 4.7 | 15.6 | 0.32 | 1.1×10-6±4.6×10-8 | 10.20±0.02 | 0.0290±0.0008 | -14.2 | 0.30 |
| 2 | CX6-7(1) | 2021-06-28 | 4.4 | 15.6 | 0.30 | 1.3×10-6±6.5×10-8 | 9.80±0.02 | 0.0280±0.0004 | -17.9 | 1.12 |
| 3 | CX7-4(1) | 2021-06-29 | 4.6 | 15.2 | 0.32 | 1.4×10-6±9.4×10-8 | 9.80±0.02 | 0.0280±0.0002 | -12.5 | 2.84 |
| 4 | 大气 | 5.4 | 18.2 | 0.30 | 1.4×10-6 | 9.80 | 0.0290 | -8.0 | 0.04 |
| [1] |
戴金星, 宋岩, 戴春森, 等. 1995. 中国东部无机成因气及其气藏形成条件[M]. 北京: 科学出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
邓起东, 高翔, 陈桂华, 等. 2010. 青藏高原昆仑-汶川地震系列与巴颜喀喇断块的最新活动[J]. 地学前缘, 17(5): 163-178.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
邓文泽, 刘杰, 杨志高, 等. 2022. 青海玛多 MS7.4 地震震源破裂过程反演结果的初步分析[J]. 地震地质, 44(4): 1059-1070. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.04.015.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [4] |
邓文泽, 杨志高, 席楠, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多M7.4地震的快速测定与数据产品产出[J]. 中国地震, 37(2): 541-550.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
江娃利, 谢新生. 2006. 东昆仑活动断裂带强震地表破裂分段特征[J]. 地质力学学报, 12(2): 132-139.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
李营, 杜建国, 王富宽, 等. 2009. 延怀盆地土壤气体地球化学特征[J]. 地震学报, 31(1): 82-91.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
李智敏, 李文巧, 李涛, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震的发震构造和地表破裂初步调查[J]. 地震地质, 43(3): 722-737.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
刘冠中. 2014. 巴颜喀拉块体边界断裂的跨断层形变与地震活动[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
刘再华, 袁道先, 何师意, 等. 2000. 地热CO2-水-碳酸盐岩系统的地球化学特征及其CO2来源: 以四川黄龙沟、 康定和云南中甸下给为例[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 30(2): 209-214.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
潘家伟, 白明坤, 李超, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震地表破裂带及发震构造[J]. 地质学报, 95(6): 1655-1670.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
陶明信, 徐永昌, 史宝光, 等. 2005. 中国不同类型断裂带的地幔脱气与深部地质构造特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 35(5): 441-451.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
王博, 周永胜, 钟骏, 等. 2022. 滇西北断裂带土壤气地球化学特征及对断层活动性的启示[J]. 地震地质, 44(2): 428-447.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
王未来, 房立华, 吴建平, 等. 2021. 2021年青海玛多 MS7.4 地震序列精定位研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 51(7): 1193-1202.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
王先彬, 徐胜, 陈践发, 等. 1993. 腾冲火山区温泉气体组分和氦同位素组成特征[J]. 科学通报, 38(9): 814-817.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
王永敏, 赵铮, 孙涛, 等. 2016. 三峡库区典型农田系统大气汞浓度及不同自然界面释汞通量[J]. 环境科学, 37(9): 3300-3307.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
闻学泽. 2018. 巴颜喀拉块体东边界千年破裂历史与2008年汶川、 2013年芦山和2017年九寨沟地震[J]. 地震学报, 40(3): 255-267.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
徐胜, 管芦峰, 张茂亮, 等. 2022. 青藏高原东缘鲜水河-安宁河断裂带深源气体释放[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 52(2): 291-308.
|
|
DOI |
|
| [18] |
徐永昌, 沈平, 陶明信, 等. 1994. 中国含油气盆地天然气中氦同位素分布[J]. 科学通报, 39(16): 1505-1508.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
徐志国, 梁姗姗, 张广伟, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震发震构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(8): 2657-2670. doi: 10.6038/cjg2021P0390.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [20] |
姚文倩, 王子君, 刘静, 等. 2022. 2021年青海玛多 MW7.4 地震同震地表破裂长度的讨论[J]. 地震地质, 44(2): 541-559. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.02.016.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [21] |
张建勇, 王新, 陈凌, 等. 2022. 基于余震重定位和震源机制解研究青海玛多 MS7.4 地震序列的发震构造和断裂形态[J]. 地球物理学报, 65(2): 552-562. doi: 10.6038/cjg2022P0516.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [22] |
张裕明, 李闽峰, 孟勇琦, 等. 1996. 巴颜喀拉山地区断层活动性研究及其地震地质意义 [G]//中国地震局地质研究所编. 活动断裂研究(5). 北京: 地震出版社:154-171.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
张喆, 许力生. 2021. 2021年青海玛多 MW7.5 地震矩心矩张量解[J]. 地震学报, 43(3): 387-391.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
赵韬, 王莹, 马冀, 等. 2021. 2021年青海玛多7.4级地震序列重定位和震源机制特征[J]. 地震地质, 43(4): 790-805. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.04.004.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [25] |
赵振燊. 2012. 甘东南地震重点危险区主要活动断裂带断层气地球化学特征[D]. 兰州: 中国地震局兰州地震研究所: 1-66.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
周保, 李五福, 董福辰, 等. 2023. 青海省玛多县“5·22 MS7.4 地震”地表破裂与次生灾害发育特征[J]. 地质通报: 42(1): 84-91.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
周晓成, 王传远, 柴炽章, 等. 2011. 海原断裂带东南段土壤气体地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质, 33(1): 123-132.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
DOI URL |
| [29] |
DOI |
| [30] |
DOI URL |
| [31] |
DOI URL |
| [32] |
DOI URL |
| [33] |
DOI URL |
| [34] |
DOI URL |
| [35] |
DOI URL |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
DOI URL |
| [38] |
DOI URL |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
PMID |
| [41] |
DOI URL |
| [42] |
DOI URL |
| [43] |
DOI URL |
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
DOI |
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
DOI URL |
| [48] |
DOI |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
DOI URL |
| [51] |
DOI URL |
| [52] |
DOI URL |
| [53] |
DOI URL |
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
DOI URL |
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
DOI URL |
| [59] |
DOI URL |
| [60] |
DOI URL |
| [61] |
DOI URL |
| [62] |
DOI |
| [63] |
DOI URL |
| [64] |
DOI URL |
| [65] |
DOI URL |
| [66] |
PMID |
| [67] |
DOI URL |
| [68] |
DOI URL |
| [69] |
DOI URL |
| [70] |
DOI URL |
| [71] |
DOI URL |
| [72] |
DOI URL |
| [73] |
DOI URL |
| [74] |
DOI |
| [75] |
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王喜龙, 罗银花, 金秀英, 杨梦尧, 孔祥瑞. 辽南地区断裂带的断层土壤气地球化学特征及其对区域应力调整的指示[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 710-734. |
| [2] | 蒋雨函, 王子思, 刘佳琪, 梁卉, 周启超, 高小其. 中国地震断裂带氢气观测研究现状[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 622-637. |
| [3] | 苟家宁, 刘子维, 江颖, 张晓彤. 震前重力扰动与背景噪声时空变化特征以玛多MS7.4与漾濞MS6.4地震为例[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 252-268. |
| [4] | 蒋雨函, 高小其, 杨朋涛, 刘冬英, 孙小龙, 向阳, 朱成英, 汪成国. 新疆北天山地区断裂带断层土壤气的地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1597-1614. |
| [5] | 朱成英, 闫玮, 麻荣, 李志海, 汪成国, 黄建明, 周晓成. 2017年8月9日精河MS6.6地震宏观烈度及其余震分布的断层气体地球化学表征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(5): 1225-1239. |
| [6] | 路畅, 周晓成, 李营, 刘磊, 颜玉聪, 徐岳仁. 玛多MS7.4 地表破裂带与东昆仑断裂温泉的水文地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1101-1126. |
| [7] | 李春果, 王宏伟, 温瑞智, 强生银, 任叶飞. 2021年青海玛多MS7.4地震随机有限断层三维地震动模拟[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1085-1100. |
| [8] | 姚生海, 盖海龙, 殷翔, 李鑫. 青海玛多MS7.4地震地表破裂带的基本特征和典型现象[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1060-1072. |
| [9] | 韦进, 郝洪涛, 韩宇飞, 胡敏章, 江颖, 刘子维. 基于连续重力台观测的玛多MS7.4地震的同震重力变化特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 984-998. |
| [10] | 宋向辉, 王帅军, 潘素珍, 宋佳佳. 2021年玛多MS7.4地震的深部构造背景[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 757-770. |
| [11] | 曲长胜, 邱隆伟, 杨勇强, 余宽宏, 汤丽莉, 万敏. 准噶尔盆地吉木萨尔凹陷二叠系芦草沟组火山活动的环境响应[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(3): 789-802. |
| [12] | 程佳, 徐锡伟. 巴颜喀拉块体周缘强震间应力作用与丛集活动特征初步分析[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(1): 133-154. |
| [13] | 李东雨, 陈立春, 梁明剑, 高帅坡, 曾蒂, 王虎, 李彦宝. 鲜水河断裂带乾宁段古地震事件与大震复发行为[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(4): 623-643. |
| [14] | 上官志冠, 孙明良, 李恒忠. 云南腾冲地区现代地热流体活动类型[J]. 地震地质, 1999, 21(4): 437-442. |
| [15] | 上官志冠. 滇西实验场区主要活动断裂地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质, 1988, 10(4): 134-142. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||