地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 1240-1256.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.05.010
崔建勇1)( ), 张曼玉1,2), 宋冬梅1,3),*(
), 张曼玉1,2), 宋冬梅1,3),*( ), 罗升4), 单新建5), 王斌1)
), 罗升4), 单新建5), 王斌1)
收稿日期:2021-09-22
修回日期:2021-12-30
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-11-28
通讯作者:
宋冬梅
作者简介:崔建勇, 男, 1976年生, 2006年于北京师范大学获地图学与地理信息系统专业博士学位, 讲师, 现主要研究方向为地震热红外异常信息提取, E-mail: cui_jianyong@upc.edu.cn。
基金资助:
CUI Jian-yong1)( ), ZHANG Man-yu1,2), SONG Dong-mei1,3)(
), ZHANG Man-yu1,2), SONG Dong-mei1,3)( ), LUO Sheng4), SHAN Xin-jian5), WANG Bin1)
), LUO Sheng4), SHAN Xin-jian5), WANG Bin1)
Received:2021-09-22
Revised:2021-12-30
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-11-28
Contact:
SONG Dong-mei
摘要:
地表温度(LST)是研究地表与大气之间物质和能量交换、 地表过程变化以及地热探测与地震热异常前兆等方面不可或缺的重要参数, 然而云覆盖现象导致MODIS LST产品存在大量空值, 限制了LST的广泛应用。文中提出了一种基于同类地物不同时刻LST日变化相关性的MODIS LST重建算法。以新疆和田为研究区, 使用2003-2015年MODIS 8d合成地表温度产品为实验数据, 根据一天中同类地物不同时刻LST之间的相关性, 以地表覆盖类型产品为依据, 分别创建各类地物上午、 下午和晚上与凌晨的LST回归模型, 将三者的LST拟合回归至凌晨时刻的LST, 然后取上午、 下午和晚上拟合结果的最优组合以实现对凌晨LST的两步重建。实验结果表明, 该方法的最小误差为0.57K, 误差均在1.2K以下, 平均误差为0.92K。经验证, 将该方法应用于其余3个时刻的地表温度重建工作中仍可得到较好的补值效果。与现有的LST补值方法进行对比可知, 本方法以少量辅助数据实现了较高的补值精度和补值率, 可为基于温度的地表过程研究和地震热异常检测等研究提供坚实的数据基础。
崔建勇, 张曼玉, 宋冬梅, 罗升, 单新建, 王斌. 基于同类地物地表温度日变化相关性的MODIS LST重建算法[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(5): 1240-1256.
CUI Jian-yong, ZHANG Man-yu, SONG Dong-mei, LUO Sheng, SHAN Xin-jian, WANG Bin. MODIS LST RECONSTRUCTION ALGORITHM BASED ON DIURNAL CORRELATION OF SURFACE TEMPERATURE OF SIMILAR LAND FEATURES[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(5): 1240-1256.
| 产品数据名称 | MOD11A2 | MYD11A2 |
|---|---|---|
| 空间分辨率 | 1km | 1km |
| 时间分辨率 | 8d | 8d |
| 温度单位 | K | K |
| 所属卫星 | Terra | Aqua |
| 传感器过境时间 | 上午10:30、 晚上10:30 | 下午1:30、 凌晨1:30 |
表1 MODIS地表温度数据的相关参数
Table1 Related parameters of MODIS land surface temperature data
| 产品数据名称 | MOD11A2 | MYD11A2 |
|---|---|---|
| 空间分辨率 | 1km | 1km |
| 时间分辨率 | 8d | 8d |
| 温度单位 | K | K |
| 所属卫星 | Terra | Aqua |
| 传感器过境时间 | 上午10:30、 晚上10:30 | 下午1:30、 凌晨1:30 |
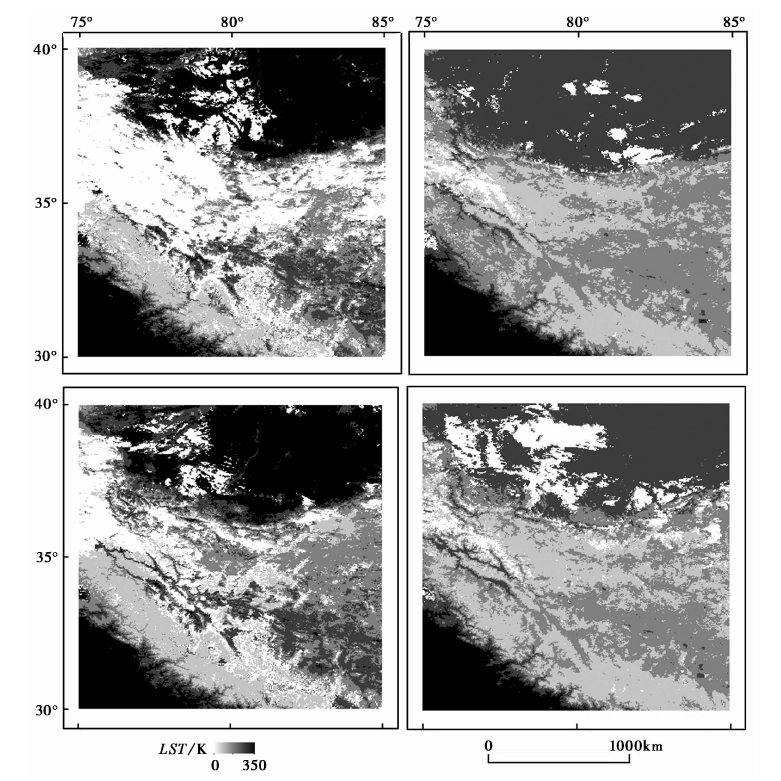
图2 新疆和田地区MODIS地表温度不同时段的缺值情况 白色区域表示缺值; 左上角、 右上角、 左下角和右下角分别为MYD11A2下午1:30和凌晨1:30、 MOD11A2上午10:30和晚上10:30的缺值情况
Fig. 2 Absence of MODIS surface temperature in different periods in Hotan, Xinjiang.
| 地物类型 | 数据类型 | R2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1阶 | 2阶 | 3阶 | 4阶 | 5阶 | ||
| 水体 | MOD_DAY | 0.423 | 0.423 | 0.436 | 0.445 | 0.453 |
| MOD_NIGHT | 0.39 | 0.940 | 0.940 | 0.940 | 0.940 | |
| 稀树草原 | MOD_DAY | 0.880 | 0.890 | 0.891 | 0.894 | 0.903 |
| MOD_NIGHT | 0.981 | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.982 | |
| 裸地 | MOD_DAY | 0.573 | 0.590 | 0.590 | 0.614 | 0.628 |
| MOD_NIGHT | 0.964 | 0.965 | 0.965 | 0.965 | 0.965 |
表2 温度拟合的效果评估
Table2 Evaluation of fitting effect of night temperature
| 地物类型 | 数据类型 | R2 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1阶 | 2阶 | 3阶 | 4阶 | 5阶 | ||
| 水体 | MOD_DAY | 0.423 | 0.423 | 0.436 | 0.445 | 0.453 |
| MOD_NIGHT | 0.39 | 0.940 | 0.940 | 0.940 | 0.940 | |
| 稀树草原 | MOD_DAY | 0.880 | 0.890 | 0.891 | 0.894 | 0.903 |
| MOD_NIGHT | 0.981 | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.982 | 0.982 | |
| 裸地 | MOD_DAY | 0.573 | 0.590 | 0.590 | 0.614 | 0.628 |
| MOD_NIGHT | 0.964 | 0.965 | 0.965 | 0.965 | 0.965 |
| 期数 | 补值误差/K | 补值率/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方案1 | 方案2 | 方案3 | 方案4 | 方案5 | 方案1 | 方案2 | 方案3 | 方案4 | 方案5 | |
| 2004-43 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 3.00 | 3.06 | 2.85 | 99 | 100 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| 2007-41 | 1.03 | 1.15 | 2.65 | 2.74 | 2.52 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| 2007-43 | 1.15 | 1.3 | 2.36 | 2.48 | 2.42 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 99 |
| 2009-38 | 1.28 | 1.4 | 2.59 | 2.7 | 2.53 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2013-39 | 1.26 | 1.34 | 2.62 | 2.64 | 2.74 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2013-40 | 0.99 | 1.18 | 2.58 | 2.6 | 3.1 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 99 | 97 |
| 2014-40 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.48 | 100 | 100 | 97 | 94 | 95 |
| 2015-25 | 1.34 | 1.58 | 2.54 | 2.4 | 2.85 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2015-43 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 2.85 | 2.94 | 2.87 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 99 |
| 平均 | 1.06 | 1.20 | 2.64 | 2.70 | 2.71 | 99.89 | 100.00 | 99.33 | 98.78 | 98.67 |
表3 5种补值方案的效果对比
Table3 Comparison of compensation effect of five complementary methods
| 期数 | 补值误差/K | 补值率/% | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 方案1 | 方案2 | 方案3 | 方案4 | 方案5 | 方案1 | 方案2 | 方案3 | 方案4 | 方案5 | |
| 2004-43 | 0.89 | 0.99 | 3.00 | 3.06 | 2.85 | 99 | 100 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| 2007-41 | 1.03 | 1.15 | 2.65 | 2.74 | 2.52 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 99 | 99 |
| 2007-43 | 1.15 | 1.3 | 2.36 | 2.48 | 2.42 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 99 |
| 2009-38 | 1.28 | 1.4 | 2.59 | 2.7 | 2.53 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2013-39 | 1.26 | 1.34 | 2.62 | 2.64 | 2.74 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2013-40 | 0.99 | 1.18 | 2.58 | 2.6 | 3.1 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 99 | 97 |
| 2014-40 | 0.79 | 0.93 | 2.6 | 2.7 | 2.48 | 100 | 100 | 97 | 94 | 95 |
| 2015-25 | 1.34 | 1.58 | 2.54 | 2.4 | 2.85 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2015-43 | 0.79 | 0.94 | 2.85 | 2.94 | 2.87 | 100 | 100 | 100 | 99 | 99 |
| 平均 | 1.06 | 1.20 | 2.64 | 2.70 | 2.71 | 99.89 | 100.00 | 99.33 | 98.78 | 98.67 |
| 期数 | 2004-43 | 2007-41 | 2007-43 | 2010-38 | 2013-39 | 2013-40 | 2014-40 | 2015-25 | 2015-43 | 平均 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 补值 误差 /K | 区域1 | 上午 | 0.86 | 1.14 | 1.38 | 1.07 | 1.44 | 1.51 | 1.34 | 1.68 | 1.14 | 1.28 |
| 下午 | 0.92 | 1.11 | 1.38 | 1.22 | 1.58 | 1.53 | 1.29 | 1.87 | 1.15 | 1.33 | ||
| 晚上 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 1.30 | 0.79 | 0.92 | ||
| 凌晨 | 1.05 | 1.06 | 0.90 | 0.73 | 1.07 | 1.17 | 0.57 | 0.92 | 0.80 | 0.92 | ||
| 区域2 | 上午 | 1.32 | 1.29 | 1.62 | 1.28 | 1.57 | 1.25 | 1.23 | 1.95 | 1.06 | 1.39 | |
| 下午 | 1.27 | 1.33 | 1.75 | 1.37 | 1.45 | 1.48 | 1.21 | 1.83 | 1.07 | 1.41 | ||
| 晚上 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 1.12 | 1.07 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 1.37 | 0.70 | 0.93 | ||
| 凌晨 | 0.89 | 1.03 | 1.15 | 1.28 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.79 | 1.34 | 0.79 | 1.02 |
表4 重建前后的精度对比
Table4 Comparison of accuracy before and after reconstruction
| 期数 | 2004-43 | 2007-41 | 2007-43 | 2010-38 | 2013-39 | 2013-40 | 2014-40 | 2015-25 | 2015-43 | 平均 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 补值 误差 /K | 区域1 | 上午 | 0.86 | 1.14 | 1.38 | 1.07 | 1.44 | 1.51 | 1.34 | 1.68 | 1.14 | 1.28 |
| 下午 | 0.92 | 1.11 | 1.38 | 1.22 | 1.58 | 1.53 | 1.29 | 1.87 | 1.15 | 1.33 | ||
| 晚上 | 0.95 | 0.99 | 0.85 | 0.85 | 0.89 | 1.05 | 0.58 | 1.30 | 0.79 | 0.92 | ||
| 凌晨 | 1.05 | 1.06 | 0.90 | 0.73 | 1.07 | 1.17 | 0.57 | 0.92 | 0.80 | 0.92 | ||
| 区域2 | 上午 | 1.32 | 1.29 | 1.62 | 1.28 | 1.57 | 1.25 | 1.23 | 1.95 | 1.06 | 1.39 | |
| 下午 | 1.27 | 1.33 | 1.75 | 1.37 | 1.45 | 1.48 | 1.21 | 1.83 | 1.07 | 1.41 | ||
| 晚上 | 0.73 | 0.81 | 1.12 | 1.07 | 0.92 | 0.89 | 0.75 | 1.37 | 0.70 | 0.93 | ||
| 凌晨 | 0.89 | 1.03 | 1.15 | 1.28 | 0.96 | 0.99 | 0.79 | 1.34 | 0.79 | 1.02 |
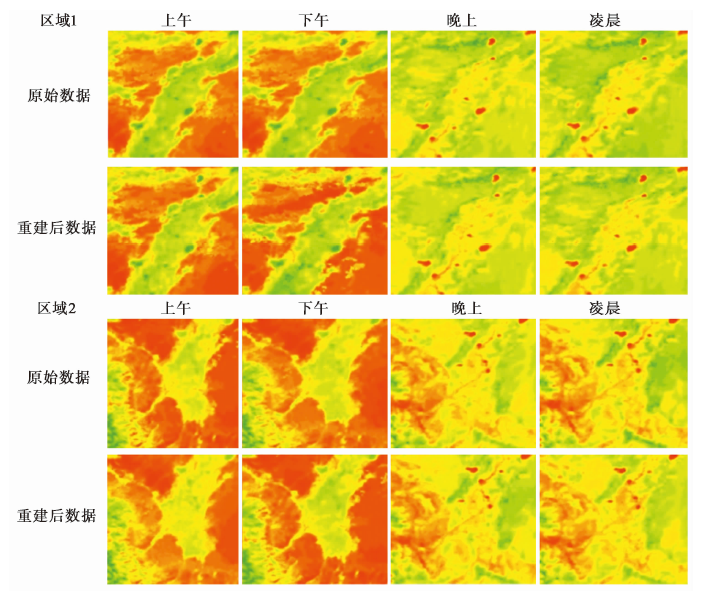
图9 不同区域、 不同时间地表温度重建前后的效果对比(以2015年第43期为例)
Fig. 9 Comparison of effects before and after LAND surface temperature reconstruction in different regions and at different times(a case study of the 43rd issue of 2015).
| 期数 | 本文重建方法 | 对比方法 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 补值误差/K | 补值贡献率/% | 空间域加权平均 补值误差/K | ||
| 第1步 | 第2步 | |||
| 2004-43 | 1.05 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 1.06 |
| 2007-41 | 1.06 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 1.18 |
| 2007-43 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 1.10 |
| 2010-38 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 0 | 1.05 |
| 2013-39 | 1.07 | 1.00 | 0 | 0.89 |
| 2013-40 | 1.17 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 1.08 |
| 2014-40 | 0.57 | 1.00 | 0 | 1.33 |
| 2015-25 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0 | 1.60 |
| 2015-43 | 0.80 | 1.00 | 0 | 0.91 |
| 平均 | 0.92 | 1.13 |
表5 补值精度对比
Table5 Comparison of supplementary value accuracy
| 期数 | 本文重建方法 | 对比方法 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 补值误差/K | 补值贡献率/% | 空间域加权平均 补值误差/K | ||
| 第1步 | 第2步 | |||
| 2004-43 | 1.05 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 1.06 |
| 2007-41 | 1.06 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 1.18 |
| 2007-43 | 0.90 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 1.10 |
| 2010-38 | 0.73 | 1.00 | 0 | 1.05 |
| 2013-39 | 1.07 | 1.00 | 0 | 0.89 |
| 2013-40 | 1.17 | 0.99 | 0.01 | 1.08 |
| 2014-40 | 0.57 | 1.00 | 0 | 1.33 |
| 2015-25 | 0.92 | 1.00 | 0 | 1.60 |
| 2015-43 | 0.80 | 1.00 | 0 | 0.91 |
| 平均 | 0.92 | 1.13 |
| 来源 | 方法 | 所用数据类型的数量 | 平均误差/K |
|---|---|---|---|
| 齐会娟, | 谐波分析、 S-G滤波 | 3 | 2.00 |
| 黄晶晶, | 1 | 2.34 | |
| Kang et al., | 多时相重建 | 4 | 4.55 |
| Zeng et al., | 4 | 4.71 | |
| 吴迪, | 回归分析模型 | 4 | 1.25 |
| Zhao et al., | 3 | 1.41 | |
| Gutierrez et al., | 3 | 1.42 | |
| 李楠等, | 多源数据融合 | 1 | 1.13 |
| 赵冰, | 6 | 1.42 | |
| 王爱辉等, | 相似像元重建 | 3 | 2.17 |
| Tan et al., | 5 | 3.66 | |
| 张德军等, | RSDAST模型 | 1 | 1.15 |
| 本文所提出的方法 | 非线性回归模型 | 2 | 0.92 |
表6 现有方法的重建精度对比
Table6 Comparison of reconstruction accuracy of existing methods
| 来源 | 方法 | 所用数据类型的数量 | 平均误差/K |
|---|---|---|---|
| 齐会娟, | 谐波分析、 S-G滤波 | 3 | 2.00 |
| 黄晶晶, | 1 | 2.34 | |
| Kang et al., | 多时相重建 | 4 | 4.55 |
| Zeng et al., | 4 | 4.71 | |
| 吴迪, | 回归分析模型 | 4 | 1.25 |
| Zhao et al., | 3 | 1.41 | |
| Gutierrez et al., | 3 | 1.42 | |
| 李楠等, | 多源数据融合 | 1 | 1.13 |
| 赵冰, | 6 | 1.42 | |
| 王爱辉等, | 相似像元重建 | 3 | 2.17 |
| Tan et al., | 5 | 3.66 | |
| 张德军等, | RSDAST模型 | 1 | 1.15 |
| 本文所提出的方法 | 非线性回归模型 | 2 | 0.92 |
| [1] |
陈顺云, 马瑾, 刘培洵, 等. 2014. 利用卫星遥感热场信息探索现今构造活动: 以汶川地震为例[J]. 地震地质, 36(3): 775-793. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.018.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈顺云, 马瑾, 刘培洵, 等. 2009. 中国大陆地表温度年变基准场研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(9): 2273-2281.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
陈顺云, 马瑾, 刘培洵, 等. 2004. 中国地表亮度温度年变基准场[J]. 地震地质, 26(3): 528-538.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
樊子德, 龚健雅, 刘博, 等. 2016. 顾及时空异质性的缺失数据时空插值方法[J]. 测绘学报, 45(4): 458-465.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
黄晶晶. 2019. 2003-2017年江浙沪地表温度重建及其时空变化分析[D]. 金华: 浙江师范大学:1-56.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
李楠, 崔耀平, 刘素洁, 等. 2018. 基于多源遥感数据的地表温度空值插补[J]. 测绘, 41(2): 57-61.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
刘文宝, 孟庆岩, 张继超, 等. 2020. 基于偏度的地震热红外异常提取[J]. 地震地质, 42(6): 1509-1524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.06.015.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [8] |
齐会娟. 2017. 陆表温度的重建及其在气温空间模拟中的应用研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆师范大学:1-46.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
裘伟, 李享元, 程衍富. 2014. 基于小波和曲线拟合对瞬变电磁信号去噪的优化[J]. 现代电子技术, 37(11): 61-64.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
王爱辉, 杨英宝, 潘鑫, 等. 2021. 顾及时空特征的FY-4A云覆盖像元地表温度重建模型研究[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 46(6): 1-15.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
王慧, 孙亚勇, 黄诗峰, 等. 2018. LAI和FVC植被参数对VIC模型土壤含水量模拟的影响研究[J]. 中国水利水电科学研究院学报, 16(2): 141-148, 155.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
王新闯, 王世东, 张合兵. 2013. 基于MOD17A3的河南省NPP时空格局[J]. 生态学杂志, 32(10): 2797-2805.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
吴迪. 2018. 基于FY-2F静止气象卫星数据的地表温度重建研究[D]. 南京: 南京信息工程大学:1-57.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
张德军, 杨世琦, 王永前, 等. 2021. 基于FY3C地表温度重建的多云地区旱情监测评估[J]. 自然资源学报, 36(4): 1047-1061.
|
|
DOI URL |
|
| [15] |
赵冰. 2020. 基于MODIS的地表温度时间序列重建及驱动因素分析[D]. 青岛: 山东科技大学:1-40.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
周义, 覃志豪, 包刚. 2014. 热红外遥感图像中云覆盖像元地表温度估算研究进展[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析, 34(2): 364-369.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
DOI URL |
| [19] |
DOI URL |
| [20] |
|
| [21] |
DOI URL |
| [22] |
DOI URL |
| [23] |
DOI URL |
| [24] |
DOI URL |
| [25] |
DOI URL |
| [26] |
DOI URL |
| [27] |
DOI URL |
| [28] |
DOI URL |
| [29] |
DOI URL |
| [30] |
|
| [1] | 宋冬梅, 时洪涛, 单新建, 刘雪梅, 崔建勇, 沈晨, 屈春燕, 邵红梅, 王一博, 臧琳, 陈伟民, 孔建. 基于热异常信息与BP神经网络的中强地震预测试验[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(2): 649-660. |
| [2] | 刘放, 辛华, 任越霞, 张铁宝, 路茜. MODIS亮温增温异常点比值的时序分析方法及其在台湾一些5级以上地震前的异常变化[J]. 地震地质, 2007, 29(1): 172-179. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||