地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 909-924.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.04.006
沈军1,2)( ), 戴训也1,2),*(
), 戴训也1,2),*( ), 肖淳1,2), 焦轩凯1,2), 白其乐格尔1,2), 邓梅3), 刘泽众4), 夏方华5), 刘玉5), 刘明5)
), 肖淳1,2), 焦轩凯1,2), 白其乐格尔1,2), 邓梅3), 刘泽众4), 夏方华5), 刘玉5), 刘明5)
收稿日期:2021-05-06
修回日期:2021-07-16
出版日期:2022-08-20
发布日期:2022-09-23
通讯作者:
戴训也
作者简介:沈军, 男, 1966年生, 博士, 研究员, 1998年于中国地震局地质研究所获构造地质学专业博士学位, 主要从事地震地质和综合减灾研究, 电话: 13651172760, E-mail: shenjuneq@qq.com。
基金资助:
SHEN Jun1,2)( ), DAI Xun-ye1,2),*(
), DAI Xun-ye1,2),*( ), XIAO Chun1,2), JIAO Xuan-kai1,2), BAI Qilegeer1,2), DENG Mei3), LIU Ze-zhong4), XIA Fang-hua5), LIU Yu5), LIU Ming5)
), XIAO Chun1,2), JIAO Xuan-kai1,2), BAI Qilegeer1,2), DENG Mei3), LIU Ze-zhong4), XIA Fang-hua5), LIU Yu5), LIU Ming5)
Received:2021-05-06
Revised:2021-07-16
Online:2022-08-20
Published:2022-09-23
Contact:
DAI Xun-ye
摘要:
夏垫断裂是1679年三河-平谷8级地震的发震断层, 在其西侧发现一条新的断裂, 称其为夏垫西断裂。文中采用6条浅层地震剖面确定了该断层在三河市内的位置; 采用联排钻孔探测方法并应用磁化率测井技术, 结合释光测年, 研究了该断裂的晚第四纪活动性。该断裂蜿蜒曲折, 总体走向NE, 倾向NW。在垂直剖面上表现为正断层性质, 它是燕郊半地堑型断陷东南缘的主控断裂。该断裂与夏垫断裂倾向相反, 与夏垫断裂之间夹一地垒, 地垒最窄处<1km。由10个钻孔的岩心柱状图和测井曲线及8个有效的测年数据组成的钻孔联合剖面显示, 该隐伏断裂的上断点埋深约为12m, 错断了晚更新世晚期地层, 错断的最新地层的测年结果为(36.52±5.39)ka。晚更新世以来的垂直滑动速率约为0.075mm/a, 晚更新世晚期以来的滑动速率约为0.03mm/a。该断裂在平面上可能与夏垫断裂组成雁列构造, 二者在深部存在密切的联系, 同属于一条切过整个地壳的深大断裂。
中图分类号:
沈军, 戴训也, 肖淳, 焦轩凯, 白其乐格尔, 邓梅, 刘泽众, 夏方华, 刘玉, 刘明. 夏垫西断裂的晚第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 909-924.
SHEN Jun, DAI Xun-ye, XIAO Chun, JIAO Xuan-kai, BAI Qilegeer, DENG Mei, LIU Ze-zhong, XIA Fang-hua, LIU Yu, LIU Ming. STUDY ON THE LATE QUATERNARY ACTIVITY OF THE WEST XIADIAN FAULT IN BEIJING PLAIN[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(4): 909-924.
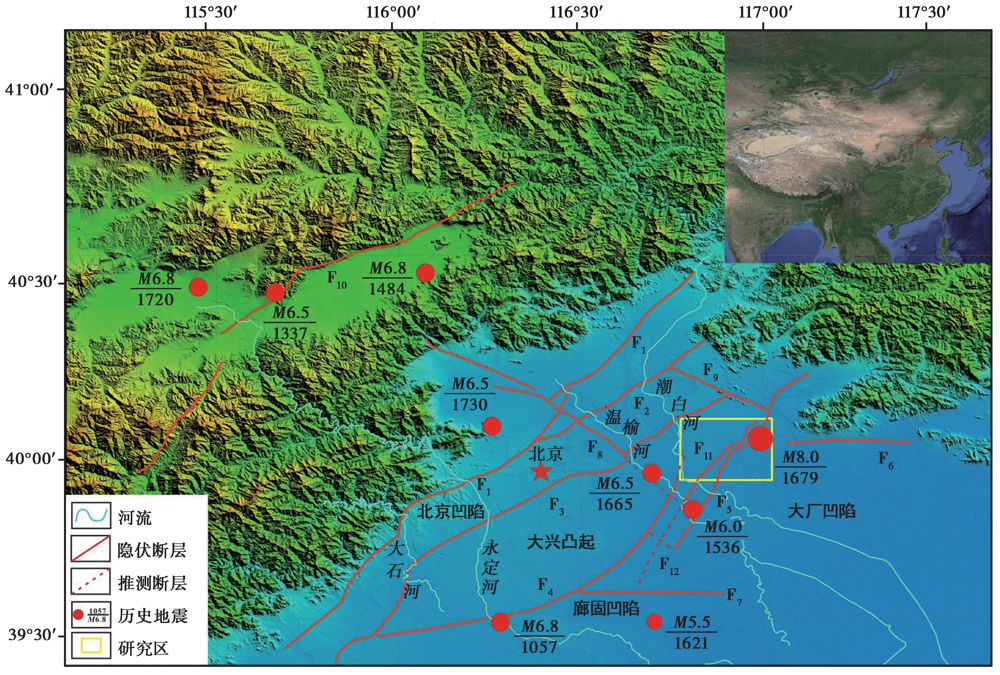
图1 研究区的地理位置与隐伏断裂构造分布(据何付兵等, 2020修改) F1黄庄-高丽营断裂; F2顺义-良乡断裂; F3南苑-通县断裂; F4大兴断裂; F5夏垫断裂; F6皮各庄断裂; F7桐柏断裂; F8南口-孙河断裂; F9二十里长山断裂; F10延怀盆地山前断裂; F11夏垫西断裂; F12姚辛庄断裂
Fig. 1 Location and buried faults distribution of the study area(adapted after HE Fu-bing et al., 2020).
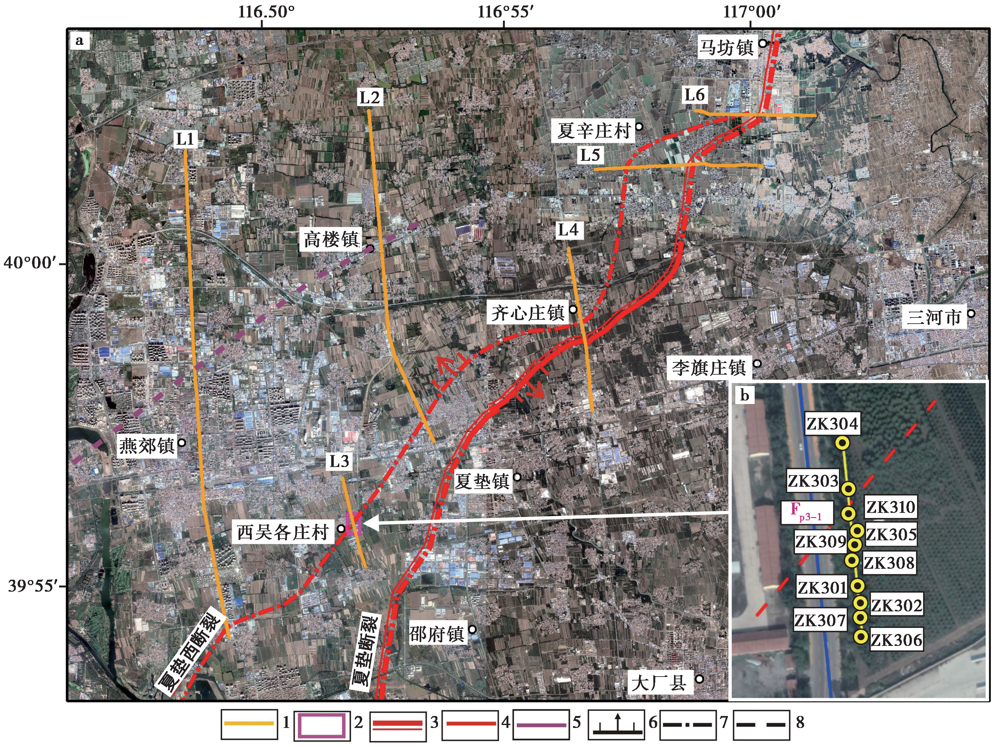
图2 a 浅层地震勘探测线和联合钻孔探测剖面位置; b 联合钻孔剖面钻孔分布图 1 地震测线及编号; 2 联排钻孔剖面的位置; 3 全新世断层; 4 晚更新世断层; 5 早中更新世断层; 6 隐伏断层; 7 地表断层; 8 推测断层
Fig. 2 Location of shallow seismic survey line(a)and combined borehole profile(b).
| 线号 | 起点坐标 | 终点坐标 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 点号 | 东经 | 北纬 | 点号 | 东经 | 北纬 | |
| L1 | 100 | 116°48'10.37″ | 40°1'36.77″ | 14558 | 116°49'5.82″ | 39°53'54.21″ |
| L2 | 100 | 116°51'57.21″ | 40°2'15.47″ | 10190 | 116°53'18.71″ | 39°57'0.88″ |
| L3 | 100 | 116°50'15.53″ | 39°55'47.56″ | 3000 | 116°50'35.89″ | 39°54'15.67″ |
| L4 | 100 | 116°56'5.16″ | 40°0'4.69″ | 4700 | 116°56'35.05″ | 39°57'30.20″ |
| L5 | 100 | 116°56'37.87″ | 40°1'20.09″ | 5078 | 117°0'4.97″ | 40°1'23.06″ |
| L6 | 100 | 116°58'42.32″ | 40°2'15.44″ | 3674 | 117°1'10.67″ | 40°2'11.11″ |
表1 浅层地震勘探测线的坐标
Table 1 Parameters of shallow seismic exploration line
| 线号 | 起点坐标 | 终点坐标 | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 点号 | 东经 | 北纬 | 点号 | 东经 | 北纬 | |
| L1 | 100 | 116°48'10.37″ | 40°1'36.77″ | 14558 | 116°49'5.82″ | 39°53'54.21″ |
| L2 | 100 | 116°51'57.21″ | 40°2'15.47″ | 10190 | 116°53'18.71″ | 39°57'0.88″ |
| L3 | 100 | 116°50'15.53″ | 39°55'47.56″ | 3000 | 116°50'35.89″ | 39°54'15.67″ |
| L4 | 100 | 116°56'5.16″ | 40°0'4.69″ | 4700 | 116°56'35.05″ | 39°57'30.20″ |
| L5 | 100 | 116°56'37.87″ | 40°1'20.09″ | 5078 | 117°0'4.97″ | 40°1'23.06″ |
| L6 | 100 | 116°58'42.32″ | 40°2'15.44″ | 3674 | 117°1'10.67″ | 40°2'11.11″ |
| 钻孔编号 | 坐标(WGS84) | 孔深/m | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 纬度 | 经度 | ||
| ZK304 | 39°54'38.6″N | 116°50'33.5″E | 83.80 |
| ZK303 | 39°54'37.6″N | 116°50'33.6″E | 77.20 |
| ZK305 | 39°54'36.4″N | 116°50'33.9″E | 67.30 |
| ZK308 | 39°54'36.1″N | 116°50'33.8″E | 45.60 |
| ZK301 | 39°54'35.8″N | 116°50'33.9″E | 66.50 |
| ZK302 | 39°54'35.2″N | 116°50'34.0″E | 73.80 |
| ZK307 | 39°54'34.8″N | 116°50'34.0″E | 50.50 |
| ZK306 | 39°54'34.5″N | 116°50'34.0″E | 50.80 |
| ZK309 | 39°54'36.4″N | 116°50'33.8″E | 27.60 |
| ZK310 | 39°54'37.2″N | 116°50'33.7″E | 36.80 |
表2 L3浅层地震测线上西吴各庄联排钻孔剖面各钻孔的坐标及孔深
Table 2 Coordinates and depths of combined row drillholes at Xiwugezhuang on the shallow seismic exploration line L3
| 钻孔编号 | 坐标(WGS84) | 孔深/m | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 纬度 | 经度 | ||
| ZK304 | 39°54'38.6″N | 116°50'33.5″E | 83.80 |
| ZK303 | 39°54'37.6″N | 116°50'33.6″E | 77.20 |
| ZK305 | 39°54'36.4″N | 116°50'33.9″E | 67.30 |
| ZK308 | 39°54'36.1″N | 116°50'33.8″E | 45.60 |
| ZK301 | 39°54'35.8″N | 116°50'33.9″E | 66.50 |
| ZK302 | 39°54'35.2″N | 116°50'34.0″E | 73.80 |
| ZK307 | 39°54'34.8″N | 116°50'34.0″E | 50.50 |
| ZK306 | 39°54'34.5″N | 116°50'34.0″E | 50.80 |
| ZK309 | 39°54'36.4″N | 116°50'33.8″E | 27.60 |
| ZK310 | 39°54'37.2″N | 116°50'33.7″E | 36.80 |
| 野外编号 | 埋深 /m | 238U/Bg·kg-1 | 232Th/Bg·kg-1 | 40K/Bg·kg-1 | 实测 含水量 /% | 年剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | 等效剂量 /Gy | 年龄 /ka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK301-osl1 | 3.50 | 17.42±1.56 | 41.16±4.39 | 662.89±0.73 | 19.2 | 2.91±0.1 | 44.47±4.11 | 15.3±2.11 |
| ZK301-osl5 | 32.80 | 36.86±29.6 | 38.17±4.66 | 784.53±16.48 | 21.0 | 3.01±0.1 | 273.17±31.99 | 90.64±14.10 |
| ZK301-osl6 | 42.50 | 75.5±5.21 | 47.54±4.37 | 598.8±10.24 | 14.9 | 3.03±0.1 | 401.34±22.18 | 132.64±15.44 |
| ZK303-osl1 | 3.15 | 49.41±0.346 | 48.48±2.37 | 746.14±10.22 | 6.9 | 3.57±0.1 | 41.36±2.89 | 11.58±1.44 |
| ZK303-osl3 | 15.35 | 29.47±3.28 | 37.81±2.92 | 677.15±18.28 | 4.4 | 3.28±0.1 | 119.88±12.71 | 36.52±5.39 |
| ZK303-osl6 | 30.85 | 68.06±8.66 | 46.34±3.34 | 800.45±18.48 | 12.0 | 4.21±0.1 | 231.68±16.33 | 59.74±7.43 |
| ZK303-osl10 | 50.15 | 26.17±13.14 | 39.33±3.88 | 758.05±7.28 | 3.8 | 3.54±0.1 | 396.59±53.91 | 112.00±19.07 |
| ZK303-osl12 | 55.95 | 72.12±4.48 | 45.05±2.39 | 759.66±8.43 | 16.0 | 3.85±0.1 | 454.65±51.76 | 118.20±18.10 |
表3 年龄样品测试结果
Table 3 The dating results of the samples
| 野外编号 | 埋深 /m | 238U/Bg·kg-1 | 232Th/Bg·kg-1 | 40K/Bg·kg-1 | 实测 含水量 /% | 年剂量率 /Gy·ka-1 | 等效剂量 /Gy | 年龄 /ka |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZK301-osl1 | 3.50 | 17.42±1.56 | 41.16±4.39 | 662.89±0.73 | 19.2 | 2.91±0.1 | 44.47±4.11 | 15.3±2.11 |
| ZK301-osl5 | 32.80 | 36.86±29.6 | 38.17±4.66 | 784.53±16.48 | 21.0 | 3.01±0.1 | 273.17±31.99 | 90.64±14.10 |
| ZK301-osl6 | 42.50 | 75.5±5.21 | 47.54±4.37 | 598.8±10.24 | 14.9 | 3.03±0.1 | 401.34±22.18 | 132.64±15.44 |
| ZK303-osl1 | 3.15 | 49.41±0.346 | 48.48±2.37 | 746.14±10.22 | 6.9 | 3.57±0.1 | 41.36±2.89 | 11.58±1.44 |
| ZK303-osl3 | 15.35 | 29.47±3.28 | 37.81±2.92 | 677.15±18.28 | 4.4 | 3.28±0.1 | 119.88±12.71 | 36.52±5.39 |
| ZK303-osl6 | 30.85 | 68.06±8.66 | 46.34±3.34 | 800.45±18.48 | 12.0 | 4.21±0.1 | 231.68±16.33 | 59.74±7.43 |
| ZK303-osl10 | 50.15 | 26.17±13.14 | 39.33±3.88 | 758.05±7.28 | 3.8 | 3.54±0.1 | 396.59±53.91 | 112.00±19.07 |
| ZK303-osl12 | 55.95 | 72.12±4.48 | 45.05±2.39 | 759.66±8.43 | 16.0 | 3.85±0.1 | 454.65±51.76 | 118.20±18.10 |
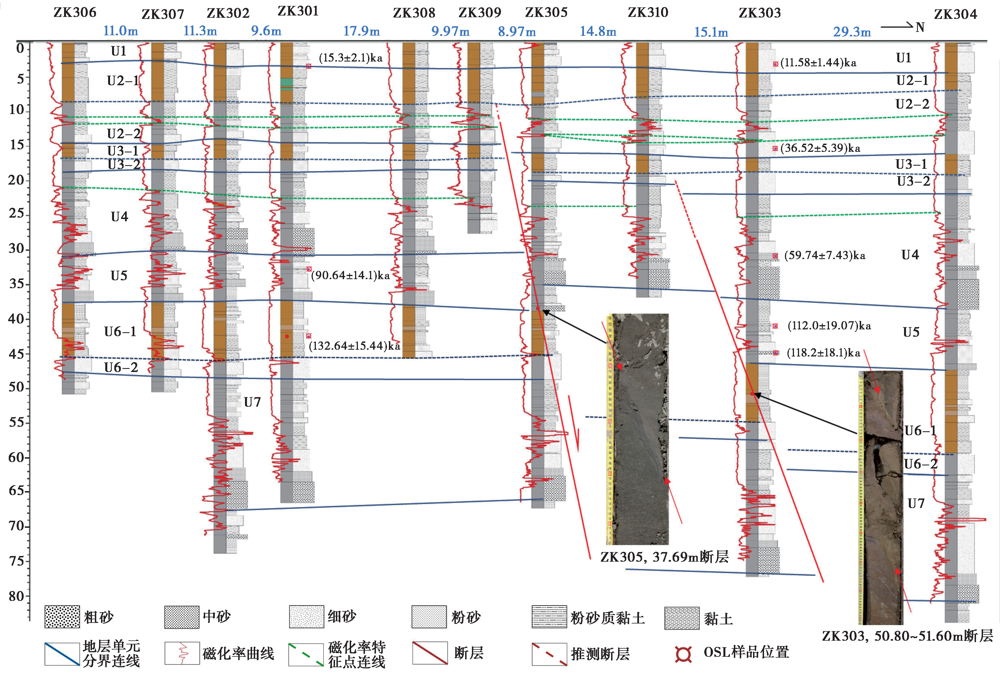
图9 L3测线的西吴各庄钻孔柱状图叠加磁化率测井曲线联合剖面图
Fig. 9 Combined profile of borehole histogram superimposed with magnetic susceptibility logging curve at Xiwugezhuang on the survey line L3.
| [1] | 高景华, 徐明才, 荣立新, 等. 2008. 利用地震剖面研究夏垫断裂西南段的活动性[J]. 地震地质, 30(2): 497-504. |
| GAO Jing-hua, XU Ming-cai, RONG Li-xin, et al. 2008. Activity of the southwest segment of Xiadian Fault investigated by seismic reflection profiling[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(2): 497-504. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 高清武. 1992. 地震前H2、 Hg等断层气的异常变化[J]. 中国地震, 8(3): 53-59. |
| GAO Qing-wu. 1992. Anomalous variation of H2, Hg and other fault soil gases before earthquakes[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 8(3): 53-59. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 高战武, 陈棋福, 黄金莉, 等. 2010. 北京地区主要活动断裂深部速度结构特征及强震构造分析[J]. 震灾防御技术, 5(3): 271-280. |
| GAO Zhan-wu, CHEN Qi-fu, HUANG Jin-li, et al. 2010. Velocity structure beneath the active faults in Beijing area and their seismotectonic characteristics[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 5(3): 271-280. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 桂宝玲. 2011. 伸展盆地构造几何学、运动学: 以渤海湾盆地廊固凹陷为例[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学. |
| GUI Bao-ling. 2011. The structural geometry and kinemics of extensional basin: An example from Langfang-Gu’an depression, Bohai Gulf Basin[D]. China University of Geosciences, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 何付兵. 2019. 南口-孙河断裂几何学、 运动学特征及与地裂缝关系研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. |
| HE Fu-bing. 2019. Study on geometry and kinematics of the Nankou-Sunhe Fault and its relationship with ground fissures[D]. Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 何付兵, 白凌燕, 王继明, 等. 2013. 夏垫断裂带深部构造特征与第四纪活动性讨论[J]. 地震地质, 35(3): 490-505. |
| HE Fu-bing, BAI Ling-yan, WANG Ji-ming, et al. 2013. Deep structure and Quaternary activities of the Xiadian fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 35(3): 490-505. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 何付兵, 徐锡伟, 何振军, 等. 2020. 利用浅层地震反射剖面探测研究大兴断裂北段新近纪-第四纪的构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 42(4): 893-908. |
| HE Fu-bing, XU Xi-wei, HE Zhen-jun, et al. 2020. Research on Neogene-Quaternary stratigraphic structure and shallow tectonic features in the north section of Daxing fault zone based on shallow seismic reflection profiling[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(4): 893-908. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 江娃利, 侯治华, 肖振敏, 等. 2000. 北京平原夏垫断裂齐心庄探槽古地震事件分析[J]. 地震地质, 22(4): 413-422. |
| JIANG Wa-li, HOU Zhi-hua, XIAO Zhen-min, et al. 2000. Study on paleoearthquakes of Qixinzhuang trench at the Xiadian Fault, Beijing plain[J]. Seismology and Geology, 22(4): 413-422. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 江娃利, 侯治华, 谢新生. 2001. 北京平原南口-孙河断裂带昌平旧县探槽古地震事件研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 31(6): 501-509. |
|
JIANG Wa-li, HOU Zhi-hua, XIE Xin-sheng. 2001. Research on paleoearthquakes in Jiuxian trenches across Nankou-Sunhe fault zone in Changping County of Beijing plain[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 45(2): 160-173.
DOI URL |
|
| [10] | 刘保金, 胡平, 孟勇奇, 等. 2009. 北京地区地壳精细结构的深地震反射剖面探测研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(9): 82-90. |
| LIU Bao-jin, HU Ping, MENG Yong-qi, et al. 2009. Research on fine crustal structure using deep seismic reflection profile in Beijing region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(9): 82-90. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 刘保金, 张先康, 陈颙, 等. 2011. 三河-平谷8.0级地震区地壳结构和活动断裂研究: 利用单次覆盖深反射和浅层地震剖面[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(5): 1251-1259. |
| LIU Bao-jin, ZHANG Xian-kang, CHEN Yong, et al. 2011. Research on crustal structure and active fault in the Sanhe-Pinggu earthquake(M8.0)zone based on single-fold deep seismic reflection and shallow seismic reflection profiling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(5): 1251-1259. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 毛昌伟, 丁锐, 龚正. 2010. 1679年三河-平谷8级地震地表断层陡坎的GPS测量[G].地壳构造与地壳应力文集. 北京: 地震出版社: 11-18. |
| MAO Chang-wei, DING Rui, GONG Zheng, et al. 2010. GPS survey of the surface fault scarp of 1679 Sanhe-Pinggu M8 earthquake [G]//Institute of Crustal Dynamics, CEA(ed).Corpus of Tectonics and Crustal Stress. Seismological Press, Beijing: 11-18. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 孟宪梁, 杜春涛, 王瑞, 等. 1983. 1679年三河-平谷大震的地震断裂带[J]. 地震, 3(3): 18-23. |
| MENG Xian-liang, DU Chun-tao, WANG Rui, et al. 1983. Rupture of the Sanhe-Pinggu earthquake of 1679[J]. Earthquake, 3(3): 18-23. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 冉勇康, 邓起东, 杨晓平, 等. 1997. 1679年三河-平谷8级地震发震断层的古地震及其重复间隔[J]. 地震地质, 19(3): 193-201. |
| RAN Yong-kang, DENG Qi-dong, YANG Xiao-ping, et al. 1997. Paleoearthquakes and recurrence interval on the seismogenic fault of 1679 Sanhe-Pinggu M8 earthquake, Hebei and Beijing[J]. Seismology and Geology, 19(3): 193-201. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 向宏发, 方仲景, 贾三发, 等. 1994. 隐伏断裂研究及其工程应用: 以北京平原区为例[M]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| XIANG Hong-fa, FANG Zhong-jing, JIA San-fa, et al. 1994. Research of Buried Fault and Its Engineering Applications: A Case Study of the Beijing Plain Area[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 向宏发, 方仲景, 徐杰, 等. 1988. 三河-平谷8级地震区的构造背景与大震重复性研究[J]. 地震地质, 10(1): 15-28. |
| XIANG Hong-fa, FANG Zhong-jing, XU Jie, et al. 1988. Tectonic setting and earthquake repeatability on the seismogenic fault of 1679 M8.0 Sanhe-Pinggu earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 10(1): 15-28. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 徐锡伟, 吴卫民, 张先康, 等. 2002. 首都圈地区地壳最新构造变动与地震[M]. 北京: 科学出版社. |
| XU Xi-wei, WU Wei-min, ZHANG Xian-kang, et al. 2002. The Latest Crustal Deformation and Earthquake in North China[M]. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 于晓辉, 沈军, 戴训也, 等. 2019. 夏垫断裂带古地震事件在断塞塘沉积物中的响应[J]. 地震地质, 41(4): 872-886. |
| YU Xiao-hui, SHEN Jun, DAI Xun-ye, et al. 2019. The response of sag pond sedimentation to the paleoearthquake event on the Xiadian fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 41(4): 872-886. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 张世民, 王丹丹, 刘旭东, 等. 2008. 北京南口-孙河断裂晚第四纪古地震事件的钻孔剖面对比与分析[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 38(7): 881-895. |
|
ZHANG Shi-min, WANG Dan-dan, LIU Xu-dong, et al. 2008. Using borehole core analysis to reveal Late Quaternary paleoearthquakes along the Nankou-Sunhe Fault, Beijing[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 51(8): 1154-1168.
DOI URL |
|
| [20] | 张艺. 2014. 冀中坳陷三维连片区新生代断裂活动性研究[D]. 东营: 中国石油大学. |
| ZHANG Yi. 2014. Study on Cenozoic fault activity of the three-dimensional continuous area in Jizhong depression[D]. China University of Petroleum, Dongying. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 赵红格, 刘池洋. 2002. 大兴断裂分段性研究[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 23(4): 368-371. |
| ZHAO Hong-ge, LIU Chi-yang. 2002. Research on the segmentation of Daxing Fault[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 23(4): 368-371. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 赵金仁, 张先康, 张成科, 等. 2004. 利用宽角反射/折射和深反射探测剖面揭示三河-平谷大震区深部结构特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 47(4): 646-653. |
| ZHAO Jin-ren, ZHANG Xian-kang, ZHANG Cheng-ke, et al. 2004. Deep structural features of the Sanhe-Pinggu great earthquake area imaged by wide-angle and deep seismic reflection profiling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(4): 646-653. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 周永恒, 杨肖肖, 丰成君, 等. 2021. 北京平原区黄庄-高丽营断裂(房山-涞水段)第四纪活动特征的浅层综合探测证据[J]. 地球学报, 42(5): 677-689. |
| ZHOU Yong-heng, YANG Xiao-xiao, FENG Cheng-jun, et al. 2021. Evidence of shallow synthetic exploration of Quaternary activity characteristics along Fangshan-Laishui section of Huangzhuang-Gaoliying Fault in Beijing Plain[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 42(5): 677-689. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | Deng M, Shen J, Li X, et al. 2019. Analysis of paleoseismic events of Dahuzhuang trench at Xiadian Fault[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 33(3): 71-84. |
| [25] | Yu Z, Pan H, Xi H, et al. 2019. Late Quaternary paleoseismicity of the Xiadian Fault in the North China Plain with implications for earthquake potential[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 184: 1-17. |
| [1] | 李晓妮, 杨晨艺, 李高阳, 冯希杰, 黄引弟, 李陈侠, 李苗, 裴跟弟, 王万合. 渭河盆地东南缘渭南塬前北侧分支断层的浅部结构及晚第四纪活动[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 484-499. |
| [2] | 张鹏, 汪勇, 范小平, 许奎, 刘嘉彬. 幕府山-焦山断裂镇江段第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 63-75. |
| [3] | 李正芳, 李彦宝, 周本刚, 朱国军, 刘保金, 吴健. 北京平原大兴凸起东缘断裂全新世活动的新认识[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1671-1681. |
| [4] | 张鹏, 许奎, 范小平, 张媛媛, 汪勇, 郝景润. 镇江地区主要NW向断裂的第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(1): 144-157. |
| [5] | 卢帮华, 王萍, 王慧颖, 赖忠平, 邓志辉, 毕丽思, 王万合. 珠江三角洲西缘西江断裂鹤山—磨刀门段的活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(6): 1370-1384. |
| [6] | 王继, 高战武, 刘芳晓, 王万合, 赵国存, 徐伟. 用浅层人工地震方法探测唐山—河间—磁县地震构造带内的活动断裂[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(4): 866-880. |
| [7] | 梁明剑, 陈立春, 冉勇康, 李彦宝, 王栋, 高帅坡, 韩明明, 曾蒂. 鲜水河断裂带雅拉河段晚第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(2): 513-525. |
| [8] | 张鹏, 张媛媛, 许汉刚, 刘建达, 陈建强, 李丽梅, 李金良, 顾勤平, 蒋新. 苏锡常断裂的第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(5): 1172-1184. |
| [9] | 顾勤平, 杨浩, 赵启光, 孟科, 王金艳, 李云, 马董伟. 金坛-如皋断裂北东段浅层地震勘探新证据[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(3): 743-758. |
| [10] | 马兴全, 孙杰, 赵显刚, 王文旭, 蔡颖哲, 万娜. 河套断陷带包头断裂第四纪活动性研究[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(4): 874-884. |
| [11] | 许汉刚, 范小平, 冉勇康, 顾勤平, 张鹏, 李丽梅, 赵启光, 王金艳. 郯庐断裂带宿迁段F5断裂浅层地震勘探新证据[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(1): 31-43. |
| [12] | 张鹏, 李丽梅, 冉勇康, 曹筠, 许汉刚, 蒋新. 郯庐断裂带安丘-莒县断裂江苏段晚第四纪活动特征研究[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(4): 1162-1176. |
| [13] | 王银, 孟广魁, 柴炽章, 雷启云, 杜鹏, 谢晓峰. 隐伏活断层探测中的精定位技术——以银川盆地芦花台断裂为例[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(1): 256-268. |
| [14] | 张鹏, 李丽梅, 刘建达, 许汉刚, 李金良, 顾勤平, 蒋新. 徐州废黄河断裂的第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(1): 208-221. |
| [15] | 石峰, 李安, 杨晓平, 徐锡伟, 何宏林. 甘孜-玉树断裂带东南段晚第四纪活动性研究[J]. 地震地质, 2013, 35(1): 50-63. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||