地震地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (4): 739-756.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.04.001
吴桂桔1,3)( ), 于炳飞2), 郝洪涛1,3), 胡敏章1,3), 谈洪波1)
), 于炳飞2), 郝洪涛1,3), 胡敏章1,3), 谈洪波1)
收稿日期:2021-06-08
修回日期:2021-06-23
出版日期:2021-08-20
发布日期:2021-09-29
作者简介:吴桂桔, 女, 1983年生, 2012年于中国地质大学(武汉)获地球探测与信息技术专业博士学位, 副研究员, 主要从事综合地球物理场解释与重力学科地震会商工作, E-mail: wugjsky@126.com。
基金资助:
WU Gui-ju1,3)( ), YU Bing-fei2), HAO Hong-tao1,3), HU Min-zhang1,3), TAN Hong-bo1)
), YU Bing-fei2), HAO Hong-tao1,3), HU Min-zhang1,3), TAN Hong-bo1)
Received:2021-06-08
Revised:2021-06-23
Online:2021-08-20
Published:2021-09-29
摘要:
2021年5月21日云南大理白族自治州漾濞县发生了3次较强地震, 最高震级为M6.4, 造成巨大经济损失和人员伤亡。 为厘清漾濞地震的发震构造与孕震环境, 文中将已有的高精度重力数据、 流动重力测网点数据和EGM2008模型数据融合为2.5km点距的高精度网格数据, 并以漾濞地震为中心, 提取了2条长重力剖面和10条短重力剖面, 采用归一化梯度成像方法获取研究区内三维地壳成像特征, 重点分析了漾濞震区沿红河断裂北段、 维西-巍山断裂、 永胜-宾川断裂和洱源-鹤庆断裂等的深浅接触关系及其深部孕震环境。 结果表明: 1)重力归一化梯度陡变带的倾角、 倾向与地质上的中大型断裂吻合较好, 如怒江断裂、 澜沧江断裂、 红河断裂、 安宁河断裂和则木河断裂等; 2)中下地壳重力归一化梯度连续性较好, 且中上地壳为高低转换带时, M≥6.0地震频发, 特别是维西-巍山断裂、 永胜-宾川断裂及红河断裂北段交会的区域; 3)漾濞地震震中附近, 上地壳存在归一化梯度高低强变形带且相互靠拢, 在深度约15km处会聚, 震中投影与维西-巍山断裂及其次生断裂在深度约10km处交会, 且地壳20km以下重力归一化梯度值连续性较好, 推断漾濞3次地震的发震构造为维西-巍山断裂及其次生断裂。 文中结果对地震发震机制和发震地点的判定具有非常重要的科学意义和参考价值。
中图分类号:
吴桂桔, 于炳飞, 郝洪涛, 胡敏章, 谈洪波. 漾濞震区及周缘深部构造特征与发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 739-756.
WU Gui-ju, YU Bing-fei, HAO Hong-tao, HU Min-zhang, TAN Hong-bo. THE DEEP STRUCTURAL CHARACTERISTICS AND THE SEIS-MOGENIC STRUCTURE OF THE YANGBI EARTHQUAKE REGION AND ITS SURROUNDING AREAS[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2021, 43(4): 739-756.
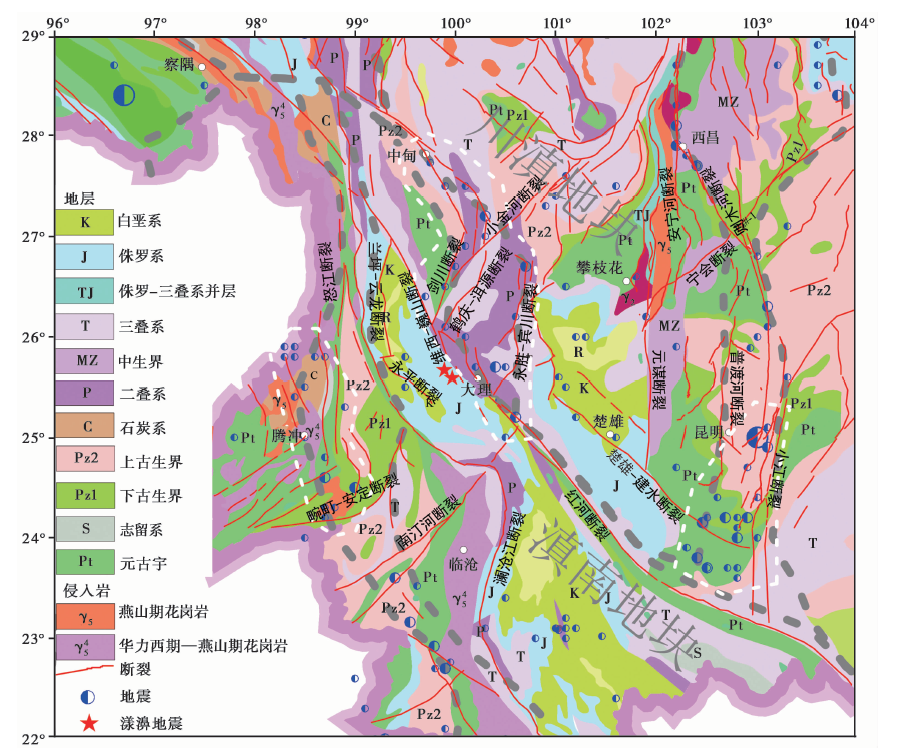
图1 研究区简易构造地质图(据邓起东等, 2007) 灰色虚线为块体分界线, 红色实线为断裂, 蓝色半圆形为M≥6.0地震震中,白色圆圈为地名, 白色虚线框为研究区内地震频发区域
Fig. 1 Simple tectonic geological map of the study area(after DENG Qi-dong et al., 2007).
| 断层名称 | 倾向 | 倾角 |
|---|---|---|
| 澜沧江断裂 | SW | 60°~70° |
| 兰坪-云龙断裂 | SW | >60° |
| 红河断裂北段 | SW | >60° |
| 永胜-宾川断裂 | W | 近90° |
| 维西-巍山断裂 | NE | >50° |
| 怒江断裂南段 | NW | >50° |
| 则木河断裂 | NE | 60°~70° |
| 雄楚-建水断裂 | SW | 70° |
表1 主要断层信息
Tabel 1 Major faults information
| 断层名称 | 倾向 | 倾角 |
|---|---|---|
| 澜沧江断裂 | SW | 60°~70° |
| 兰坪-云龙断裂 | SW | >60° |
| 红河断裂北段 | SW | >60° |
| 永胜-宾川断裂 | W | 近90° |
| 维西-巍山断裂 | NE | >50° |
| 怒江断裂南段 | NW | >50° |
| 则木河断裂 | NE | 60°~70° |
| 雄楚-建水断裂 | SW | 70° |
| [1] | 白志明, 王椿镛. 2004. 云南遮放-宾川和孟连-马龙宽角地震剖面的层析成像研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 47(2): 257-267. |
| BAI Zhi-ming, WANG Chun-yong. 2004. Tomography research of the Zhefang-Binchuan and Menglian-Malong wide-angle seismic profiles in Yunnan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 47(2): 257-267. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 2003. 中国活动构造与地震活动[J]. 地学前缘, 10(8): 66-73. |
| DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Pei-zhen, RAN Yong-kang, et al. 2003. Active tectonics and earthquake activities in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(8): 66-73. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 邓起东, 冉勇康, 杨晓平, 等. 2007. 中国活动构造图[M]. 北京: 地质出版社. |
| DENG Qi-dong, RAN Yong-kang, YANG Xiao-ping, et al. 2007. Active Tectonics Map of China[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 方盛明, 赵成彬, 柴炽章, 等. 2009. 银川断陷盆地地壳结构与构造的地震学证据[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(7): 1768-1775. |
| FANG Sheng-ming, ZHAO Cheng-bin, CHAI Chi-zhang, et al. 2009. Seismic evidence of crustal structures in the Yinchuan faulted basin[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(7): 1768-1775. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 郭飚, 刘启元, 陈九辉, 等. 2009. 川西龙门及邻区地壳上地幔远震P波层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(2): 346-355. |
| GUO Biao, LIU Qi-yuan, CHEN Jiu-hui, et al. 2009. Teleseismic P-wave tomography of the crust and upper mantle in Longmenshan area, west Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(2): 346-355. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 郝天珧, 江为为, 胥颐, 等. 2005. 红河断裂带研究区深部结构特点的地球物理研究[J]. 地球物理学进展, 20(3): 584-593. |
| HAO Tian-yao, JIANG Wei-wei, XU Yi, et al. 2005. Geophysical research on deep structure feature in study region of Red River fault zone[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 20(3): 584-593. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 黄金莉, 宋晓东, 汪素云. 2003. 川滇地区上地幔顶部Pn速度细结构[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 144-151. |
| HUANG Jin-li, SONG Xiao-dong, WANG Su-yun. 2003. The Pn velocity structure of upper mantle in Sichuan-Yunnan region[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 33(S1): 144-151. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 李昱, 姚华建, 刘启元, 等. 2010. 川西地区台阵环境噪声瑞利波相速度层析成像[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(4): 842-852. |
| LI Yu, YAO Hua-jian, LIU Qi-yuan, et al. 2010. Phase velocity array tomography of Rayleigh waves in western Sichuan from ambient seismic noise[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(4): 842-852. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 马宏生, 张国民, 闻学泽, 等. 2008. 川滇地区三维P波速度结构反演与构造分析[J]. 地球科学, 33(5): 591-602. |
|
MA Hong-sheng, ZHANG Guo-ming, WEN Xue-ze, et al. 2008. 3-D P wave velocity structure tomographic inversion and its tectonic interpretation in southwest China[J]. Earth Science-Journal of China University of Geosciences, 33(5): 591-602. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [10] | 唐伯熊, 吴国华. 1991. 重力测量研究断裂活动的尝试[J]. 地震, 6:73-76. |
| TANG Bo-xiong, WU Guo-hua. 1991. Fault activity study by gravimetry[J]. Earthquake, 6:73-76. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 唐伯熊, 吴国华, 罗剑寒. 1990. 红河断裂带上的重力测量[J]. 地震研究, 13(3): 273-276. |
| TANG Bo-xiong, WU Guo-hua, LUO Jian-han. 1990. Gravity measurement along Red River fault zone[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 13(3): 273-276. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 滕吉文, 司芗, 王谦身, 等. 2015. 青藏高原地球科学研究中的核心问题与理念的厘定[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(1): 103-124. |
| TENG Ji-wen, SI Xiang, WANG Qian-shen, et al. 2015. Collation and stipulation of the core science problems and theoretical concept in the geoscience study on the Tibetan plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(1): 103-124. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 滕吉文, 王谦身, 王光杰, 等. 2006. 喜马拉雅 “东构造结”地区的特异重力场与深部地壳结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(4): 1045-1052. |
| TENG Ji-wen, WANG Qian-shen, WANG Guang-jie, et al. 2006. Specific gravity field and deep crustal structure of the “Himalayas east structural knot”[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 49(4): 1045-1052. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 吴桂桔, 谈洪波, 孙凯, 等. 2020. 贺兰山-银川地堑及邻区重力异常特征及构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(3): 1002-1013. |
| WU Gui-ju, TAN Hong-bo, SUN Kai, et al. 2020. Characteristics and tectonic significance of gravity anomalies in the Helanshan-Yinchuan graben and adjacent areas[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(3): 1002-1013. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 徐涛, 张明辉, 田小波, 等. 2014. 丽江-清镇剖面上地壳结构及其与鲁甸MS6.5地震孕震环境的关系[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(9): 3069-3079. |
| XU Tao, ZHANG Ming-hui, TIAN Xiao-bo, et al. 2014. Upper crustal velocity of Lijiang-Qingzhen profile and its relationship with the seismogenic environment of the MS6.5 Ludian earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(9):3069-3079. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 徐锡伟, 张培震, 闻学泽, 等. 2005. 川西及邻近地区活动构造基本特征与强震复发模型[J]. 地震地质, 27(3): 446-461. |
| XU Xi-wei, ZHANG Pei-zhen, WEN Xue-ze, et al. 2005. Features of active tectonics and recurrence behaviors of strong earthquake in the western Sichuan Province and its adjacent regions[J]. Seismology and Geology, 27(3): 446-461. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 杨文采, 孙艳云, 于常青. 2015. 青藏高原地壳密度变形带及构造分区[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(11): 4115-4128. |
| YANG Wen-cai, SUN Yun-yan, YU Chang-qing. 2015. Crustal density of deformation zones of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and their geological implications[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(11): 4115-4128. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 詹艳, 赵国泽, 王继军, 等. 2005. 青藏高原东北缘海原弧形构造区地壳电性结构探测研究[J]. 地震学报, 27(4): 431-440. |
| ZHAN Yan, ZHAO Guo-ze, WANG Ji-jun, et al. 2005. Crustal electric structure of Haiyuan arcuate tectonic region in the northeastern margin of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau, China[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 27(4): 431-440. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 张健, 石耀霖. 2002. 青藏高原隆升及伸展变形中的重力位能[J]. 地球物理学报, 45(2): 226-232. |
| ZHANG Jian, SHI Yao-lin. 2002. The role of gravitational potential energy in raising and spreading of Qinghai-Xizang Plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 45(2): 226-232. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等. 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12-20. |
| ZHANG Pei-zhen, DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Guo-min, et al. 2003. Active tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in the continent of China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 33(S1): 12-20. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 张燕, 程顺有, 赵炳坤, 等. 2013. 青藏高原构造结构特点: 新重力异常成果的启示[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(4): 1369-1380. |
| ZHANG Yan, CHENG Shun-you, ZHAO Bing-kun, et al. 2013. The feature of tectonics in the Tibet Plateau from new regional gravity signals[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(4): 1369-1380. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 张忠杰, 白志明, 王椿镛, 等. 2005. 三江地区地壳结构及动力学意义: 云南遮放-宾川地震反射/折射剖面的启示[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 35(4): 314-319. |
| ZHANG Zhong-jie, BAI Zhi-ming, WANG Chun-yong, et al. 2005. The crustal structure under Sanjiang and its dynamic implications: Revealed by seismic reflection/refraction profile between Zhefang and Binchuan, Yunnan[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 35(4): 314-319. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 郑文俊, 张培震, 袁道阳, 等. 2019. 中国大陆活动构造基本特征及其对区域动力过程的控制[J]. 地质力学学报, 25(5): 699-721. |
| ZHENG Wen-jun, ZHANG Pei-zhen, YUAN Dao-yang, et al. 2019. Basic characteristics of active tectonics and associated geodynamic processes in continental China[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 25(5): 699-721. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] |
Ardestani E V. 2004. Detection of near-surface anomalies through 2-D normalized full gradient of gravity data[J]. Journal of Earth Science, 30(2): 1-6.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Bai D, Unsworth M, Meju M, et al. 2010. Crustal deformation of the eastern Tibetan plateau revealed by magnetotelluric imaging[J]. Nature Geoscience, 3(5): 358-362.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Bao X, Sun X, Xu M, et al. 2015. Two crustal low-velocity channels beneath SE Tibet revealed by joint inversion of Rayleigh wave dispersion and receiver functions[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 415:16-24.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Dondurur D. 2005. Depth estimates for Slingram electromagnetic anomalies from dipping sheet-like bodies by the normalized full gradient method[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 162:2179-2195.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Hu J F, Su Y J, Zhu X G, et al. 2005. S-wave velocity and Poisson’s ratio structure of crust in Yunnan and its implication[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 48(2): 210-218. |
| [29] |
Huang J L, Shen C Y, Li H. 1998. Robust inversion analysis of local gravity anomalies caused by geological dislocation model of faults[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 11(1): 103-113.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Li Y, Wu Q, Zhang R, et al. 2008. The crust and upper mantle structure beneath Yunnan from joint inversion of receiver functions and Rayleigh wave dispersion data[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 170(1-2): 134-146.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Xu Q, Zhao J, Yuan X, et al. 2015. Mapping crustal structure beneath southern Tibet: Seismic evidence for continental crustal underthrusting[J]. Gondwana Research, 27(4): 1487-1493.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Zhang X, Wang Y. 2009. Crustal and upper mantle velocity structure in Yunnan, Southwest China[J]. Tectonophysics, 471(3-4): 171-185.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 徐志萍, 张扬, 杨利普, 徐顺强, 姜磊, 唐淋, 林吉焱. 河南省及邻区主要活动断裂的深部构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1521-1538. |
| [2] | 李君, 王勤彩, 崔子健, 张佩, 周琳, 周辉. 川滇菱形块体东边界及邻区震源机制解与构造应力场空间分布特征[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(6): 1395-1412. |
| [3] | 吴贵灵, 祝成宇, 王国灿, 张攀. 青藏高原东南缘地貌边界性质的界定及其对高原东南缘扩展模式的启示[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(2): 281-299. |
| [4] | 徐志萍, 王夫运, 姜磊, 徐顺强, 唐淋. 川滇地区莫霍面深度和地壳厚度[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(6): 1318-1331. |
| [5] | 王虎, 冉勇康, 陈立春, 梁明剑, 高帅坡, 李彦宝, 徐良鑫. 安宁河断裂带南段滑动速率估计[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(5): 967-979. |
| [6] | 姜磊, 徐志萍, 方盛明, 杨利普, 李怡青, 徐顺强. 利用重震资料研究豫北及邻区地壳结构特征与地震分布[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(2): 323-336. |
| [7] | 谈洪波, 申重阳, 玄松柏, 吴桂桔, 杨光亮, 汪健. 鲁甸MS6.5地震孕育环境的重力学分析[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(2): 356-373. |
| [8] | 王鑫, 张景发, 姜文亮, 蒋洪波, 田甜, 高敏, 付萍杰. 郯庐断裂带南段重力异常及不同深度的横向构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(2): 370-385. |
| [9] | 王鑫, 张景发, 付萍杰, 高敏. 沂沭断裂带重力场及地壳结构特征[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(3): 731-747. |
| [10] | 王虎, 冉勇康, 李彦宝, 陈立春. 川西地区安宁河断层古地震行为及其与则木河断层的比较[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(3): 706-717. |
| [11] | 刘国成, 秦尊丽, 贺日政, 吴燕冈. 藏北高原钾质火山岩区的均衡重力异常与密度结构[J]. 地震地质, 2013, 35(4): 817-832. |
| [12] | 王刚, 王二七. 挤压造山带中的伸展构造及其成因——以滇中地区晚新生代构造为例[J]. 地震地质, 2005, 27(2): 188-199. |
| [13] | 程万正, 刁桂苓, 吕弋培, 张永久, 李桂芳, 陈天长. 川滇地块的震源力学机制、运动速率和活动方式[J]. 地震地质, 2003, 25(1): 71-87. |
| [14] | 殷秀华, 黎益仕, 刘占坡. 塔里木盆地重力场与地壳上地幔结构[J]. 地震地质, 1998, 20(4): 370-378. |
| [15] | 殷秀华, 刘铁胜, 刘占坡. 均衡重力异常和地壳表、浅层地质结构[J]. 地震地质, 1993, 15(2): 149-156. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||