地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1421-1447.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.06.005
收稿日期:2021-12-05
修回日期:2022-02-27
出版日期:2022-12-20
发布日期:2023-01-21
通讯作者:
付碧宏
作者简介:李昭, 女, 1996年生, 2022年于中国科学院空天信息创新研究院获地图学与地理信息系统专业硕士学位, 主要研究方向为资源与环境遥感、 活动构造与构造地貌学, E-mail: lizhao@aircas.ac.cn。
基金资助:
LI Zhao1,2)( ), FU Bi-hong1),*(
), FU Bi-hong1),*( )
)
Received:2021-12-05
Revised:2022-02-27
Online:2022-12-20
Published:2023-01-21
Contact:
FU Bi-hong
摘要:
位于东昆仑断裂带东段的玛沁-玛曲段主断裂带由数条规模不等、 羽状斜列的次级断裂组成, 其晚第四纪滑动速率自西向东呈现梯度式降低的原因仍存在较大争议。精确查明玛沁-玛曲段主断裂带及其分支断裂的几何学和运动学特征, 可为探讨东昆仑断裂带东段的构造转换机制、 评价地震危险性提供重要线索。地貌指数定量分析是活动构造研究中的重要方法之一。其中, 面积-高程积分(HI)和河流坡降指数(SL)可有效揭示区域构造变形信息, 而地势起伏度(TR)能直观地反映区域构造活动的侵蚀响应程度。文中利用30m精度的AW3D30数据系统地定量提取玛沁-玛曲段主断裂带及其周边整个流域的TR指数、 流域盆地的HI指数及主要河流的Hack剖面、 SL指数及归一化坡降指数(SLK), 通过构造地貌与河道形态揭示区域构造活动的地貌响应特征, 探讨不同构造段落的活动强度。研究结果表明, 沿玛沁-玛曲段主断裂带的HI指数、 Hack剖面、 SLK指数及TR指数等值呈自西向东连续下降的变化特征, 其中, HI值自西部的0.77~0.89向E下降至0.15~0.36, TR所反映的地表侵蚀量从欧拉秀玛乡西侧的400m向E降至玛曲县东侧的(61±11)m, 而Hack剖面的上凸程度与其SLK异常显著性则具有西高东低的分布特征, 这与沿主断裂带晚第四纪滑动速率自西向东梯度递减的趋势基本一致, 表明地貌指数值变化与断裂活动强度密切相关; 地貌指数的空间分布差异性揭示了玛沁-玛曲段主断裂带及分支断裂(阿万仓断裂和尕海断裂)的晚第四纪构造活动性具有西段最强, 中段、 东段逐渐减弱的显著分段特征。结合野外构造地貌调查和验证认为, 玛沁-玛曲段主断裂带的晚第四纪活动性从玛沁-欧拉秀玛一带的断裂交会区开始向E逐渐减弱。因此, 推断东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段晚第四纪左旋走滑速率向E降低的现象与其主断裂带及阿万仓断裂、 尕海断裂等分支断裂构成的马尾状断裂系统密切相关, 分支断裂通过左旋走滑与逆冲变形共同吸收和调节了东昆仑断裂带东段向E扩展过程中的部分运动分量, 对东昆仑断裂带东段的构造转换与变形分解起到了关键作用。
中图分类号:
李昭, 付碧宏. 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段晚第四纪构造活动特征的地貌响应定量研究[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1421-1447.
LI Zhao, FU Bi-hong. QUANTITATIVE ANALYSES OF GEOMORPHOLOGIC FEATURES IN RESPONSE TO LATE QUATERNARY TECTONIC ACTI-VITIES ALONG THE MAQIN-MAQU SEGMENT, EAST KUNLUN FAULT ZONE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(6): 1421-1447.

图 1 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段的活动构造图(据邓起东(2002)和Fu等(2011)修改) EKLF 东昆仑断裂; AWCF 阿万仓断裂; GHF 尕海断裂; CMHF 西藏大沟-昌马河断裂; LMSF 郎木寺断裂; GDF 贵德断裂;LTF 临潭-宕昌断裂; MJXSNF 玛积雪山南缘断裂; ZTF 中铁断裂; GDSF 光盖山-迭山断裂。 底图为30m AW3D30数据
Fig. 1 Map showing major active faults developed along the Maqin-Maqu segment of the East Kunlun fault zone (modified from DENG Qi-dong, 2002 and Fu et al., 2011).
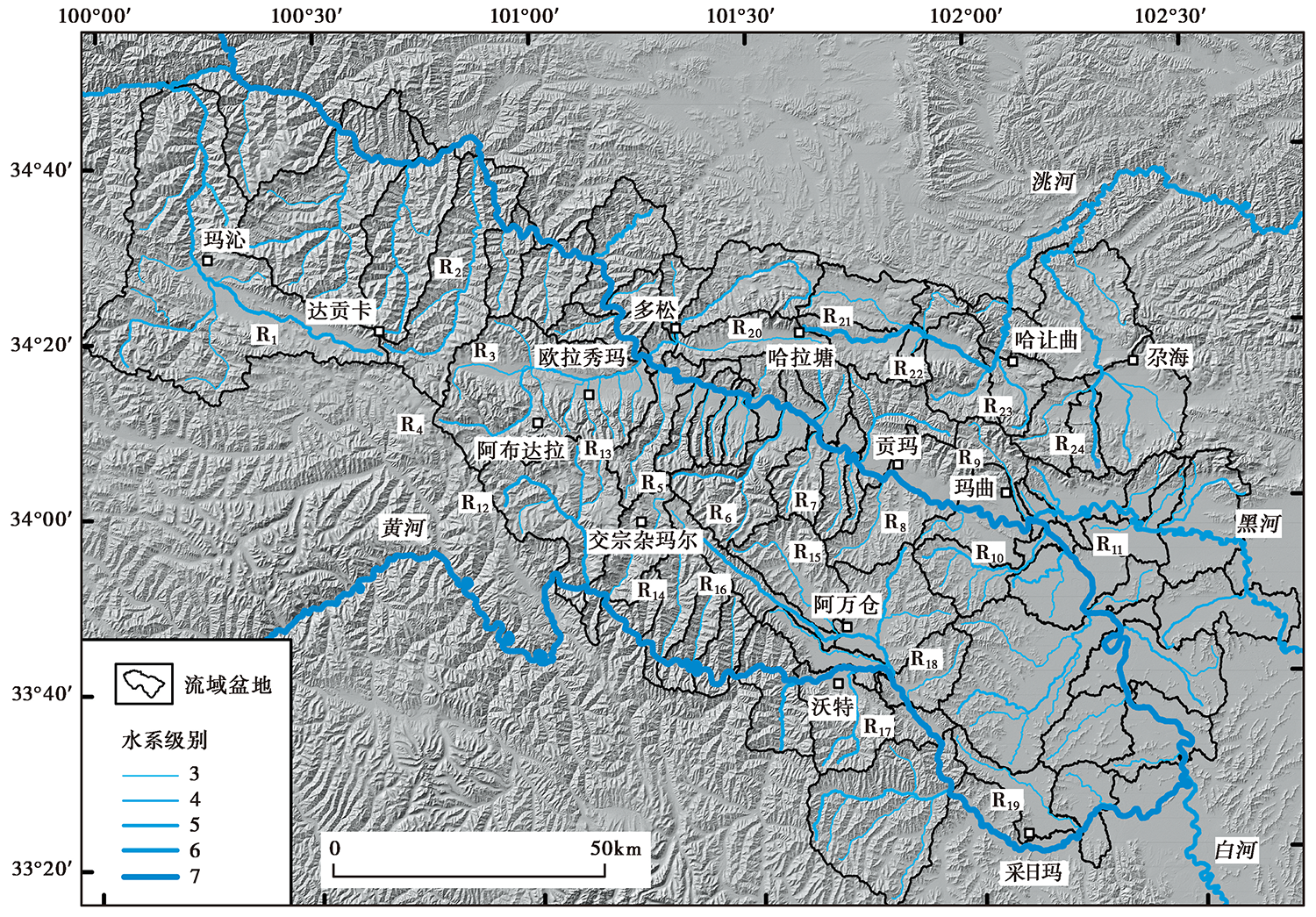
图 3 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段的水系分级和流域分布图
Fig. 3 River system grading and drainage basins distribution map along the Maqin-Maqu segment in the East Kunlun fault zone.
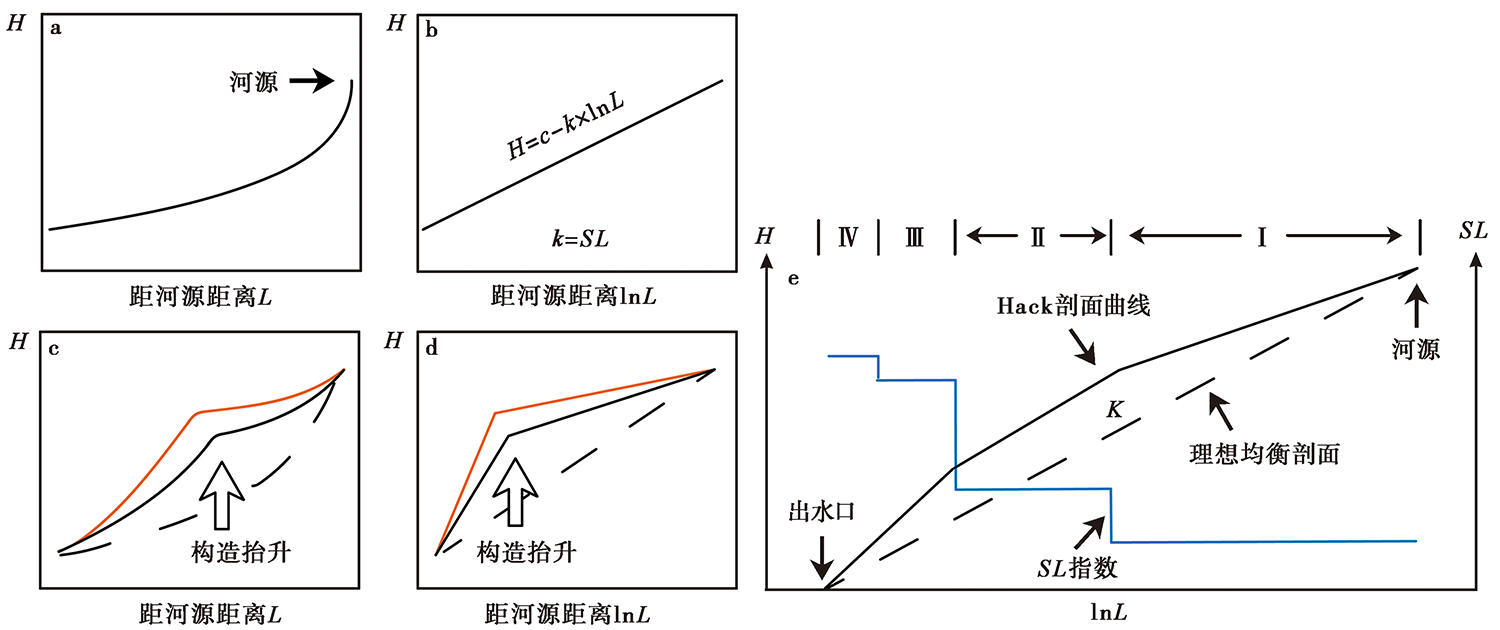
图 4 Hack剖面示意图(据Chen等(2003)修改) a 理想均衡状态下的河流纵剖面; b 半对数坐标下的理想均衡河流纵剖面, 即Hack剖面, 其斜率k为SL指数; c、 d 受构造抬升而隆起的河流纵剖面及相应Hack剖面形态; e “弯曲”的Hack剖面可分为4段线性拟合河段(Ⅰ、 Ⅱ、 Ⅲ、 Ⅳ)且每段均有固定的SL值, 其拟合直线的斜率K为均衡坡降指标, 代表动态平衡状态下的理想河流剖面
Fig. 4 Conceptual diagram of Hack profiles(modified from Chen et al., 2003).
| 断裂带名称 | 分段 | 河流编号 | 河长/km | 均衡坡降指数K | Kmean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 玛沁—玛曲段 主断裂带 | 玛沁—欧拉秀玛段(西段) | R1 | 109.05 | 97.43 | 95.30 |
| R2 | 69.00 | 99.90 | |||
| R3 | 59.70 | 82.66 | |||
| R4 | 37.95 | 101.19 | |||
欧拉秀玛—贡玛段(中段) | R5 | 36.30 | 82.67 | 77.47 | |
| R6 | 40.20 | 89.67 | |||
| R7 | 22.95 | 71.06 | |||
| R8 | 26.25 | 66.49 | |||
玛曲段(东段) | R9 | 29.85 | 60.95 | 32.67 | |
| R10 | 42.75 | 30.57 | |||
| R11 | 14.70 | 6.50 | |||
| 阿万仓断裂 | 阿布达拉段(北西段) | R4 | 37.95 | 101.19 | 74.15 |
| R12 | 46.80 | 73.94 | |||
| R13 | 21.00 | 47.33 | |||
交宗杂玛尔—沃特段(中段) | R14 | 41.55 | 60.86 | 62.62 | |
| R15 | 66.45 | 75.83 | |||
| R16 | 39.00 | 51.19 | |||
沃特—采日玛段(南东段) | R17 | 29.40 | 41.52 | 33.22 | |
| R18 | 24.45 | 42.98 | |||
| R19 | 43.50 | 15.17 | |||
| 尕海断裂 | 多松段(西段) | R20 | 37.60 | 40.25 | 40.25 |
哈拉塘—哈让曲段(中段) | R21 | 74.10 | 65.45 | 55.47 | |
| R22 | 13.35 | 54.11 | |||
| R23 | 19.95 | 46.86 | |||
| 尕海段(东段) | R24 | 91.80 | 50.83 | 50.83 |
表1 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段的河流地貌参数
Table1 The river geomorphic parameters of the Maqin-Maqu segment in the East Kunlun fault zone
| 断裂带名称 | 分段 | 河流编号 | 河长/km | 均衡坡降指数K | Kmean |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 玛沁—玛曲段 主断裂带 | 玛沁—欧拉秀玛段(西段) | R1 | 109.05 | 97.43 | 95.30 |
| R2 | 69.00 | 99.90 | |||
| R3 | 59.70 | 82.66 | |||
| R4 | 37.95 | 101.19 | |||
欧拉秀玛—贡玛段(中段) | R5 | 36.30 | 82.67 | 77.47 | |
| R6 | 40.20 | 89.67 | |||
| R7 | 22.95 | 71.06 | |||
| R8 | 26.25 | 66.49 | |||
玛曲段(东段) | R9 | 29.85 | 60.95 | 32.67 | |
| R10 | 42.75 | 30.57 | |||
| R11 | 14.70 | 6.50 | |||
| 阿万仓断裂 | 阿布达拉段(北西段) | R4 | 37.95 | 101.19 | 74.15 |
| R12 | 46.80 | 73.94 | |||
| R13 | 21.00 | 47.33 | |||
交宗杂玛尔—沃特段(中段) | R14 | 41.55 | 60.86 | 62.62 | |
| R15 | 66.45 | 75.83 | |||
| R16 | 39.00 | 51.19 | |||
沃特—采日玛段(南东段) | R17 | 29.40 | 41.52 | 33.22 | |
| R18 | 24.45 | 42.98 | |||
| R19 | 43.50 | 15.17 | |||
| 尕海断裂 | 多松段(西段) | R20 | 37.60 | 40.25 | 40.25 |
哈拉塘—哈让曲段(中段) | R21 | 74.10 | 65.45 | 55.47 | |
| R22 | 13.35 | 54.11 | |||
| R23 | 19.95 | 46.86 | |||
| 尕海段(东段) | R24 | 91.80 | 50.83 | 50.83 |
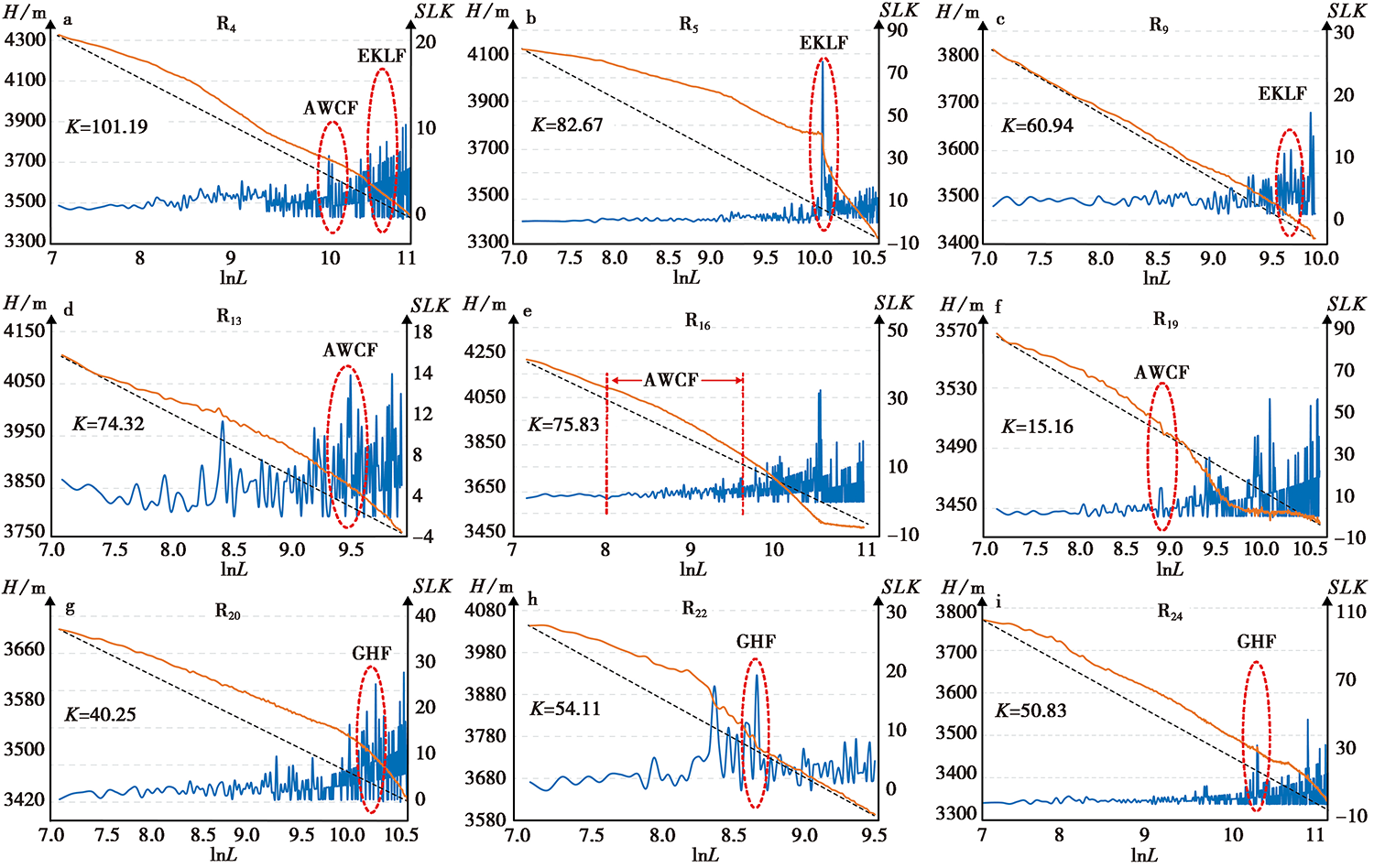
图 7 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段的河流Hack剖面与相对应的SLK 蓝色实线代表SLK, 黄色实线为对应河段的Hack剖面, 红色虚线表示河段中SLK异常区
Fig. 7 Hack profile and SLK index along the Maqin-Maqu segment in the East Kunlun fault zone.
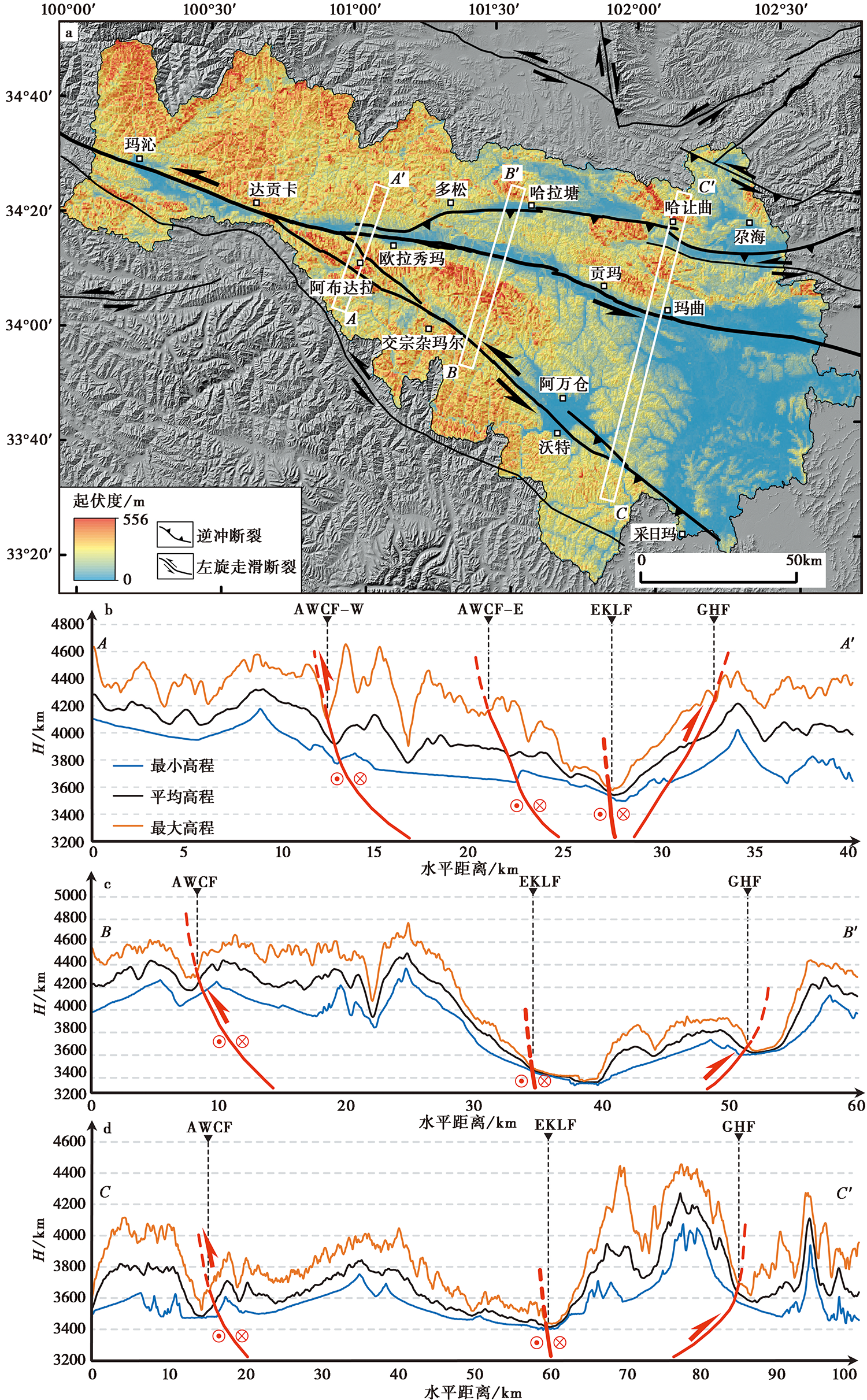
图 8 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段的TR空间分布图 a 基于高程阈值法提取的东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段的地势起伏分布图; b-d 基于高程条带法提取的东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段的二维面性地势起伏信息, 其中AA'、 BB'、 CC'分别横跨玛沁-玛曲段主断裂带及分支阿万仓断裂、尕海断裂的西段、 中段、 东段
Fig. 8 Topographic relief map of the Maqin-Maqu segment in the East Kunlun fault zone.
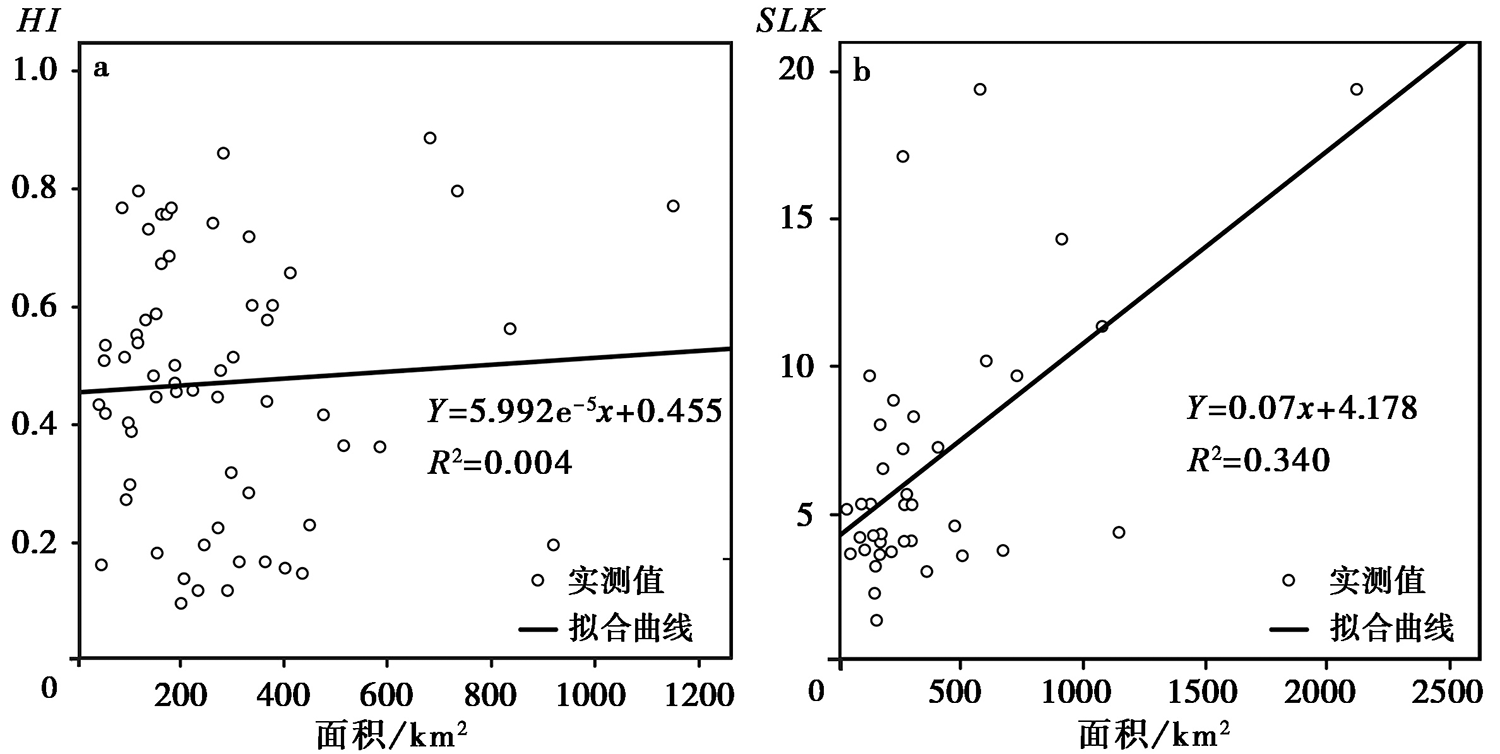
图 9 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段的HI、 SLK与流域面积的Kendall相关性分析 a HI值与其相应流域面积的Kendall相关性统计结果, 相关系数τ为-0.024, 显示二者无显著相关性; b SLK的平均值与其相应流域面积的Kendall相关性统计结果, 相关系数τ为0.283, 表明二者之间相关程度较低
Fig. 9 Correlation analysis between geomorphic index(HI, SLK) and basin area of the Maqin-Maqu segment in the East Kunlun fault zone.

图 10 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段HI与岩性的相关性分析 a 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段及其周边地区HI与岩性分布的叠加图, 其中, 地层颜色及其指示意义如图2所示; b 不同形成时代的岩石与其对应HI的K-W分析结果; c 不同类型的岩石与其对应HI的K-W分析结果。图中岩石类型划分为: 1 灰岩; 2 变质碎屑岩与碳酸盐岩; 3 构造混杂岩; 4 花岗岩; 5 砂岩、 砾岩; 6 灰岩与泥灰岩; 7 砂岩、板岩; 8 砂岩、 板岩与碳酸盐岩; 9 冰碛物
Fig. 10 Correlation analysis between HI and lithology of the Maqin-Maqu segment in the East Kunlun fault zone.
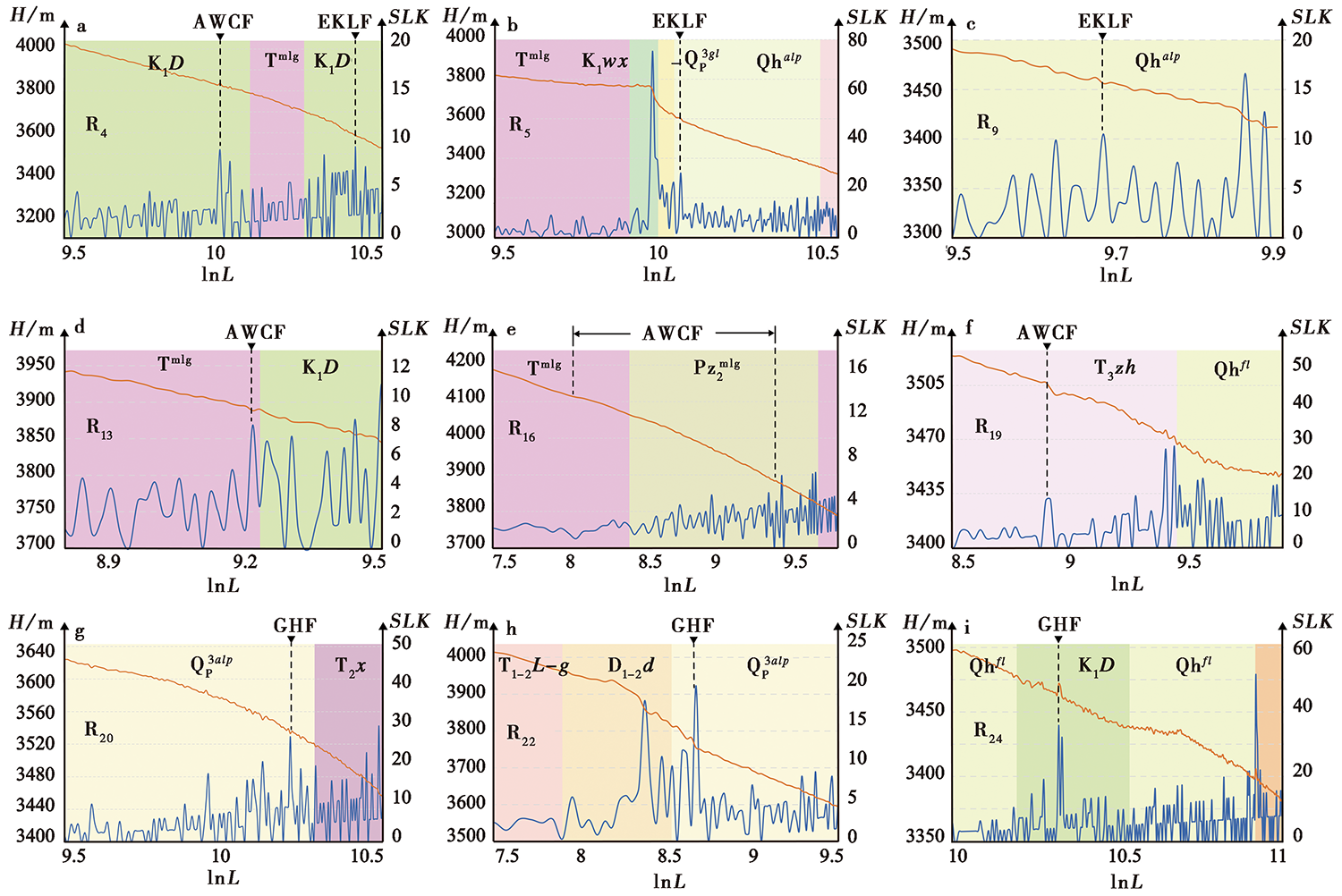
图 11 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段SLK与岩性的相关性分析 蓝色实线为SLK, 黄色实线为对应河段的Hack剖面, 黑色虚线指示断裂, 岩性代号同图2
Fig. 11 Correlation analysis between SLK and lithology of the Maqin-Maqu segment in the East Kunlun fault zone.

图 12 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段的构造地貌特征 a 玛沁-玛曲段主断裂带的构造解译图, 底图为30m AW3D30数据; b 玛沁县西侧断层陡坎地貌的三维显示图, 底图为Google卫星图; c 基于野外无人机实测的断裂切割山前冲洪积物并左旋断错系列水系的地貌特征; d 欧拉秀玛乡西侧发育的反向断层陡坎及断塞塘构造地貌; e 欧拉秀玛乡东侧断层的线性地貌; f 玛曲县西侧南高北低的断层陡坎线性地貌, 底图为基于无人机正射测量获得DEM数据; g 基于图f中的DEM数据测量得到的断层陡坎高度示意图
Fig. 12 Tectono-geomorpgic characteristics along the Maqin-Maqu segment.
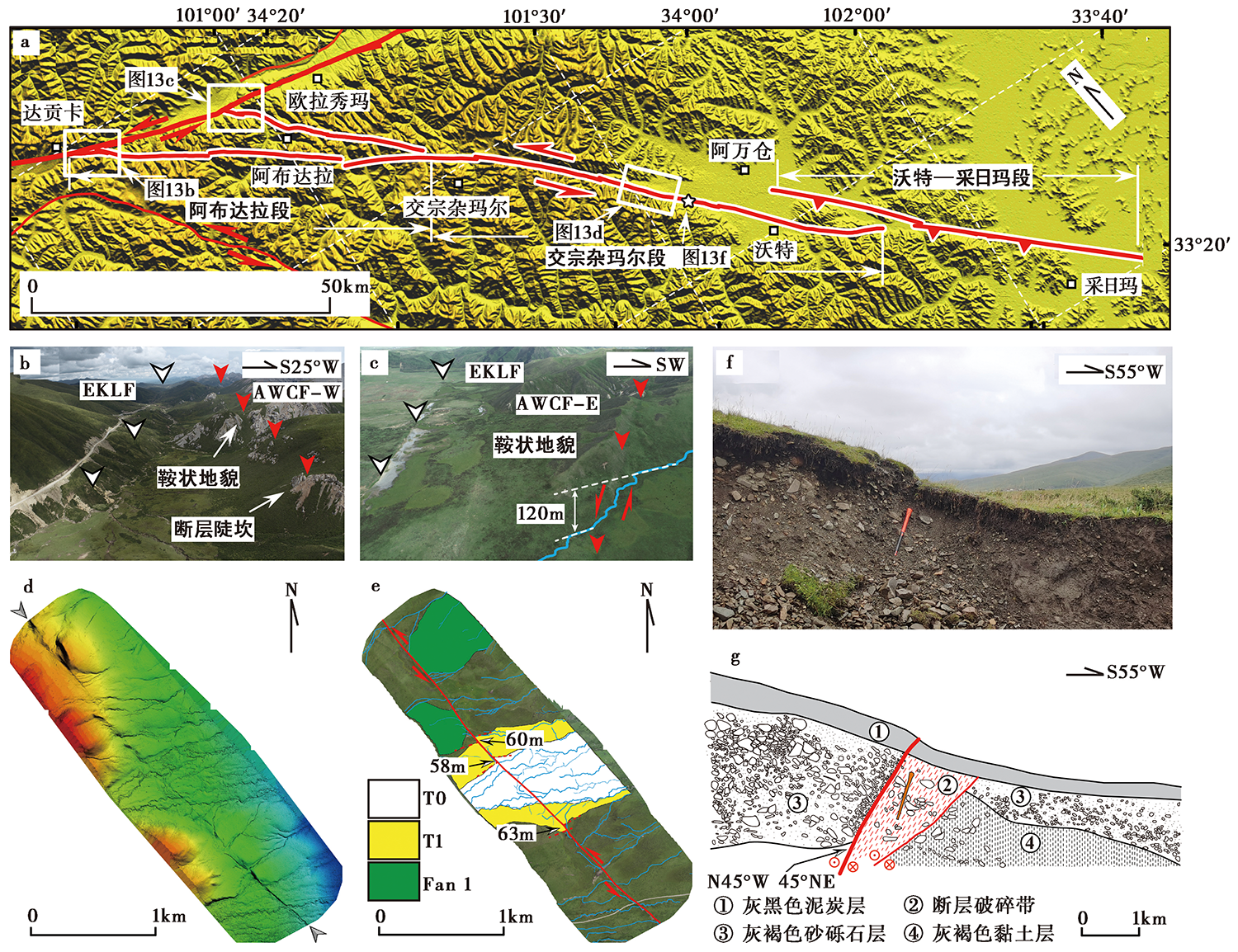
图 13 阿万仓断裂的构造地貌特征 a 阿万仓断裂的构造解译图, 底图为30m AW3D30数据; b 达贡卡东侧阿万仓断裂北西段西支无人机高精度图像显示出的线性断层陡坎与鞍状地貌; c 欧拉秀玛西侧阿万仓断裂北西段东支无人机高精度图像显示出的线性断层沟槽及水系、 山脊的同步左旋位错; d 无人机DEM图像显示的阿万仓断裂中段线性断错地貌特征; e 阿万仓断裂中段基于无人机高精度图像的活动断裂解译图; f 阿万仓断裂中段的断层剖面; g 图f的断层剖面解译图, 红色实线指示断层
Fig. 13 Tectono-geomorphic characteristics along the Awancang Fault.

图 14 尕海断裂的构造地貌特征 a 尕海断裂的解译图, 底图为30m AW3D30数据; b 哈拉塘-哈让曲段线性断错地貌的三维显示图, 底图为Google卫星图; c 基于无人机航拍图像显示的尕海断裂中段处的断层陡坎、 鞍状地貌及水系左旋错动现象; d 断裂切过山坡形成的线性断层陡坎地貌; e 活动断裂于山麓地带形成的线性断层沟槽与挤压鼓包
Fig. 14 Tectono-geomorphic characteristics along the Gahai Fault.
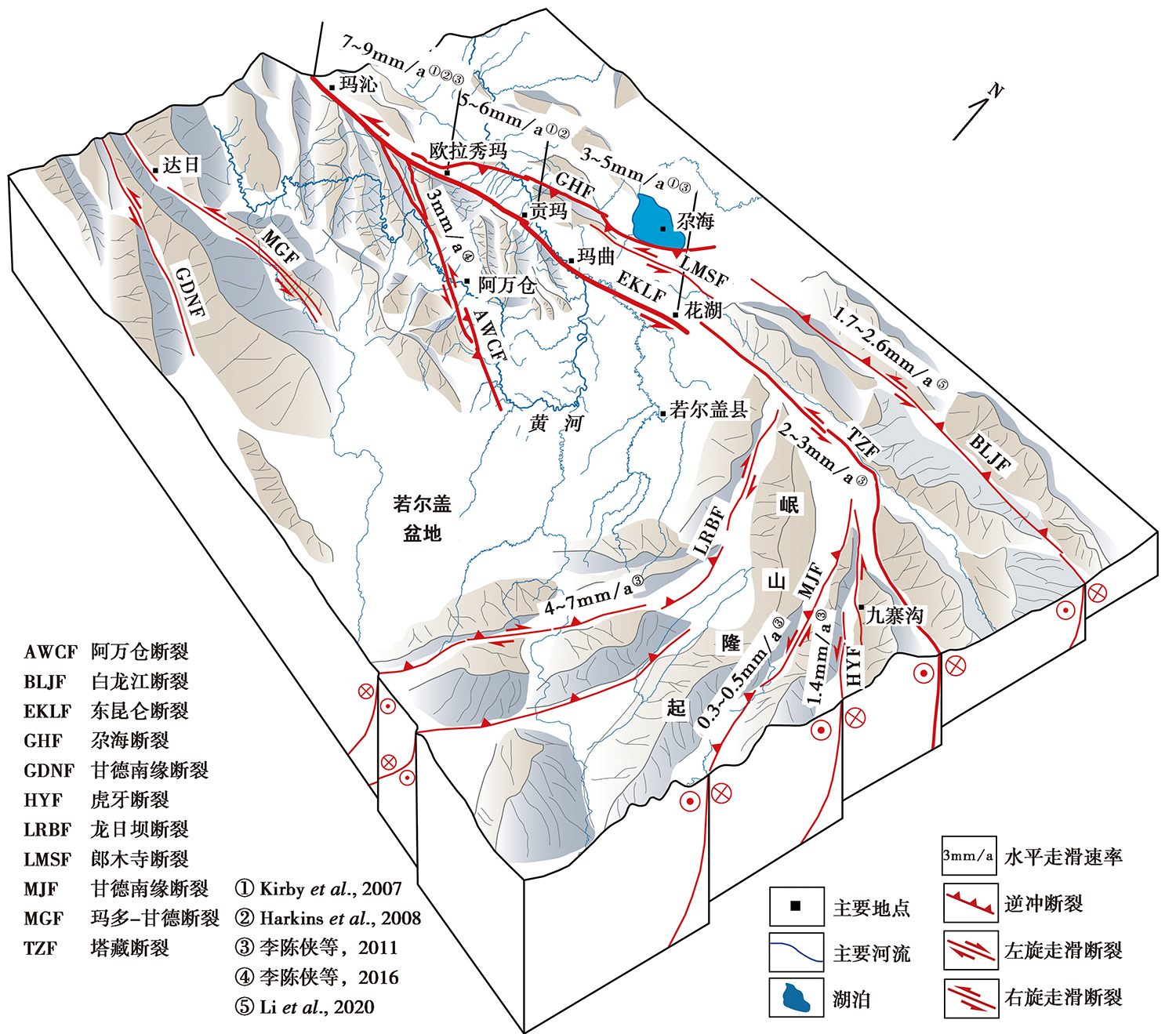
图 15 东昆仑断裂带东段沿走向滑动速率向E递减的构造变形模型示意图 断裂数据来自邓起东(2002)、 Fu等(2011)及野外调查结果
Fig. 15 Three-dimensional tectonic deformation model showing the eastward slip rate gradients along the East Kunlun fault zone.
| [1] | 常直杨. 2014. 青藏高原东缘白龙江流域地貌定量化参数体系研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学. |
| CHANG Zhi-yang. 2014. Research on quantitative geomorphologic indices of Bailongjiang drainage basin in the eastern Tibet Plateau based on digital elevation models[D]. Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 邓起东. 2002. 中国活动构造研究的进展与展望[J]. 地质论评, 48(2): 169-177. |
| DENG Qi-dong. 2002. Advances and overview on researches of active tectonics in China[J]. Geological Review, 48(2): 169-177. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 付碧宏, 时丕龙, 贾营营. 2009. 青藏高原大型走滑断裂带晚新生代构造地貌生长及水系响应[J]. 地质科学, 44(4): 1343-1363. |
| FU Bi-hong, SHI Pi-long, JIA Ying-ying. 2009. Late Cenozoic tectono-geomorphic growth and drainage response along the large-scale strike-slip fault system, Tibetan plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 44(4): 1343-1363. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] |
高明星, 陈桂华, 徐锡伟. 2015. 地貌参数指示的临潭-宕昌断裂带最新构造隆升差异与地震活动[J]. 地震地质, 37(3): 709-718. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.03.004.
DOI |
| GAO Ming-xing, CHEN Gui-hua, XU Xi-wei. 2015. Geomorphic indices indicated recent differential tectonic uplift of the Lintan-Dangchang Fault and the Minxian-Zhangxian earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 37(3): 709-718. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 高锐, 王海燕, 王成善, 等. 2011. 青藏高原东北缘岩石圈缩短变形: 深地震反射剖面再处理提供的证据[J]. 地球学报, 32(5): 513-520. |
| GAO Rui, WANG Hai-yan, WANG Cheng-shan, et al. 2011. Lithospheric deformation shortening of the northeastern Tibetan plateau: Evidence from reprocessing of deep seismic reflection data[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 32(5): 513-520. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] |
韩海辉, 高婷, 易欢, 等. 2012. 基于变点分析法提取地势起伏度: 以青藏高原为例[J]. 地理科学, 32(1): 101-104.
DOI |
|
HAN Hai-hui, GAO Ting, YI Huan, et al. 2012. Extraction of relief amplitude based on change point method: A case study on the Tibetan plateau[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 32(1): 101-104. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
| [7] | 侯冰飞. 2020. 黄河源区气候变化与径流补给的关联性分析[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学. |
| HOU Bing-fei. 2020. Analysis of inter-relationships between climate change and runoff discharge in the headwater region of Yellow River[D]. Beijing Forestry University, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 李陈侠, 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 等. 2011. 东昆仑断裂带中东部地震破裂分段性与走滑运动分解作用[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 41(9): 1295-1310. |
| LI Chen-xia, XU Xi-wei, WEN Xue-ze, et al. 2011. Rupture segmentation and slip partitioning of the mid-eastern part of the Kunlun Fault, north Tibetan plateau[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 41(9): 1295-1310. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] |
李陈侠, 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 等. 2009. 东昆仑断裂东段玛沁-玛曲段几何结构特征[J]. 地震地质, 31(3): 441-458. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2009.03.007.
DOI |
| LI Chen-xia, XU Xi-wei, WEN Xue-ze, et al. 2009. The segmental characteristics of geometrical structure of the East Kunlun active fault(Maqin-Maqu segment)[J]. Seismology and Geology, 31(3): 441-458. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] |
李陈侠, 袁道阳, 杨虎, 等. 2016. 东昆仑断裂带东段分支断裂--阿万仓断裂晚第四纪构造活动特征[J]. 地震地质, 38(1): 44-64. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.01.004.
DOI |
| LI Chen-xia, YUAN Dao-yang, YANG Hu, et al. 2016. The tectonic activity characteristics of Awancang Fault in the late Quaternary, the sub-strand of the Eastern Kunlun Fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(1): 44-64. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 李春峰, 贺群禄, 赵国光. 2005. 东昆仑活动断裂带东段古地震活动特征[J]. 地震学报, 25(1): 60-67. |
| LI Chun-feng, HE Qun-lu, ZHAO Guo-guang. 2005. Paleo-earthquake studies on the eastern section of the Kunlun Fault[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 25(1): 60-67. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 刘根友. 2004. 高精度GPS定位及地壳形变分析若干问题的研究[D]. 武汉: 中国科学院测量与地球物理研究所. |
| LIU Gen-you. 2004. Some key issues relating to high precision GPS positioning and crustal deformation analysis[D]. Institute of Geodesy and Geophysics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Wuhan. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 刘战庆. 2011. 东昆仑南缘布青山构造混杂岩带地质特征及区域构造研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学. |
| LIU Zhan-qing. 2011. Study on the geological characteristics and tectonic of Buqingshan melanges belt, the south margin of East Kunlun Mountains[D]. Chang'an University, Xi'an. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 潘家伟, 白明坤, 李超, 等. 2021. 2021年青海玛多 MS7.4 地震地表破裂带及发震构造[J]. 地质学报, 95(6): 1655-1670. |
| PAN Jia-wei, BAI Ming-kun, LI Chao, et al. 2021. Coseismic surface rupture and seismogenic structure of the 2021-05-22 Maduo(Qinghai) MS7.4 earthquake[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(6): 1655-1670. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 庞亚瑾, 程惠红, 张怀, 等. 2017. 巴颜喀拉块体东缘形变及九寨沟地震孕震环境数值分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(10): 4046-4055. |
| PANG Ya-jin, CHENG Hui-hong, ZHANG Huai, et al. 2017. Numerical modeling of crustal deformation in the eastern margin of the Bayan Har block and analysis of seismogenic environment of the 2017 Jiuzhaigou earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(10): 4046-4055. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] |
宋向辉, 王帅军, 潘素珍, 等. 2021. 2021年玛多 MS7.4 地震的深部构造背景[J]. 地震地质, 43(4): 757-770. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.04.002.
DOI |
| SONG Xiang-hui, WANG Shuai-jun, PAN Su-zhen, et al. 2021. Deep seismotectonic environment of the 2021 Madoi MS7.4 earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(4): 757-770. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] |
苏琦, 袁道阳, 谢虹. 2016a. 祁连山-河西走廊黑河流域地貌特征及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 38(3): 560-581. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.03.005.
DOI |
| SU Qi, YUAN Dao-yang, XIE Hong. 2016a. Geomorphic features of the Heihe River drainage basin in western Qilianshan-Hexi Corridor and its tectonic implications[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(3): 560-581. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
苏琦, 袁道阳, 谢虹, 等. 2016b. 祁连山西段疏勒河流域地貌特征及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 38(2): 240-258. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.02.002.
DOI |
| SU Qi, YUAN Dao-yang, XIE Hong, et al. 2016b. Geomorphic features of the Shule River drainage basin in Qilianshan and its insight into tectonic implications[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(2): 240-258. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 闻学泽. 2018. 巴颜喀拉块体东边界千年破裂历史与2008年汶川、 2013 年芦山和2017年九寨沟地震[J]. 地震学报, 40(3): 255-267. |
| WEN Xue-ze. 2018. The 2008 Wenchuan, 2013 Lushan and 2017 Jiuzhaigou earthquakes, Sichuan, in the last more than one thousand years of rupture history of the eastern margin of the Bayan Har block[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 40(3): 255-267. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 武文娇. 2018. 山西省典型全球开放DEM数据的对比分析[D]. 太原: 太原理工大学. |
| WU Wen-jiao. 2018. Analysis and comparison of typical open global digital elevation models in Shanxi Province[D]. Taiyuan University of Technology, Taiyuan. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 徐晶, 邵志刚, 刘静, 等. 2017. 基于库仑应力变化分析巴颜喀拉地块东端的强震相互关系[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(10): 4056-4068. |
| XU Jing, SHAO Zhi-gang, LIU Jing, et al. 2017. Analysis of interaction between great earthquakes in the eastern Bayan Har block based on changes of Coulomb stress[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(10): 4056-4068. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] |
徐伟, 刘志成, 袁兆德, 等. 2017. 华山山前河流地貌参数及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 39(6): 1316-1335. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.06.015.
DOI |
| XU Wei, LIU Zhi-cheng, YUAN Zhao-de, et al. 2017. River geomorphic parameters of the Huashan piedmont and their tectonic implications[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(6): 1316-1335. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 詹艳, 梁明剑, 孙翔宇, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震深部环境及发震构造模式[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(7): 2231-2251. |
| ZHAN Yan, LIANG Ming-jian, SUN Xiang-yu, et al. 2021. Deep structure and seismogenic pattern of the 2021.5.22 Madoi(Qinghai) MS7.4 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(7): 2231-2251. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 张国民, 田勤俭, 王辉. 2003. 可可西里-东昆仑活动构造带强震活动研究[J]. 地学前缘, 10(1): 39-46. |
| ZHANG Guo-min, TIAN Qin-jian, WANG Hui. 2003. Strong earthquake activities in Kekexili-East Kunlun Mountains active fault zone, Northwest China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(1): 39-46. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 张会平, 刘少峰, 孙亚平, 等. 2006. 基于SRTM-DEM区域地形起伏的获取及应用[J]. 国土资源遥感, (1): 31-35. |
| ZHANG Hui-ping, LIU Shao-feng, SUN Ya-ping, et al. 2006. The acquisition of local topographic relief and its application: An SRTM-DEM analysis[J]. Remote Sensing for Land & Resources, (1): 31-35. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 张岳桥, 马寅生, 杨农, 等. 2005. 西秦岭地区东昆仑-秦岭断裂系晚新生代左旋走滑历史及其向东扩展[J]. 地球学报, 25(1): 1-8. |
| ZHANG Yue-qiao, MA Yin-sheng, YANG Nong, et al. 2005. Late Cenozoic left-slip faulting process of the East Kunlun-Qinling fault system in West Qinling region and its eastward propagation[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 25(1): 1-8. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 赵国华, 李勇, 颜照坤, 等. 2014. 龙门山中段山前河流Hack剖面和面积-高程积分的构造地貌研究[J]. 第四纪研究, 34(2): 302-310. |
| ZHAO Guo-hua, LI Yong, YAN Zhao-kun, et al. 2014. Tectonic geomorphology analysis of piedmont rivers of the middle Longmenshan Basin on Hack profile and hypsometric integral[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 34(2): 302-310. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 赵洪壮, 李有利, 杨景春, 等. 2010. 面积高度积分的面积依赖与空间分布特征[J]. 地理研究, 29(2): 271-282. |
|
ZHAO Hong-zhuang, LI You-li, YANG Jing-chun, et al. 2010. Influence of area and space dependence for hypsometric integral and its geological implications[J]. Geographical Research, 29(2): 271-282. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
| [29] |
周朝, 何宏林, 魏占玉, 等. 2020. 地貌参数方法在小尺度地貌研究中的应用: 以北天山独山子背斜为例[J]. 地震地质, 42(6): 1492-1508. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.06.014.
DOI |
| ZHOU Chao, HE Hong-lin, WEI Zhan-yu, et al. 2020. The application of geomorphic indexes in small-scale geomorphology: A case study in Dushanzi anticline in the northern Chinese Tian Shan Foreland[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(6): 1492-1508. (in Chinese) | |
| [30] |
Alipoor R, Poorkermani M, Zare M, et al. 2011. Active tectonic assessment around Rudbar Lorestan dam site, High Zagros Belt(SW of Iran)[J]. Geomorphology, 128(1-2): 1-14.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Brookfield M E. 1998. The evolution of the great river systems of southern Asia during the Cenozoic India-Asia collision: Rivers draining southwards[J]. Geomorphology, 22(3): 285-312.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Chen Y C, Sung Q, Cheng K Y. 2003. Along-strike variations of morphotectonic features in the western foothills of Taiwan: Tectonic implications based on stream-gradient and hypsometric analysis[J]. Geomorphology, 56(1-2): 109-137.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Du J X, Fu B H, Guo Q, et al. 2019. Segmentation and termination of the surface rupture zone produced by the 1932 MS7.6 Changma earthquake: New insights into the slip partitioning of the eastern Altyn Tagh fault system[J]. The Geological Society of America, 12(1): 19-39. |
| [34] |
Font M, Amorese D, Lagarde J L. 2010. DEM and GIS analysis of the stream gradient index to evaluate effects of tectonics: The Normandy intraplate area(NW France)[J]. Geomorphology, 119(3): 172-180.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Fu B H, Awata Y. 2007. Displacement and timing of left-lateral faulting in the Kunlun fault zone, northern Tibet, inferred from geologic and geomorphic features[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 29(2-3): 253-265.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Fu B H, Walker R, Sandiford M. 2011. The 2008 Wenchuan earthquake and active tectonics of Asia[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(4): 797-804.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Gao M X, Zeilinger G, Xu X W, et al. 2013. DEM and GIS analysis of geomorphic indices for evaluating recent uplift of the northeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau, China[J]. Geomorphology, 190: 61-72.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Hack J T. 1973. Stream-profile analysis and stream-gradient index[J]. Journal of Research of the US Geological Survey, 1(4): 421-429. |
| [39] |
Hamdouni R E, Irigaray C, Fernández T, et al. 2008. Assessment of relative active tectonics, southwest border of the Sierra Nevada(southern Spain)[J]. Geomorphology, 96(1-2): 150-173.
DOI URL |
| [40] | Harkins N, Kirby N. 2008. Fluvial terrace riser degradation and determination of slip rates on strike-slip faults: An example from the Kunlun Fault, China[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 35(5): 1-6. |
| [41] |
Hurtrez J E, Sol C, Lucazeau F. 1999. Effect of drainage area on hypsometry from an analysis of small-scale drainage basins in the Siwalik Hills(Central Nepal)[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 24(9): 799-808.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Kirby E, Harkins N. 2013. Distributed deformation around the eastern tip of the Kunlun Fault[J]. International Journal of Earth Sciences(Geologische Rundschau), 102(7): 1759-1772. |
| [43] | Kirby E, Harkins N, Wang E, et al. 2007. Slip rate gradients along the eastern Kunlun Fault[J]. Tectonics, 26(2): 1-16. |
| [44] | Li H L, Zhang Y, Dong S, et al. 2020. Neotectonics of the Bailongjiang and Hanan faults: New insights in the late Cenozic deformation along the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau[J]. CSA Bulletin, 132(9-10): 1845-1862. |
| [45] |
Obaid A K, Allen M B. 2019. Landscape expressions of tectonics in the Zagros fold-and-thrust belt[J]. Tectonophysics, 766(B2): 20-30.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Pérez-Peña J V, Azañón J M, Azor A. 2009a. CalHypso: An ArcGIS extension to calculate hypsometric curves and their statistical moments. Applications to drainage basin analysis in SE Spain[J]. Computers and Geosciences, 35(6): 1214-1223.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Pérez-Peña J V, Azañón J M, Azor A, et al. 2009b. Spatial analysis of stream power using GIS: SLK anomaly maps[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 34(1): 16-25.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Pike R J, Wilson S E. 1971. Elevation-relief ratio, hypsometric integral, and geomorphic area-altitude analysis[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 82(4): 1079-1084.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Resor P G, Cooke M L, Marshall S T, et al. 2018. Influence of fault geometry on the spatial distribution of long-term slip with implications for determining representative fault-slip rates[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 108(4): 1837-1852.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Sarp G, Toprak V, Duzgun S. 2012. Activity level of tectonic basins, western section of the North Anatolian fault zone, Turkey[J]. International Geology Review, 55(3): 350-366.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Seeber L, Gornitz V. 1983. River profiles along the Himalayan Arc as indicators of active tectonics[J]. Tectonophysics, 92(4): 335-367.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Strahler A N. 1952. Hypsometric(area-altitude)analysis of erosional topography[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 63(11): 1117-1142.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Sun X Y, Zhan Y, Zhao L Q, et al. 2019. Electrical structure of the Kunlun-Qinling fault system, northeastern Tibetan plateau, inferred from 3-D inversion of magnetotelluric data[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 181(3): 103910.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
van der Woerd J, Tapponnier P, Ryerson F J, et al. 2002. Uniform postglacial slip-rate along the central 600km of the Kunlun Fault(Tibet), from 26Al, 10Be, and 14C dating of riser offsets, and climatic origin of the regional morphology[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 148(3): 356-388.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Whipple K X, Meade B J. 2006. Orogen response to changes in climatic and tectonic forcing[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 243(1-2): 218-228.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Whipple K X, Tucker G E. 1999. Dynamics of the stream-power river incision model: Implications for height limits of mountain ranges, landscape response timescales, and research needs[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 104(B8): 17661-17674.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
Yin A, Rumelhart P E, Butler R, et al. 2002. Tectonic history of the Altyn Tagh fault system in northern Tibet inferred from Cenozoic sedimentation[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 114(10): 1257-1295.
DOI URL |
| [58] | Zechar J D, Frankel K L. 2009. Incorporating and reporting uncertainties in fault slip rates[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 114(B12): 1-9. |
| [59] |
Zhu L, Ji L, Jiang F Y. 2020. Variations in locking along the East Kunlun Fault, Tibetan plateau, China, using GPS and leveling data[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 177(10): 1-15.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
Zhu L, Ji L, Liu C. 2021. Interseismic slip rate and locking along the Maqin-Maqu segment of the East Kunlun Fault, northern Tibetan plateau, based on Sentinel-1 images[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 211(121): 104703.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 高泽民, 刘兴旺, 邵延秀, 谢虹. 河套盆地北缘大青山地区构造地貌特征[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(6): 1317-1332. |
| [2] | 王躲, 尹功明, 韩非, 刘春茹, 毛泽斌. 格仁错断裂带流域地貌特征及其构造指示意义[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(2): 304-322. |
| [3] | 苏琦, 袁道阳, 谢虹, 邵延秀, 梁明剑. 祁连山西段疏勒河流域地貌特征及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(2): 240-258. |
| [4] | 梁明剑, 周荣军, 闫亮, 赵国华, 郭红梅. 青海达日断裂中段构造活动与地貌发育的响应关系探讨[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(1): 28-38. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||