地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (5): 1142-1155.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.05.004
姬昊1)( ), 刘春茹1),*(
), 刘春茹1),*( ), 张沛全2), 李冰溯2), 聂冠军2), 魏传义1), 尹功明1)
), 张沛全2), 李冰溯2), 聂冠军2), 魏传义1), 尹功明1)
收稿日期:2021-07-19
修回日期:2021-12-24
出版日期:2022-10-20
发布日期:2022-11-28
通讯作者:
刘春茹
作者简介:姬昊, 男, 1996年生, 现为中国地震局地质研究所构造地质学专业在读博士研究生, 主要研究方向为断层带演化及年代学, E-mail: jihao9610@126.com。
基金资助:
JI Hao1)( ), LIU Chun-ru1)(
), LIU Chun-ru1)( ), ZHANG Pei-quan2), LI Bing-su2), NIE Guan-jun2), WEI Chuan-yi1), YIN Gong-ming1)
), ZHANG Pei-quan2), LI Bing-su2), NIE Guan-jun2), WEI Chuan-yi1), YIN Gong-ming1)
Received:2021-07-19
Revised:2021-12-24
Online:2022-10-20
Published:2022-11-28
Contact:
LIU Chun-ru
摘要:
在缺乏第四纪沉积物覆盖的碳酸盐岩基岩区, 难以确定断层的第四纪活动历史。碳酸盐岩基岩区断层活动往往会在断层面上形成重结晶碳酸盐, 这为利用ESR方法研究此类断层的第四纪活动历史提供了物质基础。文中采集了那坡断裂系北段一条R剪切断层基岩面的3个重结晶碳酸盐样品, 并开展ESR测年研究。结果表明, 该断层的活动时代大致为距今0.2Ma, 根据里德尔剪切模型推测, 那坡断裂的主干断层可能发生过晚于距今0.2Ma的构造活动; 同时, 碳酸盐岩基岩区断层活动产生的重结晶碳酸盐作为直接记录断层活动信息的测年材料, 具有广阔的应用前景。
姬昊, 刘春茹, 张沛全, 李冰溯, 聂冠军, 魏传义, 尹功明. 重结晶碳酸盐在碳酸盐岩区基岩断层定年中的应用--以广西那坡断裂北段R剪切断层为例[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(5): 1142-1155.
JI Hao, LIU Chun-ru, ZHANG Pei-quan, LI Bing-su, NIE Guan-jun, WEI Chuan-yi, YIN Gong-ming. APPLICATION OF RECRYSTALLIZED CARBONATES TO THE DATING OF BEDROCK FAULTS IN CARBONATE ROCK AREA--A CASE STUDY ON THE R-SHEAR FAULT OF THE NORTHERN SECTION OF THE NAPO FAULT SYSTEM[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(5): 1142-1155.
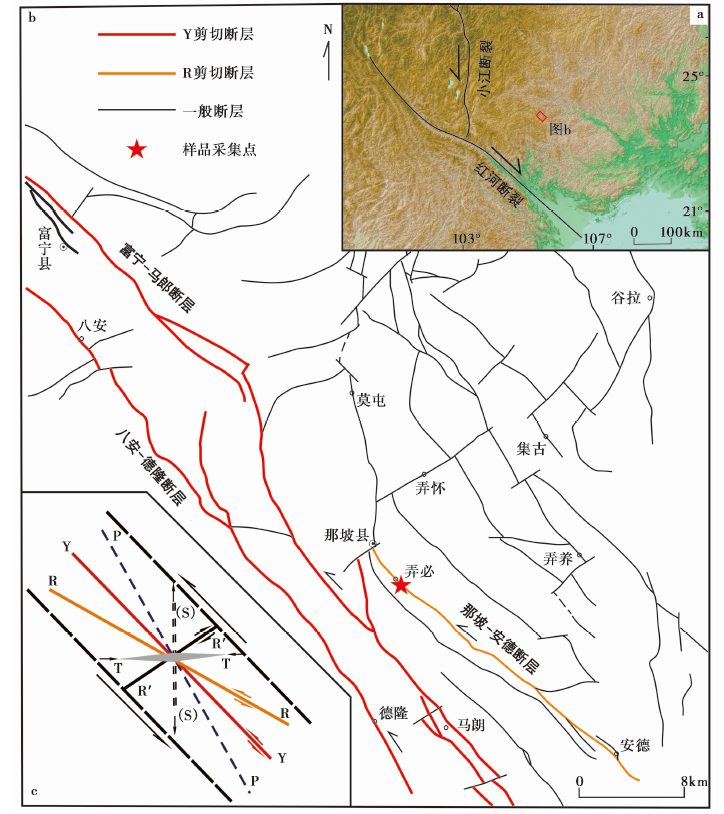
图1 那坡断裂北段的断层展布特征 a 研究区位置; b 那坡断裂北段断层的展布特征; b 里德尔剪切模型, 修改自文献(Lin et al., 2011)
Fig. 1 Fault distribution characteristics of the northern segment of the Napo fault zone.
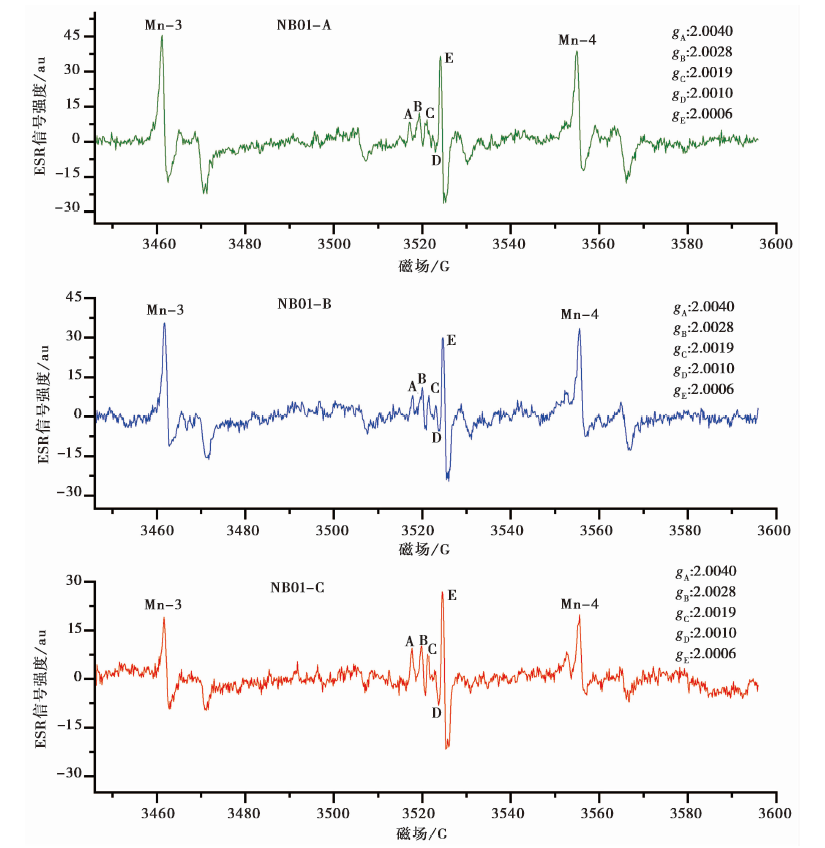
图3 重结晶碳酸盐样品(NB01-A、 NB01-B和NB01-C)的ESR谱图(20℃, 辐照剂量为796.2Gy)
Fig. 3 ESR spectra of recrystallized carbonate samples(NB01-A, NB01-B and NB01-C) (20℃, radiation dose of 796.2Gy).
| 样品编号 | U/μg·g-1 | Th/μg·g-1 | K/% | α剂量率/Gy·ka-1 | β剂量率/Gy·ka-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB01-A | 0.134±0.007 | 0.700±0.035 | 0.058±0.003 | 0.114±0.009 | 0.084±0.004 |
| NB01-B | 0.192±0.010 | 1.100±0.055 | 0.086±0.004 | 0.173±0.014 | 0.125±0.006 |
| NB01-C | 0.147±0.007 | 0.826±0.041 | 0.065±0.003 | 0.131±0.010 | 0.095±0.005 |
表1 重结晶碳酸盐样品(NB01-A、 NB01-B和NB01-C)自身提供的α和β剂量率
Table1 The α and β dose rates provided by recrystallized carbonate samples(NB01-A, NB01-B and NB01-C)
| 样品编号 | U/μg·g-1 | Th/μg·g-1 | K/% | α剂量率/Gy·ka-1 | β剂量率/Gy·ka-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB01-A | 0.134±0.007 | 0.700±0.035 | 0.058±0.003 | 0.114±0.009 | 0.084±0.004 |
| NB01-B | 0.192±0.010 | 1.100±0.055 | 0.086±0.004 | 0.173±0.014 | 0.125±0.006 |
| NB01-C | 0.147±0.007 | 0.826±0.041 | 0.065±0.003 | 0.131±0.010 | 0.095±0.005 |
| 样品编号 | U/μg·g-1 | Th/μg·g-1 | K/% | β剂量率/Gy·ka-1 | γ剂量率/Gy·ka-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB01-JY | 0.480±0.024 | 0.060±0.003 | 0.004±0.002 | 0.037±0.003 | 0.058±0.005 |
表2 样品周围环境(基岩)产生的β和γ剂量率
Table2 The β and γ dose rates generated by the surrounding environment(bedrock)of samples
| 样品编号 | U/μg·g-1 | Th/μg·g-1 | K/% | β剂量率/Gy·ka-1 | γ剂量率/Gy·ka-1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB01-JY | 0.480±0.024 | 0.060±0.003 | 0.004±0.002 | 0.037±0.003 | 0.058±0.005 |
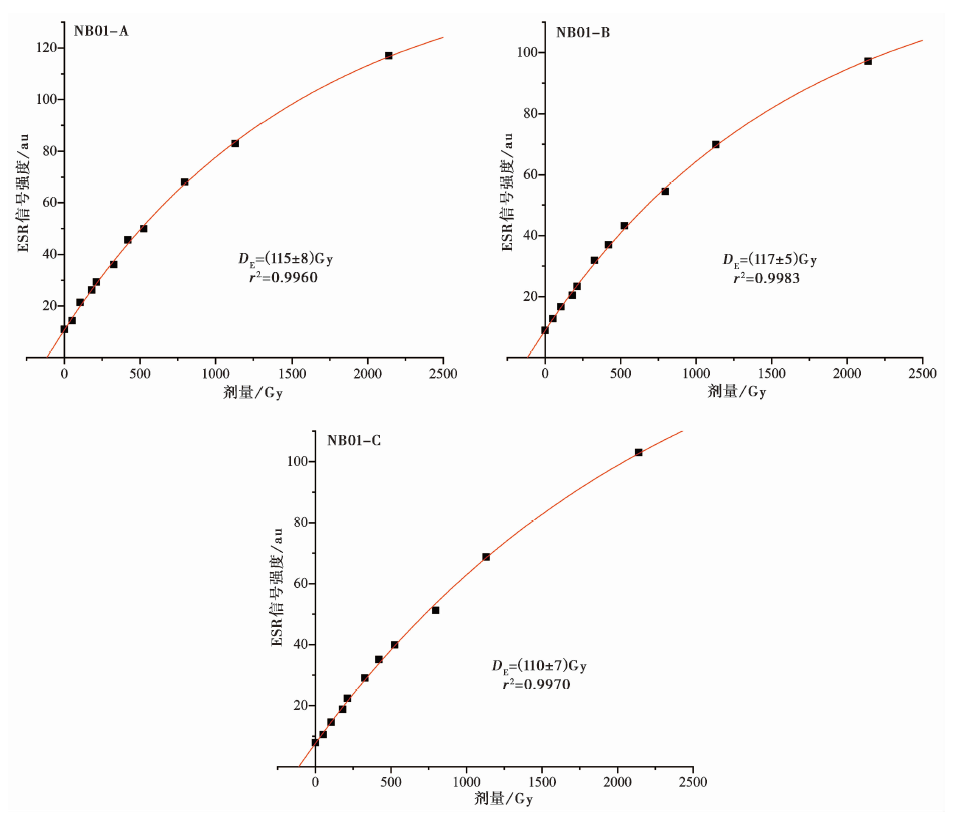
图4 重结晶碳酸盐样品(NB01-A、 NB01-B和NB01-C)g=2.00 0 6信号的附加剂量响应曲线
Fig. 4 Additive dose curves of g=2.00 0 6 for recrystallized carbonate samples(NB01-A, NB01-B and NB01-C).
| 样品编号 | 海拔 /m | α剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | β剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | γ剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | 宇宙剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | 总剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | 等效剂量 /Gy | 年龄 /ka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB01-A | 1 223 | 0.114±0.009 | 0.079±0.004 | 0.058±0.005 | 0.290 | 0.541±0.054 | 115±8 | 213±15 |
| NB01-B | 1 223 | 0.173±0.014 | 0.100±0.005 | 0.058±0.005 | 0.290 | 0.621±0.062 | 117±5 | 188±8 |
| NB01-C | 1 223 | 0.131±0.010 | 0.085±0.005 | 0.058±0.005 | 0.290 | 0.564±0.056 | 110±7 | 195±12 |
表3 重结晶碳酸盐样品(NB01-A、 NB01-B和NB01-C)的总剂量率、 等效剂量及测年结果
Table3 Total dose rates, equivalent doses, and ages of recrystallized carbonate samples (NB01-A, NB01-B and NB01-C)
| 样品编号 | 海拔 /m | α剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | β剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | γ剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | 宇宙剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | 总剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | 等效剂量 /Gy | 年龄 /ka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NB01-A | 1 223 | 0.114±0.009 | 0.079±0.004 | 0.058±0.005 | 0.290 | 0.541±0.054 | 115±8 | 213±15 |
| NB01-B | 1 223 | 0.173±0.014 | 0.100±0.005 | 0.058±0.005 | 0.290 | 0.621±0.062 | 117±5 | 188±8 |
| NB01-C | 1 223 | 0.131±0.010 | 0.085±0.005 | 0.058±0.005 | 0.290 | 0.564±0.056 | 110±7 | 195±12 |
| [1] |
陈以健, 卢景芬, 蔡同茂, 等. 1988. 西沙珊瑚砂屑灰岩的ESR年龄测定[J]. 地质论评, 34(3): 254-261.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
刁少波, 贺行良, 何乐龙, 等. 2018. 深海碳酸盐岩ESR测年信号的热力学特征[J]. 海洋地质前沿, 34(8): 1-6.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
丁锐, 任俊杰, 张世民, 等. 2018. 丽江-小金河断裂中段晚第四纪古地震历史[J]. 地震地质, 40(3): 622-640.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
高璐, 尹功明, 刘春茹, 等. 2011. 六盘山东麓断裂断层泥ESR测年研究[J]. 核技术, 34(2): 121-125.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
广西壮族自治区地方志编纂委员会. 1990. 广西通志(地震志)[M]. 南宁: 广西人民出版社:14-15.
|
|
Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region Local Chronicle Compilation Committee. 1990. Guangxi General Chronicle(Seismic Chronicle)[M]. Guangxi People Press, Nanning: 14-15. (in Chinese)
|
|
| [6] |
何宏林, 魏占玉, 毕丽思, 等. 2015. 利用基岩断层面形貌定量特征识别古地震: 以霍山山前断裂为例[J]. 地震地质, 37(2): 400-412.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
侯建军, 刘锡大, 游象照, 等. 1993. 桂西活动走滑断裂系的地表变形组合特征及其与地震活动的关系[J]. 地震学报, 15(1): 119-122.
|
|
DOI URL |
|
| [8] |
贾丽, 鲍继飞, 尹功明, 等. 2006. 方解石脉ESR定年信号和测量条件的研究[J]. 地震地质, 28(4): 668-674.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李有利, 杨景春. 1998. 地衣形态量计在同震滑坡研究中的应用[J]. 山地研究, 16(3): 167-170.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
刘星. 1998. 云南石林地区钙华的ESR测年及其地质意义[J]. 中国岩溶, 17(1): 9-14.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
刘行松, 史兰斌, 唐汉军, 等. 1993. 方解石脉在断层新活动研究中的应用[J]. 中国科学(B辑), 23(4): 430-436.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
聂冠军, 杨仕升, 张沛全, 等. 2019. 右江地区新生代走滑断裂活动特征及其构造意义[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 43(6): 1094-1105.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
史兰斌, 林传勇, 刘行松, 等. 1996. 基岩区断层新活动年代学研究的问题讨论[J]. 地震地质, 18(4): 319-324.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
温孝胜, 刘韶. 1995. 南永一井珊瑚礁岩心的ESR年龄分析[J]. 海洋学报, 17(5): 88-94.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
邢如连, 呼俊致, 原思训, 等. 1989. ESR法测定石笋类碳酸盐年代的研究[J]. 中国岩溶, 8(2): 89-99.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
许顺山, 彭华,
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
业渝光, 和杰, 刁少波, 等. 1990. 西沙石岛风成灰岩的ESR和14C年龄[J]. 海洋地质与第四纪地质, 10(2): 103-110.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
业渝光, 和杰, 刁少波, 等. 1991. 南海全新世珊瑚礁ESR和铀系年龄的研究[J]. 地质论评, 37(2): 165-171.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
业渝光, 周世光. 1998. 珊瑚礁中Mn2+的ESR信号及其气候指示意义[J]. 海洋与湖沼, 29(5): 547-551.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
尹功明, 孙瑛杰, 业渝光, 等. 2001. 大荔人所在层位贝壳的电子自旋共振年龄[J]. 人类学学报, 20(1): 34-38.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
尹金辉, 杨雪, 郑勇刚. 2016. 基岩就地14C测年及古地震潜在应用[J]. 地震地质, 38(3): 773-782.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
张沛全, 张继恩, 周青云, 等. 2019. 富宁-那坡断裂系相关的里德尔剪切模型与地震分布[C]. 第二届构造地质与地球动力学青年学术论坛, 南京.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
|
| [24] |
|
| [25] |
|
| [26] |
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
DOI URL |
| [29] |
DOI URL |
| [30] |
DOI URL |
| [31] |
DOI URL |
| [32] |
DOI URL |
| [33] |
|
| [34] |
|
| [35] |
DOI URL |
| [36] |
DOI URL |
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
DOI URL |
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
DOI URL |
| [41] |
DOI URL |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
DOI URL |
| [44] |
DOI URL |
| [45] |
|
| [46] |
|
| [47] |
DOI URL |
| [48] |
DOI URL |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
PMID |
| [1] | 闫小兵, 周永胜, 李自红, 扈桂让, 任瑞国, 郝雪景. 山西浮山断裂的晚第四纪活动与位移速率[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 35-45. |
| [2] | 邹俊杰, 何宏林, 横山祐典, 魏占玉, 石峰, 郝海健, 庄其天, 孙稳, 周朝, 白滨吉起. 基岩断层面的古地震研究方法:国内外应用现状及展望[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(6): 1539-1562. |
| [3] | 周永胜. 基岩区断层黏滑与蠕滑的地质标志和岩石力学实验证据[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(5): 1266-1272. |
| [4] | 邹俊杰, 何宏林, 石峰, 魏占玉, 苏鹏, 闫小兵. 利用灰岩断层面形貌特征识别罗云山山前断裂古地震信息[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(2): 400-418. |
| [5] | 何宏林, 魏占玉, 毕丽思, 徐岳仁. 利用基岩断层面形貌定量特征识别古地震——以霍山山前断裂为例[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(2): 400-412. |
| [6] | 许建东, 周本刚, 魏海泉, 赵波, 潘波, 栾鹏. 火山岩地区断层活动时代鉴定中的问题及其讨论[J]. 地震地质, 2008, 30(2): 553-561. |
| [7] | 黄培华. 用电子自旋共振(ESR)测年法测定断层活动年代的探讨[J]. 地震地质, 1994, 16(3): 269-274. |
| [8] | 陈以健, 赵颇, 卢景芬, 乔力. 黄河小浪底水库区断层的ESR年龄测定[J]. 地震地质, 1989, 11(4): 83-90. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||