地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 1029-1045.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.04.013
李倩( ), 宋前进, 酆少英, 姬计法, 段永红, 何银娟, 秦晶晶
), 宋前进, 酆少英, 姬计法, 段永红, 何银娟, 秦晶晶
收稿日期:2021-03-15
修回日期:2021-08-17
出版日期:2022-08-20
发布日期:2022-09-23
作者简介:李倩, 女, 1985年生, 2016年于中国石油大学(北京)获地质资源与地质工程专业博士学位, 高级工程师, 从事地壳深浅结构的反射地震探测与研究, 电话: 0371-56865137, E-mail: lijianan_1987@163.com。
基金资助:
LI Qian( ), SONG Qian-jin, FENG Shao-ying, JI Ji-fa, DUAN Yong-hong, HE Yin-juan, QIN Jing-jing
), SONG Qian-jin, FENG Shao-ying, JI Ji-fa, DUAN Yong-hong, HE Yin-juan, QIN Jing-jing
Received:2021-03-15
Revised:2021-08-17
Online:2022-08-20
Published:2022-09-23
摘要:
长70km、 近EW向穿过兰聊断裂带中南段及其邻区的深地震反射剖面, 揭示了该区地壳的精细结构和断裂的深、 浅构造特征, 对深入了解该区的深部地震构造环境、 探讨东濮凹陷的深部动力学过程及其构造演化都起着十分关键的作用。研究结果表明, 兰聊断裂带的深、 浅部构造特征及其两侧的地壳反射结构特征区别较大, 该区地壳由脆性的上地壳和韧性的下地壳组成。上地壳反射波组特征明显, 构造形态清晰可辨: 兰聊断裂以西存在大量向E倾斜的强反射同相轴, 代表了中生代以来不同时代的沉积界面, 其中一套起伏变化形态向E缓倾的基底斜坡是箕状沉积凹陷的底界; 兰聊断裂以东, 基底反射波表现为一组近水平的连续性较好的强反射波组, 平行不整合于古生界奥陶系或更古老的地层之上; 在兰聊断裂上盘还发育有同向及反向次级断裂, 共同控制了箕状沉积盆地东濮凹陷的构造格局。下地壳反射结构较为简单, 整体上以弧状反射为主, 其能量较强、 延续长度较短。莫霍面表现为横向上分段连续、 纵向上持续一定时间的强反射条带, 在兰聊断裂下方的莫霍面反射波组能量明显减弱, 与两侧反射特征截然不同。剖面揭示了2条错断莫霍面的深大断裂(FD1 和FD2), 向下延入上地幔顶部, 为本区上地幔软流物质的上涌与能量交换创造了条件, 也可能是下地壳弧状反射产生的原因。
中图分类号:
李倩, 宋前进, 酆少英, 姬计法, 段永红, 何银娟, 秦晶晶. 深地震反射剖面揭示的兰聊断裂带中南段深部特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 1029-1045.
LI Qian, SONG Qian-jin, FENG Shao-ying, JI Ji-fa, DUAN Yong-hong, HE Yin-juan, QIN Jing-jing. DEEP STRUCTURES OF THE MIDDLE-SOUTHERN SEGMENT OF LANLIAO FAULT ZONE REVEALED BY DEEP SEISMIC REFLECTION PROFILE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(4): 1029-1045.
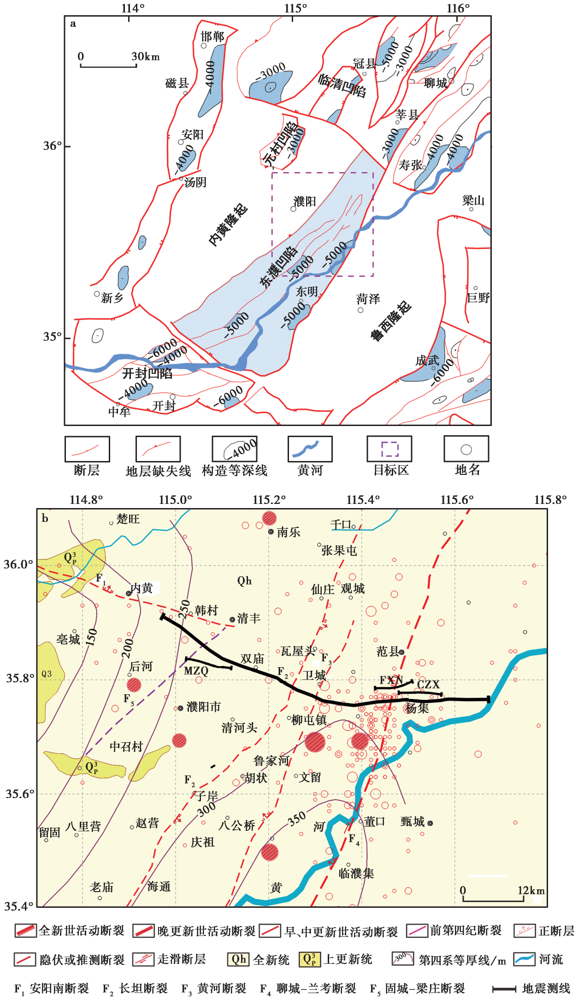
图1 研究区的地质构造图和深地震反射探测剖面的位置 a 研究区的地质构造图, 紫色框内为研究目标区; b 深地震反射探测剖面的位置, 黑线为深地震反射测线, 红线为断层线
Fig. 1 Geological structure map of the research area and the location of the deep seismic reflection profile.
| 项 目 | 观测系统参数 | 说 明 |
|---|---|---|
| 测线长度 | 70km | |
| 正常炮 | 炮间距180m, 药量30kg, 井深40m | 采用钻孔爆破震源激发 |
| 大炮 | 炮间距1000m, 药量96kg, 井深40~50m | 双井或三井组合 |
| 接收参数 | 道距30m、 接收道数1160道, 记录长度30s、 采样间隔4ms | |
| 覆盖次数 | ≥90次 | |
| 地震仪器 | 采集: 428XL遥测数字地震仪;接收: 12个固有频率为10Hz的检波器串组合 |
表1 观测系统参数表
Table 1 Geometry parameters
| 项 目 | 观测系统参数 | 说 明 |
|---|---|---|
| 测线长度 | 70km | |
| 正常炮 | 炮间距180m, 药量30kg, 井深40m | 采用钻孔爆破震源激发 |
| 大炮 | 炮间距1000m, 药量96kg, 井深40~50m | 双井或三井组合 |
| 接收参数 | 道距30m、 接收道数1160道, 记录长度30s、 采样间隔4ms | |
| 覆盖次数 | ≥90次 | |
| 地震仪器 | 采集: 428XL遥测数字地震仪;接收: 12个固有频率为10Hz的检波器串组合 |
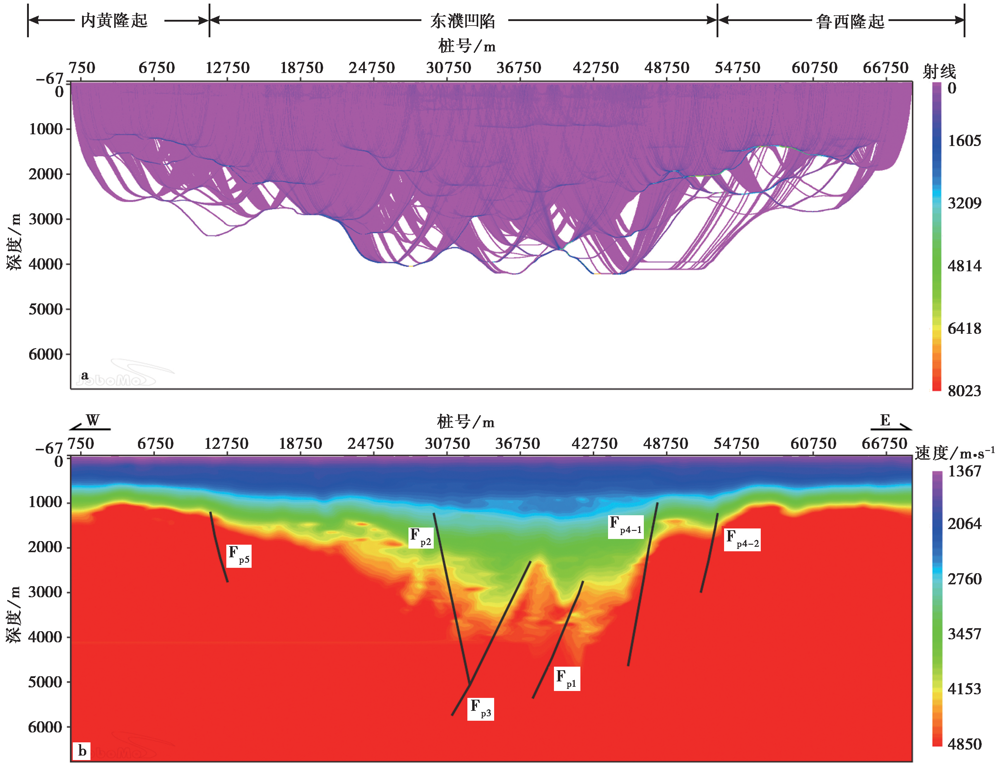
图3 a 初至波射线路径; b 基底速度结构 Fp1濮城断裂; Fp2长垣断裂; Fp3卫西断裂; Fp4-1、 Fp4-2 兰聊断裂; Fp5 固城-梁庄断裂
Fig. 3 Ray paths of first-arrival waves(a)and P-wave velocity structure(b).
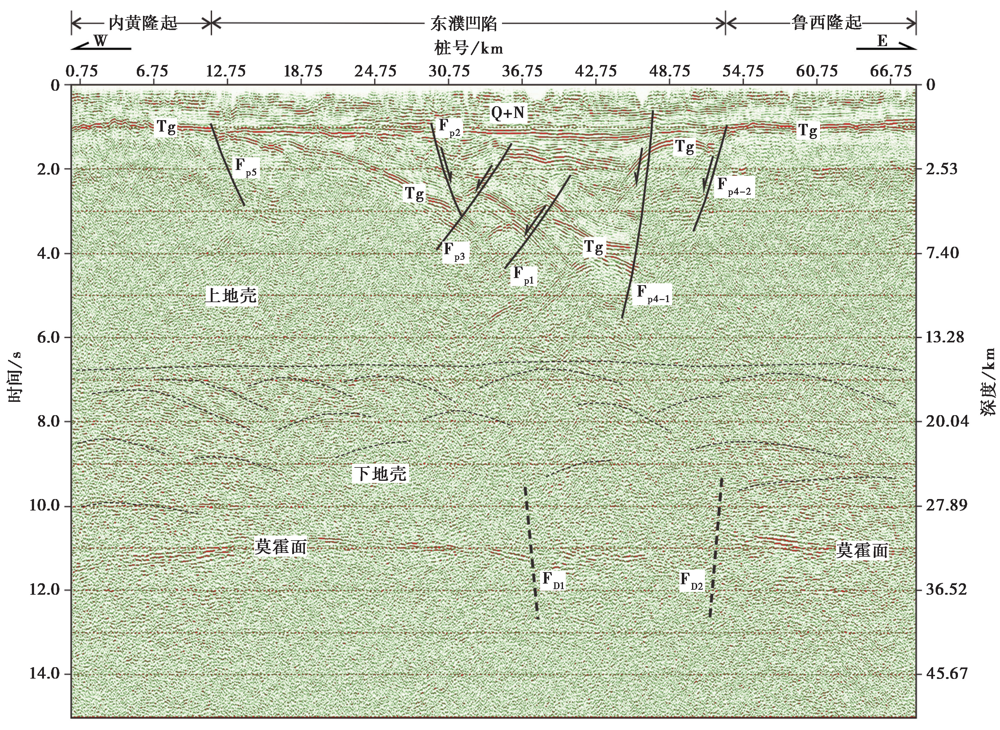
图4 深地震反射时间剖面和解释结果 Fp1 濮城断裂; Fp2 长垣断裂; Fp3 卫西断裂; Fp4-1、 Fp4-2 兰聊断裂; Fp5 固城-梁庄断裂; FD1、 FD2 地壳深断裂; Tg 基底反射波
Fig. 4 Time section and interpretation of deep seismic reflection profile.
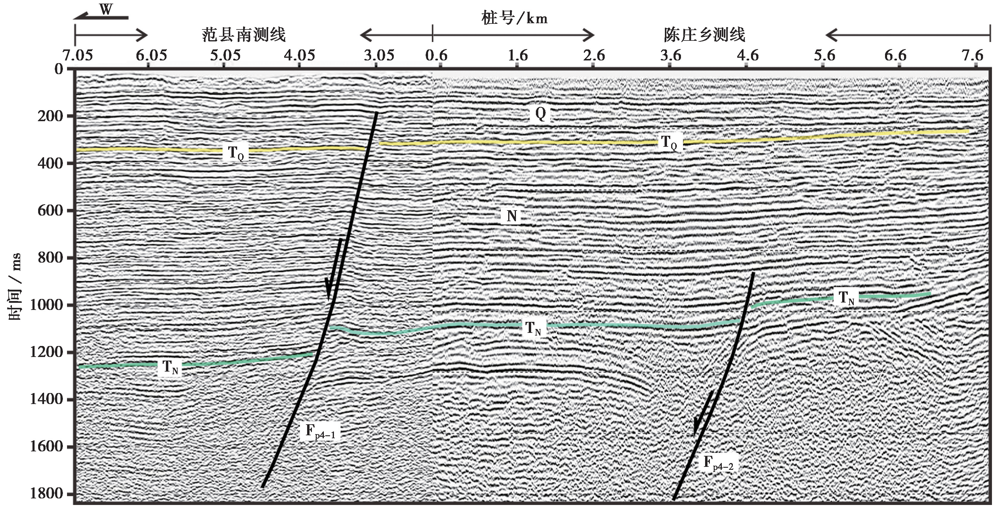
图5 跨兰聊断裂的浅层地震反射时间剖面 Fp4-1、 Fp4-2 兰聊断裂; Q 第四系; N 新近系; TQ 第四系底界; TN 新近系底界
Fig. 5 Stacked time section of shallow seismic reflection across Lanliao Fault.
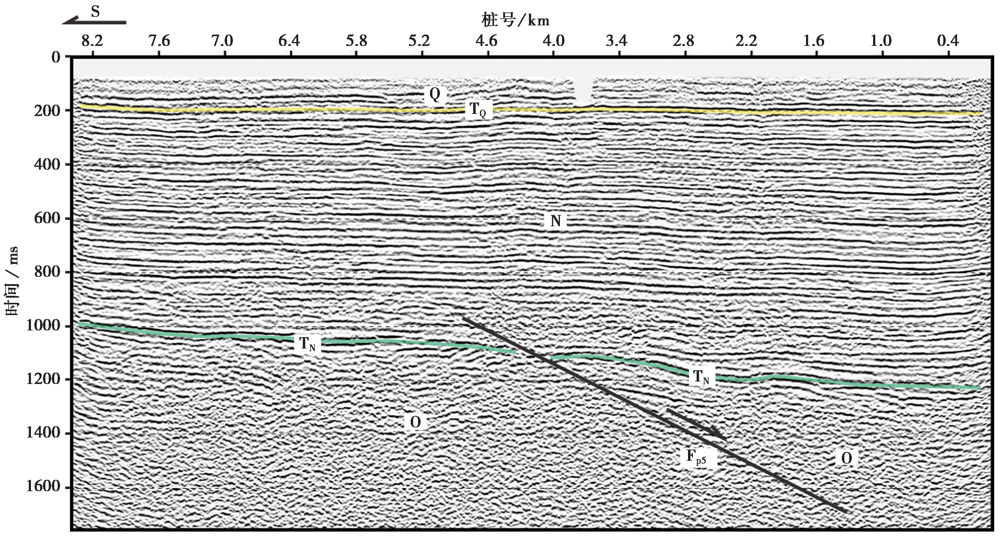
图6 跨固城-梁庄断裂的浅层地震反射时间剖面 Fp5 固城-梁庄断裂; Q 第四系; N 新近系; O 奥陶系; TQ 第四系底界; TN 新近系底界
Fig. 6 Stacked time section of shallow seismic reflection across Gucheng-Liangzhuang Fault.
| [1] | 酆少英, 高锐, 龙长兴, 等. 2011. 银川地堑地壳挤压应力场: 深地震反射剖面[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(3): 692-697. |
| FENG Shao-ying, GAO Rui, LONG Chang-xing, et al. 2011. The compressive stress field of Yinchuan garben: Deep seismic reflection profile[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(3): 692-697. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] |
酆少英, 刘保金, 李倩, 等. 2020. 深地震反射剖面揭示的华北地块南缘地壳的精细结构[J]. 地震地质, 42(3): 581-594. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.03.003.
DOI |
| FENG Shao-ying, LIU Bao-jin, LI Qian, et al. 2020. The fine crustal structure of the southern margin of North China block revealed by deep seismic reflection profile[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(3): 581-594. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 郭慧丽, 徐佩芬. 2011. 地震层析成像在华北克拉通地区的研究进展[J]. 地球物理学进展, 26(5): 1557-1565. |
| GUO Hui-li, XU Pei-fen. 2011. Progress of seismic tomography applied in the North China Craton[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 26(5): 1557-1565. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 金溪. 2010. 浅层地震初至波层析成像方法技术研究[D]. 西安: 长安大学. |
| JIN Xi. 2010. Study on the near-surface seismic waves tomography method and technology[D]. Chang'an University, Xi'an. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 冷玥. 2019. 东濮凹陷新生代沉降史模拟研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学. |
| LENG Yue. 2019. Simulation study on the history of the Cenozoic subsidence in Dongpu Sag[D]. China University of Geosciences, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 李松林, 赖晓玲, 刘宝峰, 等. 2011. 由诸城-宜川人工地震剖面反演结果看太行山两侧岩石圈结构的差异[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 41(5): 668-677. |
| LI Song-lin, LAI Xiao-ling, LIU Bao-feng, et al. 2011. Differences in lithospheric structures between two sides of Taihang Mountains obtained from the Zhucheng-Yichuan deep seismic sounding profile[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 41(5): 668-677. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 刘保金, 酆少英, 姬计法, 等. 2015. 郯庐断裂带中南段的岩石圈精细结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(5): 1610-1621. |
| LIU Bao-jin, FENG Shao-ying, JI Ji-fa, et al. 2015. Fine lithosphere structure beneath the middle-southern segment of the Tan-Lu fault zone[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(5): 1610-1621. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 刘保金, 何宏林, 石金虎, 等. 2012. 太行山东缘汤阴地堑地壳结构和活动断裂探测[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(10): 3266-3276. |
| LIU Bao-jin, HE Hong-lin, SHI Jin-hu, et al. 2012. Crustal structure and active faults of the Tangyin graben in the eastern margin of Taihang Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(10): 3266-3276. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 刘保金, 胡平, 孟勇奇, 等. 2009. 北京地区地壳精细结构的深地震反射剖面探测研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(9): 2264-2272. |
| LIU Bao-jin, HU Ping, MENG Yong-qi, et al. 2009. Research on fine crustal structure using deep seismic reflection profile in Beijing region[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(9): 2264-2272. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 刘保金, 张先康, 陈颙, 等. 2011. 三河-平谷8.0级地震区地壳结构和活动断裂研究: 利用单次覆盖深反射和浅层地震剖面[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(5): 1251-1259. |
| LIU Bao-jin, ZHANG Xian-kang, CHEN Yong, et al. 2011. Research on crustal structure and active fault in the Sanhe-Pinggu earthquake(M8.0)zone based on single-fold deep seismic reflection and shallow seismic reflection profiling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(5): 1251-1259. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 罗省贤, 李录明. 2004. 地面地震初至波层析反演复杂表层速度结构方法[J]. 地球科学进展, 19(S1): 30-34. |
| LUO Sheng-xian, LI Lu-ming. 2004. The method of ground surface seismic first break tomographic inversion for complicated surface model[J]. Advances in Earth Sciences, 19(S1): 30-34. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 漆家福, 王德仁, 陈书平, 等. 2006. 兰聊断层的几何学、 运动学特征对东濮凹陷构造样式的影响[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 27(4): 451-459. |
| QI Jia-fu, WANG De-ren, CHEN Shu-ping, et al. 2006. Impact of geometry and kinematics of Lanliao Fault on structural styles in Dongpu sag[J]. Oil & Gas Geology, 27(4): 451-459. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 漆家福, 张一伟, 陆克政, 等. 1995. 渤海湾新生代裂陷盆地的伸展模式及其动力学过程[J]. 石油实验地质, 17(4): 316-323. |
| QI Jia-fu, ZHANG Yi-wei, LU Ke-zheng, et al. 1995. Extensional pattern and dynamic process of the Cenozoic rifting basin in the Bohai Bay[J]. Experimental Petroleum Geology, 17(4): 316-323. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 秦晶晶, 刘保金, 许汉刚, 等. 2020. 地震折射和反射方法研究郯庐断裂带宿迁段的浅部构造特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(2): 505-516. |
| QIN Jing-jing, LIU Bao-jin, XU Han-gang, et al. 2020. Exploration of shallow structural characteristics in the Suqian segment of the Tanlu fault zone based on seismic refraction and reflection method[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(2): 505-516. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 任青芳, 张先康, 张成科, 等. 1998. 汤阴地堑及邻区的壳幔结构与地震危险性[J]. 中国地震, 14(2): 157-166. |
| REN Qing-fang, ZHANG Xian-kang, ZHANG Cheng-ke, et al. 1998. The crust-mantle structure and earthquake risk in Tangyin graben and its adjacent area[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 14(2): 157-166. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 施发剑. 2012. 兰聊断裂带的形成与演化[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学. |
| SHI Fa-jian. 2012. The formation and evolution of Lanliao fault zone[D]. China University of Geosciences, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 孙杰, 王斐斐, 马兴全, 等. 2020. 聊城-兰考断裂中段第四纪活动研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 40(12): 1254-1258. |
| SUN Jie, WANG Fei-fei, MA Xing-quan, et al. 2020. Study on Quaternary activity at the middle part of Liaocheng-Lankao Fault[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 40(12): 1254-1258. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 孙思敏, 彭仕宓, 汪新文. 2003. 东濮凹陷兰聊断层的分段特征及其石油地质意义[J]. 石油学报, 24(3): 26-30. |
| SUN Si-min, PENG Shi-mi, WANG Xin-wen. 2003. Segmentation characteristics of Lanliao Fault in Dongpu Depression[J]. Acta Petroleisinica, 24(3): 26-30. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 王椿镛, 王贵美, 林中洋, 等. 1993. 用深地震反射方法研究邢台地震区地壳细结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 36(4): 445-452. |
| WANG Chun-yong, WANG Gui-mei, LIN Zhong-yang, et al. 1993. A study on fine crustal structure in Xingtai earthquake area based on deep seismic reflection profiling[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 36(4): 445-452. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 王椿镛, 张先康, 吴庆举. 1994. 冀中拗陷内深地震反射剖面揭示的滑脱构造[J]. 科学通报, 39(7): 625-628. |
| WANG Chun-yong, ZHANG Xian-kang, WU Qing-ju. 1994. The detachment structure of Jizhong sag revealed by deep seismic reflection profile[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 39(7): 625-628. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 王光杰, 滕吉文, 张先康. 2007. 鲁西地区的地壳结构及壳内近直立高速异常体的发现[J]. 地球物理学报, 50(5): 1480-1487. |
| WANG Guang-jie, TENG Ji-wen, ZHANG Xian-kang. 2007. The crustal structure of western Shandong and the high velocity body in the crust[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 50(5): 1480-1487. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 魏光兴, 周翠英, 侯海峰, 等. 1985. 聊城-兰考断裂带及其邻区现代地壳应力场与地震活动[J]. 华北地震科学, 3(2): 19-29. |
| WEI Guang-xing, ZHOU Cui-ying, HOU Hai-feng, et al. 1985. Modern crust stress field and seismicity in Liaocheng-Lankao fault zone and its adjacent area[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 3(2): 19-29. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 向宏发, 王学潮, 郝书俭, 等. 2000. 聊城-兰考隐伏断裂的第四纪活动性: 中国东部平原区一条重要的隐伏活动断裂[J]. 中国地震, 16(4): 307-315. |
| XIANG Hong-fa, WANG Xue-chao, HAO Shu-jian, et al. 2000. Activity of Liaocheng-Lankao buried fault in Quaternary[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 16(4): 307-315. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 徐翰. 2018. 渤海湾盆地东濮凹陷形成与演化的数值模拟与构造分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学. |
| XU Han. 2018. Numerical simulation and structural analysis on the formation and evolution of the Dongpu Sag, Bohai Bay Basin[D]. China University of Geosciences, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 徐志萍, 方盛明, 李德庆, 等. 2017a. 利用布格重力资料研究华北裂陷盆地地壳结构特征[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 37(3): 246-250. |
| XU Zhi-ping, FANG Sheng-ming, LI De-qing, et al. 2017a. Characteristics of the crustal structure in North China rift-depression basin using Bouguer gravity data[J]. Journal of Geodesy and Geodynamics, 37(3): 246-250. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 徐志萍, 徐顺强, 姜磊, 等. 2017b. 冀鲁豫交界区流动地磁场总强度异常特征及地震活动性分析[J]. 山西地震, (3): 28-33, 39. |
| XU Zhi-ping, XU Shun-qiang, JIANG Lei, et al. 2017b. Anomaly variation of mobile geomagnetic total intensity and seismicity analysis in juncture area of Heibei, Shangdong and Henan[J]. Earthquake Research in Shanxi, (3): 28-33, 39. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 闫成国, 曹井泉, 陈宇坤, 等. 2020. 深地震反射剖面揭示的天津地区张渤带地壳精细结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(12): 4431-4439. |
| YAN Cheng-guo, CAO Jing-quan, CHEN Yu-kun, et al. 2020. Fine crustal structures of Zhangjiakou-Bohai tectonic zone in Tianjin area revealed by a deep seismic reflection profile[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(12): 4431-4439. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 杨文采, 陈志德. 2005. 中国东部的多重拱弧地震构造[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 35(12): 1120-1130. |
| YANG Wen-cai, CHEN Zhi-de. 2005. Deep seismic structure of multiple arches in eastern China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 35(12): 1120-1130. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 杨文采, 李幼铭. 1993. 应用地震层析成像[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. |
| YANG Wen-cai, LI You-ming. 1993. Applied Seismic Tomography[M]. Geological Publishing House, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 于平, 杨冬, 杨宝俊. 2003. 华北地台聊城-兰考断裂地球物理场基本特征及其构造意义[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 33(1): 106-110. |
| YU Ping, YANG Dong, YANG Bao-jun. 2003. The basic character of geophysical field and the tectonic significance of Liaocheng-Lankao Fault in Northern China Platform[J]. Journal of Jilin University(Earth Science Edition), 33(1): 106-110. (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 张成科, 赵金仁, 任青芳, 等. 1994. 豫北及其外围地区地壳上地幔结构研究[J]. 地震地质, 16(3): 243-253. |
| ZHANG Cheng-ke, ZHAO Jin-ren, REN Qing-fang, et al. 1994. Study on crust and upper mantle structure in north Henan and its surroundings[J]. Seismology and Geology, 16(3): 243-253. (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | 张先康, 赵金仁, 刘国华, 等. 2002. 三河-平谷8.0级大震区震源细结构的深地震反射探测研究[J]. 中国地震, 18(4): 326-336. |
| ZHANG Xian-kang, ZHAO Jin-ren, LIU Guo-hua, et al. 2002. Study on fine crustal structure of the Sanhe-Pinggu earthquake(M8.0)region by deep seismic reflection profiling[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 18(4): 326-336. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | 赵兴兰, 魏光兴. 1984. 聊城-兰考断裂带地震活动图象[J]. 华北地震科学, 2(2): 8-13. |
| ZHAO Xing-lan, WEI Guang-xing. 1984. Seismicity image of Liaocheng-Lankao fault zone[J]. North China Earthquake Sciences, 2(2): 8-13. (in Chinese) |
| [1] | 周铭, 段永红, 檀玉娟, 邱勇. 基于密集台阵的东濮凹陷中北段浅层速度结构[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 517-535. |
| [2] | 酆少英, 刘保金, 李倩, 袁洪克, 朱国军, 田一鸣, 王宏伟, 侯黎华, 邓小娟, 谭雅丽. 深地震反射剖面揭示的华北地块南缘地壳的精细结构[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(3): 581-594. |
| [3] | 翁爱华, 李建平, 范小平, 李斯睿, 韩江涛, 李大俊, 李亚彬, 赵祥阳, 唐裕. 大地电磁测深揭示的1668年郯城8.5级地震震中地壳精细结构[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(2): 396-409. |
| [4] | 刘保金, 曲国胜, 孙铭心, 刘亢, 赵成彬, 徐锡伟, 酆少英, 寇昆朋. 唐山地震区地壳结构和构造:深地震反射剖面结果[J]. 地震地质, 2011, 33(4): 901-912. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||