地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (3): 669-685.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.03.007
范晔1,2)( ), 汤吉1),*(
), 汤吉1),*( ), 缪杰3), 叶青2), 崔腾发4), 董泽义1), 韩冰1), 孙贵成5)
), 缪杰3), 叶青2), 崔腾发4), 董泽义1), 韩冰1), 孙贵成5)
收稿日期:2021-10-12
修回日期:2021-11-25
出版日期:2022-06-20
发布日期:2022-08-02
通讯作者:
汤吉
作者简介:范晔, 女, 1987年生, 2022年于中国地震局地质研究所获固体地球物理学专业博士学位, 高级工程师, 研究方向为地震电磁数据处理与解释, 电话: 010-59959160, E-mail: fanye_1987@163.com。
基金资助:
FAN Ye1,2)( ), TANG Ji1),*(
), TANG Ji1),*( ), MIAO Jie3), YE Qing2), CUI Teng-fa4), DONG Ze-yi1), HAN Bing1), SUN Gui-cheng5)
), MIAO Jie3), YE Qing2), CUI Teng-fa4), DONG Ze-yi1), HAN Bing1), SUN Gui-cheng5)
Received:2021-10-12
Revised:2021-11-25
Online:2022-06-20
Published:2022-08-02
Contact:
TANG Ji
摘要:
文中使用时间域波形分析、 滑动傅式去年变分析、 归一化变化速率方法和矢量方位角方法处理分析了2020年7月12日古冶 MS5.1 地震震中距400km范围内的地电阻率、 地电场、 极低频观测数据。在排除各台站仪器运行、 台站观测环境、 空间电磁活动等影响因素后, 认为有6个地电阻率台站于震前出现了“趋势性下降—加速下降—震后恢复”的变化过程, 7个地电阻率台站在震前1a内的归一化变化速率超过±2.4阈值; 滦县地电场NS和NW向测道于震前3个月出现先下降后回升的变化, 且矢量方位角在震前向古冶地震方向偏移, 后恢复为沿滦县-乐亭断裂方向; 文安和丰宁极低频台清晰地记录到16hz天然源磁场同震变化, 磁场垂直分量的变化超过水平分量的2倍, 由于台站的地下结构存在巨大差异, 2个台站的电场观测值差别较大, 且电场同震扰动淹没在背景噪声中。文中利用首都圈极低频台站观测数据反演了地下电性结构, 发现古冶地震的震源位于电性发生变化的边界附近, 北边为高阻区, 西南方向为低阻区, 宝坻和文安处于局部低阻区, 并据此初步分析了古冶地震的电磁现象特征。针对异常空间选择性问题, 认为可能与京津唐地区NEE和NW向2个主要共轭构造方向有关。对地震电磁异常机理开展研究时, 应从地震电磁同震现象入手, 从地震电磁信号产生的源和传播路径2方面展开相关工作。
中图分类号:
范晔, 汤吉, 缪杰, 叶青, 崔腾发, 董泽义, 韩冰, 孙贵成. 2020年7月12日唐山古冶5.1级地震的电磁现象[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 669-685.
FAN Ye, TANG Ji, MIAO Jie, YE Qing, CUI Teng-fa, DONG Ze-yi, HAN Bing, SUN Gui-cheng. THE ELECTROMAGNETIC ANOMALY OF TANGSHAN GUYE MS5.1 EARTHQUAKE ON JULY 12, 2020[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(3): 669-685.
| 测 项 | 区域 台网 | 台站 | 震中距 /km | 仪器型号 | 数据可用性 | 异常变化 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地电阻率 | 河北 | 后土桥 | 55.9 | ZD8M | 可用 | NS、 EW趋势性下降 | |
| 天津 | 宝坻新台 | 86.2 | ZD8M | 可用 | 2020-06归一化速率超阈值 | ||
| 天津 | 塘沽 | 105.0 | ZD8M | 基本可用 | NS趋势性下降 2019-11归一化速率超阈值 | 城市轻轨运行 | |
| 北京 | 平谷马坊 | 126.5 | ZD8BI | 可用 | NS趋势性下降 2019-10归一化速率超阈值 | 城市轻轨运行 | |
| 北京 | 通州西集 | 129.8 | ZD8MI | 基本可用 | 城市轻轨运行 | ||
| 天津 | 青光 | 135.6 | ZD8BI | 可用 | 2019-07归一化速率超阈值 | ||
| 天津 | 徐庄子 | 163.9 | ZD8M | 基本可用 | 2020-06 NS、 EW相对变化3.64% | 2019年底 NS测道外线路挖断 | |
| 河北 | 沧县兴济 | 190.3 | ZD8M | 可用 | 2020-02归一化速率超阈值 | ||
| 北京 | 延庆张庄 | 222.0 | ZD8M | 可用 | EW趋势性下降 | ||
| 内蒙古 | 赤峰 | 281.0 | ZD8BI | 基本可用 | |||
| 辽宁 | 锦州义县 | 309.1 | ZD8M | 基本可用 | |||
| 内蒙古 | 宝昌 | 351.9 | ZD8BI | 基本可用 | 测区内有施工影响 | ||
| 河北 | 阳原 | 367.4 | ZD8M | 可用 | NW趋势性下降 2020-05归一化速率超阈值 | ||
| 辽宁 | 台安 | 383.3 | ZD8B | 不可用 | 2019-04仪器停测 | ||
| 辽宁 | 阜新 | 388.6 | ZD8M | 基本可用 | 2019-10 EW、 NW 归一化速率超阈值 | 工厂漏电干扰 | |
| 地电场 | 河北 | 滦县 | 35.3 | ZD9A-2B | 可用 | 2020-04 NSL、 NWL趋势性下降 | |
| 河北 | 后土桥 | 55.9 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 漏电干扰2019-12-26 更换NS长极距电极 | ||
| 天津 | 宝坻新台 | 86.2 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 设备漏电 | ||
| 北京 | 通州西集 | 129.8 | ZD9A-Ⅱ | 不可用 | 2019-11-17后无数 | ||
| 天津 | 静海 | 163.2 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 测区地铁干扰 | ||
| 天津 | 徐庄子 | 163.9 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 测区地铁干扰 | ||
| 河北 | 沧县兴济 | 190.3 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 2019-11-26启用新电极 | ||
| 山东 | 无棣大山 | 209.4 | GEF-2 | 不可用 | 2019年换外线路, 2020-07更换电极 | ||
| 北京 | 延庆张庄 | 222.0 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | |||
| 辽宁 | 锦州义县 | 309.1 | ZD9A-Ⅱ | 基本可用 | |||
| 内蒙古 | 宝昌 | 351.9 | ZD9A-Ⅱ | 基本可用 | |||
| 河北 | 阳原 | 367.4 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | |||
| 山东 | 安丘 | 387.5 | ZD9A-Ⅱ | 基本可用 | |||
| 辽宁 | 阜新 | 388.6 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 工厂漏电 | ||
| 极低频 | 天津 | 宝坻 | 86.4 | ADU-07e | 不可用 | 服务器原因数据不全 | |
| 河北 | 文安 | 198.2 | ADU-07e | 可用 | 2020-07-12同震扰动 | ||
| 山东 | 大山 | 207.7 | ADU-07e | 不可用 | 服务器原因数据不全 | ||
| 河北 | 丰宁 | 219.3 | ADU-07e | 可用 | 2020-07-12同震扰动 | ||
| 河北 | 怀来 | 254.9 | ADU-07e | 可用 | |||
| 辽宁 | 大连 | 288.9 | ADU-07e | 不可用 | 服务器原因数据不全 | ||
| 辽宁 | 营口 | 370.0 | ADU-07e | 不可用 | 服务器原因数据不全 | ||
| 山东 | 莱阳 | 372.4 | ADU-07e | 可用 | |||
| 山东 | 安丘 | 387.7 | ADU-07e | 不可用 | 服务器原因数据不全 |
表1 地电台网运行情况
Table 1 The operation status of the geo-electrical network
| 测 项 | 区域 台网 | 台站 | 震中距 /km | 仪器型号 | 数据可用性 | 异常变化 | 备注 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 地电阻率 | 河北 | 后土桥 | 55.9 | ZD8M | 可用 | NS、 EW趋势性下降 | |
| 天津 | 宝坻新台 | 86.2 | ZD8M | 可用 | 2020-06归一化速率超阈值 | ||
| 天津 | 塘沽 | 105.0 | ZD8M | 基本可用 | NS趋势性下降 2019-11归一化速率超阈值 | 城市轻轨运行 | |
| 北京 | 平谷马坊 | 126.5 | ZD8BI | 可用 | NS趋势性下降 2019-10归一化速率超阈值 | 城市轻轨运行 | |
| 北京 | 通州西集 | 129.8 | ZD8MI | 基本可用 | 城市轻轨运行 | ||
| 天津 | 青光 | 135.6 | ZD8BI | 可用 | 2019-07归一化速率超阈值 | ||
| 天津 | 徐庄子 | 163.9 | ZD8M | 基本可用 | 2020-06 NS、 EW相对变化3.64% | 2019年底 NS测道外线路挖断 | |
| 河北 | 沧县兴济 | 190.3 | ZD8M | 可用 | 2020-02归一化速率超阈值 | ||
| 北京 | 延庆张庄 | 222.0 | ZD8M | 可用 | EW趋势性下降 | ||
| 内蒙古 | 赤峰 | 281.0 | ZD8BI | 基本可用 | |||
| 辽宁 | 锦州义县 | 309.1 | ZD8M | 基本可用 | |||
| 内蒙古 | 宝昌 | 351.9 | ZD8BI | 基本可用 | 测区内有施工影响 | ||
| 河北 | 阳原 | 367.4 | ZD8M | 可用 | NW趋势性下降 2020-05归一化速率超阈值 | ||
| 辽宁 | 台安 | 383.3 | ZD8B | 不可用 | 2019-04仪器停测 | ||
| 辽宁 | 阜新 | 388.6 | ZD8M | 基本可用 | 2019-10 EW、 NW 归一化速率超阈值 | 工厂漏电干扰 | |
| 地电场 | 河北 | 滦县 | 35.3 | ZD9A-2B | 可用 | 2020-04 NSL、 NWL趋势性下降 | |
| 河北 | 后土桥 | 55.9 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 漏电干扰2019-12-26 更换NS长极距电极 | ||
| 天津 | 宝坻新台 | 86.2 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 设备漏电 | ||
| 北京 | 通州西集 | 129.8 | ZD9A-Ⅱ | 不可用 | 2019-11-17后无数 | ||
| 天津 | 静海 | 163.2 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 测区地铁干扰 | ||
| 天津 | 徐庄子 | 163.9 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 测区地铁干扰 | ||
| 河北 | 沧县兴济 | 190.3 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 2019-11-26启用新电极 | ||
| 山东 | 无棣大山 | 209.4 | GEF-2 | 不可用 | 2019年换外线路, 2020-07更换电极 | ||
| 北京 | 延庆张庄 | 222.0 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | |||
| 辽宁 | 锦州义县 | 309.1 | ZD9A-Ⅱ | 基本可用 | |||
| 内蒙古 | 宝昌 | 351.9 | ZD9A-Ⅱ | 基本可用 | |||
| 河北 | 阳原 | 367.4 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | |||
| 山东 | 安丘 | 387.5 | ZD9A-Ⅱ | 基本可用 | |||
| 辽宁 | 阜新 | 388.6 | ZD9A-2B | 基本可用 | 工厂漏电 | ||
| 极低频 | 天津 | 宝坻 | 86.4 | ADU-07e | 不可用 | 服务器原因数据不全 | |
| 河北 | 文安 | 198.2 | ADU-07e | 可用 | 2020-07-12同震扰动 | ||
| 山东 | 大山 | 207.7 | ADU-07e | 不可用 | 服务器原因数据不全 | ||
| 河北 | 丰宁 | 219.3 | ADU-07e | 可用 | 2020-07-12同震扰动 | ||
| 河北 | 怀来 | 254.9 | ADU-07e | 可用 | |||
| 辽宁 | 大连 | 288.9 | ADU-07e | 不可用 | 服务器原因数据不全 | ||
| 辽宁 | 营口 | 370.0 | ADU-07e | 不可用 | 服务器原因数据不全 | ||
| 山东 | 莱阳 | 372.4 | ADU-07e | 可用 | |||
| 山东 | 安丘 | 387.7 | ADU-07e | 不可用 | 服务器原因数据不全 |
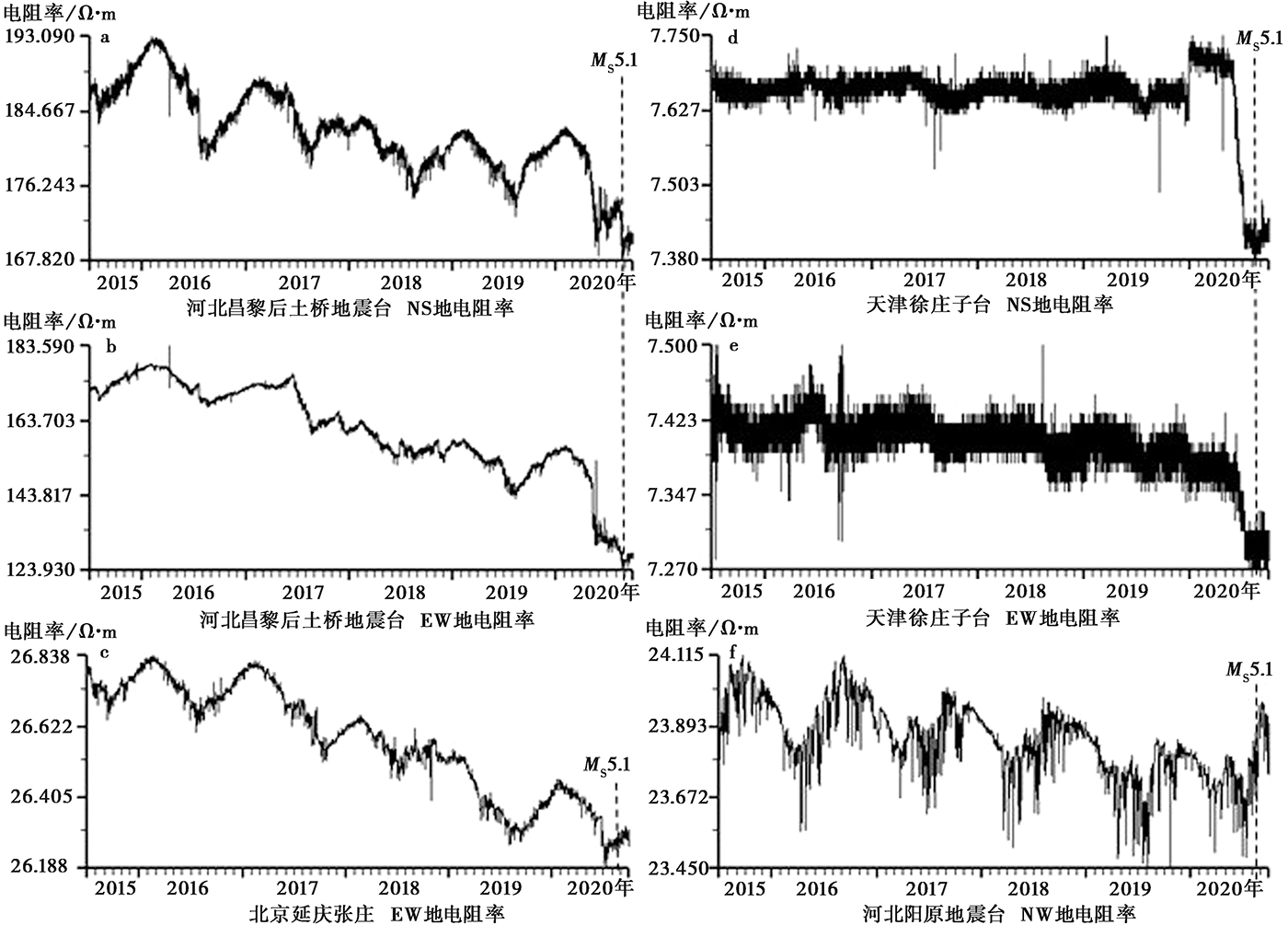
图 2 地电阻率原始(a、 b、 d、 e)和日均值(c、 f)时间序列的趋势性下降变化曲线
Fig. 2 The original(a, b, d, e) and the daily average(c, f) time series of geo-resistivity decreasing trend curve.
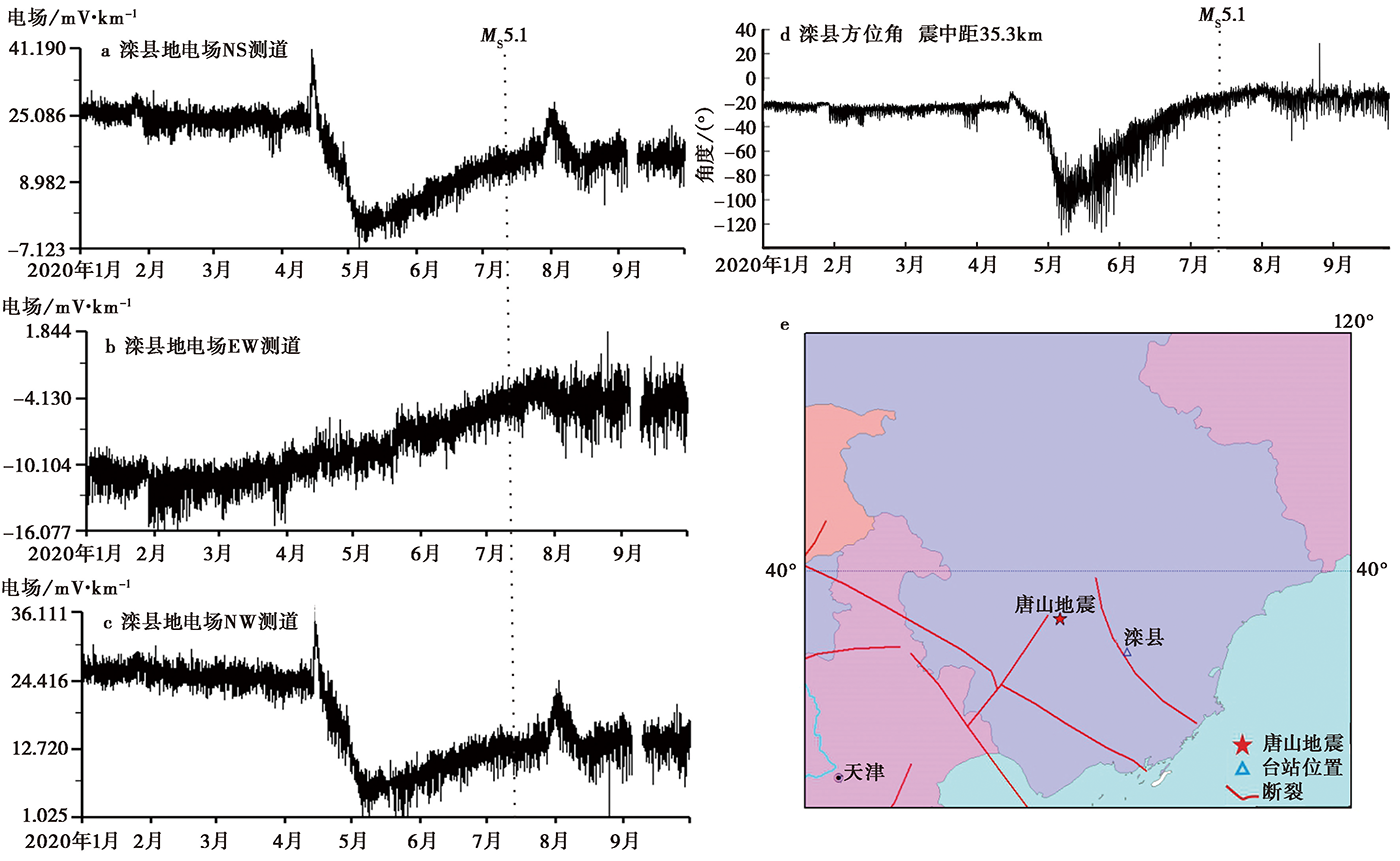
图 5 滦县台长极距测道的地电场时间序列曲线(a—c)、 矢量方位角(d)和台站点位图(e)
Fig. 5 The geo-electric field time series(a—c), azimuth angle(d)and the station map(e)of Luanxian station.
| [1] | 安张辉, 杜学彬, 谭大诚, 等. 2013. 四川芦山 MS7.0 和汶川 MS8.0 地震前地电场变化研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(11): 3868—3876. |
| AN Zhang-hui, DU Xue-bin, TAN Da-cheng, et al. 2013. Study on the geoelectric field variation of Sichuan Lushan MS7.0 and Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(11): 3868—3876 (in Chinese). | |
| [2] | 丁鉴海. 2009. 地磁日变地震预报方法及其震例研究[M]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| DING Jian-hai. 2009. Geomagnetic Diurnal Variation Earthquake Prediction Method and Earthquake Cases[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing (in Chinese). | |
| [3] | 杜学彬, 李宁, 叶青, 等. 2007. 强地震附近视电阻率各向异性变化的原因[J]. 地球物理学报, 50(6): 1802—1810. |
| DU Xue-bin, LI Ning, YE Qing, et al. 2007. A possible reason for the anisotropic changes in apparent resistivity near the focal region of strong earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 50(6): 1802—1810 (in Chinese). | |
| [4] | 杜学彬, 孙君嵩, 陈军营. 2017. 地震预测中的地电阻率数据处理方法[J]. 地震学报, 39(4): 531—548. |
| DU Xue-bin, SUN Jun-song, CHEN Jun-ying. 2017. Processing methods for the observation data of georesistivity in earthquake prediction[J]. Acta Seisologica Sinica, 39(4): 531—548 (in Chinese). | |
| [5] | 范晔, 崔腾发, 杜学彬, 等. 2020a. 中国大陆地电场日变化特征及影响因素[J]. 中国地震, 36(2): 234—243. |
| FAN Ye, CUI Teng-fa, DU Xue-bin, et al. 2020a. Feature and influence factors of the diurnal variation of geoelectric field in China[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 36(2): 234—243 (in Chinese). | |
| [6] | 范晔, 叶青, 刘高川. 2020b. 地电暴事件判别方法及特征分析[J]. 地震工程学报, 42(1): 107—115. |
| FAN Ye, YE Qing, LIU Gao-chuan. 2020b. Discrimination method and characteristic analysis of geoelectric storms[J]. China Earthquake Engineering Journal, 42(1): 107—115 (in Chinese). | |
| [7] | 贾立峰, 乔子云, 张国苓, 等. 2017. 2013年辽宁灯塔M5.1地震地磁异常变化特征[J]. 地震研究, 40(3): 437—443. |
| JIA Li-feng, QIAO Zi-yun, ZHANG Guo-ling, et al. 2017. Variation of the geomagnetic anomaly characteristics before the Liaoning Dengta M5.1 earthquake in 2013[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 40(3): 437—443 (in Chinese). | |
| [8] | 李伟, 马钦忠, 王冠明. 2014. 地电场多极距观测装置的异常识别和分析[J]. 中国地震, 30(1): 91—101. |
| LI Wei, MA Qin-zhong, WANG Guan-ming. 2014. Abnormal signal recognition by multi-dipole observation of geoelectric field[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 30(1): 91—101 (in Chinese). | |
| [9] | 钱家栋, 陈有发, 金安忠. 1985. 地电阻率法在地震预报中的应用[M]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| QIAN Jia-dong, CHEN You-fa, JIN An-zhong. 1985. Application of Apparent Resistivity Method in Earthquake Prediction[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing (in Chinese). | |
| [10] | 谭大诚, 王兰炜, 赵家骝, 等. 2011. 潮汐地电场谐波和各向波形的影响要素[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(7): 1842—1853. |
| TAN Da-cheng, WANG Lan-wei, ZHAO Jia-liu, et al. 2011. Influence factors of harmonic waves and directional waveforms of tidal geoelectrical field[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(7): 1842—1853 (in Chinese). | |
| [11] | 汤吉, 詹艳, 王立凤, 等. 2008. 5月12日汶川8.0级地震强余震观测的电磁同震效应[J]. 地震地质, 30(3): 739—745. |
| TANG Ji, ZHAN Yan, WANG Li-feng, et al. 2008. Coseismic signal associated with aftershock of the MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(3): 739—745 (in Chinese). | |
| [12] | 汤吉, 詹艳, 王立凤, 等. 2010. 汶川地震强余震的电磁同震效应[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(3): 526—534. |
| TANG Ji, ZHAN Yan, WANG Li-feng, et al. 2010. Electromagnetic coseismic effect associated with aftershock of Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(3): 526—534 (in Chinese). | |
| [13] | 王同利, 胡乐银, 崔博闻, 等. 2013. 北京城市轨道交通对地电场观测的干扰影响[J]. 地震地质, 35(4): 887—893. |
| WANG Tong-li, HU Le-yin, CUI Bo-wen, et al. 2013. A preliminary analysis on the interference generated by urban railway transit in Beijing to the geoelectric field observations[J]. Seismology and Geology, 35(4): 887—893 (in Chinese). | |
| [14] | 温瑞智, 王宏伟. 2020. 2020年7月12日唐山古冶 MS5.1 地震的强震动特征[J]. 地震科学进展, 50(7): 9—13. |
| WEN Rui-zhi, WANG Hong-wei. 2020. Strong motion recordings in MS5.1 Guye, Tangshan earthquake on July 12, 2020[J]. Progress in Earthquake Sciences, 50(7): 9—13 (in Chinese). | |
| [15] | 席继楼, 关华平, 刘超, 等. 2018. 几次大地震前后地电场中长期变化分析与研究[J]. 地震, 38(2): 117—126. |
| XI Ji-lou, GUAN Hua-ping, LIU Chao, et al. 2018. Immediate to long-term changes of geoelectric potential difference before and after several large earthquakes[J]. Earthquake, 38(2): 117—126 (in Chinese). | |
| [16] | 席继楼, 赵家骝, 关歆莹, 等. 2015. 地电场观测中的工频干扰抑制方法研究[J]. 地震, 35(4): 53—63. |
| XI Ji-lou, ZHAO Jia-liu, GUAN Xin-ying, et al. 2015. Methods for restraining power frequency interferences in geo-electric field observation[J]. Earthquake, 35(4): 53—63 (in Chinese). | |
| [17] | 解滔, 王同利, 肖武军, 等. 2020. 2020年7月12日唐山 MS5.1 地震前通州台井下地电阻率变化[J]. 中国地震, 36(3): 375—382. |
| XIE Tao, WANG Tong-li, XIAO Wu-jun, et al. 2020. Apparent resistivity variations before Tangshan MS5.1 earthquake on July 12, 2020 recorded at Tongzhou station[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 36(3): 375—382 (in Chinese). | |
| [18] | 徐文耀. 2009. 地球电磁现象物理学[M]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社. |
| XU Wen-yao. 2009. Physics of Electromagnetic Phenomena of the Earth[M]. Universityof Science and Technology of China Press, Hefei (in Chinese). | |
| [19] |
章鑫, 王丽, 杜学彬. 2016. 大地电流研究进展与展望[J]. 地球科学进展, 31(7): 708—717.
DOI |
| ZHANG Xin, WANG Li, DU Xue-bin. 2016. A review of studies on the telluric currents[J]. Advances in Earth Science, 31(7): 708—717 (in Chinese). | |
| [20] |
Du X B, Ruan A G, Fan S H, et al. 2001. Anisotropy of the apparent resistivity variation rate near the epicentral region for strong earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 14(3): 303—314.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
Du X B. 2011. Two types of changes in apparent resistivity in earthquake prediction[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 54(1): 145—156.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Fan Y, Tang J, Han B, et al. 2018. The background variation of natural source ELF and its EM abnormal phenomena in Yunnan earthquakes[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 32(1): 130—140. |
| [23] | Huang Q H, Ikeya M. 1998. Seismic electromagnetic signals(SEMS)explained by a simulation experiment using electromagnetic waves[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 109(3-4): 107—114. |
| [24] |
Huang Q H, Lin Y F. 2010. Selectivity of seismic electric signal (SES) of the 2000 Izu earthquake swarm: A 3D FEM numerica1 simulation model[J]. Proceedings of the Japan Academy, Series B, 86(3): 257—264.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Lu J, Xie T, Li M, et al. 2016. Monitoring shallow resistivity changes prior to the 12 May 2008 MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake on the Longmen Shan tectonic zone, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 675: 244—257.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Ma Q Z. 2002. The boundary element method for 3-D DC resistivity modeling in layered earth[J]. Geophysics, 67(2): 610—617.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Park S K, Strauss D J, Aceves R L. 1996. Some observations about the statistical significance and physical mechanisms of the VAN method of earthquake prediction, Greece [G]//Lighthill S J. A Critical Review of VAN: Earthquake Prediction from Seismic Electrical Signals. Singapore: World Scientific Publishing: 267—285. |
| [28] |
Sarlis N, Lazaridou M, Kapiris P, et al. 1999. Numerical model of the selectivity effect and the ΔV/L criterion[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 26(21): 3245—3248.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Ye Q, Fan Y, Du X B, et al. 2018. Diurnal characteristics of geoelectric fields and their changes associated with the Alxa Zuoqi MS5.8 earthquake on 15 April 2015(Inner Mongolia)[J]. Earthquake Science, 31(1): 35—43.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 董泽义, 汤吉, 赵国泽, 陈小斌, 崔腾发, 韩冰, 姜峰, 王立凤. 首都圈极低频电磁台网区地下电性结构探测[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 649-668. |
| [2] | 章鑫, 范晔, 叶青, 钱银苹. HVDC入地电流对地电场的影响规律及入地极定位[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 718-735. |
| [3] | 韩冰, 汤吉, 赵国泽, 王立凤, 董泽义, 范晔, 孙贵成. 极低频台站同震电磁信号特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 753-770. |
| [4] | 池海江, 温佳. 怀来极低频电磁观测监控与管理方法的实现[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 821-830. |
| [5] | 戴勇, 高立新, 杨彦明, 魏建民, 格根. 地电阻率变化成因分析——以宝昌台为例[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(3): 647-662. |
| [6] | 解滔, 卢军, 闫伟. 地电阻率日变化成因分析[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(6): 1464-1480. |
| [7] | 张继红, 赵国泽, 董泽义, 王立凤, 韩冰, 王庆林, 唐廷梅, 王梅. 郯庐断裂带安丘、莒县电磁台地壳电性结构研究[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(5): 1239-1253. |
| [8] | 李建凯, 汤吉. 主成分分析法和局部互相关追踪法在地震电磁信号提取与分析中的应用[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(3): 517-535. |
| [9] | 安张辉, 詹艳, 陈小斌, 姜峰, 高悦. 滑动自相关方法在地电阻率观测资料分析中的应用初探[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(4): 1019-1029. |
| [10] | 高曙德, 赵国泽, 汤吉, 苏永刚, 詹艳, 王立凤. 2008年中国大陆6.0级以上地震前后电磁脉冲异常现象[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(4): 987-1004. |
| [11] | 解滔, 卢军. 地表固定干扰源影响下地电阻率观测随时间变化特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(4): 922-936. |
| [12] | 解滔, 卢军. 地电阻率三维影响系数及其应用[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(4): 1125-1135. |
| [13] | 韩冰, 汤吉, 赵国泽, 毕亚新, 王立凤, 程远志. 小波极大值方法及其在电磁异常信号提取中的应用[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(3): 765-779. |
| [14] | 王同利, 胡乐银, 崔博闻, 宋艳茹. 北京城市轨道交通对地电场观测的干扰影响[J]. 地震地质, 2013, 35(4): 887-893. |
| [15] | 赵国泽, 王立凤, 詹艳, 汤吉, 肖骑彬, 陈小斌, 王继军, 蔡军涛, 汪晓, 杨静. 地震预测人工源极低频电磁新技术(CSELF)和第一个观测台网[J]. 地震地质, 2012, (4): 576-585. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||