地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 686-700.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.03.008
赵凌强1,2,3)( ), 詹艳1,2),*(
), 詹艳1,2),*( ), 王庆良3), 孙翔宇1,2), 韩静1,2), 操聪3), 张松3), 蔡妍4)
), 王庆良3), 孙翔宇1,2), 韩静1,2), 操聪3), 张松3), 蔡妍4)
收稿日期:2021-05-12
修回日期:2021-08-08
出版日期:2022-06-20
发布日期:2022-08-02
通讯作者:
詹艳
作者简介:赵凌强, 男, 1988年生, 2020年于中国地震局地质研究所获固体地球物理学专业博士学位, 高级工程师, 研究方向为大地电磁数据处理与解释, E-mail: zhaolingqiang0926@126.com。
基金资助:
ZHAO Ling-qiang1,2,3)( ), ZHAN Yan1,2),*(
), ZHAN Yan1,2),*( ), WANG Qing-liang3), SUN Xiang-yu1,2), HAN Jing1,2), CAO Cong3), ZHANG Song3), CAI Yan4)
), WANG Qing-liang3), SUN Xiang-yu1,2), HAN Jing1,2), CAO Cong3), ZHANG Song3), CAI Yan4)
Received:2021-05-12
Revised:2021-08-08
Online:2022-06-20
Published:2022-08-02
Contact:
ZHAN Yan
摘要:
文中利用相位张量分解技术、 三维NLCG反演方法对一条跨过1303年洪洞8级地震区、 长160km的大地电磁剖面的数据进行了分解和反演计算, 再结合研究区及其附近的形变场、 最新地震地质和地球物理调查结果以及2008年1月—2012年12月的小地震精定位结果等资料进行综合分析。研究表明, 霍山山前断裂是研究区内明显的大型电性边界带, 在中深部表现为低阻特征, 贯穿了整个地壳尺度, 该断裂为NNE走向的右旋正断裂, 可能是划分鄂尔多斯地块和华北地块的基底断裂。以霍山山前断裂为界, 西侧鄂尔多斯地块表现为层状的稳定构造环境, 而东侧华北地块的中下地壳岩石圈破坏严重且存在减薄的趋势。大地电磁探测结果支持1303年洪洞8级地震的发震断裂为霍山山前断裂的观点, 地震可能发生在霍山山前断裂下方的低阻体中, 震源深度可能介于10~20km之间。1303年洪洞8级地震的孕震环境可能受多重因素控制, 研究区东侧中下地壳可能存在的软流圈物质不断上涌引起了华北地块的区域拉张作用, 进而导致霍山山前断裂发生倾向滑动可能是地震的主控因素。
中图分类号:
赵凌强, 詹艳, 王庆良, 孙翔宇, 韩静, 操聪, 张松, 蔡妍. 大地电磁数据揭示的1303年洪洞8级地震区精细结构[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 686-700.
ZHAO Ling-qiang, ZHAN Yan, WANG Qing-liang, SUN Xiang-yu, HAN Jing, CAO Cong, ZHANG Song, CAI Yan. THE SEISMOGENIC STRUCTURE OF THE 1303 HONGTONG M8 EARTHQUAKE INFERRED FROM MAGNETOTELLURIC IMAGING[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(3): 686-700.
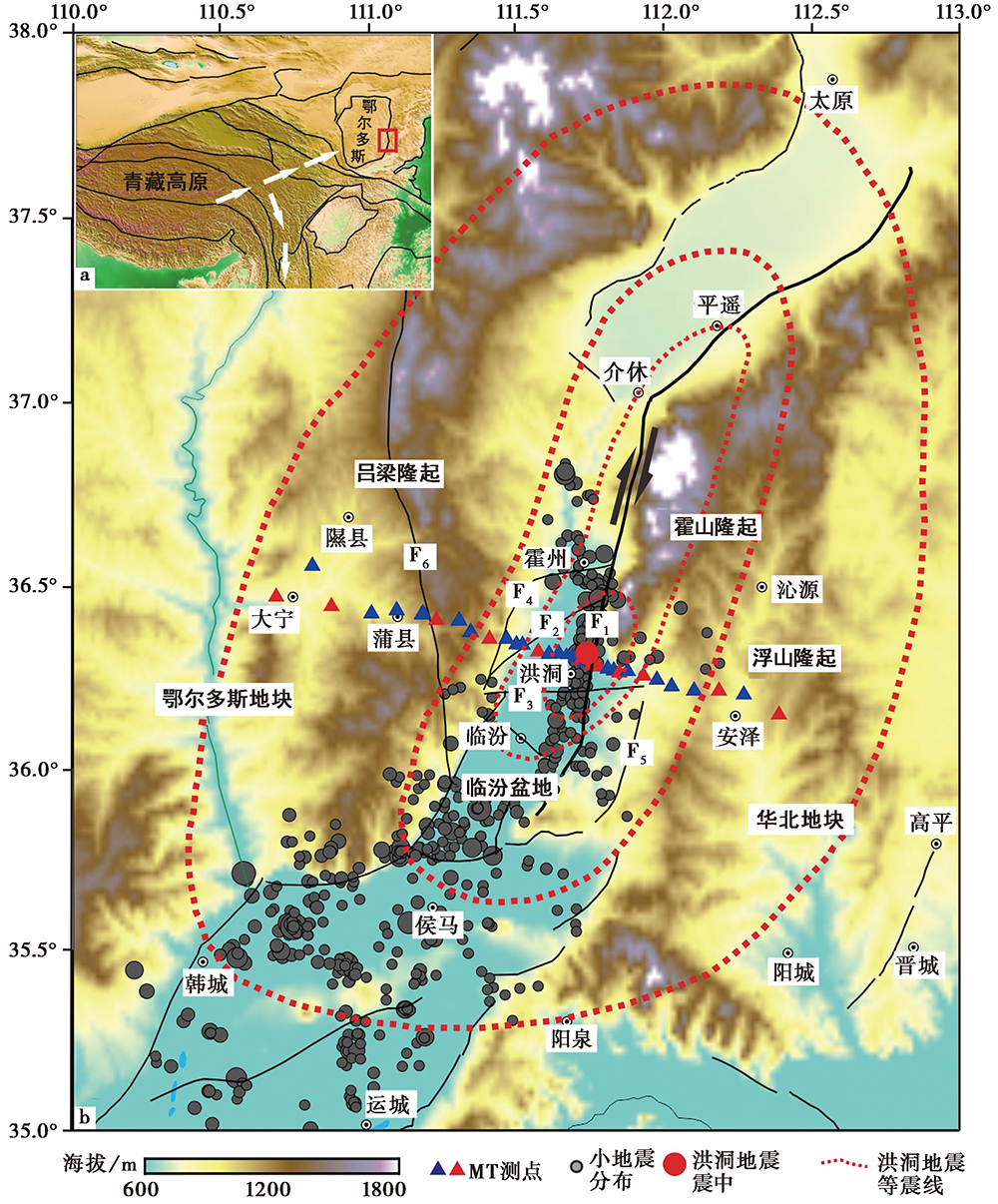
图 1 a 区域构造简图; b 研究区断裂和大地电磁实测点位图 F1霍山山前断裂; F2万安断裂; F3苏堡-魏村断裂; F4贾村断裂; F5浮山山前断裂;F6离石断裂。 1303年洪洞8级地震等震线分布图修改自高孟潭等(2004)和Xu等(2018)
Fig. 1 The tectonic outline map(a), the faults and magnetotelluric measurement sites of the study area(b).
| [1] | 蔡军涛, 陈小斌, 赵国泽. 2010. 大地电磁资料精细处理和二维反演解释技术研究(一): 阻抗张量分解与构造维性分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(10): 2516—2526. |
| CAI Jun-tao, CHEN Xiao-bin, ZHAO Guo-ze. 2010. Refined techniques for data processing and two-dimensional inversion in magnetotelluricⅠ: Tensor decomposition and dimensionality analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(10): 2516—2526 (in Chinese). | |
| [2] | 陈小斌, 臧绍先, 魏荣强. 2011. 稳定的鄂尔多斯地块在整体运动吗?[J]地球物理学报, 54(7): 1750—1757. |
| CHEN Xiao-bin, ZANG Shao-xian, WEI Rong-qiang. 2011. Is the stable Ordos block migrating as an entire block?[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(7): 1750—1757 (in Chinese). | |
| [3] | 陈小斌, 赵国泽, 詹艳. 2004. MT资料处理与解释的Windows可视化集成系统[J]. 石油地球物理勘探, 39(S1): 11—16. |
| CHEN Xiao-bin, ZHAO Guo-ze, ZHAN Yan. 2004. A visual integrated windows system for MT data processing and interpretation[J]. Oil Geophysical Prospecting, 39(S1): 11—16 (in Chinese). | |
| [4] | 陈兆辉, 王椿镛, 楼海. 2018. 鄂尔多斯地块地壳上地幔速度结构及构造意义[J]. 科学通报, 63(3): 327—339. |
| CHEN Zhao-hui, WANG Chun-yong, LOU Hai. 2018. Crust and upper mantle velocity structure beneath the Ordos Block and its tectonic significance[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(3): 327—339 (in Chinese). | |
| [5] | 邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 2003. 中国活动构造与地震活动[J]. 地学前缘, 10(S1): 66—73. |
| DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Pei-zhen, RAN Yong-kang, et al. 2003. Active tectonics and earthquake activities in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(S1): 66—73 (in Chinese). | |
| [6] | 高孟潭, 金学申, 安卫平, 等. 2004. 1303年洪洞8级地震GIS 系统与震害分布特征分析[J]. 地震学报, 26(4): 363—368. |
| GAO Meng-tan, JIN Xue-shen, AN Wei-ping, et al. 2004. The GIS and analysis of earthquake damage distribution of the 1303 Hongdong M=8 earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 26(4): 363—368 (in Chinese). | |
| [7] | 国家地震局“鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系”课题组. 1988. 鄂尔多斯周缘活动断裂系[M]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| The Research Group on “Active Fault System around Orods Massif”, State Seismological Bureau. 1988. Active Fault System around Massif[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing (in Chinese). | |
| [8] | 胡新亮, 刁桂苓, 高景春, 等. 2002. 用现今小震推断洪洞、 临汾2次历史大震的震源断层[J]. 中国地震, 18(1): 76—85. |
| HU Xin-liang, DIAO Gui-ling, GAO Jing-chun, et al. 2002. Application of present small earthquakes to infer the focal faults of two large historical earthquakes in Hongdong and Linfen, Shanxi Province[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 18(1): 76—85 (in Chinese). | |
| [9] | 李晨晶, 白登海, 薛帅, 等. 2017. 鄂尔多斯地块深部岩石圈电性结构研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(5): 1788—1799. |
| LI Chen-jing, BAI Deng-hai, XUE Shuai, et al. 2017. A magnitotelluric study of the deep electric structure beneath the Ordos Block[J]. Chinese Journal Geophysics, 60(5): 1788—1799 (in Chinese). | |
| [10] | 李自红, 刘保金, 袁洪克, 等. 2014. 临汾盆地地壳精细结构和构造: 地震反射剖面结果[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(5): 1487—1497. |
| LI Zi-hong, LIU Bao-jin, YUAN Hong-ke, et al. 2014. Fine crustal structure and tectonics of Linfen Basin from the results of seismic reflect profile[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(5): 1487—1497 (in Chinese). | |
| [11] | 刘钟尹, 陈小斌, 蔡军涛. 2017. toPeak: 一个大地电磁三维反演的可视化客户端软件[C]. 第十三届中国国际地球物理学术讨论会. |
| LIU Zhong-yin, CHEN Xiao-bin, CAI Jun-tao. 2017. toPeak: A visual client software for magnetotelluric three-dimensional inversion[C]//13th China International Geophysical Symposium (in Chinese). | |
| [12] | 江娃利, 邓起东, 徐锡伟, 等. 2004. 1303年山西洪洞8级地震地表破裂带[J]. 地震学报, 26(4): 355—362. |
| JIANG Wa-li, DENG Qi-dong, XU Xi-wei, et al. 2004. Structure rupture zone of the 1303 Hongdong M=8 earthquake, Shanxi Province[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 26(4): 355—362 (in Chinese). | |
| [13] | 孟宪梁, 于慎谔, 奚云. 1985. 山西洪洞8级地震形变遗迹研究[J]. 地震地质, 7(4): 1—10. |
| MENG Xian-liang, YU Shen-e, XI Yun. 1985. The investigations of deformation traces of MS=8.0 earthquake in Hongdong, Shanxi Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 7(4): 1—10 (in Chinese). | |
| [14] |
孙翔宇, 詹艳, 赵凌强, 等. 2020. 东昆仑断裂带东端和2017年九寨沟7.0级地震区深部电性结构探测[J]. 地震地质, 42(1): 182—197. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.01.012.
DOI |
| SUN Xiang-yu, ZHAN Yan, ZHAO Ling-qiang, et al. 2020. Electrical structure of the 2017 MS7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake region and the eastern terminus of the east Kunlun Fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(1): 182—197 (in Chinese). | |
| [15] | 汤吉, 詹艳, 赵国泽, 等. 2005. 青藏高原东北缘玛沁—兰州—靖边剖面地壳上地幔电性结构研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 48(5): 1205—1216. |
| TANG Ji, ZHAN Yan, ZHAO Guo-ze, et al. 2005. Electrical structure of crust and upper mantle in Maqin-Lanzhou-Jingbian section, northeastern margin of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 48(5): 1205—1216. | |
| [16] | 王鑫, 詹艳, 赵国泽, 等. 2010. 鄂尔多斯断块西缘构造带北段深部电性结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 50(3): 595—604. |
| WANG Xin, ZHAN Yan, ZHAO Guo-ze, et al. 2010. Deep electric structure beneath the northern section of the western margin of the Ordos Basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 50(3): 595—604 (in Chinese). | |
| [17] |
翁爱华, 李建平, 范小平, 等. 2018. 大地电磁测深揭示的1668 年郯城8.5级地震震中地壳精细结构[J]. 地震地质, 40(2): 396—409. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.02.008.
DOI |
| WENG Ai-hua, LI Jian-ping, FAN Xiao-ping, et al. 2018. Fine electrical structure beneath the epicenter of 1668 Tancheng MS8.5 earthquake revealed by MT sounding[J]. Seismology and Geology, 40(2): 396—409 (in Chinese). | |
| [18] | 谢新生, 江娃利, 王焕贞, 等. 2004. 山西太谷断裂带全新世活动及其与1303年洪洞8级地震的关系[J]. 地震学报, 26(3): 281—293. |
| XIE Xin-sheng, JIANG Wa-li, WANG Huan-zhen, et al. 2004. Holocene activities of the Taigu fault zone, Shanxi Province, in relation to the 1303 Hongdong M=8 earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 26(3): 281—293 (in Chinese). | |
| [19] | 许林斌, 魏文博, 金胜, 等. 2017. 鄂尔多斯地块北部至阴山造山带深部电性结构特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(2): 575—584. |
| XU Lin-bin, WEI Wen-bo, JIN Sheng, et al. 2017. Study of deep electrical structure along a profile from northern Ordos block to Yinshan orogenic belt[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(2): 575—584 (in Chinese). | |
| [20] | 徐锡伟, 邓起东. 1990. 山西霍山山前断裂晚第四纪活动特征和1303年洪洞8级地震[J]. 地震地质, 12(1): 21—30. |
| XU Xi-wei, DENG Qi-dong. 1990. The features of Late Quaternary activity of the piedmont fault of Mt Huoshan Shanxi Province and 1303 Hongdong earthquake(MS=8)[J]. Seismology and Geology, 12(1): 21—30 (in Chinese). | |
| [21] | 徐岳仁. 2012. 山西霍山山前断裂带晚第四纪活动特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. |
| XU Yue-ren. 2012. A study on the late Quaternary faulting of the Huoshan piedmont fault zone in the central Shanxi faulted basin belt[D]. Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing (in Chinese). | |
| [22] | 詹艳, 赵国泽, Unsworth M, 等. 2013. 龙门山断裂带西南段4.20芦山7.0级地震区的深部结构和孕震环境[J]. 科学通报, 58(20): 1917—1924. |
| ZHAN Yan, ZHAO Guo-ze, Unsworth M, et al. 2013. Deep structure beneath the southwestern section of the Longmenshan fault zone and seismogenetic context of the 4·20 MS7.0 earthquake[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 58(20): 1917—1924 (in Chinese). | |
| [23] | 詹艳, 赵国泽, 王继军, 等. 2008. 1927年古浪8级大震区及其周边地块的深部电性结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(2): 220—229. |
| ZHAN Yan, ZHAO Guo-ze, WANG Ji-jun, et al. 2008. Deep electric structure beneath the epicenter of the 1927 Gulang M8 earthquake and its adjacent areas from magnetotelluric sounding[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(2): 220—229 (in Chinese). | |
| [24] | 赵国泽, 詹艳, 王立凤, 等. 2010. 鄂尔多斯断块地壳电性结构[J]. 地震地质, 32(3): 345—359. |
| ZHAO Guo-ze, ZHAN Yan, WANG Li-feng, et al. 2010. Electric structure of the crust beneath the Ordos fault block[J]. Seismology and Geology, 32(3): 345—359 (in Chinese). | |
| [25] |
赵凌强, 詹艳, 赵国泽, 等. 2015. 基于深部电性结构特征的2013年甘肃岷县漳县 MS6.6 地震孕震环境探讨[J]. 地震地质, 37(2): 541—554. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.02.016.
DOI |
| ZHAO Ling-qiang, ZHAN Yan, ZHAO Guo-ze, et al. 2015. The seismogenic environment of the 2013 Minxian-Zhangxian MS6.6 earthquake based on the deep electrical structure[J]. Seismology and Geology, 37(2): 541—554 (in Chinese). | |
| [26] | 赵凌强, 詹艳, 孙翔宇, 等. 2019. 利用大地电磁技术揭示2016年1月21日青海门源 MS6.4 地震隐伏地震构造和孕震环境[J]. 地球物理学报, 62(6): 2088—2100. |
| ZHAO Ling-qiang, ZHAN Yan, SUN Xiang-yu, et al. 2019. The hidden seismogenic structure and dynamic environment of the 21 January Menyuan, Qinghai, MS6.4 earthquake inferred from magnetotelluric imaging[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 62(6): 2088—2100 (in Chinese). | |
| [27] | 赵凌强, 詹艳, 王庆良, 等. 2020. 祁连山东端冷龙岭隆起及邻区深部电性结构与孕震构造背景[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(3): 1014—1025. |
| ZHAO Ling-qiang, ZHAN Yan, WANG Qing-liang, et al. 2020. The deep electrical structure and seismogenic background of Lenglongling uplift and its adjacent areas in the eastern end of Qilian Mountains[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(3): 1014—1025 (in Chinese). | |
| [28] |
赵凌强, 詹艳, 周本刚, 等. 2018. 1631年常德历史地震区深部结构的大地电磁探测研究[J]. 地震地质, 40(1): 155—170. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.01.012.
DOI |
| ZHAO Ling-qiang, ZHAN Yan, ZHOU Ben-gang, et al. 2018. Deep structure beneath the 1631 Changde, Hunan M6 earthquake area derived from magnetotelluric sounding[J]. Seismology and Geology, 40(1): 155—170 (in Chinese). | |
| [29] |
Bibby H M, Caldwell T G, Brown C. 2005. Determinable and non-determinable parameters of galvanic distortion in magnetotellurics[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 163(3): 915—930.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Caldwell T G, Bibbly H M, Brown C. 2004. The magnetotelluric phase tensor[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 158(2): 457—469.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Chave A D, Thomson D J, Ander M E. 1987. On the robust estimation of power spectra, coherences and transfer functions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 92(B1): 633—648.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Egbert G D, Booker J R. 1986. Robust estimation of geomagnetic transfer functions[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 87(1): 173—194. |
| [33] |
Egbert G D, Kelbert A. 2012. Computational recipes for electromagnetic inverse problems[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 189(1): 251—267.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Hao M, Wang Q L, Cui D X, et al. 2016. Present-day crustal vertical motion around the Ordos block constrained by precise leveling and GPS data[J]. Surveys in Geophysics, 37: 923—936.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
Heise W T, Caldwell G, Bibby H M, et al. 2008. Three-dimensional modelling of magnetotelluric data from the Rotokawa geothermal field, Taupo volcanic zone, New Zealand[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 173:740—750.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Rodi W, Mackie R L. 2001. Nonlinear conjugate gradients algorithm for 2-D magnetotelluric inversion[J]. Geophysics, 66(1): 174—187.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Sun X Y, Zhan Y, Unsworth M, et al. 2020. 3-D magnetotelluric imaging of the easternmost Kunlun Fault: Insights into strain partitioning and the seismotectonics of the Jiuzhaigou MS7.0 earthquake[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 125: e2020JB019731. |
| [38] | Sun X Y, Zhan Y, Zhao L Q, et al. 2019. Electrical structure of the Kunlun-Qinling fault system and 2017 M7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake inferred from 3-D inversion of magnetotelluric data[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 181:10391. |
| [39] |
Xu Y R, He H L, Deng Q D, et al. 2018. The CE 1303 Hongdong earthquake and the Huoshan piedmont fault, Shanxi graben: Implications for magnitude limits of normal fault earthquakes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123(4): 3098—3121.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Zhang H Q, Huang Q H, Zhao G Z, et al. 2016. Three-dimensional conductivity model of crust and uppermost mantle at the northern Trans-North China Orogen: Evidence for a mantle source of Datong volcanoes[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 453: 182—192.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Zhang Y G, Zheng W J, Wang Y J, et al. 2018. Contemporary deformation of the North China Plain from global positioning system data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 45(4): 1851—1859.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Zhao G Z, Unsworth M J, Zhan Y, et al. 2012. Crustal structure and rheology of the Longmenshan and Wenchuan MW7.9 earthquake epicentral area from magnetotelluric data[J]. Geology, 40(12): 1139—1142.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 赵凌强, 胡亚轩, 王庆良, 祝意青, 操聪, 李仲巍, 綦伟, 汶宇龙. 吉林龙岗火山区深部电性结构特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 845-858. |
| [2] | 董泽义, 汤吉, 赵国泽, 陈小斌, 崔腾发, 韩冰, 姜峰, 王立凤. 首都圈极低频电磁台网区地下电性结构探测[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 649-668. |
| [3] | 韩静, 詹艳, 孙翔宇, 赵国泽, 刘雪华, 包雨鑫, 孙建宝, 彭远黔. 强电磁干扰环境下的大地电磁数据特征及处理[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 736-752. |
| [4] | 张赟昀, 王培杰, 陈小斌, 詹艳, 韩冰, 王立凤, 赵国泽. 强干扰环境下的大地电磁时间序列处理过程[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 786-801. |
| [5] | 刘钟尹, 陈小斌, 蔡军涛, 崔腾发, 赵国泽, 汤吉, 欧阳飚. 大地电磁三维反演云计算系统toPeak的设计与实现[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 802-820. |
| [6] | 阮帅, 汤吉, 董泽义, 王立凤, 邓琰, 韩冰. 基于三维大地电磁AR-QN反演的长白山天池火山区电性结构[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(6): 1282-1300. |
| [7] | 孙翔宇, 詹艳, 赵国泽, 赵凌强, 邓琰, 胡亚轩, 胡久常, 向小娟. 琼东北马鞍岭-雷虎岭火山区深部岩浆系统大地电磁三维探测[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(3): 640-653. |
| [8] | 孙翔宇, 詹艳, 赵凌强, 陈小斌, 李陈侠, 孙建宝, 韩静, 崔腾发. 东昆仑断裂带东端和2017年九寨沟7.0级地震区深部电性结构探测[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(1): 182-197. |
| [9] | 姜峰, 陈小斌, 董泽义, 崔腾发, 刘钟尹, 王培杰. 利用单剖面大地电磁三维反演识别沙德和玉农希断裂[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(6): 1444-1463. |
| [10] | 张继红, 赵国泽, 董泽义, 王立凤, 韩冰, 王庆林, 唐廷梅, 王梅. 郯庐断裂带安丘、莒县电磁台地壳电性结构研究[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(5): 1239-1253. |
| [11] | 徐岳仁, 何宏林, 李文巧, 张伟恒, 田勤俭. 1303年洪洞地震宏观震中修订的新证据[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(5): 945-966. |
| [12] | 赵凌强, 詹艳, 王庆良, 孙翔宇, 杨皓, 陈小斌. 1954年甘肃民勤7级地震区深部电性结构特征及地震构造环境研究[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(3): 552-565. |
| [13] | 韩江涛, 王天琪, 刘文玉, 刘国兴, 韩松, 刘立家. 阿尔山火山群深部“拱桥式”岩浆系统及其稳定性分析[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(3): 590-610. |
| [14] | 周耀明, 朱文斌, 陈正乐, 朱炳玉, 薛峰. 准噶尔盆地克-百断裂带火山岩分布特征的重磁资料解释[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(3): 641-655. |
| [15] | 翁爱华, 李建平, 范小平, 李斯睿, 韩江涛, 李大俊, 李亚彬, 赵祥阳, 唐裕. 大地电磁测深揭示的1668年郯城8.5级地震震中地壳精细结构[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(2): 396-409. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||