地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 1273-1289.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.05.012
收稿日期:2021-06-18
修回日期:2021-11-23
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-11-28
通讯作者:
杨晓松
作者简介:宋刚, 男, 1994年生, 2021年于中国地震局地质研究所获构造地质学专业硕士学位, 主要研究方向为岩石物理学, E-mail: 13051405099@163.com。
基金资助:Received:2021-06-18
Revised:2021-11-23
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-11-28
Contact:
YANG Xiao-song
摘要:
前人研究表明, 老虎山断裂带区域未来几十年内可能会密集发生微小地震。微小地震因震级低、 信号主频率高、 能量衰减快而具有明显的近场特点。近场地壳波速结构, 尤其是浅部速度结构对高频微小地震的精确定位有极大的影响。为此, 在室温和围压介于50~500MPa的条件下, 系统地测量了该地区代表性岩石的P波速度(VP)。实验表明, 在低压范围内, VP随着压力的增加呈对数增加; 在压力高于临界压力Pc时, VP随着压力的增加呈线性趋势增加。Pc介于200~450MPa, 平均值为262.5MPa。结晶岩的Pc平均值为250MPa, 砂岩的Pc平均值为271.4MPa; 经对比发现, 砂岩的Pc明显高于结晶岩。这可归因于在低压范围内裂纹孔隙随着压力的增加而闭合, 而在高压范围内裂纹孔隙基本完全闭合。因此, 提高近场微小地震的定位精度应考虑弹性波波速随压力的非线性增加。此外, 实验结果显示此区域岩石弹性波速度是深度的函数。
宋刚, 杨晓松. 甘肃省老虎山断裂带区域地壳纵波速度的实验[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(5): 1273-1289.
SONG Gang, YANG Xiao-song. EXPERIMENTAL STUDY ON THE P-WAVE VELOCITY OF THE CRUST IN THE LAOHUSHAN FAULT ZONE IN GANSU PROVINCE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(5): 1273-1289.
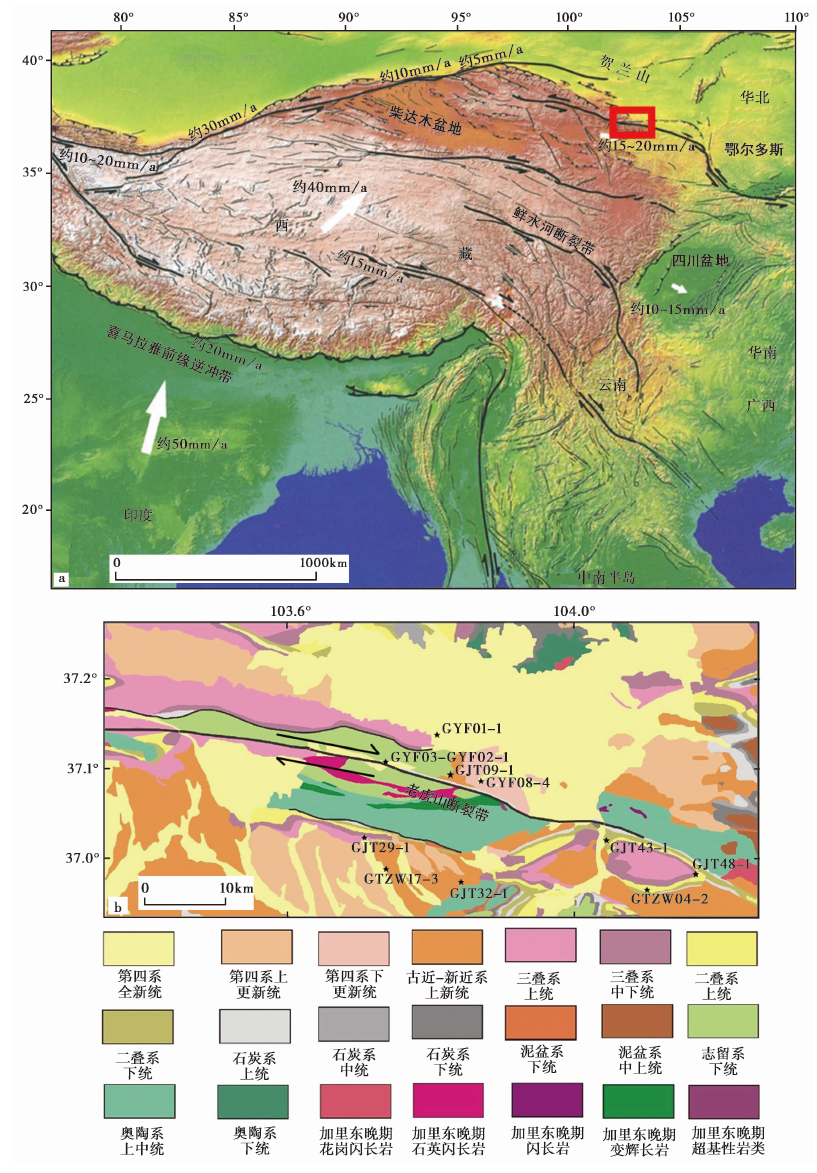
图1 a 老虎山断裂带的大地构造位置(据 Tapponnier et al., 2001); b 老虎山断裂带区域地质图和实验样品采集点位①(①甘肃省地质局第一区域地质测量队,1970,永登地质矿产图。)
Fig. 1 The geotectonic location of Laohushan fault zone(after Tapponnier et al., 2001)(a), and the regional geological map of Laohushan fault zone and sample collection points in the experiment(b).
| 界 | 系 | 统 | 厚度 | 岩性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新生界 | 第四系 | 全新统 | >5m | 疏松沙砾夹亚砂土。 |
| 上更新统 | >30m | 疏松黄土(新黄土)夹砂砾层。 | ||
| 下更新统 | >100m | 灰色块状砾岩夹透镜状砂岩。 | ||
| 古近-新近系 | 上新统 | >800m | 浅黄色及橘红色砂质泥岩、 中细粒砂岩夹含砾砂岩。 | |
| 中生界 | 三叠系 | 上统 | 595~3 914m | 灰绿色、 浅灰绿色细砂岩夹碳质页岩及页岩。有时含薄煤层。底部为含砾粗砂岩。 |
| 中下统 | 296~445m | 浅紫灰色厚层砂岩, 偶夹含砾砂岩、 泥质粉砂岩, 底部含砂质结核。 | ||
| 古生界 | 二叠系 | 上统 | 376m | 紫色中粗粒砂岩为主, 夹同色泥岩、 粉砂岩。 |
| 下统 | 327m | 灰绿、 黄灰及紫杂色砂岩、 泥质粉砂岩互层, 上部常夹不稳定砾岩。 | ||
石炭系 | 上统 | 222m | 深灰色砂岩、 页岩夹灰岩、 粉砂岩, 含薄煤层。 | |
| 中统 | 67m | 灰色及深灰色中细粒砂岩夹泥岩及页岩, 含煤层。 | ||
| 下统 | 39m | 深灰色厚层灰岩, 底部含透镜状石膏, 上部为砂页岩。 | ||
| 泥盆系 | 上统 | 44~104m | 紫色中粗粒砂岩及泥质粉砂岩、 粉砂岩互层, 底部为不稳定砾岩。 | |
| 志留系 | 下统 | >3 861m | 灰绿色、 黄灰色变质石英长石砂岩、 长石砂岩、 千枚岩, 其次为凝灰质砂岩, 千枚状粉砂岩及板岩。在北部(布台区域)夹少量变玄武岩、 变安山岩、 凝灰岩、 片岩及结晶灰岩。 | |
奥陶系 | 上中统 | 2 807m | 灰绿色为主的安山凝灰岩、 英安凝灰岩、 安山玢岩、 硅质岩、 板岩、 灰岩及细砂岩、 千枚岩。北部(布台区域)夹中酸性及中基性的火山岩。 | |
| 下统 | >2 000m | 灰色、 灰绿色变质长石石英砂岩、 千枚岩, 偶夹不稳定火山岩及硅质灰岩。 |
表1 研究区地层及相应岩性① (①甘肃省地质局第一区域地质测量队, 1970, 永登地质矿产图。)
Table1 Stratigraphy and corresponding lithology of the study area
| 界 | 系 | 统 | 厚度 | 岩性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 新生界 | 第四系 | 全新统 | >5m | 疏松沙砾夹亚砂土。 |
| 上更新统 | >30m | 疏松黄土(新黄土)夹砂砾层。 | ||
| 下更新统 | >100m | 灰色块状砾岩夹透镜状砂岩。 | ||
| 古近-新近系 | 上新统 | >800m | 浅黄色及橘红色砂质泥岩、 中细粒砂岩夹含砾砂岩。 | |
| 中生界 | 三叠系 | 上统 | 595~3 914m | 灰绿色、 浅灰绿色细砂岩夹碳质页岩及页岩。有时含薄煤层。底部为含砾粗砂岩。 |
| 中下统 | 296~445m | 浅紫灰色厚层砂岩, 偶夹含砾砂岩、 泥质粉砂岩, 底部含砂质结核。 | ||
| 古生界 | 二叠系 | 上统 | 376m | 紫色中粗粒砂岩为主, 夹同色泥岩、 粉砂岩。 |
| 下统 | 327m | 灰绿、 黄灰及紫杂色砂岩、 泥质粉砂岩互层, 上部常夹不稳定砾岩。 | ||
石炭系 | 上统 | 222m | 深灰色砂岩、 页岩夹灰岩、 粉砂岩, 含薄煤层。 | |
| 中统 | 67m | 灰色及深灰色中细粒砂岩夹泥岩及页岩, 含煤层。 | ||
| 下统 | 39m | 深灰色厚层灰岩, 底部含透镜状石膏, 上部为砂页岩。 | ||
| 泥盆系 | 上统 | 44~104m | 紫色中粗粒砂岩及泥质粉砂岩、 粉砂岩互层, 底部为不稳定砾岩。 | |
| 志留系 | 下统 | >3 861m | 灰绿色、 黄灰色变质石英长石砂岩、 长石砂岩、 千枚岩, 其次为凝灰质砂岩, 千枚状粉砂岩及板岩。在北部(布台区域)夹少量变玄武岩、 变安山岩、 凝灰岩、 片岩及结晶灰岩。 | |
奥陶系 | 上中统 | 2 807m | 灰绿色为主的安山凝灰岩、 英安凝灰岩、 安山玢岩、 硅质岩、 板岩、 灰岩及细砂岩、 千枚岩。北部(布台区域)夹中酸性及中基性的火山岩。 | |
| 下统 | >2 000m | 灰色、 灰绿色变质长石石英砂岩、 千枚岩, 偶夹不稳定火山岩及硅质灰岩。 |
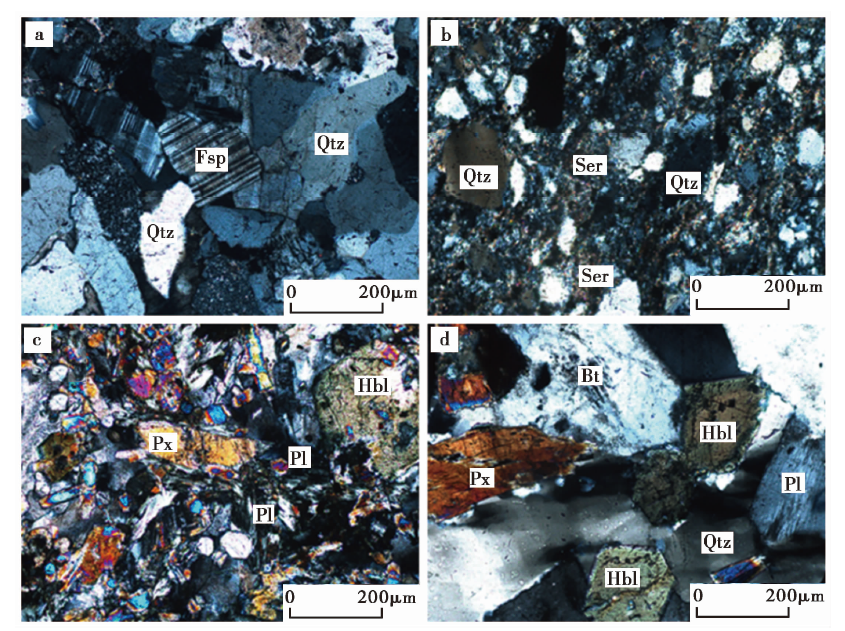
图3 老虎山断裂带区域代表性岩石的显微结构 a 砂岩GTZW04-2; b 变质砂岩GJT09-1; c 变辉长岩GYF08-2; d 闪长岩GYF08-4。显微镜放大倍数为5倍。Px 辉石; Hbl 角闪石; Pl 斜长石; Qtz 石英; Fsp 长石; Ser 绢云母; Bt 黑云母
Fig. 3 Microtextures of representative rocks in the Laohushan fault zone area.
| 样品编号 | 采样地点 | 坐标 | L0 /mm | R /mm | ρ /g·cm-3 | 岩性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GJT29-1-// | 正路乡红岘村 | 37.02°N, 103.70°E | 39.94 | 20.01 | 2.555 3 | 砂岩 |
| GJT29-1-⊥ | 正路乡红岘村 | 37.02°N, 103.70°E | 39.92 | 20.00 | 2.559 1 | 砂岩 |
| GJT43-1 | 喜泉乡沙塘子村 | 37.01°N, 103.81°E | 40.01 | 20.03 | 2.622 7 | 中粒砂岩 |
| GJT48-1 | 中泉乡金坪村 | 36.98°N, 104.16°E | 40.02 | 20.01 | 2.384 2 | 砂岩 |
| GTZW04-2 | 中泉乡白水村 | 36.96°N, 104.10°E | 40.00 | 20.03 | 2.544 4 | 砂岩 |
| GYF01-1 | 寺滩乡官草村 | 37.13°N, 103.80°E | 40.00 | 20.04 | 2.578 2 | 砂岩 |
| GYF03-GYF02-1 | 老虎沟 | 37.11°N, 103.74°E | 39.92 | 20.05 | 2.679 0 | 砂岩 |
| GJT32-1 | 正路乡黄羊淌村 | 36.97°N, 103.84°E | 40.04 | 20.05 | 2.835 9 | 变辉长岩 |
| GYF08-2 | 寺滩乡大庄村 | 37.81°N, 103.87°E | 39.95 | 20.04 | 2.950 4 | 变辉长岩 |
| GYF08-4 | 寺滩乡大庄村 | 37.81°N, 103.87°E | 39.98 | 20.04 | 2.952 1 | 闪长岩 |
| GTZW17-3 | 正路乡红岘村 | 36.99°N, 103.74°E | 40.00 | 20.01 | 2.787 9 | 英云闪长岩 |
| GJT09-1 | 寺滩乡大庄村 | 37.09°N, 103.82°E | 39.94 | 20.04 | 2.679 0 | 变质砂岩 |
表2 老虎山断裂带区域代表性岩石样品的名称、 采样地点、 经纬度、 初始长度、 初始直径、 初始密度及岩性
Table2 Name of sampling site, latitude and longitude, initial length, initial diameter, initial density and lithology of the representative rock samples in the Laohushan fault zone area
| 样品编号 | 采样地点 | 坐标 | L0 /mm | R /mm | ρ /g·cm-3 | 岩性 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GJT29-1-// | 正路乡红岘村 | 37.02°N, 103.70°E | 39.94 | 20.01 | 2.555 3 | 砂岩 |
| GJT29-1-⊥ | 正路乡红岘村 | 37.02°N, 103.70°E | 39.92 | 20.00 | 2.559 1 | 砂岩 |
| GJT43-1 | 喜泉乡沙塘子村 | 37.01°N, 103.81°E | 40.01 | 20.03 | 2.622 7 | 中粒砂岩 |
| GJT48-1 | 中泉乡金坪村 | 36.98°N, 104.16°E | 40.02 | 20.01 | 2.384 2 | 砂岩 |
| GTZW04-2 | 中泉乡白水村 | 36.96°N, 104.10°E | 40.00 | 20.03 | 2.544 4 | 砂岩 |
| GYF01-1 | 寺滩乡官草村 | 37.13°N, 103.80°E | 40.00 | 20.04 | 2.578 2 | 砂岩 |
| GYF03-GYF02-1 | 老虎沟 | 37.11°N, 103.74°E | 39.92 | 20.05 | 2.679 0 | 砂岩 |
| GJT32-1 | 正路乡黄羊淌村 | 36.97°N, 103.84°E | 40.04 | 20.05 | 2.835 9 | 变辉长岩 |
| GYF08-2 | 寺滩乡大庄村 | 37.81°N, 103.87°E | 39.95 | 20.04 | 2.950 4 | 变辉长岩 |
| GYF08-4 | 寺滩乡大庄村 | 37.81°N, 103.87°E | 39.98 | 20.04 | 2.952 1 | 闪长岩 |
| GTZW17-3 | 正路乡红岘村 | 36.99°N, 103.74°E | 40.00 | 20.01 | 2.787 9 | 英云闪长岩 |
| GJT09-1 | 寺滩乡大庄村 | 37.09°N, 103.82°E | 39.94 | 20.04 | 2.679 0 | 变质砂岩 |
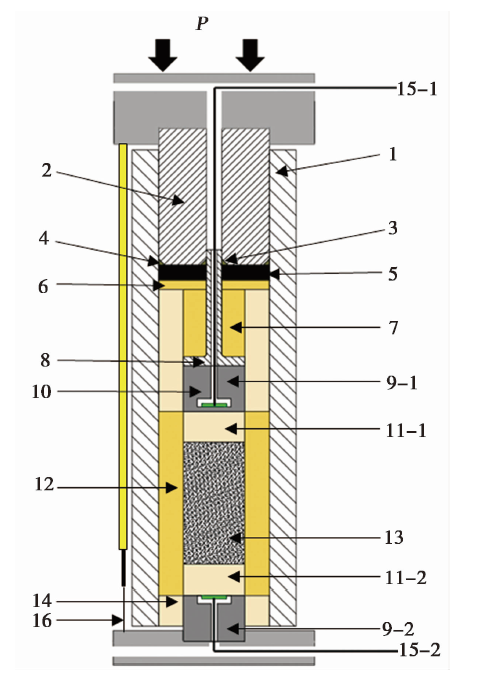
图4 样品装配图和超声波换能器的布置图 1 碳化钨样品腔; 2 具有45°倒角的碳化钨活塞压头; 3 内铜三角密封圈; 4 外铜三角密封圈; 5 铅垫; 6 叶蜡石垫; 7 叶蜡石柱; 8 T型钢管护套; 9-1、 9-2 上、 下超声波换能器; 10 氧化铝外套; 11-1、 11-2 上、 下刚玉柱; 12 叶蜡石外套; 13 样品; 14 氧化铝外套; 15-1、 15-2 超声波换能器引线; 16 位移传感器
Fig. 4 The sample assembly drawing and the layout drawing of the ultrasonic transducer.
| P/MPa | 0.1 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂岩 | 4.25 | 4.88 | 5.09 | 5.22 | 5.33 | 5.40 | 5.47 | 5.51 | 5.56 | 5.64 | 5.67 | 5.71 | 5.74 | 5.78 |
| 侵入岩 | 4.87 | 5.90 | 6.05 | 6.26 | 6.34 | 6.39 | 6.47 | 6.52 | 6.60 | 6.67 | 6.70 | 6.75 | 6.78 | 6.81 |
| 变质砂岩 | 4.83 | 5.62 | 5.71 | 5.77 | 5.83 | 5.85 | 5.87 | 5.91 | 5.95 | 5.96 | 5.98 | 6.01 | 6.02 |
表3 砂岩、 侵入岩和变质砂岩的平均P波速度
Table3 The average VP of sandstone, intrusive rock, metamorphic sandstone and all samples
| P/MPa | 0.1 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 砂岩 | 4.25 | 4.88 | 5.09 | 5.22 | 5.33 | 5.40 | 5.47 | 5.51 | 5.56 | 5.64 | 5.67 | 5.71 | 5.74 | 5.78 |
| 侵入岩 | 4.87 | 5.90 | 6.05 | 6.26 | 6.34 | 6.39 | 6.47 | 6.52 | 6.60 | 6.67 | 6.70 | 6.75 | 6.78 | 6.81 |
| 变质砂岩 | 4.83 | 5.62 | 5.71 | 5.77 | 5.83 | 5.85 | 5.87 | 5.91 | 5.95 | 5.96 | 5.98 | 6.01 | 6.02 |
| P/MPa | 0.1 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vm | 3.80 | 4.72 | 5.02 | 5.17 | 5.30 | 5.35 | 5.43 | 5.47 | 5.53 | 5.60 | 5.63 | 5.69 | 5.71 | 5.75 |
| Vmax-Vmin | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.04 |
| A | 15.12 | 8.76 | 1.80 | 1.01 | 0.83 | 0.88 | 1.08 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 1.19 | 0.89 | 1.25 | 0.64 |
表4 三叠系上统砂岩GJT29-1的各向异性
Table4 Anisotropy of Upper Triassic sandstone GJT29-1
| P/MPa | 0.1 | 50 | 75 | 100 | 125 | 150 | 175 | 200 | 250 | 300 | 350 | 400 | 450 | 500 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vm | 3.80 | 4.72 | 5.02 | 5.17 | 5.30 | 5.35 | 5.43 | 5.47 | 5.53 | 5.60 | 5.63 | 5.69 | 5.71 | 5.75 |
| Vmax-Vmin | 0.58 | 0.41 | 0.09 | 0.05 | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.06 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.04 |
| A | 15.12 | 8.76 | 1.80 | 1.01 | 0.83 | 0.88 | 1.08 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 0.91 | 1.19 | 0.89 | 1.25 | 0.64 |
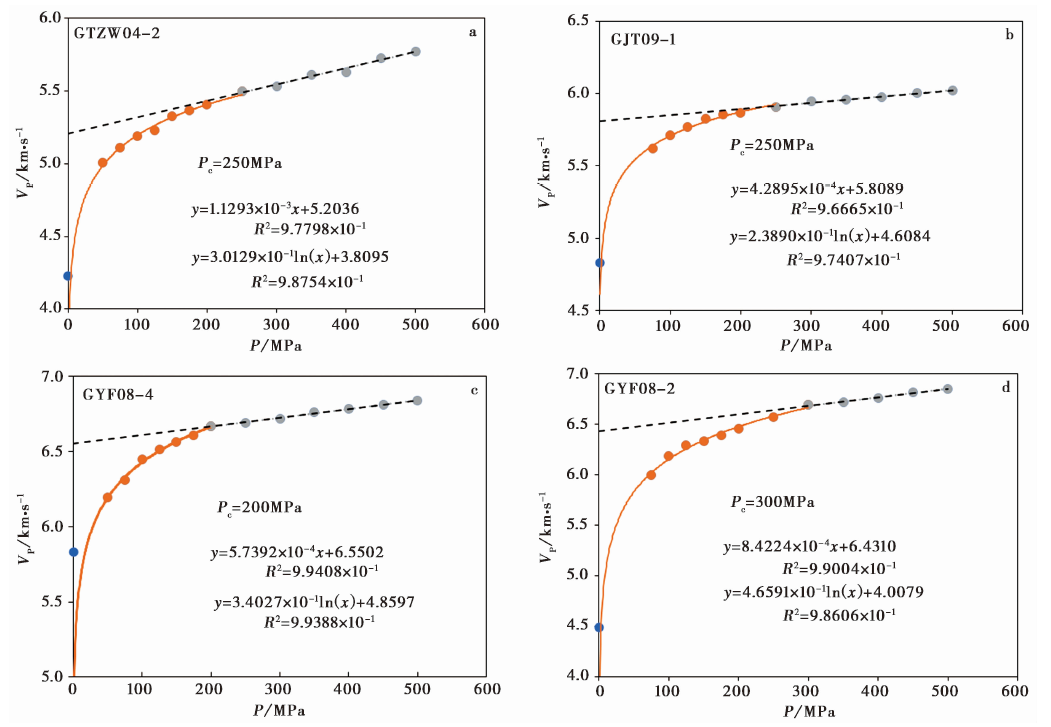
图7 岩石实验样品的P波速度和相关拟合曲线 4块岩石样品的速度-压力数据和拟合曲线, 依次为: a 砂岩样品GTZW04-2; b 变质砂岩样品GJT09-1;c 闪长岩样品GYF08-4; d 变辉长岩样品GYF08-2。黄色实线表示对数变化, 黑色虚线表示线性变化
Fig. 7 The P-wave velocity and the associated fitting curve of the test rock samples.
| 样品 | Pc/MPa | /km·s-1 | Dv/km·s-1·MPa-1 | R2 | av/km·s-1·MPa-1 | cv/km·s-1 | R2(非线性) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GJT29-1-// | 200 | 5.332 | 9.156×10-4 | 0.97 | 0.431 2 | 3.213 | 0.98 |
| GJT29-1-⊥ | 200 | 5.278 | 9.162×10-4 | 0.98 | 0.636 9 | 2.146 | 0.93 |
| GJT43-1 | 450 | 5.805 | 2.821×10-4 | 1.00 | 0.124 6 | 5.153 | 0.97 |
| GJT48-1 | 300 | 4.935 | 7.894×10-4 | 1.00 | 0.557 9 | 2.035 | 1.00 |
| GTZW04-2 | 250 | 5.204 | 11.293×10-4 | 0.98 | 0.301 3 | 3.810 | 0.99 |
| GYF01-1 | 200 | 5.610 | 6.746×10-4 | 0.82 | 0.603 1 | 2.633 | 0.94 |
| GYF03-GYF02-1 | 300 | 5.609 | 7.391×10-4 | 0.97 | 0.520 0 | 2.870 | 0.99 |
| GJT32-1 | 250 | 6.375 | 6.771×10-4 | 0.97 | 0.285 1 | 4.964 | 1.00 |
| GYF08-2 | 300 | 6.431 | 8.422×10-4 | 0.99 | 0.465 9 | 4.008 | 0.99 |
| GYF08-4 | 200 | 6.550 | 5.739×10-4 | 0.99 | 0.340 3 | 4.860 | 0.99 |
| GTZW17-3 | 250 | 6.389 | 9.390×10-4 | 0.94 | 0.621 3 | 3.159 | 0.98 |
| GJT09-1 | 250 | 5.809 | 4.290×10-4 | 0.97 | 0.238 9 | 4.608 | 0.97 |
表5 老虎山断裂带区域岩石P波速度的拟合参数
Table5 Fitting parameters of rock P-wave velocity in Laohushan fault zone area
| 样品 | Pc/MPa | /km·s-1 | Dv/km·s-1·MPa-1 | R2 | av/km·s-1·MPa-1 | cv/km·s-1 | R2(非线性) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GJT29-1-// | 200 | 5.332 | 9.156×10-4 | 0.97 | 0.431 2 | 3.213 | 0.98 |
| GJT29-1-⊥ | 200 | 5.278 | 9.162×10-4 | 0.98 | 0.636 9 | 2.146 | 0.93 |
| GJT43-1 | 450 | 5.805 | 2.821×10-4 | 1.00 | 0.124 6 | 5.153 | 0.97 |
| GJT48-1 | 300 | 4.935 | 7.894×10-4 | 1.00 | 0.557 9 | 2.035 | 1.00 |
| GTZW04-2 | 250 | 5.204 | 11.293×10-4 | 0.98 | 0.301 3 | 3.810 | 0.99 |
| GYF01-1 | 200 | 5.610 | 6.746×10-4 | 0.82 | 0.603 1 | 2.633 | 0.94 |
| GYF03-GYF02-1 | 300 | 5.609 | 7.391×10-4 | 0.97 | 0.520 0 | 2.870 | 0.99 |
| GJT32-1 | 250 | 6.375 | 6.771×10-4 | 0.97 | 0.285 1 | 4.964 | 1.00 |
| GYF08-2 | 300 | 6.431 | 8.422×10-4 | 0.99 | 0.465 9 | 4.008 | 0.99 |
| GYF08-4 | 200 | 6.550 | 5.739×10-4 | 0.99 | 0.340 3 | 4.860 | 0.99 |
| GTZW17-3 | 250 | 6.389 | 9.390×10-4 | 0.94 | 0.621 3 | 3.159 | 0.98 |
| GJT09-1 | 250 | 5.809 | 4.290×10-4 | 0.97 | 0.238 9 | 4.608 | 0.97 |
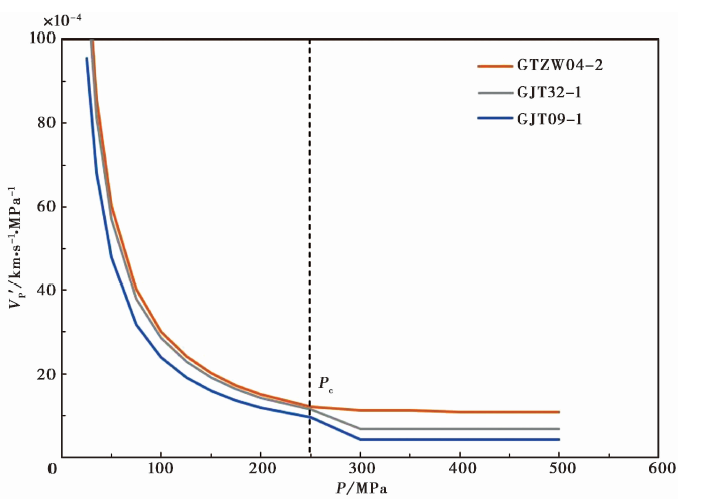
图8 老虎山断裂带区域的岩石P波速度的压力导数(V'P) GTZW04-2为砂岩样品; GJT32-1为侵入岩样品; GJT09-1为变质砂岩样品。三者的临界压力Pc均为250MPa
Fig. 8 The pressure derivative(V'P) of the rock P-wave velocity in the Laohushan fault zone area.
| [1] |
陈红汉, 吴悠, 肖秋苟. 2013. 青藏高原中-新生代沉积盆地热体制与古地温梯度演化[J]. 地球科学(中国地质大学学报), 38(3): 541-552.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
崔笃信, 王庆良, 胡亚轩, 等. 2009. 用GPS数据反演海原断裂带断层滑动速率和闭锁深度[J]. 地震学报, 31(5): 516-525.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
何文贵, 刘百篪, 吕太乙, 等. 1994. 老虎山断裂带的分段性研究[J]. 西北地震学报, 16(3): 66-72.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
胡圣标, 何丽娟, 汪集旸. 2001. 中国大陆地区大地热流数据汇编(第三版)[J]. 地球物理学报, 44(5): 611-626.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
李彦川. 2016. 基于GPS的海原断裂变形特征及强震危险性分析[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东).
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
刘百篪, 袁道阳, 何文贵, 等. 1993. 海原断裂带西端强震危险性分析[J]. 西北地震学报, 14(S1): 49-56.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
田玥, 陈晓非. 2002. 地震定位研究综述[J]. 地球物理学进展, 17(1): 147-155.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
张明洋. 2019. 蒙脱石弹性性质的实验研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等. 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12-20.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
张诗笛, 刘力强, 刘培洵, 等. 2014. 超高频地震信号观测[J]. 地震地质, 36(1): 230-242.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
张元生, 周民都, 荣代潞, 等. 2004. 祁连山中东段地区三维速度结构研究[J]. 地震学报, 26(3): 247-255.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
DOI URL |
| [13] |
|
| [14] |
DOI URL |
| [15] |
DOI URL |
| [16] |
DOI URL |
| [17] |
DOI URL |
| [18] |
DOI URL |
| [19] |
|
| [20] |
DOI URL |
| [21] |
DOI URL |
| [22] |
DOI URL |
| [23] |
DOI URL |
| [24] |
|
| [1] | 李翠平, 唐茂云, 郭卫英, 王小龙, 董蕾. 荣昌及周边三维速度结构初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 205-219. |
| [2] | 曹颖, 钱佳威, 黄江培, 张国权, 付虹. 利用时移层析成像方法分析2014年云南景谷MS6.6地震震源区的P波速度变化[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1563-1585. |
| [3] | 韩晓明, 刘芳, 张帆, 陈立峰, 李娟, 李拴虎, 杨红樱. 鄂尔多斯块体东北缘的P波速度精细结构[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(1): 215-231. |
| [4] | 罗佳宏, 马文涛. 三峡库区上地壳速度结构初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(2): 329-341. |
| [5] | 何昌荣, 张流. 用负刚度及变刚度方法研究粘滑[J]. 地震地质, 1996, 18(3): 199-211. |
| [6] | 高平, 刘若新, 马宝林, 李彪, 母润昌. 绿泥石片岩和斜长角闪岩在高温高压下的物理力学性质及其应用[J]. 地震地质, 1994, 16(1): 83-88. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||
