地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 668-688.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.03.005
李继业1)( ), 晏锐2),*(
), 晏锐2),*( ), 张思萌1), 胡澜缤3), 孟令蕾3), 周晨1)
), 张思萌1), 胡澜缤3), 孟令蕾3), 周晨1)
收稿日期:2022-09-23
修回日期:2023-03-20
出版日期:2023-06-20
发布日期:2023-07-18
通讯作者:
* 晏锐, 男, 1978年生, 博士, 正研级高级工程师, 主要从事地震地下流体学和地震预测研究, E-mail: 作者简介:李继业, 男, 1981年生, 2010年于复旦大学获软件工程专业硕士学位, 主要研究方向地震综合预测、 流体地球化学研究, E-mail: jiye_li@126.com。
基金资助:
LI Ji-ye1)( ), YAN Rui2),*(
), YAN Rui2),*( ), ZHANG Si-meng1), HU Lan-bin3), MENG Ling-lei3), ZHOU Chen1)
), ZHANG Si-meng1), HU Lan-bin3), MENG Ling-lei3), ZHOU Chen1)
Received:2022-09-23
Revised:2023-03-20
Online:2023-06-20
Published:2023-07-18
摘要:
地下流体在地震孕育和发生过程中发挥着至关重要的作用。文中从黑龙江地区18个水位观测井中, 筛选出2016年以来符合一定条件的延寿台、 通河台、 肇东台、 甘南台和绥化北林台的井水位数据, 应用维尼迪柯夫调和分析方法进行潮汐分析, 得到井水位潮汐响应全日波群中的周日波潮汐因子, 分析了吉林松原宁江 MS5.0、 MS5.7、 MS5.1 地震前后周日波的高值异常变化特征, 并结合震源区ML≥3.0小地震调制比异常, 进一步探讨了周日波异常与小地震调制作用的关系。结果显示: 1)周日波潮汐因子背景变化相对稳定, 异常更容易被识别, 具有较高的信噪比。2)吉林松原宁江地震前, 井水位潮汐响应的周日波异常具有准同步性和形态一致性, 主要表现为3个及以上台站的配套性异常。3)吉林松原宁江地震发生在周日波高值配套性异常结束后的2.6个月内, 最短仅为7d, 具有明显的短临特征, 且异常持续时间、 异常幅度与震级大小相关。4)吉林松原宁江地震前震源区ML≥3.0小地震调制比存在低值异常, 主要表现为短临特征, 井水位潮汐响应的周日波异常反映内部应力状态的改变, 小地震调制比则能更好地揭示震源区构造应力达到或接近临界状态, 对二者进行联合分析有助于识别和捕捉地震前兆短临异常。
李继业, 晏锐, 张思萌, 胡澜缤, 孟令蕾, 周晨. 井水位潮汐响应与小地震调制作用的关系[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 668-688.
LI Ji-ye, YAN Rui, ZHANG Si-meng, HU Lan-bin, MENG Ling-lei, ZHOU Chen. THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN TIDAL RESPONSE OF WELL WATER LEVEL AND MODULATION OF SMALL EARTHQUAKES[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(3): 668-688.
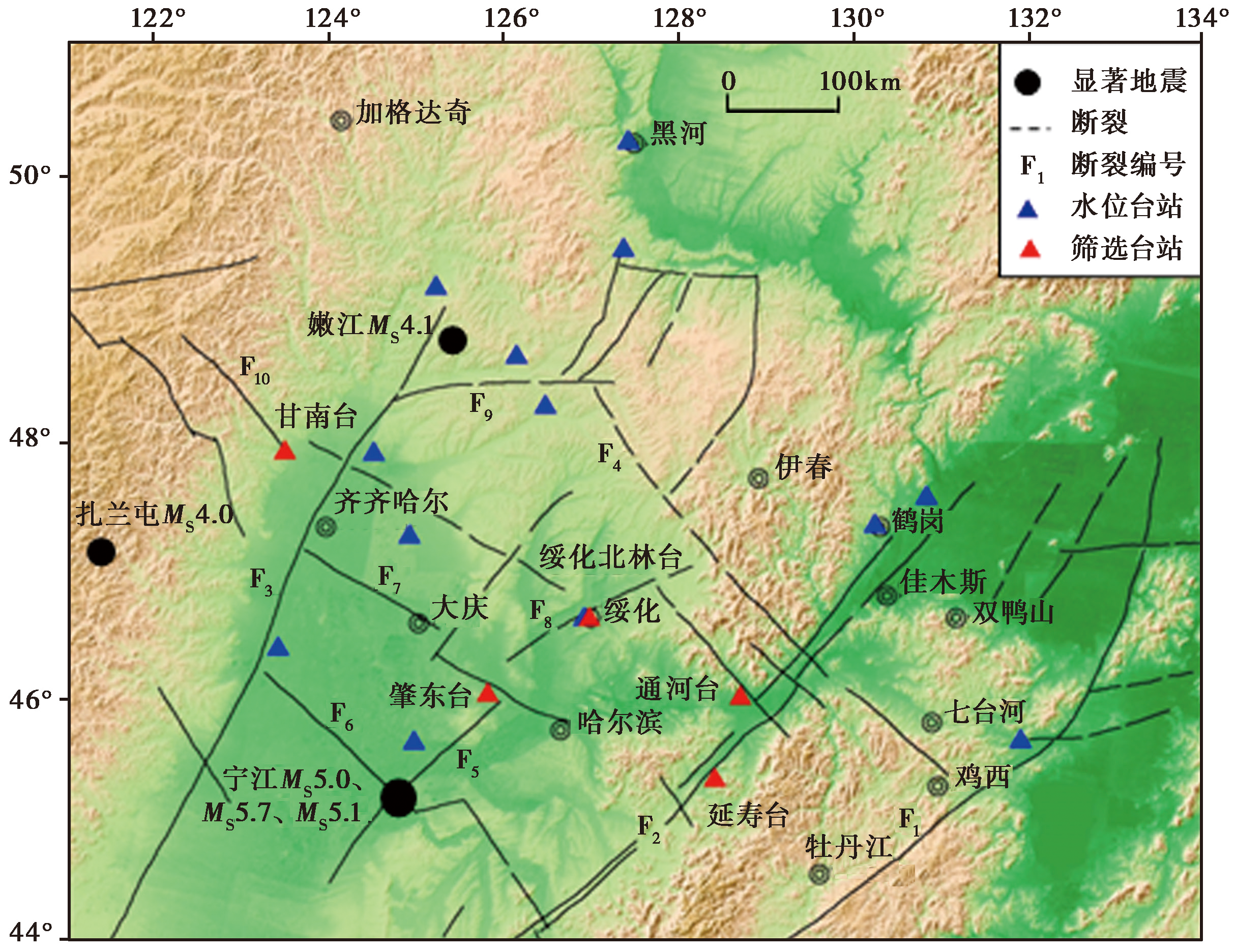
图 1 区域构造断裂及显著地震活动 F1敦密断裂; F2依舒断裂; F3嫩江断裂; F4南北河-勃利断裂; F5扶余-肇东断裂; F6松花江断裂;F7滨州断裂; F8呼兰河断裂; F9讷谟尔河断裂; F10阿伦河断裂
Fig. 1 Regional tectonic faults and significant seismic activities.
| 序号 | 台站 | 井深 /m | 观测深度 /m | 观测层岩性 | 承压水类型 | 水化学类型 | 所处构造部位 | 同井 测项 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 甘南 | 130 | 45~130 | 古近-新近系玄武岩 | 孔隙承压水 | HCO3-Ca·Mg | 嫩江断裂与阿 伦河断裂交会处 | 水温 |
| 2 | 延寿 | 200 | 120~200 | 燕山期花岗岩 | 砾岩孔隙承压水 | HCO3-Na·Ca | 依舒断裂 | 水温 |
| 3 | 通河 | 200 | 180~200 | 燕山期花岗岩 | 泥岩孔隙承压水 | HCO3-Na | 依舒断裂 | 水温 |
| 4 | 肇东 | 380 | 340~350 | 白垩纪泥质粉砂岩 | 砂岩、砂砾 岩层承压水 | HCO3-Ca | 滨州断裂与扶余- 肇东断裂交会处 | 水温 |
| 5 | 绥化北林 | 191 | 138.5~150 | 白垩系泥质粉砂岩 | 第四纪承压水 | HCO3-Ca | 呼兰河断裂 | 水温 |
表 1 水位观测井的基本情况
Table 1 Basic information of water level observation well
| 序号 | 台站 | 井深 /m | 观测深度 /m | 观测层岩性 | 承压水类型 | 水化学类型 | 所处构造部位 | 同井 测项 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 甘南 | 130 | 45~130 | 古近-新近系玄武岩 | 孔隙承压水 | HCO3-Ca·Mg | 嫩江断裂与阿 伦河断裂交会处 | 水温 |
| 2 | 延寿 | 200 | 120~200 | 燕山期花岗岩 | 砾岩孔隙承压水 | HCO3-Na·Ca | 依舒断裂 | 水温 |
| 3 | 通河 | 200 | 180~200 | 燕山期花岗岩 | 泥岩孔隙承压水 | HCO3-Na | 依舒断裂 | 水温 |
| 4 | 肇东 | 380 | 340~350 | 白垩纪泥质粉砂岩 | 砂岩、砂砾 岩层承压水 | HCO3-Ca | 滨州断裂与扶余- 肇东断裂交会处 | 水温 |
| 5 | 绥化北林 | 191 | 138.5~150 | 白垩系泥质粉砂岩 | 第四纪承压水 | HCO3-Ca | 呼兰河断裂 | 水温 |
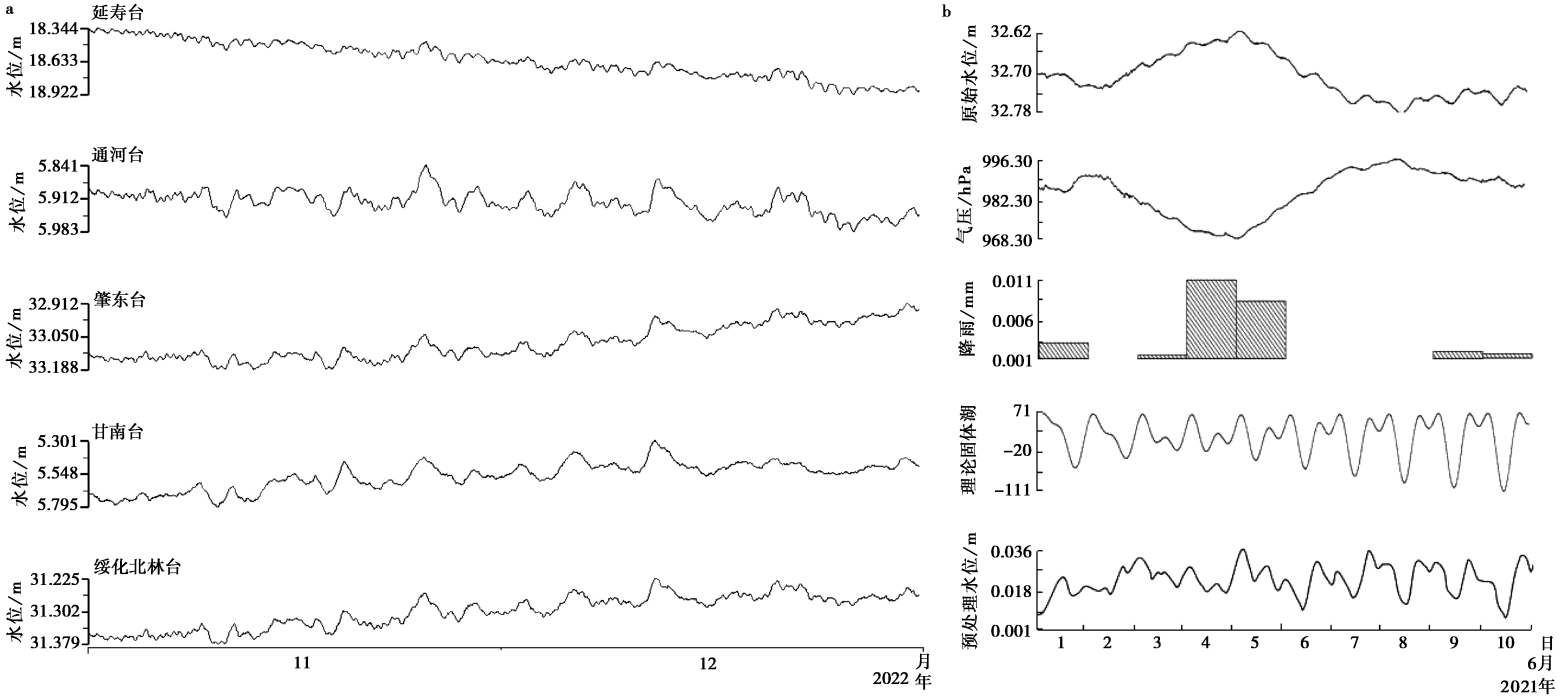
图 2 各台井水位的原始观测曲线和肇东台井水位的预处理观测曲线(整点值) a 井水位的固体潮效应、 气压效应(2022年11—12月); b 肇东台的原始水位、 气压、 降雨、 理论固体潮及预处理水位曲线(2021年6月1—10日)
Fig. 2 Original observation curves of water level of each seismic station and observation curves of water level pretreatment of Zhaodong station(integer value).

图 4 2017年吉林松原宁江 MS5.0、 MS4.6 地震前的井水位周日波配套异常
Fig. 4 The matching anomaly characteristics of a diurnal wave of the well water level before Ningjiang MS5.0 and MS4.6 earthquake in 2017.
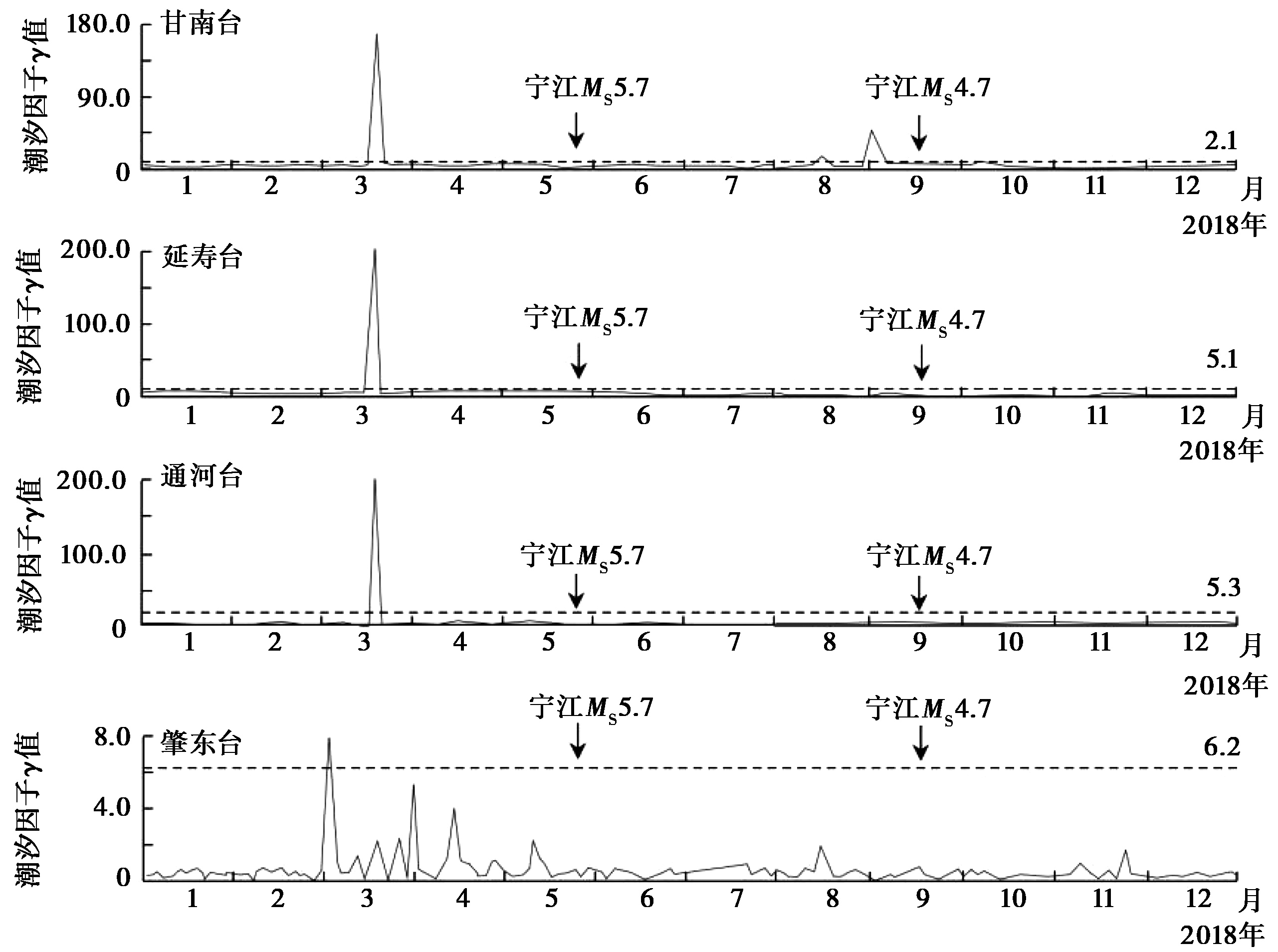
图 5 2018年吉林松原宁江 MS5.7、 MS4.7 地震前的井水位周日波配套异常
Fig. 5 The matching anomaly characteristics of the diurnal wave of the well water level before Ningjiang MS5.7 and MS4.7 earthquake in 2018.
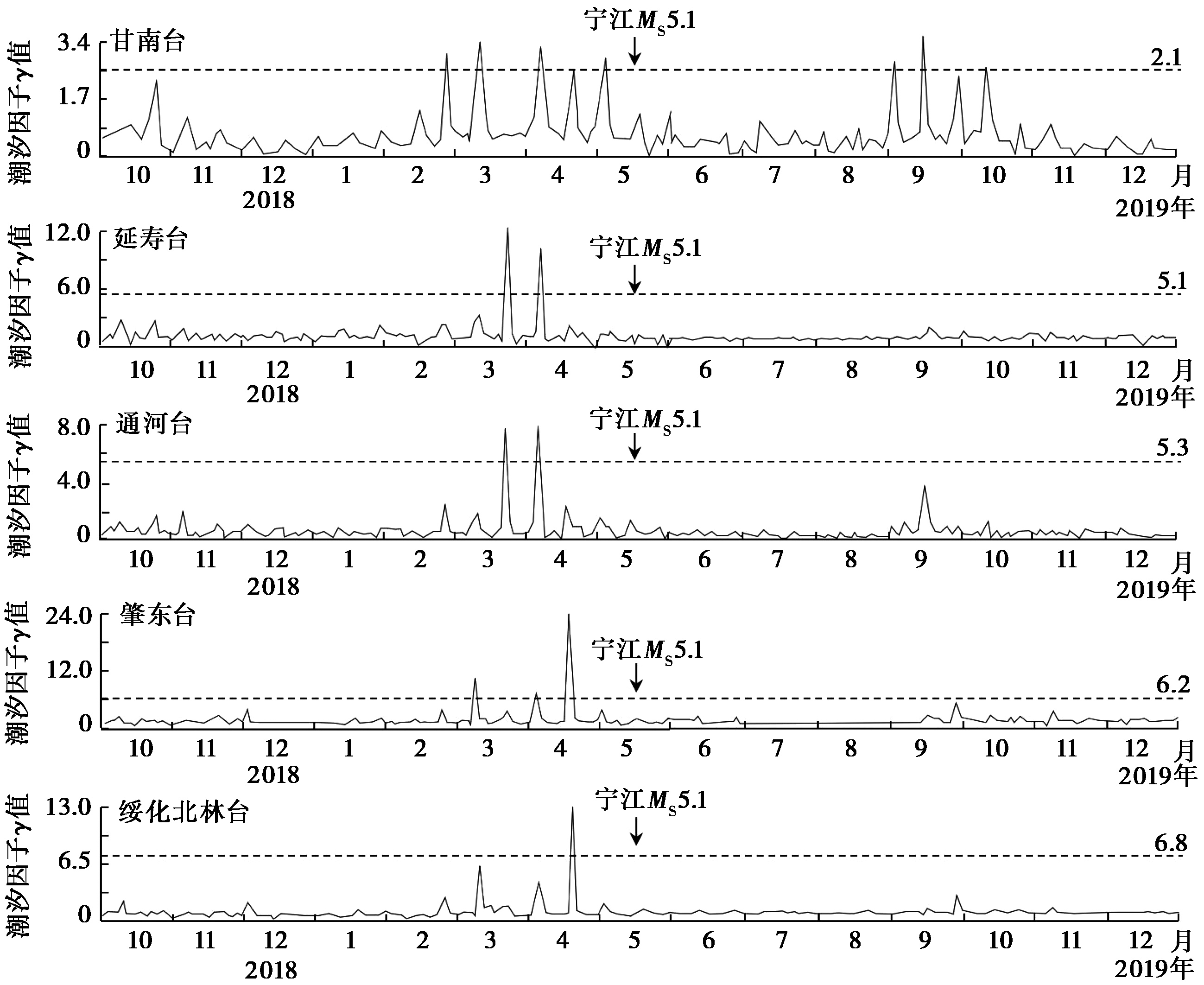
图 6 2019年吉林松原宁江 MS5.1 地震前的井水位周日波配套异常
Fig. 6 Sunday wave matching anomaly of the well water level before the 2019 Ningjiang MS5.1 earthquake in Songyuan, Jilin Province.
| 编号 | 台站 | 要素 | 2017年 7月23日 宁江 MS5.0 | 2017年 8月15日 宁江 MS4.6 | 2018年 5月28日 宁江 MS5.7 | 2018年 9月15日 宁江 MS4.7 | 2019年 5月18日 宁江 MS5.1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 甘南台 | 等待时间/d | 79 | 101 | 73 | 183 | 7 |
| 周日波异常幅度 | 11.7 | 11.7 | 174 | 174 | 3.2 | ||
| 异常峰值与背景值之比 | 5.6 | 5.6 | 83 | 83 | 1.5 | ||
| 震中距/km | 310 | 310 | 300 | 300 | 300 | ||
| 2 | 延寿台 | 等待时间/d | 73 | 183 | 40 | ||
| 周日波异常幅度 | 204 | 204 | 11.7 | ||||
| 异常峰值与背景值之比 | 40 | 40 | 2.3 | ||||
| 震中距/km | 280 | 280 | 280 | ||||
| 3 | 通河台 | 等待时间/d | 113 | 135 | 73 | 183 | 40 |
| 周日波异常幅度 | 12.3 | 12.3 | 202 | 202 | 8.0 | ||
| 异常峰值与背景值之比 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 38 | 38 | 1.5 | ||
| 震中距/km | 318 | 318 | 320 | 320 | 320 | ||
| 4 | 肇东台 | 等待时间/d | 107 | 129 | 86 | 196 | 30 |
| 周日波异常幅度 | 9.4 | 9.4 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 23.7 | ||
| 异常峰值与背景值之比 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 3.8 | ||
| 震中距/km | 107 | 107 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| 5 | 绥化北林台 | 等待时间/d | 30 | ||||
| 周日波异常幅度 | 12.8 | ||||||
| 异常峰值与背景值之比 | 1.9 | ||||||
| 震中距/km | 220 |
表 2 吉林松原宁江中强地震前井水位的周日波配套异常特征
Table 2 The matching anomaly characteristics about the diurnal wave of well water level before Qianguo and Ningjiang earthquakes
| 编号 | 台站 | 要素 | 2017年 7月23日 宁江 MS5.0 | 2017年 8月15日 宁江 MS4.6 | 2018年 5月28日 宁江 MS5.7 | 2018年 9月15日 宁江 MS4.7 | 2019年 5月18日 宁江 MS5.1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 甘南台 | 等待时间/d | 79 | 101 | 73 | 183 | 7 |
| 周日波异常幅度 | 11.7 | 11.7 | 174 | 174 | 3.2 | ||
| 异常峰值与背景值之比 | 5.6 | 5.6 | 83 | 83 | 1.5 | ||
| 震中距/km | 310 | 310 | 300 | 300 | 300 | ||
| 2 | 延寿台 | 等待时间/d | 73 | 183 | 40 | ||
| 周日波异常幅度 | 204 | 204 | 11.7 | ||||
| 异常峰值与背景值之比 | 40 | 40 | 2.3 | ||||
| 震中距/km | 280 | 280 | 280 | ||||
| 3 | 通河台 | 等待时间/d | 113 | 135 | 73 | 183 | 40 |
| 周日波异常幅度 | 12.3 | 12.3 | 202 | 202 | 8.0 | ||
| 异常峰值与背景值之比 | 2.3 | 2.3 | 38 | 38 | 1.5 | ||
| 震中距/km | 318 | 318 | 320 | 320 | 320 | ||
| 4 | 肇东台 | 等待时间/d | 107 | 129 | 86 | 196 | 30 |
| 周日波异常幅度 | 9.4 | 9.4 | 7.7 | 7.7 | 23.7 | ||
| 异常峰值与背景值之比 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 1.2 | 1.2 | 3.8 | ||
| 震中距/km | 107 | 107 | 100 | 100 | 100 | ||
| 5 | 绥化北林台 | 等待时间/d | 30 | ||||
| 周日波异常幅度 | 12.8 | ||||||
| 异常峰值与背景值之比 | 1.9 | ||||||
| 震中距/km | 220 |
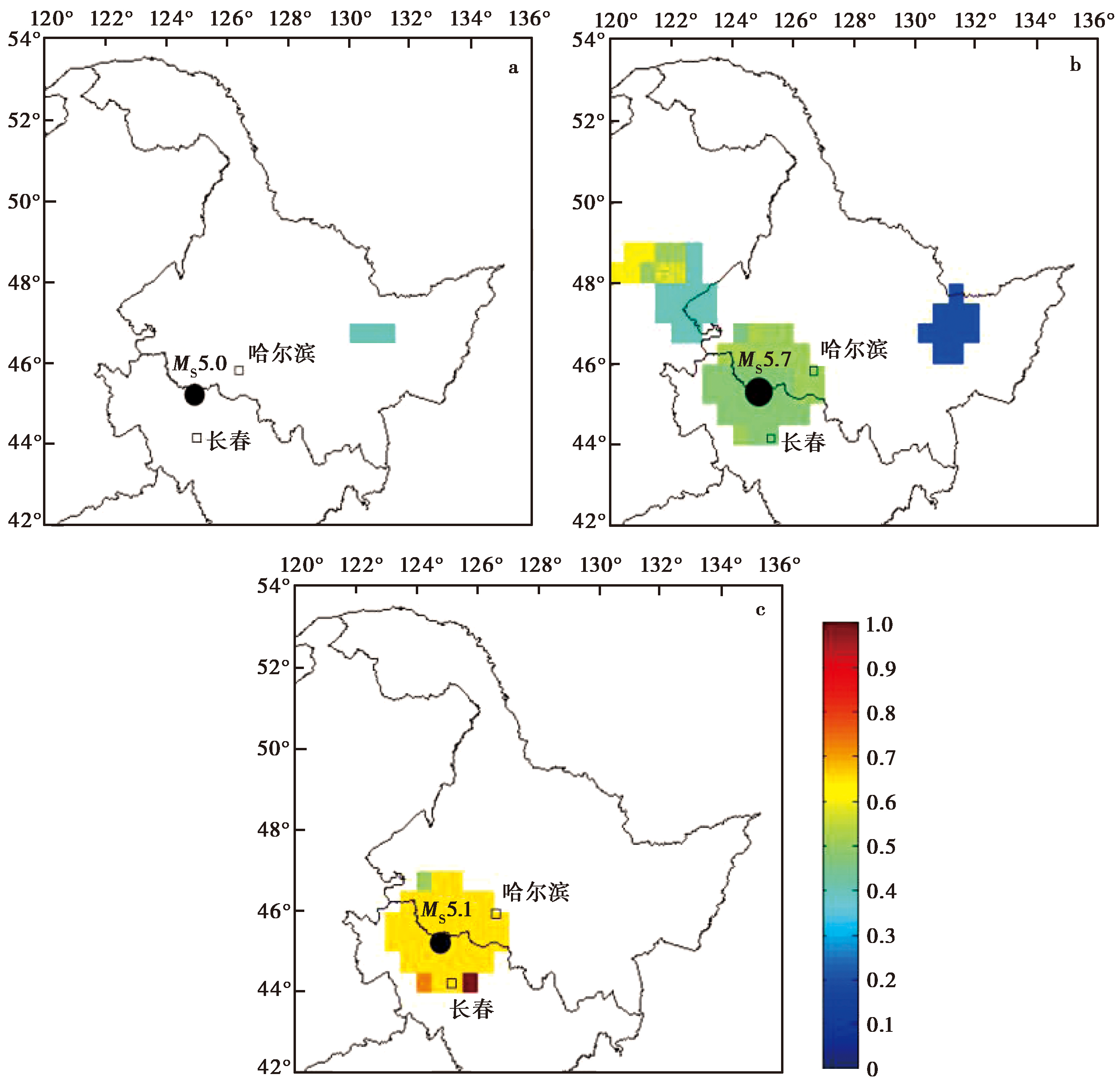
图 7 吉林松原宁江地震前一年ML≥3.0应力调制的空间异常 a 2017年宁江 MS5.0 地震; b 2018年宁江 MS5.7 地震; c 2019年宁江 MS5.1 地震
Fig. 7 Spatial anomalies of ML≥3.0 stress modulation in the year preceding the Songyuan Ningjiang earthquakes in Jilin.
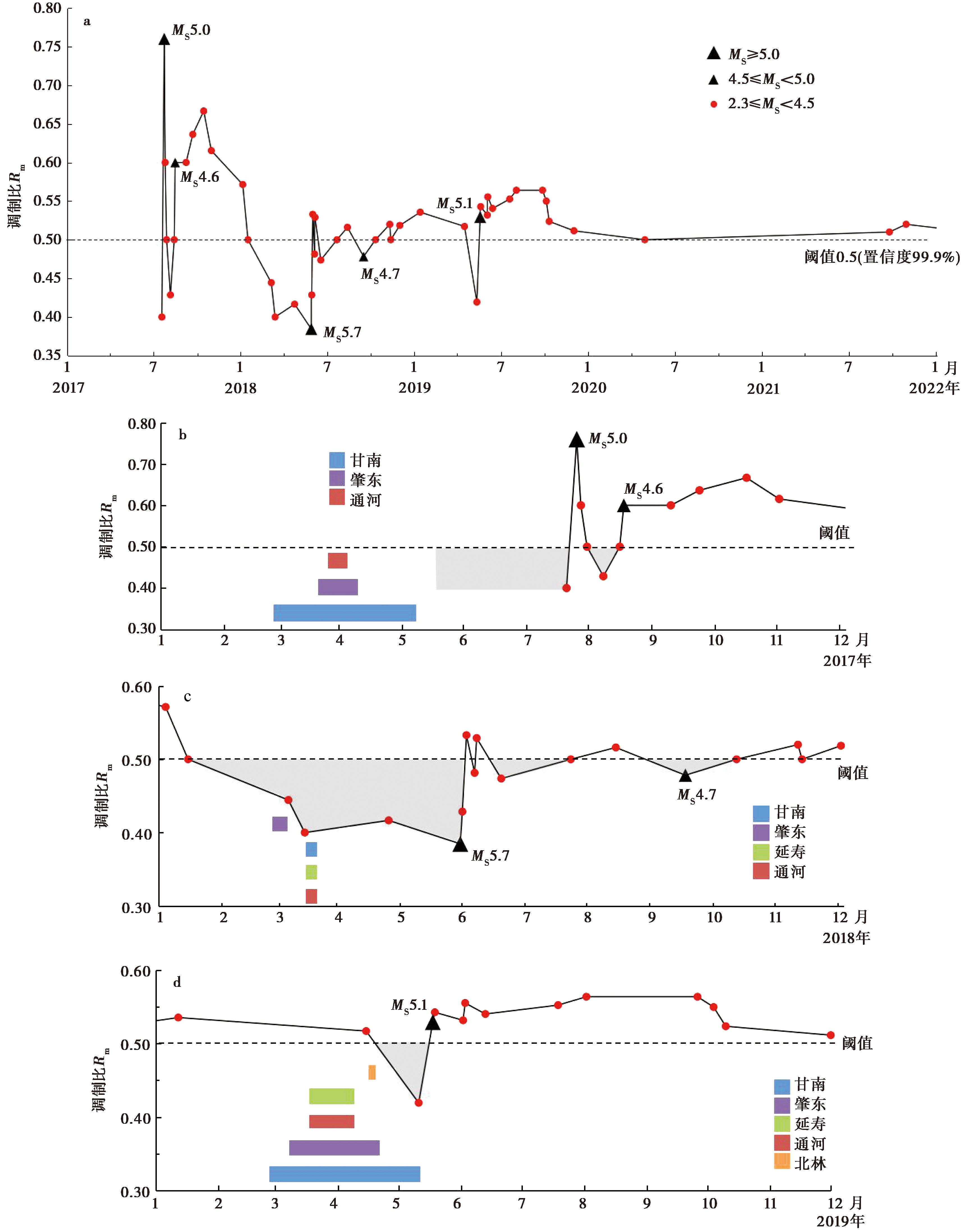
图 8 吉林松原地区ML≥3.0小地震调制与井水位周日波异常的关系 a 小地震调制比曲线(2017年6月—2020年5月); b 2017年宁江 MS5.0、 MS4.6 地震; c 2018年宁江 MS5.7、 MS4.7 地震; d 2019年宁江 MS5.1 地震
Fig. 8 The relationship between the modulation of small earthquakes with ML≥3.0 and the diurnal wave anomaly of well water level in Songyuan, Jilin Province.

图 9 岩石应力-应变曲线上的特征点与变形的阶段性(张晶等, 2005)
Fig. 9 Characteristic points and stage nature of deformation on the stress-strain curve of rock(adapted from ZHANG Jing et al., 2005).
| [1] |
曹井泉, 朝伦巴根, 刘耀炜. 2010. 承压井水位固体潮M2波海潮负荷改正[J]. 地震研究, 33(1): 75-80.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈荣华, 薛艳, 郑大林, 等. 2006. 引潮力对显著地震触发作用与大震关系的机理讨论[J]. 地震, 26(1): 66-70.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈学忠. 2021. 地震潮汐触发[J]. 地震科学进展, 51(4): 145-160.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
丁风和, 车用太, 刘耀炜, 等. 2022. 地震观测井地下水埋藏类型判定方法及依据[J]. 地震研究, 45(2): 284-289.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
顾瑾萍, 郭铁栓, 姜龙. 2012. 水平引潮力极值天体时角表征与调制的讨论[J]. 中国地震, 28(1): 61-68.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
顾瑾萍, 吕培苓, 李纲. 2000. 应力调制与预报研究[J]. 地震, 20(3): 15-24.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
韩颜颜, 孟令媛, 刘桂萍, 等. 2017. 西北地区中强震前固体潮调制比时空特征分析[J]. 地震学报, 39(5): 738-750.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
纪春玲, 董博, 章阳, 等. 2021. 2020年唐山古冶5.1级地震前流体固体潮参数时空变化研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 41(8): 821-826.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
雷兴林, 王志伟, 马胜利, 等. 2021. 关于2021年5月滇西漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列特征及成因的初步研究[J]. 地震学报, 43(3): 261-286.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
李洪丽, 刘财, 田有, 等. 2021. 松原前郭地震区孕震构造的地震层析成像研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(5): 1597-1607.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
李继业, 胡滨生, 曲永斌, 等. 2007. 黑龙江省延寿地震台竖直摆倾斜仪潮汐短临变化特征[J]. 地震地质, 29(3): 648-656.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
李继业. 2020. 松辽盆地地球物理数据处理与分析[M]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨地图出版社: 177-209.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
李金, 蒋海昆, 桂荣, 等. 2014. 新疆喀什-乌恰交会区潮汐触发地震活动的统计检验[J]. 中国地震, 30(1): 64-73.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
黎凯武. 2000. 中国大陆成组强震与强震调制比分析[J]. 地震, 20(S1): 44-50.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
李全林. 1979. 地震频度-震级关系的时空扫描[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
李文君, 曾宪伟, 马翀之. 2022. 中国大陆6级以上强震及震前小震固体潮调制异常特征分析[J]. 地震工程学报, 44(3): 638-648.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
李延兴, 许力生, 胡新康, 等. 2001. 日、 月对孕震区的水平引潮力与震源机制的关系[J]. 地震, 21(1): 1-6.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
廖欣, 刘春平, 石云, 等. 2014. 川06井水位固体潮效应变化初探[J]. 地震学报, 36(2): 299-305.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
刘春平, 廖欣, 石云, 等. 2017. 地壳应力与地下水动力响应[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-199.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
刘军, 刘小阳, 薄海光, 等. 2014. 基于引潮力附加构造应力调制的九江地震热异常时空动态过程研究[J]. 地震学报, 36(3): 514-521.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
刘俊清. 2018. 吉林省西部地区典型地震活动研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
刘序俨, 郑小菁, 王林, 等. 2009. 承压井水位观测系统对体应变的响应机制分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(12): 3147-3157.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
吕品姬, 赵斌, 陈志遥, 等. 2011. 一种新的固体潮观测数据特征量提取方法[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 31(2): 76-79, 93.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
马宗晋. 1980. 华北地壳的多(应力集中)点场与地震[J]. 地震地质, 2(1): 39-47.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
盘晓东, 刘俊清, 贾若, 等. 2018. 2018年5月28日吉林松原宁江5.7级地震研究概述[J]. 地震科学进展, (8): 151-152.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
钱建秀, 刘春平, 樊春燕, 等. 2019. 地震前后井-含水层系统潮汐参数变化特征分析: 以云南弥勒井为例[J]. 中国地震, 35(1): 169-181.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
乔子云, 陈建国. 2001. 应变固体潮NaKai拟合检验及潮汐变化的映震效果[J]. 地震, 21(3): 85-90.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
秦保燕, 汪进, 姚立珣, 等. 1986. 由调制小震法初探中、 强地震时空强预报[J]. 地壳变形与地震, 6(4): 293-303.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
秦保燕, 张晓东, 王欲仓. 1994. 震源系统小震调制比(rm)和异常面积(Srm)起伏加剧的时空特征与强震的中、 短期预报[J]. 西北地震学报, 16(3): l-10.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
邵济安, 赵谊, 张福松, 等. 2010. 黑龙江省中西部地球排气与地震活动的探讨[J]. 岩石学报, 26(12): 3651-3656.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
邵媛媛, 杨士超, 王岩, 等. 2021. 辽宁地区固体潮调制比空间异常特征震例“回溯性”研究[J]. 防灾减灾学报, 37(2): 1-8.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
孙长青, 阎春恒, 吴小平, 等. 2014. 青藏高原东部及邻区地震断层面上的潮汐应力触发效应[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(7): 2054-2064.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
孙小龙, 向阳, 李源. 2020. 深井水位对地震波、 固体潮和气压的水力响应: 以范县井为例[J]. 地震学报, 42(6): 719-731.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
唐九安, 梁子斌, 常千军, 等. 2006. 辽宁深井承压水位潮汐响应函数的初步研究[J]. 东北地震研究, 22(1): 5-10.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
王炜, 宋先月, 谢端, 等. 2001. 地震调制比及其在华北地震中期预报中的应用[J]. 地震, 21(2): 7-12.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
王玥琪, 杨立明. 2015. 维尼迪科夫调和分析对大甸子井水位潮汐因子和相位的气象影响研究[J]. 地震工程学报, 37(1): 255-259.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
吴戈, 房贺岩, 李志田, 等. 1988. 1119年前郭地震考察与研究[J]. 东北地震研究, 4(1): 67-76.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
吴小平, 黄雍, 冒蔚, 等. 2005. 云南地震的潮汐应力触发机制及相关天体位置图像[J]. 地球物理学报, 48(3): 574-583.
|
|
DOI URL |
|
| [39] |
晏锐, 黄辅琼. 2009. 黄骅井水位对苏门答腊5次地震的同震响应初步研究[J]. 中国地震, 25(3): 325-332.
|
|
|
|
| [40] |
晏锐, 田雷, 王广才, 等. 2018. 2008年汶川8.0级地震前地下流体异常回顾与统计特征分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(5): 1907-1921.
|
|
|
|
| [41] |
晏锐, 张立, 简春林. 2012. 云南曲靖井水位潮汐动态特征分析[J]. 地震学报, 34(3): 363-373.
|
|
|
|
| [42] |
尹祥础, 李世愚, 李红, 等. 1987. 从断裂力学观点探讨b值的物理实质[J]. 地震学报, (4): 364-374, 444.
|
|
|
|
| [43] |
张国民, 李丽, 黎凯武, 等. 2001. 强震成组活动与潮汐力调制触发[J]. 中国地震, 17(2): 110-120.
|
|
|
|
| [44] |
张晶, 牛安福, 高福旺, 等. 2005. 固体潮汐参数变化与地震关系研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 25(3): 86-90.
|
|
|
|
| [45] |
张晶, 郗钦文, 杨林章, 等. 2007. 引潮力与潮汐应力对强震触发的研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 50(2): 448-454.
|
|
|
|
| [46] |
张晶, 张立. 2003. 强震前形变固体潮汐资料短期信息的提取[J]. 地震, 23(3): 71-78.
|
|
|
|
| [47] |
张淑亮, 李宏伟, 吕芳, 等. 2019. 基于数值模拟与含水层垂向应力反演的静乐井水位异常分析[J]. 震灾防御技术, 14(4): 854-868.
|
|
|
|
| [48] |
张晓东, 秦保燕. 2000. 调制块比在地震中期预报中的应用[J]. 地震, 20(1): 27-31.
|
|
|
|
| [49] |
中国地震局监测预报司. 2020. 地下流体分析预测技术方法工作手册[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
Monitoring and Forecasting Department of CEA. 2020. Working Manual on Underground Fluid Analysis and Prediction Techniques and Methods[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese)
|
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
DOI URL |
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
DOI URL |
| [56] |
DOI URL |
| [57] |
DOI URL |
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
DOI URL |
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
DOI URL |
| [1] | 刘伟, 白细民, 吕少杰, 史浙明, 齐之钰, 何冠儒. 基于井水位气压效应计算含水层的水力参数[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 652-667. |
| [2] | 韩竹军, 张秉良, 曾新福, 卢福水, 郭鹏. 江西中北部基岩区断层泥显微构造特征及意义[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(4): 903-919. |
| [3] | 郭鹏, 韩竹军, 周本刚, 周庆, 毛泽斌. 安徽巢湖—铜陵地区中强地震发生的构造标志[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(4): 832-849. |
| [4] | 陈敏, 唐小勇, 郭卫英, 贺曼秋, 巩浩波, 李光科, 陈雷, 杨林, 陈凯, 谭君, 贾鸿飞. 重庆大足井水位对邻井抽水的奇异响应及其机理[J]. 地震地质, 2012, (2): 359-364. |
| [5] | 常祖峰, 安晓文, 张艳凤. 畹町断裂晚第四纪活动与水系构造变形[J]. 地震地质, 2012, (2): 228-239. |
| [6] | 韩竹军, 向宏发, 姬计法. 洞庭盆地南缘常德-益阳-长沙断裂中段活动性研究[J]. 地震地质, 2011, 33(4): 839-854. |
| [7] | 顾申宜, 张慧, 解晓静, 刘阳. 海南井水位中期和中短期异常信息的提取方法及其特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 2010, 32(4): 638-646. |
| [8] | 高小其, 王海涛, 高国英, 高歌, 王中道, 陆明勇, 桑丽荣, 杨晓芳, 郭卫英, 许秋龙. 霍尔果斯泥火山活动与新疆地区中强以上地震活动关系的初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 2008, 30(2): 464-472. |
| [9] | 向宏发, 韩竹军, 张晚霞, 曾建华, 肖和平. 中国东部中强地震发生的地震地质标志初探[J]. 地震地质, 2008, 30(1): 202-208. |
| [10] | 李继业, 胡滨生, 曲永斌, 石伟, 李国庆. 黑龙江省延寿地震台竖直摆倾斜仪潮汐短临变化特征[J]. 地震地质, 2007, 29(3): 648-656. |
| [11] | 王志才, 晁洪太, 崔昭文, 李家灵, 石荣会. 青岛及邻区NE向断裂的第四纪活动性及控震意义[J]. 地震地质, 2002, 24(2): 167-176. |
| [12] | 吕浩江. 金门东南海域中强地震活动区的地震构造背景[J]. 地震地质, 2000, 22(2): 104-110. |
| [13] | 车用太, 鱼金子, 张大维, 孙振, 简春林, 彭贵荣. 北京平原区基岩井水位的年动态特征及其成因分析[J]. 地震地质, 1994, 16(3): 255-263. |
| [14] | 张昭栋, 郑香媛, 殷积涛, 张教样. 井水位振荡试验及其结果[J]. 地震地质, 1992, 14(2): 183-188. |
| [15] | 车用太, 鱼金子. 中国大陆东部地区中强震水位异常的统计特征[J]. 地震地质, 1992, 14(1): 23-29. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||