地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (3): 593-621.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.03.001
李营1)( ), 方震2,3,4), 张晨蕾5), 李继业6), 鲍志诚7), 张翔8), 刘兆飞1), 周晓成1), 陈志1), 杜建国1)
), 方震2,3,4), 张晨蕾5), 李继业6), 鲍志诚7), 张翔8), 刘兆飞1), 周晓成1), 陈志1), 杜建国1)
收稿日期:2023-01-30
修回日期:2023-03-14
出版日期:2023-07-18
发布日期:2023-07-18
作者简介:李营, 男, 1978年生, 2007年于中国科学院地球化学研究所获流体地球化学专业博士学位, 研究员, 主要从事活动构造带流体地球化学特征及地球深部流体成因研究, E-mail: liying@ief.ac.cn。
基金资助:
LI Ying1)( ), FANG Zhen2,3,4), ZHANG Chen-lei5), LI Ji-ye6), BAO Zhi-cheng7), ZHANG Xiang8), LIU Zhao-fei1), ZHOU Xiao-cheng1), CHEN Zhi1), DU Jian-guo1)
), FANG Zhen2,3,4), ZHANG Chen-lei5), LI Ji-ye6), BAO Zhi-cheng7), ZHANG Xiang8), LIU Zhao-fei1), ZHOU Xiao-cheng1), CHEN Zhi1), DU Jian-guo1)
Received:2023-01-30
Revised:2023-03-14
Online:2023-07-18
Published:2023-07-18
摘要:
建立地震短临预测方法是减轻地震灾害损失的最有效手段, 也是科学难题。流体是地球内部最为主动、 活跃的组分, 携带了地球各圈层的地球化学信息。地震流体地球化学的组成和变化对地下物理化学条件的改变响应灵敏, 是指示地震和构造活动的有效指标。文中综述了国内外流体地球化学短临预测机理的研究进展, 介绍了国内外已经建立的流体地球化学地震短临预测模型和方法, 利用《中国震例》数据对主要预测模型和方法进行了检验分析, 评述了各方法的适用性和效能。结合团队已有的工作基础, 提出了基于前兆机理进行地震流体地球化学短临预测的思路, 并对中国地震科学实验场地球化学子系统的地震短临预测研究和应用进行了展望。
李营, 方震, 张晨蕾, 李继业, 鲍志诚, 张翔, 刘兆飞, 周晓成, 陈志, 杜建国. 地震流体地球化学短临预测研究进展与展望[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 593-621.
LI Ying, FANG Zhen, ZHANG Chen-lei, LI Ji-ye, BAO Zhi-cheng, ZHANG Xiang, LIU Zhao-fei, ZHOU Xiao-cheng, CHEN Zhi, DU Jian-guo. RESEARCH PROGRESS AND PROSPECT OF SEISMIC FLUID GEOCHEMISTRY IN SHORT-IMMINENT EARTHQUAKE PREDICTION[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(3): 593-621.
| 序号 | 经验公式 | 参数含义 | 适用范围 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ρ=100.43M | ρ为有效前兆异常区的半径,M为震级 | 是大量地球化学地震预测方法的理论基础,适用性较广泛 | Dobrovolsky et al., |
| 2 | logT=0.76M-1.83 | T为氡地震前兆异常的持续时间,M为震级 | Rikitake, | |
| 3 | ML=2logD-0.07 | D为氡地震前兆异常的持续时间,ML为震级 | 适用于美国南卡罗莱纳西北部约卡西湖2.0≤ML≤2.6的地震预测,该模型成功验证了1977年2月23日2.3级地震事件 | Talwani, |
| 4 | t(天)=10M/143 | M为震级,t为氡异常变化的天数 | 适用于美国蓝山湖地区的地震预测 | Fleischer et al., |
| 5 | M=2log(λΔR/KT)-15.3 | M为震级,λ为氡的衰变常数,ΔR为氡浓度的相对变化,K为常数,给定值为3.96×10-17,T为氡异常变化的时间 | 选取世界各地震级M>5、震中距>100km的17次主震验证了模型的有效性,表明该模型具有较为广泛的应用范围 | Ramola etal., |
| 6 | logTlong= | T为氡异常变化的时间, m为震级 | 适用于南极洲地区的地震预测模型 | Ilić et al., |
| 7 | M=1.93log103.58D | M为震级,D为震中距 | 适用于各种氡浓度检测方法 | Elmaghraby etal., |
| log10DTP=0.63M-0.483 | M为震级,D为震中距,TP为地震引起的氡浓度最高值出现的时间 | 适用于地下水和温泉中的氡浓度检测方法 | ||
| log10D =0.0347M2+0.802 | M为震级,D为震中距,Trise为氡浓度开始出现异常值到升至最高值的时间 | 适用于土壤气和降雨中的氡浓度检测方法 | ||
| log10(DTP-V/TP)=0.508M-1.58 | M为震级,D为震中距,TP-V为氡浓度从最高值变化到最低值的时间,TP为地震引起的氡浓度最高值出现的时间 | 适用于空气中放射性氡浓度检测以及地下水和土壤气中的氡浓度检测方法 |
表 1 国外地震地球化学前兆研究的经验公式
Table 1 Empirical formulas for seismic geochemical precursors abroad
| 序号 | 经验公式 | 参数含义 | 适用范围 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ρ=100.43M | ρ为有效前兆异常区的半径,M为震级 | 是大量地球化学地震预测方法的理论基础,适用性较广泛 | Dobrovolsky et al., |
| 2 | logT=0.76M-1.83 | T为氡地震前兆异常的持续时间,M为震级 | Rikitake, | |
| 3 | ML=2logD-0.07 | D为氡地震前兆异常的持续时间,ML为震级 | 适用于美国南卡罗莱纳西北部约卡西湖2.0≤ML≤2.6的地震预测,该模型成功验证了1977年2月23日2.3级地震事件 | Talwani, |
| 4 | t(天)=10M/143 | M为震级,t为氡异常变化的天数 | 适用于美国蓝山湖地区的地震预测 | Fleischer et al., |
| 5 | M=2log(λΔR/KT)-15.3 | M为震级,λ为氡的衰变常数,ΔR为氡浓度的相对变化,K为常数,给定值为3.96×10-17,T为氡异常变化的时间 | 选取世界各地震级M>5、震中距>100km的17次主震验证了模型的有效性,表明该模型具有较为广泛的应用范围 | Ramola etal., |
| 6 | logTlong= | T为氡异常变化的时间, m为震级 | 适用于南极洲地区的地震预测模型 | Ilić et al., |
| 7 | M=1.93log103.58D | M为震级,D为震中距 | 适用于各种氡浓度检测方法 | Elmaghraby etal., |
| log10DTP=0.63M-0.483 | M为震级,D为震中距,TP为地震引起的氡浓度最高值出现的时间 | 适用于地下水和温泉中的氡浓度检测方法 | ||
| log10D =0.0347M2+0.802 | M为震级,D为震中距,Trise为氡浓度开始出现异常值到升至最高值的时间 | 适用于土壤气和降雨中的氡浓度检测方法 | ||
| log10(DTP-V/TP)=0.508M-1.58 | M为震级,D为震中距,TP-V为氡浓度从最高值变化到最低值的时间,TP为地震引起的氡浓度最高值出现的时间 | 适用于空气中放射性氡浓度检测以及地下水和土壤气中的氡浓度检测方法 |
| 序号 | 方法 | 应用实例 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 分层神经网络(LNN) | 能够区分环境条件改变和地震活动引起的氡浓度变化 | Negarestani etal., |
| 2 | 模型树方法(MT) | 在无地震活动时期,计算得到较为真实的氡浓度测值,但在地震活动时期,计算出的氡浓度值与实测值相差较大,可根据该模型计算的结果与实测值之间的差异预测地震活动 | Zmazek et al., |
| 3 | 箱线图分析方法 | 分析了巴基斯坦的穆扎法拉巴德地区监测点的氡特定模式浓度,可以识别氡浓度的异常变化,预测地震活动的发生 | Aleem et al., |
| 4 | 主成分分析(PCA) 和变化点检测(CP) | 根据冰岛北部地下水中微量元素浓度的监测数据,分析与地震活动有关的水文地球化学前兆,为预测地震活动提供研究指标 | Barbieri et al., |
| 5 | 人工神经网络模型方法 (ANNs) | 建立人工神经网络模型预测东安纳托利亚断裂带的地震,对发生的147次地震进行验证,准确度较高,误差只有2.3% | Fatih et al., |
| 对斯洛文尼亚东南部断层土壤气中氡的浓度进行分析,在12次地震中识别出10次异常 | Zmazek et al., | ||
| 基于斯洛文尼亚地区的环境参数和氡浓度的监测数据预测地震,可成功预测13例地震事件中的10例 | Torkar et al., | ||
| 6 | 人工神经网络模型(ANN)、多元线性回归(MLR)和决策树(DT)方法 | 使用不同方法识别巴勒斯坦北部地区构造活动引起的氡异常,从而预测地震的发生 | Haider et al., |
| 7 | 变点分析及检测算法(DA算法)、贝叶斯CP算法 | 使用DA算法、贝叶斯CP算法对连续监测的气氡数据进行处理能够预测地震的发生,使用该方法成功预测了意大利中部地区地震 | Soldati et al., |
| 8 | 基于异常点画圆,根据氡监测网预测地震位置和震级 | 可成功验证1988年伊朗Kerman地区发生的地震 | Hashemi et al., |
表 2 国外地球化学短临预测分析方法及应用
Table 2 Geochemical short-imminent earthquake prediction and analysis methods abroad
| 序号 | 方法 | 应用实例 | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 分层神经网络(LNN) | 能够区分环境条件改变和地震活动引起的氡浓度变化 | Negarestani etal., |
| 2 | 模型树方法(MT) | 在无地震活动时期,计算得到较为真实的氡浓度测值,但在地震活动时期,计算出的氡浓度值与实测值相差较大,可根据该模型计算的结果与实测值之间的差异预测地震活动 | Zmazek et al., |
| 3 | 箱线图分析方法 | 分析了巴基斯坦的穆扎法拉巴德地区监测点的氡特定模式浓度,可以识别氡浓度的异常变化,预测地震活动的发生 | Aleem et al., |
| 4 | 主成分分析(PCA) 和变化点检测(CP) | 根据冰岛北部地下水中微量元素浓度的监测数据,分析与地震活动有关的水文地球化学前兆,为预测地震活动提供研究指标 | Barbieri et al., |
| 5 | 人工神经网络模型方法 (ANNs) | 建立人工神经网络模型预测东安纳托利亚断裂带的地震,对发生的147次地震进行验证,准确度较高,误差只有2.3% | Fatih et al., |
| 对斯洛文尼亚东南部断层土壤气中氡的浓度进行分析,在12次地震中识别出10次异常 | Zmazek et al., | ||
| 基于斯洛文尼亚地区的环境参数和氡浓度的监测数据预测地震,可成功预测13例地震事件中的10例 | Torkar et al., | ||
| 6 | 人工神经网络模型(ANN)、多元线性回归(MLR)和决策树(DT)方法 | 使用不同方法识别巴勒斯坦北部地区构造活动引起的氡异常,从而预测地震的发生 | Haider et al., |
| 7 | 变点分析及检测算法(DA算法)、贝叶斯CP算法 | 使用DA算法、贝叶斯CP算法对连续监测的气氡数据进行处理能够预测地震的发生,使用该方法成功预测了意大利中部地区地震 | Soldati et al., |
| 8 | 基于异常点画圆,根据氡监测网预测地震位置和震级 | 可成功验证1988年伊朗Kerman地区发生的地震 | Hashemi et al., |
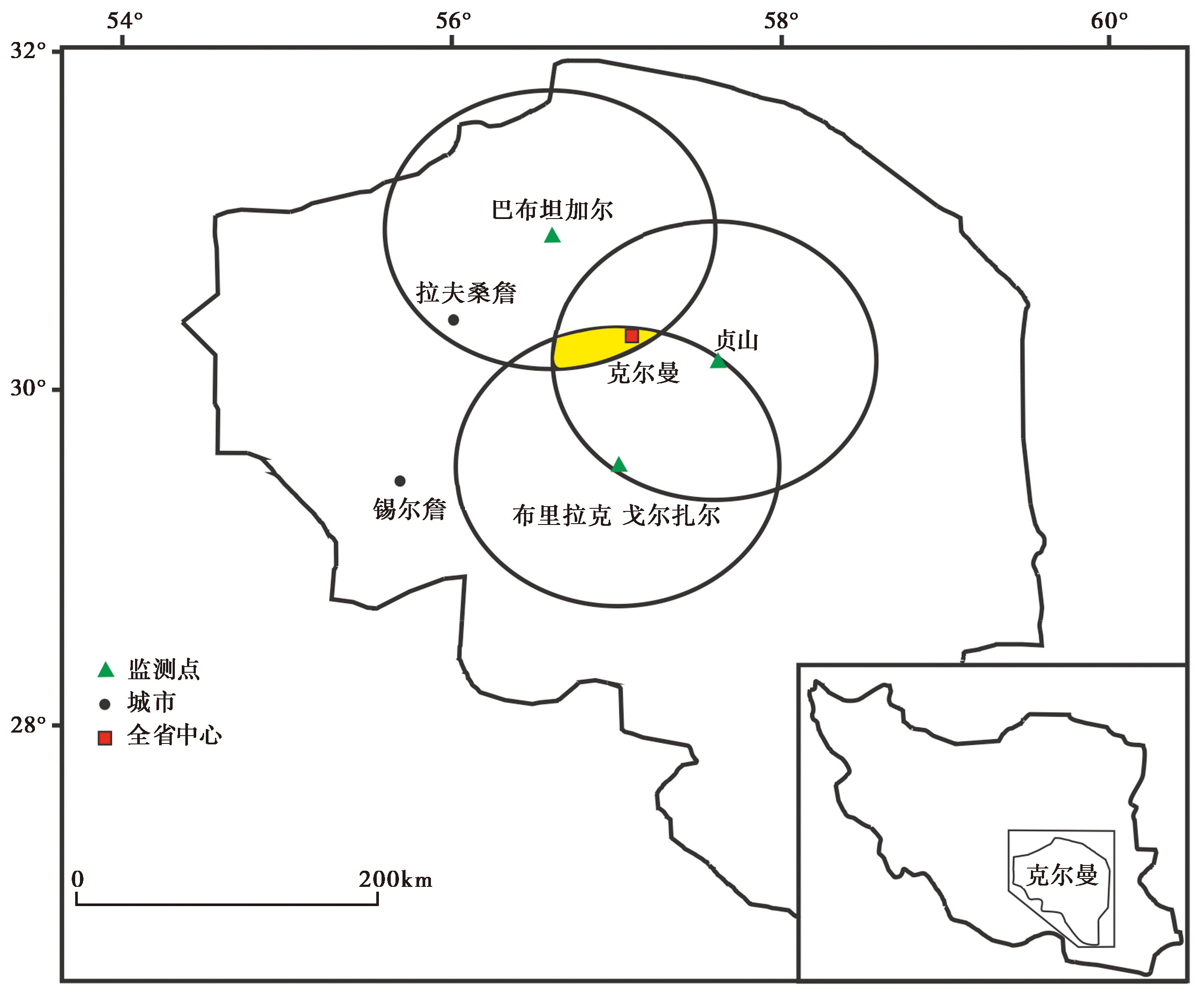
图 1 根据多个监测站氡浓度异常预测地震发生的地点(Hashemi et al., 2013)
Fig. 1 Predicting the location of earthquake according to radon concentration anomaly of several monitoring stations(after Hashemi et al., 2013).
| 序号 | 方法名称 | 适用范围 | 预测效果 | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 统计判据预报方法 | 对MS≥5地震的预测 | 对发震时间的判断有较大的不确定性 | 张炜等, |
| 2 | 水化短临预报整体化方案 | 对MS≥5地震的短临预测 | 地点预测受水化观测台网分布范围的限制 | 王吉易等, |
| 3 | 多层次跟踪预报方法 | 大(强)地震的发震时间的预测 | 方法中包含多个规则、指标和计算式,需不断修正 | 王吉易等, |
| 4 | 平面图形演化方法 | 时间和地点的预测 | 可预测MS≥6的大地震,震中及附近观测井点需密集 | 邵永新等, |
表 3 地震地球化学综合预报方法
Table 3 Comprehensive seismo-geochemical method for earthquake prediction
| 序号 | 方法名称 | 适用范围 | 预测效果 | 资料来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 统计判据预报方法 | 对MS≥5地震的预测 | 对发震时间的判断有较大的不确定性 | 张炜等, |
| 2 | 水化短临预报整体化方案 | 对MS≥5地震的短临预测 | 地点预测受水化观测台网分布范围的限制 | 王吉易等, |
| 3 | 多层次跟踪预报方法 | 大(强)地震的发震时间的预测 | 方法中包含多个规则、指标和计算式,需不断修正 | 王吉易等, |
| 4 | 平面图形演化方法 | 时间和地点的预测 | 可预测MS≥6的大地震,震中及附近观测井点需密集 | 邵永新等, |
| 地震三要素 | 震级 | 发震时间 | 发震地点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 预测标志 | 异常形态类型 | 异常形态类型 | 异常集中区的分布范围 |
| 异常持续时间 | 异常的开始、转折和结束时间 | 异常区的时空迁移和扩展方向 | |
| 异常数量 | |||
| 异常分布范围 |
表 4 主要的预测地震三要素的地震地球化学标志表(车用太等, 2004)
Table 4 Main indicators of the seismogeochemical method for tprediction of earthquake three elements(after CHE Yong-tai et al., 2004)
| 地震三要素 | 震级 | 发震时间 | 发震地点 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 预测标志 | 异常形态类型 | 异常形态类型 | 异常集中区的分布范围 |
| 异常持续时间 | 异常的开始、转折和结束时间 | 异常区的时空迁移和扩展方向 | |
| 异常数量 | |||
| 异常分布范围 |
| 序号 | 公式 | 适用震例数量 /个 | 适用比例 /% | 不适用震例数量 /个 | 不适用比例 /% | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | logT=0.76M-1.83 | 25 | 92.59 | 2 | 7.41 | Rikitake, |
| 2 | ρ=100.43M | 26 | 96.30 | 1 | 3.70 | Dobrovolsky et al., |
| 3 | log10(DTP)=0.63M-0.483 | 26 | 96.30 | 1 | 3.70 | Elmaghraby et al., |
| 4 | ML=2logD-0.07 | 4 | 14.81 | 23 | 85.19 | Talwani, |
| 5 | t(天)=10M/143 | 0 | 0.00 | 27 | 100.00 | Fleischeretal., |
| 6 | M=2log(λΔR/KT)-15.30 | 3 | 11.11 | 24 | 88.89 | Ramola et al., |
| 7 | logTlong=0.685m-1.57 | 0 | 0.00 | 29 | 100.00 | |
| 8 | D=100.32M(10<D≤50) D=100.43M(50<D≤100) D=100.56M(100<D≤500) D=100.63M(500<D≤1250) | 5 | 18.52 | 22 | 81.48 | Virk, |
| 9 | Mmin<M<Mmax,Mmin=(logR)/0.43, Mmax=(logL)/0.43 | 6 | 30.00 | 14 | 70.00 | Hashemi et al., |
表 6 基于1997—2020年《中国震例》的国外预测方法检验
Table 6 Statistics on applicability of foreign prediction formulas based on China Earthquake Cases(1997—2020)
| 序号 | 公式 | 适用震例数量 /个 | 适用比例 /% | 不适用震例数量 /个 | 不适用比例 /% | 参考文献 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | logT=0.76M-1.83 | 25 | 92.59 | 2 | 7.41 | Rikitake, |
| 2 | ρ=100.43M | 26 | 96.30 | 1 | 3.70 | Dobrovolsky et al., |
| 3 | log10(DTP)=0.63M-0.483 | 26 | 96.30 | 1 | 3.70 | Elmaghraby et al., |
| 4 | ML=2logD-0.07 | 4 | 14.81 | 23 | 85.19 | Talwani, |
| 5 | t(天)=10M/143 | 0 | 0.00 | 27 | 100.00 | Fleischeretal., |
| 6 | M=2log(λΔR/KT)-15.30 | 3 | 11.11 | 24 | 88.89 | Ramola et al., |
| 7 | logTlong=0.685m-1.57 | 0 | 0.00 | 29 | 100.00 | |
| 8 | D=100.32M(10<D≤50) D=100.43M(50<D≤100) D=100.56M(100<D≤500) D=100.63M(500<D≤1250) | 5 | 18.52 | 22 | 81.48 | Virk, |
| 9 | Mmin<M<Mmax,Mmin=(logR)/0.43, Mmax=(logL)/0.43 | 6 | 30.00 | 14 | 70.00 | Hashemi et al., |
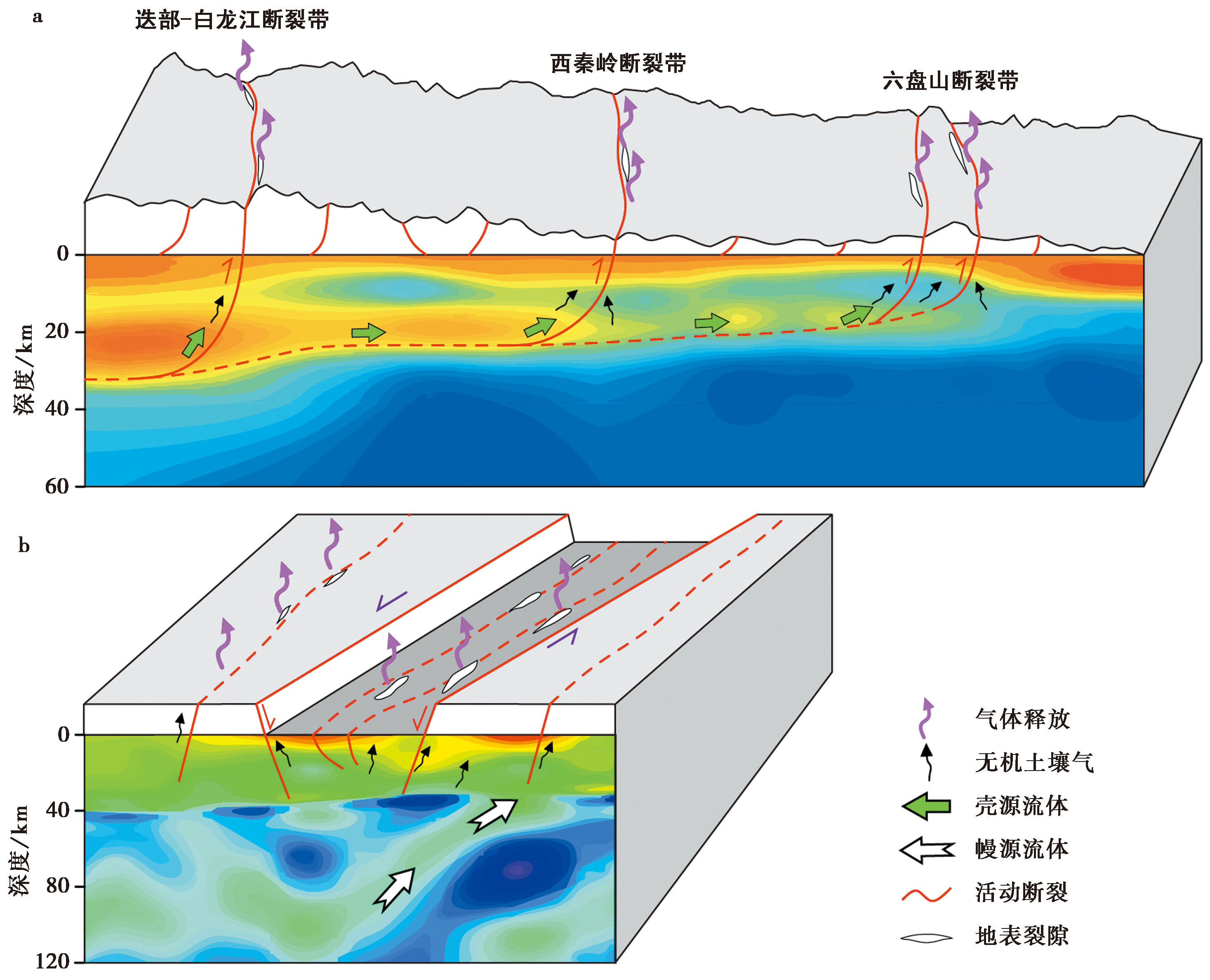
图 4 青藏高原东北缘(a)和张渤地震带(b)的气体地球化学运移示意图(Chen et al., 2022)
Fig. 4 The schematic diagram of gas geochemical migration in the northeastern margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau(a)and Zhangbo seismic belt(b)(Chen et al., 2022).
| [1] |
车用太, 刘耀炜, 何镧. 2015. 断层带土壤气中H2观测: 探索地震短临预报的新途径[J]. 地震, 35(4): 1-10.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
车用太, 王吉易, 李一兵, 等. 2004. 首都圈地下流体监测与地震预测[M]. 北京: 气象出版社: 144-150.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
丁香, 王晓青. 2000. 华北水氡异常与地震关系的Bayes判别分析[J]. 华北地震科学, 18(3): 59-65.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
杜建国, 仵柯田, 孙凤霞, 等. 2022. 隐爆角砾岩: 古地震的一种成因标志[J]. 岩石学报, 38(3): 913-922.
|
|
DOI URL |
|
| [5] |
官致君. 1999. 水化学预报方法及效能评价[J]. 四川地震, (1-2): 89-99.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
和宏伟, 和国文, 李永莉, 等. 1999. 云南地区水氡前兆异常动态演化与地震关系研究[J]. 地震研究, 22(4): 365-371.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
贺天培. 1989. 四川地区水化方法预报指标的研究[J]. 四川地震, (4): 27-36.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
蒋凤亮, 李桂如, 王基华, 等. 1989. 地震地球化学[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 184-185.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
蒋海昆, 付虹, 杨马陵. 2018a. 中国震例(2014-2015)[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
蒋海昆, 杨马陵, 付虹. 2018b. 中国震例(2007-2012)[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
蒋海昆, 杨马陵, 付虹. 2018c. 中国震例(2013)[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
蒋海昆, 杨马陵, 付虹. 2018d. 中国震例(2016-2017)[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
康春丽, 杜建国, 李圣强. 1999. 中强地震活动中汞的异常特征[J]. 地震, 19(4): 352-358.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
李君英, 唐仲兴. 1999. 华北强震水化学参量变化的模糊识别及方法评价[J]. 地震, 19(1): 71-80.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
李圣强, 杜建国, 康春丽. 2001. 信息熵在地下流体资料处理中的应用[J]. 华北地震科学, 19(2): 1-7.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
李营, 陈志, 胡乐, 等. 2022. 流体地球化学进展及其在地震预测研究中的应用[J]. 科学通报, 67(13): 1404-1420.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
李志鹏, 赵冬, 袁梅. 2015. 姑咱台气氡测值异常与地震预报探讨[J]. 四川地震, (4): 24-28.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
林纪曾. 1981. 观测数据的数学处理[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 69-72.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
刘耀炜, 任宏微, 张磊, 等. 2015. 鲁甸6.5级地震地下流体典型异常与前兆机理分析[J]. 地震地质, 37(1): 307-318.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
刘耀炜, 张元生. 1998. 共和7.0级地震前地下流体前兆的动态演化特征[J]. 西北地震学报, 20(1): 59-64.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
邵俊杰, 李营, 孙凤霞, 等. 2022. 水-岩反应过程中离子浓度变化特征实验研究及其对地震异常成因的启示[J]. 地震研究, 45(2): 187-198.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
邵永新, 李君英, 李一兵, 等. 2000. 唐山7.8级地震前水氡异常演化特征[J]. 西北地震学报, 22(3): 247-250.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
沈照理, 王焰新, 郭华明, 等. 2012. 水-岩相互作用研究的机遇与挑战[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 37(2): 207-219.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
司学芸, 孙小龙, 邵志刚, 等. 2013. 南北地震带流体资料趋势性转折与强震的关系[J]. 中国地震, 29(1): 148-156.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
孙小龙, 刘耀炜, 付虹, 等. 2020. 我国地震地下流体学科分析预报研究进展回顾[J]. 地震研究, 43(2): 216-231.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
孙小龙, 王俊, 向阳, 等. 2016. 基于《中国震例》的地下流体异常特征统计分析[J]. 地震, 36(4): 120-130.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
孙小龙, 向阳, 杨朋涛. 2018. 云南会泽井水位地震预测效能检验及其机理分析[J]. 地震学报, 40(2): 185-194.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
万迪堃, 汪成民, 李介成, 等. 1993. 地下水动态异常与地震短临预报[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 6-9.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
万永革, 吴忠良, 周公威, 等. 2002. 地震应力触发研究[J]. 地震学报, 24(5): 533-551.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
王博, 钟骏, 王熠熙, 等. 2018. 南北地震带北段流体资料地震预测效能检验[J]. 地震, 38(1): 147-156.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
汪成民, 李宣瑚, 王铁城, 等. 1990. 中国地震地下水动态观测网[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
王基华, 林元武, 高松升. 1998. 怀来断层气CO2监测及张北-尚义地震的短临预报[J]. 地震地质, 20(2): 113-116.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
王基华, 孙风民, 张培仁. 1991. H2异常和地震活动的关系[J]. 华北地震科学, 9(2): 59-64.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
王吉易, 董守宇, 陈建民, 等. 1997. 地下流体地震预报方法[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 112-131.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
王吉易, 张炜. 1991. 水化地震短临预报的整体方案[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
王吉易, 郑云贞, 张素欣, 等. 1994. 水化多层次加速前兆图像[J]. 中国地震, 10(S1): 157-165.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
王晓青, 石绍先, 丁香. 1998. 前兆异常识别的X2统计检验法及其应用[J]. 地震, 18(3): 257-264.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
魏家珍, 申春生. 1994. 首都圈地区汞测量典型震例剖析及其映震效能评价[J]. 地震, (3): 44-49.
|
|
|
|
| [39] |
邢玉安, 王吉易. 2000. 水氡动态图强震危险区预测的新方法[J]. 地震, 20(4): 1-6.
|
|
|
|
| [40] |
许绍燮. 1989. 地震预报能力评分[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 586-589.
|
|
|
|
| [41] |
晏锐, 黄辅琼, 顾瑾平. 2004. 中国大陆 7 级强震前地下流体前兆时空特征[J]. 地震, 24(1): 126-131.
|
|
|
|
| [42] |
晏锐, 田雷, 王广才, 等. 2018. 2008年汶川8.0级地震前地下流体异常回顾与统计特征分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(5): 1907-1921.
|
|
|
|
| [43] |
岳明生. 2005. 地震预测研究发展战略几点思考[J]. 国际地震动态, (5): 7-21.
|
|
|
|
| [44] |
张培仁, 王基华, 孙凤民. 1993. 氢: 预报地震的灵敏元素[J]. 地震地质, 15(1): 69-77.
|
|
|
|
| [45] |
张素欣, 张子广, 郑云贞. 2001. 水化学参量的中强地震中短期预报方法在河北及邻区的应用检验[J]. 华南地震, 21(3): 8-14.
|
|
|
|
| [46] |
张炜. 1991. 水文地球化学在地震监测预报中的应用[J]. 水文地质工程地质, 18(2): 45-47.
|
|
|
|
| [47] |
张炜, 王吉易, 鄂秀满, 等. 1988. 水文地球化学预报地震的原理与方法[M]. 北京: 教育科学出版社: 162-170.
|
|
|
|
| [48] |
张文冕, 田少柏. 1990. 地震前水氡短临异常判别指标及预报三要素的方法探讨[J]. 西北地震学报, 12(1): 30-38.
|
|
|
|
| [49] |
张晓东, 傅征祥, 张永仙, 等. 2003. 1999-2002年地震预报研究进展[J]. 地震学报, 25(5): 479-491.
|
|
|
|
| [50] |
张新基, 张慧. 1998. 地下流体异常性质定量判别方法探索与地震预报[J]. 西北地震学报, 20(3): 16-21.
|
|
|
|
| [51] |
郑云贞, 王吉易, 张素欣. 1991. 山西大同6.1级地震前河北省水化异常与地震三要素判断[J]. 华北地震科学, 9(4): 78-83.
|
|
|
|
| [52] |
钟骏, 王博, 闫玮, 等. 2021. 阿克苏断层氢气浓度动态特征及其映震效能[J]. 地震学报, 43(5): 615-627.
|
|
|
|
| [53] |
DOI URL |
| [54] |
DOI URL |
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
DOI URL |
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
DOI URL |
| [60] |
DOI URL |
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
DOI PMID |
| [63] |
DOI PMID |
| [64] |
DOI URL |
| [65] |
DOI URL |
| [66] |
DOI URL |
| [67] |
DOI URL |
| [68] |
DOI URL |
| [69] |
DOI URL |
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
DOI URL |
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
DOI URL |
| [74] |
DOI URL |
| [75] |
|
| [76] |
PMID |
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
DOI URL |
| [79] |
DOI URL |
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
DOI URL |
| [83] |
DOI URL |
| [84] |
DOI |
| [85] |
DOI |
| [86] |
|
| [87] |
DOI URL |
| [88] |
DOI URL |
| [89] |
DOI URL |
| [90] |
DOI URL |
| [91] |
|
| [92] |
DOI URL |
| [93] |
DOI URL |
| [94] |
DOI URL |
| [95] |
DOI URL |
| [96] |
DOI URL |
| [97] |
DOI URL |
| [98] |
DOI URL |
| [99] |
|
| [100] |
DOI URL |
| [101] |
DOI URL |
| [102] |
DOI URL |
| [103] |
|
| [104] |
|
| [105] |
DOI URL |
| [1] | 李继业, 晏锐, 张思萌, 胡澜缤, 孟令蕾, 周晨. 井水位潮汐响应与小地震调制作用的关系[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 668-688. |
| [2] | 王喜龙, 罗银花, 金秀英, 杨梦尧, 孔祥瑞. 辽南地区断裂带的断层土壤气地球化学特征及其对区域应力调整的指示[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 710-734. |
| [3] | 王博, 崔凤珍, 刘静, 周永胜, 徐胜, 邵延秀. 玛多 MS7.4地震断层土壤气特征与地表破裂的相关性[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 772-794. |
| [4] | 韩晓飞, 史双双, 董斌, 薛晓东, 范雪芳. 田庄断裂变形带的演化机制分析[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 795-810. |
| [5] | 刘庆, 刘韶, 张世民. 大凉山断裂带中段越西断裂晚第四纪古地震[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 321-337. |
| [6] | 蒋锋云, 季灵运, 朱良玉, 刘传金. 联合GPS和InSAR研究海原-六盘山断裂现今的地壳变形特征[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 377-400. |
| [7] | 王辽, 谢虹, 袁道阳, 李智敏, 薛善余, 苏瑞欢, 文亚猛, 苏琦. 结合野外考察的2022年门源MS6.9地震地表破裂带的高分七号影像特征[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 401-421. |
| [8] | 陈鲲, 高孟潭, 俞言祥, 徐伟进, 杜义, 李雪靖, 陆东华. 融合三维断层源和二维潜在震源区的随机抽样概率地震危险性分析算法研发[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 435-454. |
| [9] | 杨晨艺, 李晓妮, 冯希杰, 黄引弟, 裴跟弟. 秦岭北缘断裂带的重要分支——桃川-户县断层的浅部结构与第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 464-483. |
| [10] | 李晓妮, 杨晨艺, 李高阳, 冯希杰, 黄引弟, 李陈侠, 李苗, 裴跟弟, 王万合. 渭河盆地东南缘渭南塬前北侧分支断层的浅部结构及晚第四纪活动[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 484-499. |
| [11] | 刘白云, 赵莉, 刘云云, 王文才, 张卫东. 2021年5月22日青海玛多M7.4地震余震重新定位与断层面参数拟合[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 500-516. |
| [12] | 王明亮, 张扬, 徐顺强, 徐志萍. 华北坳陷中南部深部结构大地电磁探测[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 536-552. |
| [13] | 李安, 万波, 王晓先, 计昊旻, 索锐. 金州断裂盖州北鞍山段古地震破裂的新证据[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 111-126. |
| [14] | 郑海刚, 姚大全, 赵朋, 杨源源, 黄金水. 郯庐断裂带赤山段全新世新活动的特征[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 127-138. |
| [15] | 田一鸣, 杨卓欣, 王志铄, 石金虎, 张扬, 谭雅丽, 张建志, 宋威, 季通宇. 新乡-商丘断裂封丘段浅部探测和第四纪活动性的初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 139-152. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||