地震地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 757-770.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.04.002
宋向辉1,2)( ), 王帅军1), 潘素珍1), 宋佳佳1)
), 王帅军1), 潘素珍1), 宋佳佳1)
收稿日期:2021-06-15
修回日期:2021-07-05
出版日期:2021-08-20
发布日期:2021-09-29
作者简介:宋向辉, 男, 1988年生, 2013年于中国矿业大学(北京)获地球探测与信息技术专业硕士学位, 工程师, 研究方向为人工地震测深资料的处理与动力学解释, 电话: 15890142396, E-mail: songxh@gec.ac.cn。
基金资助:
SONG Xiang-hui1,2)( ), WANG Shuai-jun1), PAN Su-zhen1), SONG Jia-jia1)
), WANG Shuai-jun1), PAN Su-zhen1), SONG Jia-jia1)
Received:2021-06-15
Revised:2021-07-05
Online:2021-08-20
Published:2021-09-29
摘要:
2021年5月22日, 巴颜喀拉块体内部的玛多地区发生MS7.4地震, 震源深度约为8km, 发震断层为江错断裂。 文中利用玛多地区的深地震测深结果, 对玛多MS7.4地震震源区的地壳速度结构和深部构造背景进行了研究。 结果显示: 1)玛多地震震源在深度上位于上地壳脆性层内, 具体位于上地壳局部高速体的边缘, 上地壳特殊的上下分层结构和局部的高速异常体为玛多地震的孕育提供了介质环境。 2)玛多以南地区的深部地壳存在楔状低速体, 为深部软弱物质向NE运动提供了环境, 而玛多地区高速的下地壳阻挡了软弱物质的运移而使其垂向上涌, 导致了玛多地区上地壳应力的集中, 这可能为此次玛多地震的孕育提供了深部动力。 3)江错断裂在深部归并到东昆仑断裂上, 在剖面上构成以东昆仑走滑断层为主的反向逆冲断裂构造样式, 因此玛多地震的发生与东昆仑断裂的左旋走滑运动存在一定联系; 此外, 下地壳流的上涌也可能在一定程度上促进了玛多地区上地壳的水平滑动以及地震的发生。 综上所述, 此次玛多MS7.4地震的孕育和发生, 与玛多上地壳特殊的介质条件、 中下地壳物质的挤压流动和垂向上涌以及东昆仑主走滑断裂的水平运动密切相关。
中图分类号:
宋向辉, 王帅军, 潘素珍, 宋佳佳. 2021年玛多MS7.4地震的深部构造背景[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 757-770.
SONG Xiang-hui, WANG Shuai-jun, PAN Su-zhen, SONG Jia-jia. DEEP SEISMOTECTONIC ENVIRONMENT OF THE 2021 MADOI MS7.4 EARTHQUAKE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2021, 43(4): 757-770.
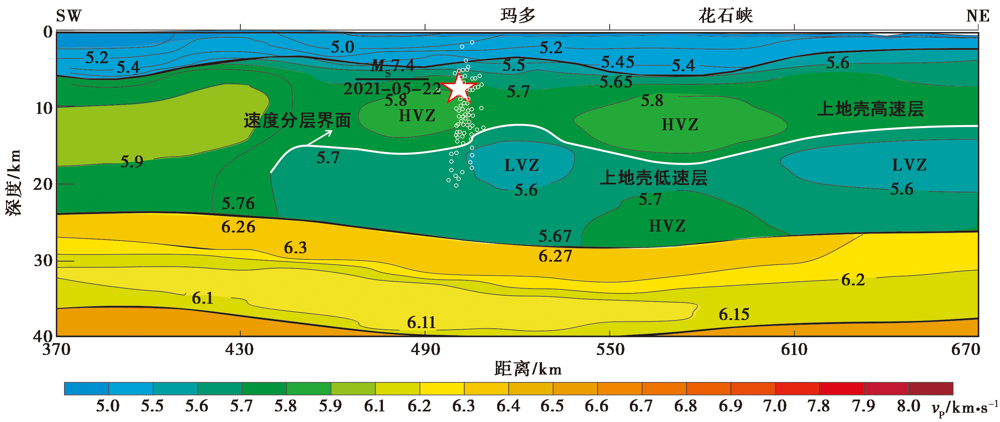
图2 玛多地区的上地壳速度结构(据张建狮等, 2014改) 白色五角星为玛多MS7.4地震主震, 白色圆圈为余震序列
Fig. 2 Upper crustal velocity and medium environments of Madoi area(modified after ZHANG Jian-shi et al., 2014).
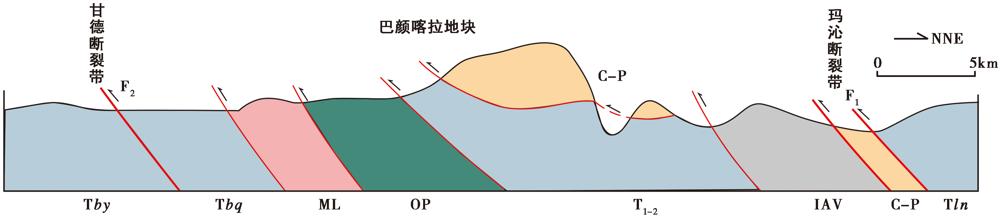
图3 巴颜喀拉块体内部及北部边界断裂带(据裴先治, 2001改) Tln 三叠系隆务河群; Tbq 三叠系布青山群; Tby 三叠系巴颜喀拉群; C-P 石炭系-二叠系台地相厚层块状生物碎屑灰岩;OP 蛇绿构造混杂岩; ML 沉积-构造混杂岩; Pt 元古宙变质基底杂岩
Fig. 3 Section of major faults in and around Bayan Har Block(modified after PEI Xian-zhi, 2001).
| [1] | 邓起东, 程绍平, 马冀, 等. 2014. 青藏高原地震活动特征及当前地震活动形势[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(7): 2025-2042. |
| DENG Qi-dong, CHENG Shao-ping, MA Ji, et al. 2014. Seismic activities and earthquake potential in the Tibetan plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(7): 2025-2042. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 高翔. 2012. 走滑断裂带变形局部化和地震成核过程探讨[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学. |
| GAO Xiang. 2012. A study on deformation localization of strike-slip fault zones and the process of earthquake nucleation[D]. Zhejiang University, Hangzhou. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 高翔, 邓起东. 2013. 巴颜喀喇断块边界断裂强震活动分析[J]. 地质学报, 87(1): 9-19. |
| GAO Xiang, DENG Qi-dong. 2013. Analysis of large earthquake in boundary faults around Bayankala fault-block[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 87(1): 9-19. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 郭文斌, 嘉世旭, 段永红, 等. 2016. 青藏高原东北缘基底结构研究: 玛多-共和-雅布赖剖面上地壳地震折射探测[J]. 地球物理学报, 59(10): 3627-3636. |
| GUO Wen-bin, JIA Shi-xu, DUAN Yong-hong, et al. A study on the basement tectonic units in the northeast margin of Tibetan plateau: The result of Maduo-Gonghe-Yabrai refraction profile[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 59(10): 3627-3636. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 嘉世旭, 林吉焱, 郭文斌, 等. 2017. 巴颜喀拉块体地壳结构多样性探测[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(6): 2226-2238. |
| JIA Shi-xu, LIN Ji-yan, GUO Wen-bin, et al. 2017. Investigation on diversity of crustal structures beneath the Bayan Har block[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(6): 2226-2238. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 李陈侠, 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 等. 2011. 东昆仑断裂带中东部地震破裂分段性与走滑运动分解作用[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 41(9): 1295-1310. |
|
LI Chen-xia, XU Xi-wei, WEN Xue-ze, et al. 2011. Rupture segmentation and slip partitioning of the mid-eastern part of the Kunlun Fault, north Tibetan plateau[J]. Science China Earth Science, 54(11): 1730-1745.
DOI URL |
|
| [7] | 李海兵, 潘家伟, 孙知明, 等. 2021. 大陆构造变形与地震活动: 以青藏高原为例[J]. 地质学报, 95(1): 194-213. |
| LI Hai-bing, PAN Jia-wei, SUN Zhi-ming, et al. 2021. Continental tectonic deformation and seismic activity: A case study from the Tibetan plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(1): 194-213. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 李永华, 吴庆举, 冯强强, 等. 2010. 青海地区S波分裂研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(6): 1374-1383. |
| LI Yong-hua, WU Qiang-ju, FENG Qiang-qiang, et al. 2010. Seismic anisotropy beneath Qinghai Province revealed by shear wave splitting[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(6): 1374-1383. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 梁光河. 2018. 基于新大陆漂移模型的地震成因与分布规律分析[J]. 科学技术与工程, 18(28): 47-57. |
| LIANG Guang-he. 2018. Analyses of the genesis and distribution law of earthquakes based on new continental drift model[J]. Science Technology and Engineering, 18(28): 47-57. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 梁光河. 2020. 印度大陆板块北漂的动力机制研究[J]. 地学前缘, 27(1): 211-220. |
| LIANG Guang-he. 2020. Study on the dynamic mechanism of northward drift of the Indian Plate[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 27(1): 211-220. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 马玉虎, 黄浩, 王培玲, 等. 2017. 2015年青海玛多5.2级地震发震构造及其预测意义[J]. 高原地震, 29(1): 1-6. |
| MA Yu-hu, HUANG Hao, WANG Pei-ling, et al. 2017. Seismogenic structure and its significance in prediction of Maduo M5.2 earthquake in Qinghai Province in 2015[J]. Plateau Earthquake Research, 29(1): 1-6. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 潘家伟, 白明坤, 李超, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多MS7.4地震地表破裂带及发震构造[J]. 地质学报, 95(6): 1655-1670. |
| PAN Jia-wei, BAI Ming-kun, LI Chao, et al. 2021. Coseismic surface rupture and seismogenic structure of the 2021-05-22 Maduo(Qinghai)MS7.4 earthquake[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(6): 1655-1670. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 裴先治. 2001. 勉略-阿尼玛卿构造带的形成演化与动力学特征[D]. 西安: 西北大学. |
| PEI Xian-zhi. 2001. Geological evolution and dynamics of the Mianlue-A'nyemaqen tectonic zone, Central China[D]. Northwest University, Xi'an. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 覃小锋. 2002. 一种走滑剪切-逆冲推覆相互转换的变形体系: 以桂东南那卜地区NE向和NW向两组韧性剪切带为例[J]. 广西地质, 15(2): 7-11, 25. |
| QIN Xiao-feng. 2002. One of the ductile deformation systems that transform each other from NE-trending dextral strike-slip to NW-trending thrust-nappe: Illustrated with an example from NE-trending ductile shear zones and NW-trending ductile shear zones in Nabu area[J]. Guangxi Geology, 15(2): 7-11, 25. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] |
冉洪流. 2011. 中国西部走滑型活动断裂的地震破裂参数与震级的经验关系[J]. 地震地质, 33(3): 577-585. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.03.008.
DOI |
| RAN Hong-liu. 2011. Empirical relations between earthquake magnitude and parameters of strike-slip seismogenic active faults associated with historical earthquakes in western China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 33(3): 577-585. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 王椿镛, 楼海, 吕智勇, 等. 2008. 青藏高原东部地壳上地幔S波速度结构: 下地壳流的深部环境[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 38(1): 22-32. |
|
WANG Chun-yong, LOU Hai, LÜ Zhi-yong, et al. 2008. S-wave crustal and upper mantle’s velocity structure in the eastern Tibetan plateau: Deep environment of lower crustal flow[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 51(2): 263-274.
DOI URL |
|
| [17] | 王未来, 房立华, 吴建平, 等. 2021. 2021年青海玛多MS7.4地震序列精定位研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 51(7): 1193-1202. |
| WANG Wei-lai, FANG Li-hua, WU Jian-ping, et al. 2021. Aftershock sequence relocation of the 2021 MS7.4 Maduo earthquake, Qinghai, China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 51(7): 1193-1202. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 熊仁伟. 2010. 玛多-甘德断裂活动性研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地震预测研究所. |
| XIONG Ren-wei. 2010. A study on the activity of Maduo-Gande Fault[D]. Graduate University of Institute of Earthquake Science, CEA, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] |
徐锡伟, 吴熙彦, 于贵华, 等. 2017. 中国大陆高震级地震危险区判定的地震地质学标志及其应用[J]. 地震地质, 39(2): 219-275. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.02.001.
DOI |
| XU Xi-wei, WU Xi-yan, YU Gui-hua, et al. 2017. Seismo-geological signatures for identifying M≥7.0 earthquake risk areas and their preliminary application in mainland China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(2): 219-275. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 许志琴, 杨经绥, 姜枚, 等. 2001. 青藏高原北部东昆仑-羌塘地区的岩石圈结构及岩石圈剪切断层[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 31(S1): 1-7. |
| XU Zhi-qin, YANG Jing-sui, JIANG Mei, et al. 2001. Lithospheric structure and shear fault from eastern Kunlun to Qiangtang in Tibet Plateau[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 31(S1): 1-7. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 许志琴, 曾令森, 杨经绥, 等. 2004. 走滑断裂、 “挤压性盆-山构造”与油气资源关系的探讨[J]. 地球科学, 29(6): 631-643. |
| XU Zhi-qin, ZENG Ling-sen, YANG Jing-sui, et al. 2004. Role of large-scale strike-slip faults in the formation of petroleum-bearing compressional basin-mountain range systems[J]. Earth Science, 29(6): 631-643. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 杨经绥, 许志琴, 李海兵, 等. 2005. 东昆仑阿尼玛卿地区古特提斯火山作用和板块构造体系[J]. 岩石矿物学杂志, 24(5): 369-380. |
| YANG Jing-sui, XU Zhi-qin, LI Hai-bing, et al. 2005. The paleo-Tethyan volcanism and plate tectonic regime in the A'nyemaqen region of east Kunlun, northern Tibet Plateau[J]. Acta Petrologica Et Mineralogica, 24(5): 369-380. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 杨文采, 侯遵泽, 于常青. 2015. 青藏高原地壳的三维密度结构和物质运动[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(11): 4223-4234. |
| YANG Wen-cai, HOU Zun-ze, YU Chang-qing. 2015. Three-dimensional density structure of the Tibetan plateau and crustal mass movement[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(11): 4223-4234. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 易桂喜, 龙锋, 梁明剑, 等. 2017. 2017年8月8日九寨沟M7.0地震及余震震源机制解与发震构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(10): 4083-4097. |
| YI Gui-xi, LONG Feng, LIANG Ming-jian, et al. 2017. Focal mechanism solutions and seismogenic structure of the 8 August 2017 M70 Jiuzhaigou earthquake and its aftershocks, northern Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(10): 4083-4097. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] |
袁道阳, 冯建刚, 郑文俊, 等. 2020. 青藏地块区大地震迁移规律与未来主体活动区探讨[J]. 地震地质, 42(2): 297-315. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.02.004.
DOI |
| YUAN Dao-yang, FENG Jian-gang, ZHENG Wen-jun, et al. 2020. Migration of large earthquakes in Tibetan block area and discussion on major active region in the future[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(2): 297-315. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 岳汉, 张竹琪, 陈永顺. 2008. 相邻左旋走滑和逆冲断层之间的相互作用: 1976年松潘震群[J]. 科学通报, 53(13): 1582-1588. |
| YUE Han, ZHANG Zhu-qi, CHEN Yong-shun. 2008. Interaction between adjacent left-lateral strike-slip faults and thrust faults: The 1976 Songpan earthquake sequence[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 53(13): 1582-1588. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 詹艳, 梁明剑, 孙翔宇, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多MS7.4地震深部环境及发震构造模式[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(7): 2232-2252. |
| ZHAN Yan, LIANG Ming-jian, SUN Xiang-yu, et al. 2021. Deep structure and seismogenic pattern of the 2021.5.22 Madoi(Qinghai) MS7.4 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(7): 2232-2252. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 张朝锋. 2019. 巴颜喀拉盆地三叠纪沉积充填及构造演化[D]. 西安: 西北大学. |
| ZHANG Chao-feng. 2019. Triassic sedimentary filling and tectonic evolution in Bayan Har Basin[D]. Northwest University, Xi'an. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] |
张建狮, 王夫运, 刘宝峰, 等. 2014. 玉树震区及邻近地区壳幔速度结构特征[J]. 地震地质, 36(2): 322-332. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.02.004.
DOI |
| ZHANG Jian-shi, WANG Fu-yun, LIU Bao-feng, et al. 2014. A study of the crust-mantle velocity structure beneath the Yushu earthquake zone and its adjacent areas[J]. Seismology and Geology, 36(2): 322-332. (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 张培震, 邓起东, 张竹琪, 等. 2013. 中国大陆的活动断裂、 地震灾害及其动力过程[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 43(10): 1607-1620. |
| ZHANG Pei-zhen, DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Zhu-qi, et al. 2013. Active faults, earthquake hazards and associated geodynamic processes in continental China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 43(10): 1607-1620. (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 张先康, 李松林, 王夫运, 等. 2003. 青藏高原东北缘、 鄂尔多斯和华北唐山震区的地壳结构差异: 深地震测深的结果[J]. 地震地质, 25(1): 52-60. |
| ZHANG Xian-kang, LI Song-lin, WANG Fu-yun, et al. 2003. Differences of crustal structures in northeastern edge of Tibet Plateau, Ordos and Tangshan earthquake region in North China: Results of deep seismic sounding[J]. Seismology and Geology, 25(1): 52-60. (in Chinese) | |
| [32] | 张喆, 许力生. 2021. 2021年青海果洛MW7.5地震矩心矩张量解[J]. 地震学报, 43(3): 1-5. |
| ZHANG Zhe, XU Li-sheng. 2021. The centroid moment tensor solution of the 2021 MW7.5 Guoluo, Qinghai, earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 43(3): 1-5. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] |
Galvé A, Hirn A, Mei J, et al. 2002. Modes of raising northeastern Tibet probed by explosion seismology[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 203(1): 35-43.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Jiang M, Galvé A, Hirn A, et al. 2006. Crustal thickening and variations in architecture from the Qaidam Basin to the Qang Tang(north-central Tibetan plateau)from wide-angle reflection seismology[J]. Tectonophysics, 412(3-4): 121-140.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Yang G L, Shen C Y, Xuan S B, et al. 2012. Estimating Moho basement and faults using gravity inversion in Yushu[J]. Geodesy and Geodynamics, 3(2): 8-13. |
| [36] |
Zhang Z J, Klemperer S, Bai Z M, et al. 2011. Crustal structure of the Paleozoic Kunlun orogeny from an active-source seismic profile between Moba and Guide in East Tibet, China[J]. Gondwana Research, 19(4): 994-1007.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王博, 崔凤珍, 刘静, 周永胜, 徐胜, 邵延秀. 玛多 MS7.4地震断层土壤气特征与地表破裂的相关性[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 772-794. |
| [2] | 苟家宁, 刘子维, 江颖, 张晓彤. 震前重力扰动与背景噪声时空变化特征以玛多MS7.4与漾濞MS6.4地震为例[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 252-268. |
| [3] | 路畅, 周晓成, 李营, 刘磊, 颜玉聪, 徐岳仁. 玛多MS7.4 地表破裂带与东昆仑断裂温泉的水文地球化学特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1101-1126. |
| [4] | 李春果, 王宏伟, 温瑞智, 强生银, 任叶飞. 2021年青海玛多MS7.4地震随机有限断层三维地震动模拟[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1085-1100. |
| [5] | 韦进, 郝洪涛, 韩宇飞, 胡敏章, 江颖, 刘子维. 基于连续重力台观测的玛多MS7.4地震的同震重力变化特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 984-998. |
| [6] | 唐茂云, 刘静, 李翠平, 王伟, 张金玉, 许强. 青藏高原东南缘的新生代盆地古高度重建研究与进展[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(3): 576-599. |
| [7] | 邓晓果, 田晓峰, 杨卓欣, 王夫运, 刘宝峰, 高占永, 郑成龙. 长江断裂带安徽段上地壳速度结构及基底特征[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(5): 1109-1128. |
| [8] | 田晓峰, 熊伟, 王夫运, 徐朝繁, 段永红, 嘉世旭. 京津地区顺义—塘沽高分辨地震折射剖面的走时成像结果及其揭示的上地壳断裂构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(2): 414-434. |
| [9] | 陈思文, 王宝善, 田晓峰, 王夫运, 刘宝峰, 李璐. 滇西北地区云县-宁蒗宽角反射/折射剖面结果[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(1): 91-106. |
| [10] | 杨婷, 吴建平, 房立华, 王长在. 滇西地区地壳速度结构及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(2): 392-404. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||