地震地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 345-366.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.01.020
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
张伟恒1)( ), 张东升1), 陈杰2,4), 田勤俭3), 何万通1),*(
), 张东升1), 陈杰2,4), 田勤俭3), 何万通1),*( )
)
收稿日期:2024-02-19
修回日期:2024-04-30
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2025-04-09
通讯作者:
何万通
作者简介:张伟恒, 男, 1993年生, 2002年于中国地震局地质研究院所获构造地质学专业博士学位, 工程师, 主要从事水电工程地质、地震地质研究工作, E-mail: zhangwh93@163.com。
基金资助:
ZHANG Wei-heng1)( ), ZHANG Dong-sheng1), CHEN Jie2,4), TIAN Qin-jian3), HE Wan-tong1),*(
), ZHANG Dong-sheng1), CHEN Jie2,4), TIAN Qin-jian3), HE Wan-tong1),*( )
)
Received:2024-02-19
Revised:2024-04-30
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-04-09
Contact:
HE Wan-tong
摘要:
基于大量震例的地表破裂带宽度统计是确定活动断层错断变形区范围最客观的方法, 能够为重大工程的活动断层避让原则和距离制定提供数据支撑。文中收集了75例文献记录的地表破裂带宽度和49例地表破裂矢量数据, 对文献记录的地表破裂带宽度进行了汇总, 并对地表破裂矢量数据进行了空间分析, 在考虑断层性质及几何结构的情况下, 获得各类地震地表破裂带宽度和分布式破裂密集分布区。根据文献记录数据统计, 正断层、逆断层、走滑断层在几何复杂段的地表破裂带宽度分别为8100m、3700m、10100m, 在平直段分别为160m、120m、400m。根据矢量数据分析, 正断层上盘、下盘, 逆断层上盘、下盘, 走滑断层在主破裂两侧连续分布地表破裂的最大范围分别约为14000m、7000m, 6400m、4300m, 17700m, 其中地表破裂密集分布区域边界与主断层的距离分别为700~800m、200~300m, 1000~1100m、400~500m, 500~600m。综合确定活动断层变形区范围边缘在正断层上盘、下盘, 逆断层上盘、下盘, 走滑断层两盘到主断层的距离分别为400~500m、200~300m, 500~600m、200~300m, 400~500m。考虑断层定位、地表破裂的新生性并排除特殊震例影响, 确定活动断层错断变形区范围边缘在边界清晰的断层平直段距主断层破裂带外围边缘的最小距离为400~500m。在断层的阶区、端部、拐折等几何复杂段及薄皮状逆断层上盘等特殊构造位置, 还应针对活动断层错断变形区范围进行专门研究。利用丰富详细的地表破裂数据能够得到更全面的认识, 文中的研究方法及结果可作为在活动断层附近选址的重大工程对活动断层避让的参考, 未来仍需要不断补充地震地表破裂数据完善文中的研究结果。
张伟恒, 张东升, 陈杰, 田勤俭, 何万通. 基于地表破裂带宽度统计的活动断层错断变形区范围分析[J]. 地震地质, 2025, 47(1): 345-366.
ZHANG Wei-heng, ZHANG Dong-sheng, CHEN Jie, TIAN Qin-jian, HE Wan-tong. THE RANGE OF DEFORMED ZONE BASED BY ACTIVE FAULT OFFSET BASED ON STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF SURFACE RUPTURE ZONE WIDTH[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(1): 345-366.
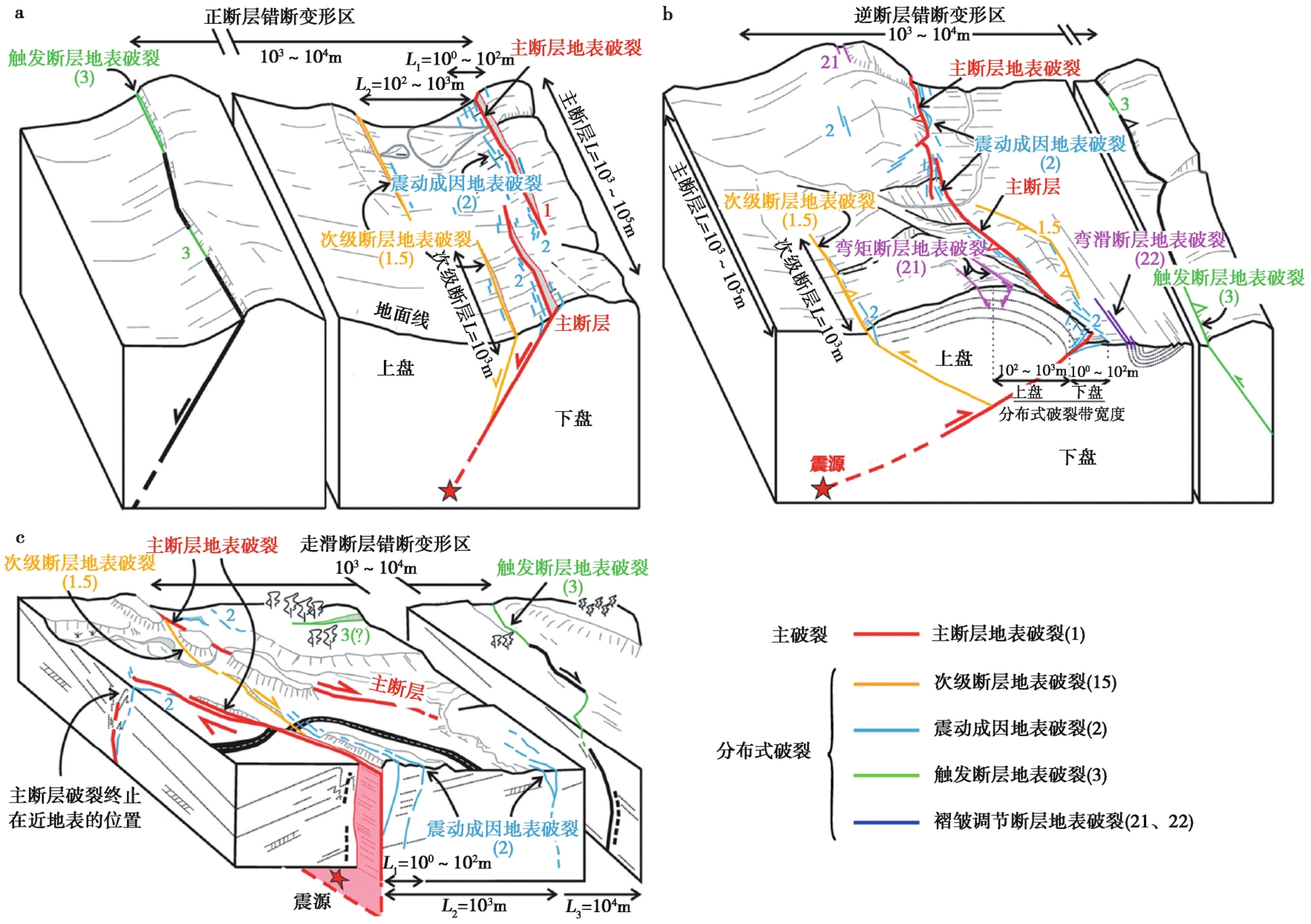
图1 活动断层地表破裂样式分布图(修改自Nurminen et al., 2022) a 正断层地震地表破裂分布样式; b逆断层地震地表破裂分布样式; c 走滑断层地震地表破裂分布样式
Fig. 1 Schematic diagram of surface rupture distribution patterns of active faults(After Nurminen et al., 2022).
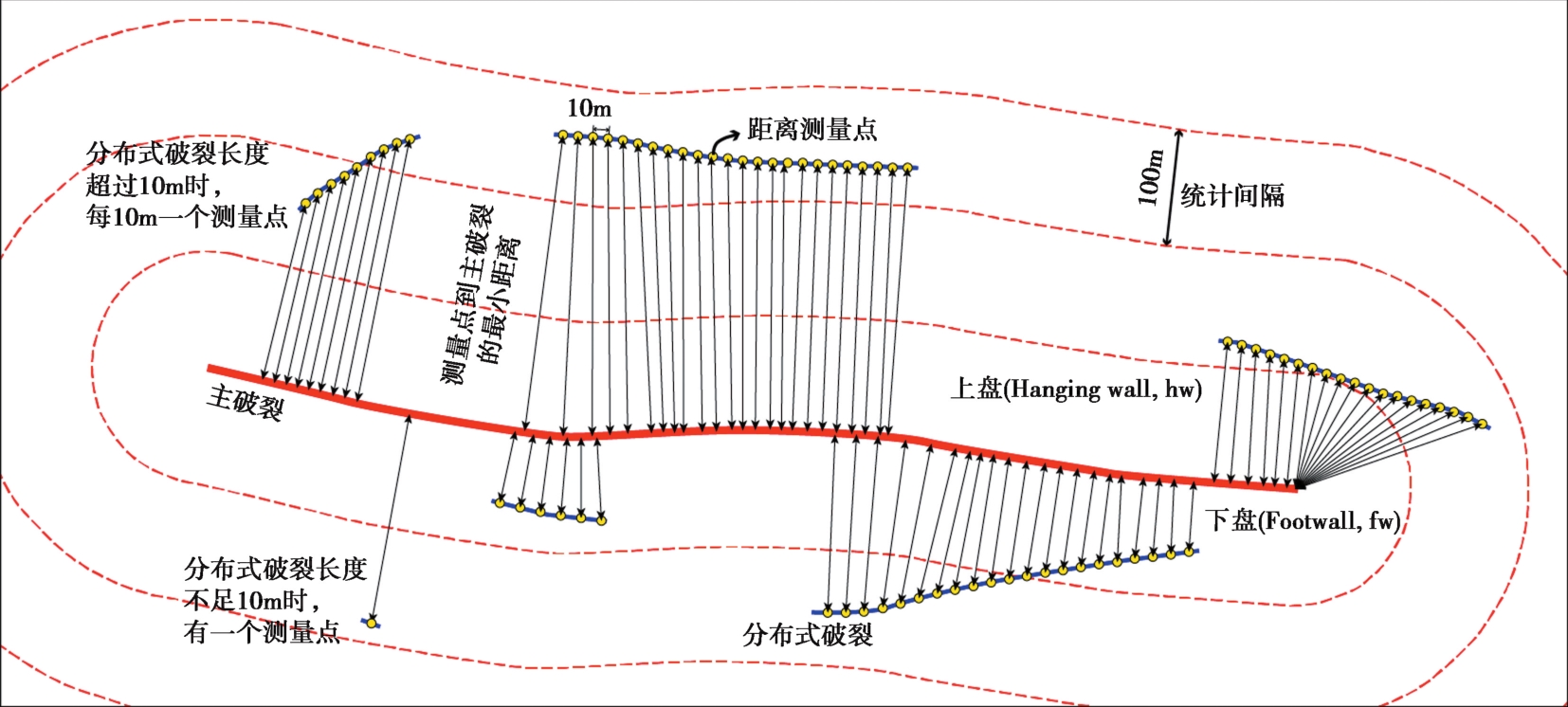
图2 分布式破裂到主破裂距离测量统计方法示意图
Fig. 2 Schematic diagram of the measuring and statistical method for the distance from distributed ruptures to the main rupture.
| 序号 | 发震时间 | 地点 | 震级 | 断层 性质 | 宽度/m | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 几何 复杂部位 | 平直段 | ||||||
| 1 | 1515-06-01 | 云南永胜 | M≥71/2 | 正断 | 8000 | 40 | 虢顺民等, |
| 2 | 1556-01-23 | 陕西华县 | MS8.0 | 正断 | 80 | 王景明, | |
| 3 | 1895-07-05 | 新疆塔什库尔干 | MS7.0 | 正断 | 825 | 60 | 李文巧等, |
| 4 | 1915-01-13 | Avezzano,Italy | MS7.0 | 正断 | 40 | 40 | Boncio et al., |
| 5# | 1915-10-03 | PleasantValley,Italy | MW6.8 | 正断 | 1350 | 120 | Boncio et al., |
| 6# | 1946-11-10 | Ancash,Peru | MW7.3 | 正断 | 150 | 70 | Boncio et al., |
| 7# | 1950-12-14 | FortSageMts,USA | MW5.6 | 正断 | 380 | 40 | Boncio et al., |
| 8# | 1954-12-16 | FairviewPeak,USA | MW7.1 | 右旋正 | 1010 | 120 | Boncio et al., |
| 9# | 1954-12-17 | DixieValley,USA | MW6.6 | 正断 | 705 | 120 | Boncio et al., |
| 10# | 1959-08-18 | HebgenLake,USA | MW7.2 | 正断 | 300 | 130 | Boncio et al., |
| 11 | 1970-03-28 | Gediz,Turky | MS7.0 | 正断 | 285 | 130 | Boncio et al., |
| 12# | 1975-08-01 | Oroville,California,USA | MW5.8 | 正断 | 450 | 30 | Boncio et al., |
| 13 | 1980-11-23 | Irpinia,Italy | MS6.8 | 正断 | 25 | 25 | Boncio et al., |
| 14# | 1981-02-25 | GulfofCorinth,Greece | MS6.4, MS6.7 | 正断 | 70 | Boncio et al., | |
| 15# | 1981-03-04 | GulfofCorinth,Greece | MW6.2 | 正断 | 458 | 115 | Boncio et al., |
| 16# | 1983-10-28 | BorahPeak,USA | MW6.9 | 正断 | 780 | 140 | Boncio et al., |
| 17 | 1986-09-13 | Kalamata,Greece | MS5.8 | 正断 | 60 | 60 | Boncio et al., |
| 18# | 1987-03-02 | Edgecumbe,NewZealand | MW6.5 | 正断 | 80 | 40 | Boncio et al., |
| 19 | 1995-05-13 | WestMacedonia,Greece | MS6.6 | 正断 | 70 | 70 | Boncio et al., |
| 20 | 1995-06-15 | Egion,Greece | MS6.2 | 正断 | 150 | 60 | Boncio et al., |
| 21 | 2006-02-23 | Machaze,Mozambique | MS7.0 | 正断 | 140 | 140 | Boncio et al., |
| 22# | 2009-04-06 | L’Aquila,Italy | MW6.3 | 正断 | 140 | 40 | Boncio et al., |
| 23 | 1906-12-23 | 新疆玛纳斯 | MS8.0 | 逆断 | 40 | 徐锡伟等, | |
| 24 | 1927-05-23 | 甘肃古浪 | MS8.0 | 逆断 | 500 | 20 | 徐锡伟等, |
| 25 | 1954-07-31 | 甘肃民勤 | MS7.0 | 左旋逆 | 100 | 20 | 黄静宜, |
| 26# | 1971-02-09 | SanFernando,USA | MW6.7 | 左旋逆 | 3087 | Boncio et al., | |
| 27# | 1980-10-10 | ElAsnam,Algeria | MW7.1 | 逆断 | 3653 | Boncio et al., | |
| 28# | 1983-06-11 | Coalinga(Nunez),USA | MW5.4 | 逆断 | 190 | Boncio et al., | |
| 29 | 1985-09-12 | 新疆乌恰 | MS7.4 | 右旋逆 | 800 | 100 | 黄静宜, |
| 30# | 1986-03-30 | MarryatCreek,Australia | MW5.7 | 逆断 | 5.7 | Boncio et al., | |
| 31# | 1988-01-22 | TennantCreek,Australia | MW6.6 | 逆断 | 1215 | Boncio et al., | |
| 32# | 1988-12-07 | Spitak,Armenia | MW6.8 | 逆断 | 330 | Boncio et al., | |
| 33# | 1993-09-29 | Killari,India | MW6.2 | 逆断 | 33.6 | Boncio et al., | |
| 34 | 1997-11-08 | 西藏玛尼 | MS7.5 | 左旋逆 | 500 | 7 | 孙鑫喆, |
| 35# | 1999-09-20 | 台湾集集 | MW7.6 | 逆断 | 2580 | Boncio et al., | |
| 36# | 2005-10-08 | Kashmir,Pakistan | MW7.6 | 逆断 | 457 | Boncio et al., | |
| 37# | 2008-05-12 | 四川汶川 | MS8.0 | 右旋逆 | 847 | 60 | Boncio et al., |
| 38# | 2014-11-22 | NaganoPrefecture,Japan | MW6.2 | 逆断 | 901 | Boncio et al., | |
| 39 | 2022-01-08 | 青海门源 | MS6.9 | 左旋逆 | 100 | 50 | 潘家伟等, |
| 40 | 1125-09-06 | 甘肃兰州 | MS7.0 | 左旋 | 1000 | 150 | 宋方敏等, |
| 41 | 1411-09-29 | 西藏当雄南 | MS8.0 | 左旋 | 1500 | 300 | 吴章明等, |
| 42 | 1833-09-08 | 云南嵩明 | MS8.0 | 左旋 | 2000 | 2 | 俞维贤等, |
| 43 | 1850-09-12 | 四川西昌 | MS7.5 | 左旋 | 25 | 黄静宜, | |
| 44# | 1872-03-26 | Owenslake,USA | MW7.5 | 走滑 | 3700 | 200 | 袁兆德等, |
| 45 | 1905-07-09 | Tsetserleg-Bolnay,Mongolian | M≥8 | 走滑 | 6700 | 200 | 袁兆德等, |
| 46 | 1920-12-16 | 宁夏海原 | MS81/2 | 逆左旋 | 250 | 250 | 黄静宜, |
| 47 | 1927-05-23 | 甘肃古浪 | MS8.0 | 逆左旋 | 300 | 40 | 侯康明等, |
| 48 | 1931-08-11 | 新疆富蕴 | MS8.0 | 右旋 | 4500 | 50 | 杨章等, |
| 49 | 1932-12-25 | 甘肃昌马 | MS7.6 | 逆走滑 | 30 | 徐锡伟等, | |
| 50 | 1933-08-25 | 四川叠溪 | MS7.5 | 逆左旋 | 50 | 黄静宜, | |
| 51 | 1936-02-07 | 甘肃康乐 | MS63/4 | 逆左旋 | 10 | 1.2 | 张波等, |
| 52 | 1937-01-07 | 青海托索湖 | MS7.5 | 逆左旋 | 200 | 60 | 李龙海等, |
| 53 | 1937-01-08 | 山东菏泽 | MS7.0 | 右旋 | 80 | 80 | 黄静宜, |
| 54 | 1947-03-17 | 青海达日 | MS7.7 | 逆左旋 | 100 | 黄静宜, | |
| 55 | 1948-05-25 | 四川理塘 | MS7.3 | 右旋 | 200 | 80 | 黄彩权, |
| 56 | 1950-08-15 | 西藏察隅 | MS8.6 | 右旋 | 2 | 黄静宜, | |
| 57 | 1951-11-18 | 西藏当雄、崩错 | MS8.0 | 正右旋 | 40 | 张德成, | |
| 58 | 1955-04-14 | 四川康定 | MS7.5 | 走滑 | 20 | 四川省地震局地震地质队, | |
| 59# | 1968-04-09 | Borregomountain,USA | MW6.6 | 走滑 | 1300 | 180 | 袁兆德等, |
| 60 | 1970-01-05 | 云南通海 | MS7.8 | 逆右旋 | 20 | 黄静宜, | |
| 61 | 1973-02-06 | 四川炉霍 | MS7.6 | 左旋 | 100 | 黄静宜, | |
| 62 | 1975-02-04 | 辽宁海城 | MS7.3 | 左旋 | 60 | 徐锡伟等, | |
| 63 | 1976-05-29 | 云南龙陵 | MS7.4 | 正右旋 | 40 | 黄静宜, | |
| 64 | 1976-07-28 | 河北唐山 | MS7.8 | 右旋 | 100 | 20 | 徐锡伟等, |
| 65 | 1981-01-24 | 四川道孚 | MS6.9 | 左旋 | 50 | 黄静宜, | |
| 66# | 1987-11-24 | SuperstitionHills,USA | MW6.5 | 走滑 | 10000 | 360 | 袁兆德等, |
| 67# | 1992-06-28 | Landers,USA | MW7.3 | 走滑 | 3900 | 290 | 袁兆德等, |
| 68# | 1999-10-16 | HectorMine,USA | MW7.1 | 走滑 | 800 | 80 | 袁兆德等, |
| 69 | 2001-11-14 | 青海昆仑山口西 | MS8.1 | 左旋 | 2800 | 30 | 徐锡伟等, |
| 70# | 2010-04-04 | ElMayor-Cucapah,Mexico | MW7.2 | 走滑 | 1000 | 60 | 袁兆德等, |
| 71 | 2010-04-14 | 青海玉树 | MS7.1 | 左旋 | 3500 | 30 | 孙鑫喆等, |
| 72# | 2010-09-03 | Darfield,NewZealand | MW7.2 | 走滑 | 300 | Quigley et al., | |
| 73 | 2014-02-12 | 新疆于田 | MW6.9 | 左旋 | 1800 | 130 | 袁兆德等, |
| 74 | 2016-11-14 | Kaikōura,NewZealand | MW7.6 | 走滑 | 2000 | 100 | 袁兆德等, |
| 75 | 2021-05-22 | 青海玛多 | MW7.4 | 左旋 | 100 | 潘家伟等, | |
表1 地震地表破裂带宽度统计表
Table1 Statistical results for the width of earthquake surface rupture zones
| 序号 | 发震时间 | 地点 | 震级 | 断层 性质 | 宽度/m | 参考文献 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 几何 复杂部位 | 平直段 | ||||||
| 1 | 1515-06-01 | 云南永胜 | M≥71/2 | 正断 | 8000 | 40 | 虢顺民等, |
| 2 | 1556-01-23 | 陕西华县 | MS8.0 | 正断 | 80 | 王景明, | |
| 3 | 1895-07-05 | 新疆塔什库尔干 | MS7.0 | 正断 | 825 | 60 | 李文巧等, |
| 4 | 1915-01-13 | Avezzano,Italy | MS7.0 | 正断 | 40 | 40 | Boncio et al., |
| 5# | 1915-10-03 | PleasantValley,Italy | MW6.8 | 正断 | 1350 | 120 | Boncio et al., |
| 6# | 1946-11-10 | Ancash,Peru | MW7.3 | 正断 | 150 | 70 | Boncio et al., |
| 7# | 1950-12-14 | FortSageMts,USA | MW5.6 | 正断 | 380 | 40 | Boncio et al., |
| 8# | 1954-12-16 | FairviewPeak,USA | MW7.1 | 右旋正 | 1010 | 120 | Boncio et al., |
| 9# | 1954-12-17 | DixieValley,USA | MW6.6 | 正断 | 705 | 120 | Boncio et al., |
| 10# | 1959-08-18 | HebgenLake,USA | MW7.2 | 正断 | 300 | 130 | Boncio et al., |
| 11 | 1970-03-28 | Gediz,Turky | MS7.0 | 正断 | 285 | 130 | Boncio et al., |
| 12# | 1975-08-01 | Oroville,California,USA | MW5.8 | 正断 | 450 | 30 | Boncio et al., |
| 13 | 1980-11-23 | Irpinia,Italy | MS6.8 | 正断 | 25 | 25 | Boncio et al., |
| 14# | 1981-02-25 | GulfofCorinth,Greece | MS6.4, MS6.7 | 正断 | 70 | Boncio et al., | |
| 15# | 1981-03-04 | GulfofCorinth,Greece | MW6.2 | 正断 | 458 | 115 | Boncio et al., |
| 16# | 1983-10-28 | BorahPeak,USA | MW6.9 | 正断 | 780 | 140 | Boncio et al., |
| 17 | 1986-09-13 | Kalamata,Greece | MS5.8 | 正断 | 60 | 60 | Boncio et al., |
| 18# | 1987-03-02 | Edgecumbe,NewZealand | MW6.5 | 正断 | 80 | 40 | Boncio et al., |
| 19 | 1995-05-13 | WestMacedonia,Greece | MS6.6 | 正断 | 70 | 70 | Boncio et al., |
| 20 | 1995-06-15 | Egion,Greece | MS6.2 | 正断 | 150 | 60 | Boncio et al., |
| 21 | 2006-02-23 | Machaze,Mozambique | MS7.0 | 正断 | 140 | 140 | Boncio et al., |
| 22# | 2009-04-06 | L’Aquila,Italy | MW6.3 | 正断 | 140 | 40 | Boncio et al., |
| 23 | 1906-12-23 | 新疆玛纳斯 | MS8.0 | 逆断 | 40 | 徐锡伟等, | |
| 24 | 1927-05-23 | 甘肃古浪 | MS8.0 | 逆断 | 500 | 20 | 徐锡伟等, |
| 25 | 1954-07-31 | 甘肃民勤 | MS7.0 | 左旋逆 | 100 | 20 | 黄静宜, |
| 26# | 1971-02-09 | SanFernando,USA | MW6.7 | 左旋逆 | 3087 | Boncio et al., | |
| 27# | 1980-10-10 | ElAsnam,Algeria | MW7.1 | 逆断 | 3653 | Boncio et al., | |
| 28# | 1983-06-11 | Coalinga(Nunez),USA | MW5.4 | 逆断 | 190 | Boncio et al., | |
| 29 | 1985-09-12 | 新疆乌恰 | MS7.4 | 右旋逆 | 800 | 100 | 黄静宜, |
| 30# | 1986-03-30 | MarryatCreek,Australia | MW5.7 | 逆断 | 5.7 | Boncio et al., | |
| 31# | 1988-01-22 | TennantCreek,Australia | MW6.6 | 逆断 | 1215 | Boncio et al., | |
| 32# | 1988-12-07 | Spitak,Armenia | MW6.8 | 逆断 | 330 | Boncio et al., | |
| 33# | 1993-09-29 | Killari,India | MW6.2 | 逆断 | 33.6 | Boncio et al., | |
| 34 | 1997-11-08 | 西藏玛尼 | MS7.5 | 左旋逆 | 500 | 7 | 孙鑫喆, |
| 35# | 1999-09-20 | 台湾集集 | MW7.6 | 逆断 | 2580 | Boncio et al., | |
| 36# | 2005-10-08 | Kashmir,Pakistan | MW7.6 | 逆断 | 457 | Boncio et al., | |
| 37# | 2008-05-12 | 四川汶川 | MS8.0 | 右旋逆 | 847 | 60 | Boncio et al., |
| 38# | 2014-11-22 | NaganoPrefecture,Japan | MW6.2 | 逆断 | 901 | Boncio et al., | |
| 39 | 2022-01-08 | 青海门源 | MS6.9 | 左旋逆 | 100 | 50 | 潘家伟等, |
| 40 | 1125-09-06 | 甘肃兰州 | MS7.0 | 左旋 | 1000 | 150 | 宋方敏等, |
| 41 | 1411-09-29 | 西藏当雄南 | MS8.0 | 左旋 | 1500 | 300 | 吴章明等, |
| 42 | 1833-09-08 | 云南嵩明 | MS8.0 | 左旋 | 2000 | 2 | 俞维贤等, |
| 43 | 1850-09-12 | 四川西昌 | MS7.5 | 左旋 | 25 | 黄静宜, | |
| 44# | 1872-03-26 | Owenslake,USA | MW7.5 | 走滑 | 3700 | 200 | 袁兆德等, |
| 45 | 1905-07-09 | Tsetserleg-Bolnay,Mongolian | M≥8 | 走滑 | 6700 | 200 | 袁兆德等, |
| 46 | 1920-12-16 | 宁夏海原 | MS81/2 | 逆左旋 | 250 | 250 | 黄静宜, |
| 47 | 1927-05-23 | 甘肃古浪 | MS8.0 | 逆左旋 | 300 | 40 | 侯康明等, |
| 48 | 1931-08-11 | 新疆富蕴 | MS8.0 | 右旋 | 4500 | 50 | 杨章等, |
| 49 | 1932-12-25 | 甘肃昌马 | MS7.6 | 逆走滑 | 30 | 徐锡伟等, | |
| 50 | 1933-08-25 | 四川叠溪 | MS7.5 | 逆左旋 | 50 | 黄静宜, | |
| 51 | 1936-02-07 | 甘肃康乐 | MS63/4 | 逆左旋 | 10 | 1.2 | 张波等, |
| 52 | 1937-01-07 | 青海托索湖 | MS7.5 | 逆左旋 | 200 | 60 | 李龙海等, |
| 53 | 1937-01-08 | 山东菏泽 | MS7.0 | 右旋 | 80 | 80 | 黄静宜, |
| 54 | 1947-03-17 | 青海达日 | MS7.7 | 逆左旋 | 100 | 黄静宜, | |
| 55 | 1948-05-25 | 四川理塘 | MS7.3 | 右旋 | 200 | 80 | 黄彩权, |
| 56 | 1950-08-15 | 西藏察隅 | MS8.6 | 右旋 | 2 | 黄静宜, | |
| 57 | 1951-11-18 | 西藏当雄、崩错 | MS8.0 | 正右旋 | 40 | 张德成, | |
| 58 | 1955-04-14 | 四川康定 | MS7.5 | 走滑 | 20 | 四川省地震局地震地质队, | |
| 59# | 1968-04-09 | Borregomountain,USA | MW6.6 | 走滑 | 1300 | 180 | 袁兆德等, |
| 60 | 1970-01-05 | 云南通海 | MS7.8 | 逆右旋 | 20 | 黄静宜, | |
| 61 | 1973-02-06 | 四川炉霍 | MS7.6 | 左旋 | 100 | 黄静宜, | |
| 62 | 1975-02-04 | 辽宁海城 | MS7.3 | 左旋 | 60 | 徐锡伟等, | |
| 63 | 1976-05-29 | 云南龙陵 | MS7.4 | 正右旋 | 40 | 黄静宜, | |
| 64 | 1976-07-28 | 河北唐山 | MS7.8 | 右旋 | 100 | 20 | 徐锡伟等, |
| 65 | 1981-01-24 | 四川道孚 | MS6.9 | 左旋 | 50 | 黄静宜, | |
| 66# | 1987-11-24 | SuperstitionHills,USA | MW6.5 | 走滑 | 10000 | 360 | 袁兆德等, |
| 67# | 1992-06-28 | Landers,USA | MW7.3 | 走滑 | 3900 | 290 | 袁兆德等, |
| 68# | 1999-10-16 | HectorMine,USA | MW7.1 | 走滑 | 800 | 80 | 袁兆德等, |
| 69 | 2001-11-14 | 青海昆仑山口西 | MS8.1 | 左旋 | 2800 | 30 | 徐锡伟等, |
| 70# | 2010-04-04 | ElMayor-Cucapah,Mexico | MW7.2 | 走滑 | 1000 | 60 | 袁兆德等, |
| 71 | 2010-04-14 | 青海玉树 | MS7.1 | 左旋 | 3500 | 30 | 孙鑫喆等, |
| 72# | 2010-09-03 | Darfield,NewZealand | MW7.2 | 走滑 | 300 | Quigley et al., | |
| 73 | 2014-02-12 | 新疆于田 | MW6.9 | 左旋 | 1800 | 130 | 袁兆德等, |
| 74 | 2016-11-14 | Kaikōura,NewZealand | MW7.6 | 走滑 | 2000 | 100 | 袁兆德等, |
| 75 | 2021-05-22 | 青海玛多 | MW7.4 | 左旋 | 100 | 潘家伟等, | |
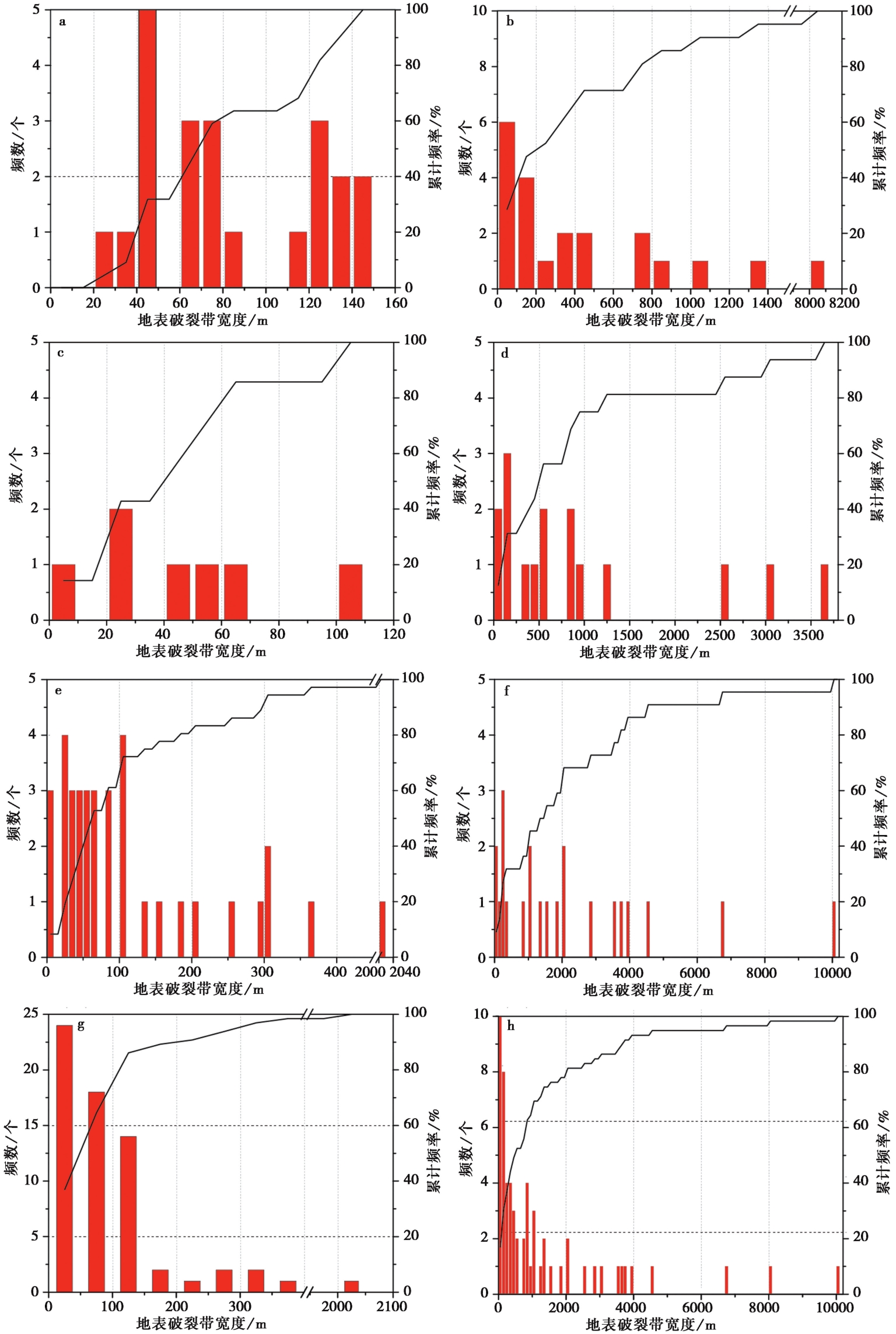
图3 地震地表破裂带宽度的文献统计结果图 a 正断层平直段; b 正断层几何复杂段; c 逆断层平直段; d 逆断层几何复杂段; e 走滑断层平直段; f 走滑断层几何复杂段; g 各型断层平直段汇总; h 各型断层几何复杂段汇总。纵坐标代表震例的统计个数
Fig. 3 Statistical results from literatures on the width of earthquake surface rupture zones.
| 序号 | 发震时间 | 地点 | 震级 | 断层 性质 | 主破裂 长度 /m | 分布式破裂统计点 数量* | 分布式破裂距主破裂 最远距离/m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上盘 | 下盘 | 上盘 | 下盘 | ||||||
| 1 | 1887-05-03 | SonoraValley,USA | MW7.5 | 正断 | 57106 | 996 | 234 | 3734 | 3913 |
| 2# | 1915-10-03 | PleasantValley,Italy | MW6.8 | 正断 | 54797 | 1428 | 300 | 1952 | 904 |
| 3# | 1946-11-10 | Ancash,Peru | MW7.3 | 正断 | 6864 | 31 | 14 | 107 | 29 |
| 4# | 1950-12-14 | FortSageMts,USA | MW5.6 | 正断 | 9040 | 37 | 0 | 367 | |
| 5# | 1954-12-16 | FairviewPeak,USA | MW7.1 | 正断 | 57067 | 3583 | 1035 | 19212 | 3811 |
| 6# | 1954-12-17 | DixieValley,USA | MW6.6 | 正断 | 53376 | 4299 | 173 | 3889 | 258 |
| 7# | 1959-08-18 | HebgenLake,USA | MW7.2 | 正断 | 36906 | 4494 | 762 | 13801 | 2992 |
| 8# | 1975-08-01 | Oroville,USA | MW5.8 | 正断 | 3380 | 3 | 26 | 451 | 26 |
| 9 | 1978-06-20 | Thessaloniki,Greece | MW6.2 | 正断 | 12363 | 1798 | 186 | 5409 | 720 |
| 10 | 1980-05-25 | MammothLake,USA | MW6.2 | 正断 | 7488 | 412 | 2664 | 11973 | 16244 |
| 11# | 1981-02-24 | Pisia,Greece | MW6.6 | 正断 | 11785 | 419 | 126 | 3776 | 760 |
| 12# | 1981-03-04 | GulfofCorinth,Greece | MW6.4 | 正断 | 10747 | 379 | 272 | 1817 | 1116 |
| 13# | 1983-10-28 | BorahPeak,USA | MW6.9 | 正断 | 27670 | 2631 | 1516 | 6568 | 6964 |
| 14# | 1987-03-02 | Edgecumbe,NewZealand | MW6.5 | 正断 | 7105 | 1111 | 424 | 10234 | 6946 |
| 15# | 2009-04-06 | L’Aquila,Italy | MW6.3 | 正断 | 1707 | 395 | 79 | 9827 | 3580 |
| 16 | 2016-08-24 | Amatrice,Italy | MW6.0 | 正断 | 3245 | 31 | 27 | 2023 | 297 |
| 17 | 2016-10-30 | Norcia,Italy | MW6.5 | 正断 | 26504 | 3102 | 353 | 14552 | 7319 |
| 18 | 1911-01-03 | Chon-Kemin,Kazakhstan/Kyrghystan | MW7.7 | 逆断 | 102140 | 10797 | 1174 | 7579 | 3538 |
| 19 | 1970-03-10 | Calingiri,Australia | MW5.0 | 逆断 | 3698 | 218 | 21 | 1191 | 21 |
| 20# | 1971-02-09 | SanFernando,USA | MW6.7 | 逆断 | 11143 | 1506 | 180 | 2713 | 512 |
| 21# | 1980-10-10 | ElAsnam,Algeria | MW7.1 | 逆断 | 30380 | 4191 | 1630 | 2556 | 2070 |
| 22# | 1983-06-11 | Coalinga(Nunez),USA | MW5.4 | 逆断 | 3792 | 15 | 42 | 219 | 197 |
| 23# | 1986-03-30 | MarryatCreek,Australia | MW5.8 | 逆断 | 13634 | 10 | 17 | 7 | 17 |
| 24# | 1988-01-22 | TennantCreek,Australia | MW6.6 | 逆断 | 32239 | 121 | 291 | 68 | 1298 |
| 25# | 1988-12-07 | Spitak,Armenia | MW6.8 | 逆断 | 6935 | 167 | 40 | 271 | 142 |
| 26# | 1993-09-29 | Killari,India | MW6.2 | 逆断 | 160 | 27 | 1 | 52 | 54 |
| 27# | 1999-09-20 | 台湾集集,中国 | MW7.6 | 逆断 | 97797 | 2561 | 321 | 2632 | 466 |
| 28# | 2005-10-08 | Kashmir,Pakistan | MW7.6 | 逆断 | 15998 | 528 | 23 | 770 | 233 |
| 29# | 2008-05-12 | 四川汶川,中国 | MS8.0 | 逆断 | 332506 | 376 | 875 | 3877 | 4216 |
| 30 | 2012-03-23 | Pukatja,Australia | MW5.4 | 逆断 | 1416 | 70 | 14 | 100 | 18 |
| 31# | 2014-11-22 | NaganoPrefecture,Japan | MW6.2 | 逆断 | 9994 | 399 | 48 | 846 | 149 |
| 32 | 2016-05-20 | Petermann,Australia | MW6.1 | 逆断 | 12263 | 85 | 50 | 100 | 128 |
| 33 | 2019-11-11 | LeTeil,France | MW4.9 | 逆断 | 5626 | 233 | 1 | 516 | 65 |
| 34# | 1872-03-26 | OwensValley,USA | MW7.5 | 走滑 | 167017 | 13360 | 9784 | ||
| 35# | 1968-04-09 | BorregoMountain,USA | MW6.6 | 走滑 | 34326 | 3874 | 2508 | ||
| 36 | 1979-10-15 | ImperialValley,USA | MW6.5 | 走滑 | 29053 | 2504 | 7365 | ||
| 37# | 1987-11-24 | SuperstitionHills,USA | MW6.6 | 走滑 | 34255 | 5093 | 8116 | ||
| 38# | 1992-06-28 | Landers,USA | MW7.3 | 走滑 | 118288 | 25812 | 16772 | ||
| 39 | 1995-01-16 | Kobe,Japan | MW6.9 | 走滑 | 10855 | 718 | 4479 | ||
| 40 | 1999-08-17 | Izmit,Turkey | MW7.6 | 走滑 | 110595 | 2159 | 19269 | ||
| 41# | 1999-10-16 | HectorMine,USA | MW7.1 | 走滑 | 94366 | 9046 | 7358 | ||
| 42 | 2002-11-03 | Denali,USA | MW7.9 | 走滑 | 77480 | 7135 | 21943 | ||
| 43 | 2010-03-26 | Pisayambo,Ecuador | MW5.0 | 走滑 | 9159 | 21 | 83 | ||
| 44# | 2010-04-04 | ElMayor-Cucapah,Mexico | MW7.2 | 走滑 | 72990 | 24290 | 120456 | ||
| 45# | 2010-09-03 | Darfield,NewZealand | MW7.2 | 走滑 | 55432 | 1369 | 122 | ||
| 46 | 2014-08-24 | Napa,USA | MW6.0 | 走滑 | 24590 | 3773 | 3161 | ||
| 47 | 2016-04-15 | Kumamoto,Japan | MW7.0 | 走滑 | 41271 | 9221 | 18502 | ||
| 48 | 2019-07-04 | Ridgecrest Ⅰ,USA | MW6.4 | 走滑 | 21409 | 9742 | 20058 | ||
| 49 | 2019-07-05 | Ridgecrest Ⅱ,USA | MW7.1 | 走滑 | 61948 | 20396 | 21548 | ||
表2 地震地表破裂矢量数据统计表
Table2 Statistical results of earthquake surface rupture vector data
| 序号 | 发震时间 | 地点 | 震级 | 断层 性质 | 主破裂 长度 /m | 分布式破裂统计点 数量* | 分布式破裂距主破裂 最远距离/m | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上盘 | 下盘 | 上盘 | 下盘 | ||||||
| 1 | 1887-05-03 | SonoraValley,USA | MW7.5 | 正断 | 57106 | 996 | 234 | 3734 | 3913 |
| 2# | 1915-10-03 | PleasantValley,Italy | MW6.8 | 正断 | 54797 | 1428 | 300 | 1952 | 904 |
| 3# | 1946-11-10 | Ancash,Peru | MW7.3 | 正断 | 6864 | 31 | 14 | 107 | 29 |
| 4# | 1950-12-14 | FortSageMts,USA | MW5.6 | 正断 | 9040 | 37 | 0 | 367 | |
| 5# | 1954-12-16 | FairviewPeak,USA | MW7.1 | 正断 | 57067 | 3583 | 1035 | 19212 | 3811 |
| 6# | 1954-12-17 | DixieValley,USA | MW6.6 | 正断 | 53376 | 4299 | 173 | 3889 | 258 |
| 7# | 1959-08-18 | HebgenLake,USA | MW7.2 | 正断 | 36906 | 4494 | 762 | 13801 | 2992 |
| 8# | 1975-08-01 | Oroville,USA | MW5.8 | 正断 | 3380 | 3 | 26 | 451 | 26 |
| 9 | 1978-06-20 | Thessaloniki,Greece | MW6.2 | 正断 | 12363 | 1798 | 186 | 5409 | 720 |
| 10 | 1980-05-25 | MammothLake,USA | MW6.2 | 正断 | 7488 | 412 | 2664 | 11973 | 16244 |
| 11# | 1981-02-24 | Pisia,Greece | MW6.6 | 正断 | 11785 | 419 | 126 | 3776 | 760 |
| 12# | 1981-03-04 | GulfofCorinth,Greece | MW6.4 | 正断 | 10747 | 379 | 272 | 1817 | 1116 |
| 13# | 1983-10-28 | BorahPeak,USA | MW6.9 | 正断 | 27670 | 2631 | 1516 | 6568 | 6964 |
| 14# | 1987-03-02 | Edgecumbe,NewZealand | MW6.5 | 正断 | 7105 | 1111 | 424 | 10234 | 6946 |
| 15# | 2009-04-06 | L’Aquila,Italy | MW6.3 | 正断 | 1707 | 395 | 79 | 9827 | 3580 |
| 16 | 2016-08-24 | Amatrice,Italy | MW6.0 | 正断 | 3245 | 31 | 27 | 2023 | 297 |
| 17 | 2016-10-30 | Norcia,Italy | MW6.5 | 正断 | 26504 | 3102 | 353 | 14552 | 7319 |
| 18 | 1911-01-03 | Chon-Kemin,Kazakhstan/Kyrghystan | MW7.7 | 逆断 | 102140 | 10797 | 1174 | 7579 | 3538 |
| 19 | 1970-03-10 | Calingiri,Australia | MW5.0 | 逆断 | 3698 | 218 | 21 | 1191 | 21 |
| 20# | 1971-02-09 | SanFernando,USA | MW6.7 | 逆断 | 11143 | 1506 | 180 | 2713 | 512 |
| 21# | 1980-10-10 | ElAsnam,Algeria | MW7.1 | 逆断 | 30380 | 4191 | 1630 | 2556 | 2070 |
| 22# | 1983-06-11 | Coalinga(Nunez),USA | MW5.4 | 逆断 | 3792 | 15 | 42 | 219 | 197 |
| 23# | 1986-03-30 | MarryatCreek,Australia | MW5.8 | 逆断 | 13634 | 10 | 17 | 7 | 17 |
| 24# | 1988-01-22 | TennantCreek,Australia | MW6.6 | 逆断 | 32239 | 121 | 291 | 68 | 1298 |
| 25# | 1988-12-07 | Spitak,Armenia | MW6.8 | 逆断 | 6935 | 167 | 40 | 271 | 142 |
| 26# | 1993-09-29 | Killari,India | MW6.2 | 逆断 | 160 | 27 | 1 | 52 | 54 |
| 27# | 1999-09-20 | 台湾集集,中国 | MW7.6 | 逆断 | 97797 | 2561 | 321 | 2632 | 466 |
| 28# | 2005-10-08 | Kashmir,Pakistan | MW7.6 | 逆断 | 15998 | 528 | 23 | 770 | 233 |
| 29# | 2008-05-12 | 四川汶川,中国 | MS8.0 | 逆断 | 332506 | 376 | 875 | 3877 | 4216 |
| 30 | 2012-03-23 | Pukatja,Australia | MW5.4 | 逆断 | 1416 | 70 | 14 | 100 | 18 |
| 31# | 2014-11-22 | NaganoPrefecture,Japan | MW6.2 | 逆断 | 9994 | 399 | 48 | 846 | 149 |
| 32 | 2016-05-20 | Petermann,Australia | MW6.1 | 逆断 | 12263 | 85 | 50 | 100 | 128 |
| 33 | 2019-11-11 | LeTeil,France | MW4.9 | 逆断 | 5626 | 233 | 1 | 516 | 65 |
| 34# | 1872-03-26 | OwensValley,USA | MW7.5 | 走滑 | 167017 | 13360 | 9784 | ||
| 35# | 1968-04-09 | BorregoMountain,USA | MW6.6 | 走滑 | 34326 | 3874 | 2508 | ||
| 36 | 1979-10-15 | ImperialValley,USA | MW6.5 | 走滑 | 29053 | 2504 | 7365 | ||
| 37# | 1987-11-24 | SuperstitionHills,USA | MW6.6 | 走滑 | 34255 | 5093 | 8116 | ||
| 38# | 1992-06-28 | Landers,USA | MW7.3 | 走滑 | 118288 | 25812 | 16772 | ||
| 39 | 1995-01-16 | Kobe,Japan | MW6.9 | 走滑 | 10855 | 718 | 4479 | ||
| 40 | 1999-08-17 | Izmit,Turkey | MW7.6 | 走滑 | 110595 | 2159 | 19269 | ||
| 41# | 1999-10-16 | HectorMine,USA | MW7.1 | 走滑 | 94366 | 9046 | 7358 | ||
| 42 | 2002-11-03 | Denali,USA | MW7.9 | 走滑 | 77480 | 7135 | 21943 | ||
| 43 | 2010-03-26 | Pisayambo,Ecuador | MW5.0 | 走滑 | 9159 | 21 | 83 | ||
| 44# | 2010-04-04 | ElMayor-Cucapah,Mexico | MW7.2 | 走滑 | 72990 | 24290 | 120456 | ||
| 45# | 2010-09-03 | Darfield,NewZealand | MW7.2 | 走滑 | 55432 | 1369 | 122 | ||
| 46 | 2014-08-24 | Napa,USA | MW6.0 | 走滑 | 24590 | 3773 | 3161 | ||
| 47 | 2016-04-15 | Kumamoto,Japan | MW7.0 | 走滑 | 41271 | 9221 | 18502 | ||
| 48 | 2019-07-04 | Ridgecrest Ⅰ,USA | MW6.4 | 走滑 | 21409 | 9742 | 20058 | ||
| 49 | 2019-07-05 | Ridgecrest Ⅱ,USA | MW7.1 | 走滑 | 61948 | 20396 | 21548 | ||
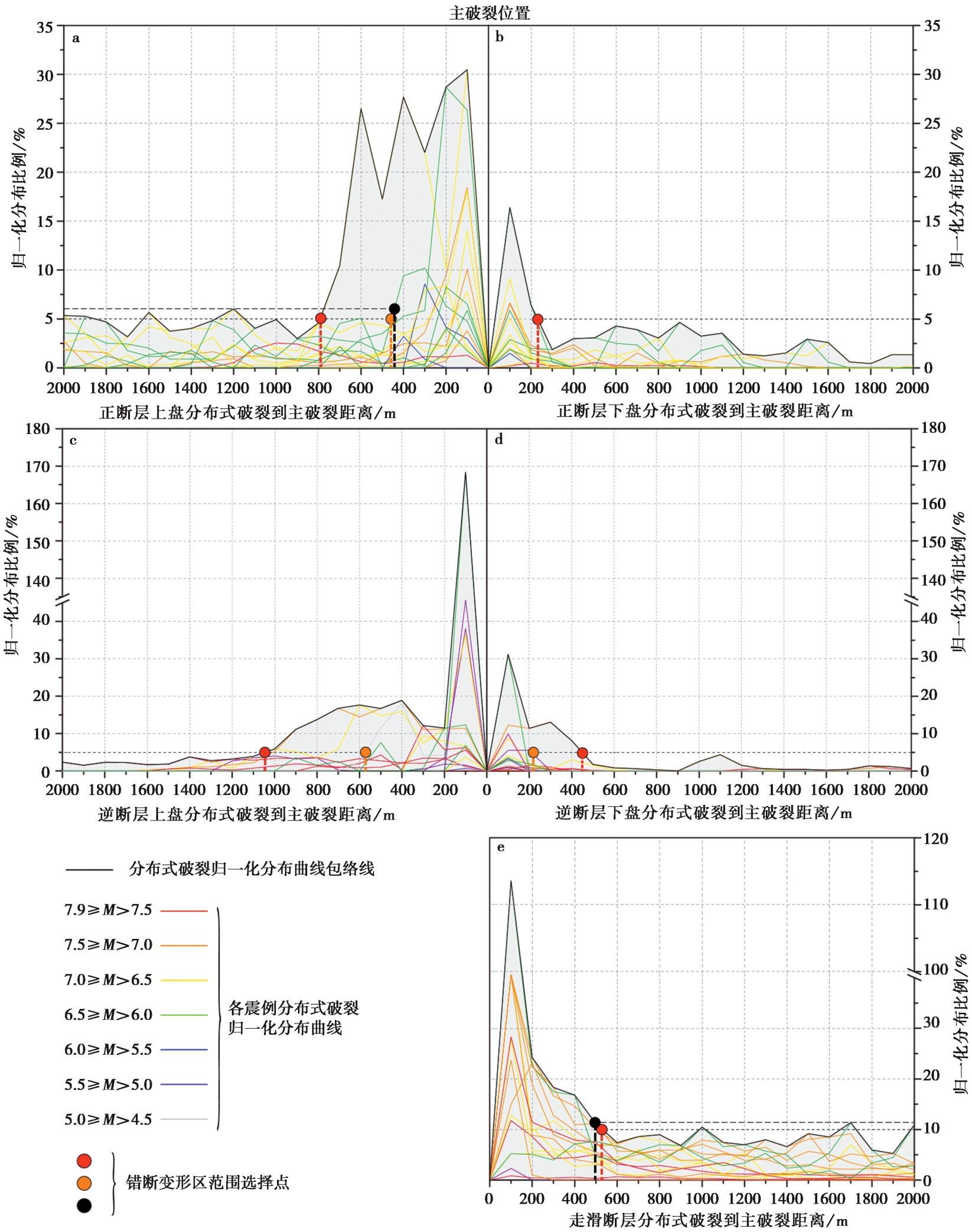
图5 矢量数据统计分布式破裂到主破裂距离的分布特征图 a 正断层上盘; b 正断层下盘; c 逆断层上盘; d 逆断层下盘; e 走滑断层
Fig. 5 Distribution feature of distributed ruptures to main rupture distance based on vector data statistics.
| 地表破裂统计分类 | 正断层 | 逆断层 | 走滑 断层 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上盘 | 下盘 | 上盘 | 下盘 | |||
| 文献 统计 | 平直段最大极值宽度/m | 160 | 120 | 2000 (仅1例) | ||
| 平直段最大宽度/m | 400 | |||||
| 几何复杂段最大宽度/m | 8100 | 3700 | 10100 | |||
| 涵盖75%震例的几何复杂段宽度/m | 1400 | 1000 | 3800 | |||
| 矢量 统计 | 分布式破裂距主破裂最远距离/m | 19212 | 16244 | 7579 | 4216 | 120456 |
| 震例汇总后连续有分布式地表破裂区域距主破裂的最远距离/m | 14000 | 7000 | 6400 | 4300 | 17700 | |
| 分布式地表破裂密集分布区边缘距主破裂距离/m | 700~800 | 200~300 | 1000~1100 | 400~500 | 500~600 | |
| 排除特殊震例后分布式地表破裂密集分布区边缘距主破裂距离/m | 400~500 | 200~300 | 500~600 | 200~300 | 400~500 | |
表3 不同统计方法获得的各类型断层地表破裂宽度统计汇总表
Table3 Summary of surface rupture width of various types of faults obtained by different statistical methods
| 地表破裂统计分类 | 正断层 | 逆断层 | 走滑 断层 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上盘 | 下盘 | 上盘 | 下盘 | |||
| 文献 统计 | 平直段最大极值宽度/m | 160 | 120 | 2000 (仅1例) | ||
| 平直段最大宽度/m | 400 | |||||
| 几何复杂段最大宽度/m | 8100 | 3700 | 10100 | |||
| 涵盖75%震例的几何复杂段宽度/m | 1400 | 1000 | 3800 | |||
| 矢量 统计 | 分布式破裂距主破裂最远距离/m | 19212 | 16244 | 7579 | 4216 | 120456 |
| 震例汇总后连续有分布式地表破裂区域距主破裂的最远距离/m | 14000 | 7000 | 6400 | 4300 | 17700 | |
| 分布式地表破裂密集分布区边缘距主破裂距离/m | 700~800 | 200~300 | 1000~1100 | 400~500 | 500~600 | |
| 排除特殊震例后分布式地表破裂密集分布区边缘距主破裂距离/m | 400~500 | 200~300 | 500~600 | 200~300 | 400~500 | |
| [1] |
常祖峰. 2021. 1515年云南永胜 73/4级大地震遗迹[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 42(S1): 176—178.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
冯先岳, 栾超群, 李军, 等. 1988. 1985年乌恰7.4级地震形变带[J]. 地震地质, 10(2): 39—45.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
虢顺民, 向宏发, 张靖, 等. 1988. 1515年云南永胜地震形变带和震级讨论[J]. 地震研究, 11(2): 153—162.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
郭婷婷, 徐锡伟, 于贵华. 2013. 逆冲型地震地表破裂带宽度与活断层“避让带”的分析研究[J]. 地震研究, 36(3): 352—357.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
侯康明. 1998. 1927年古浪8级大震地表破裂特征及形成机制[J]. 地震地质, 20(1): 20—27.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
黄彩权. 1983. 1948年理塘 71/4级地震的发震断裂及地震破裂带特征[J]. 四川地震, (2): 1—3, 49.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
黄静宜. 2016. 强震地表破裂评估方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
李红, 邓志辉, 陈连旺, 等. 2019. 走滑断层地震地表破裂带分布影响因素数值模拟研究: 以1973年炉霍 MS7.6 地震为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 62(8): 2871—2884.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
李龙海, 贾运鸿. 1981. 一九三七年青海托索湖7.5级地震形变带特征[J]. 西北地震学报, 3(3): 61—65.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
李文巧, 陈杰, 袁兆德, 等. 2011. 帕米尔高原1895年塔什库尔干地震地表多段同震破裂与发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 33(2): 260—276. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.02.002.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
李智敏, 盖海龙, 李鑫, 等. 2022. 2022年青海门源 MS6.9 地震发震构造和地表破裂初步调查[J]. 地质学报, 96(1): 330—335.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
梁宽, 何仲太, 姜文亮, 等. 2022. 2022年1月8日青海门源 MS6.9 地震的同震地表破裂特征[J]. 地震地质, 44(1): 256—278. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.01.016.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
刘洪春, 戴华光, 李龙海, 等. 2000. 对1954年民勤7级地震的初步研究[J]. 西北地震学报, 22(3): 25—28.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
潘家伟, 白明坤, 李超, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震地表破裂带及发震构造[J]. 地质学报, 95(6): 1655—1670.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
潘家伟, 李海兵,
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
邵延秀, 刘静, 高云鹏, 等. 2022. 同震地表破裂的位移测量与弥散变形分析: 以2021年青海玛多 MW7.4 地震为例[J]. 地震地质, 44(2): 506—523. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.02.014.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
四川省地震局地震地质队. 1988. 1955年康定7.5级地震[J]. 四川地震, (4): 32—35.
|
|
Seismogeological Team of Sichuan Seismological Bureau. 1988. The 1955 Kangding M7.5 earthquake[J]. Earthquake Research in Sichuan, (4): 32—35 (in Chinese).
|
|
| [18] |
宋方敏, 袁道阳, 陈桂华, 等. 2007. 1125年兰州7级地震地表破裂类型及其分布特征[J]. 地震地质, 29(4): 834—844.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
孙鑫喆. 2016. 玛尼地震与玉树地震发震断层的破裂特征与复发模型[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
孙鑫喆, 徐锡伟, 陈立春, 等. 2012. 2010年玉树地震地表破裂带典型破裂样式及其构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(1): 155—170.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
王景明. 1980. 1556年陕西华县大地震的地面破裂[J]. 地震学报, 2(4): 430—437, 453—454.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
吴章明, 申屠炯明, 曹忠权, 等. 1990. 1411年西藏当雄南8级地震地表破裂[J]. 地震地质, 12(2): 98—108, 193—194.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
徐锡伟, 郭婷婷, 刘少卓, 等. 2016. 活动断层避让相关问题的讨论[J]. 地震地质, 38(3): 477—502. doi: 10.3936/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.03.001.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
徐锡伟, 于贵华, 马文涛, 等. 2002. 活动断层地震地表破裂“避让带”宽度确定的依据与方法[J]. 地震地质, 24(4): 470—483.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
徐锡伟, 于贵华, 马文涛, 等. 2008. 昆仑山地震(MW7.8)破裂行为、变形局部化特征及其构造内涵讨论[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 38(7): 785—796.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
杨章, 戈澍谟. 1980. 对1931年新疆富蕴地震断裂带及构造运动特征的初步认识[J]. 地震地质, 2(3): 31—37, 82.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
于克涛, 蒋溥. 1990. 论地震地表破裂及其工程地震意义[J]. 地质灾害与防治, 1(2): 90—92, 65.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
俞维贤, 汪一鹏, 宋方敏, 等. 1996. 1833年云南嵩明8级大地震地表破裂带的考查研究[J]. 地震研究, 19(4): 385—390.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
袁兆德, 刘静, 李雪, 等. 2021. 2014年新疆于田 MS7.3 地震地表破裂带精细填图及其破裂特征[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 51(2): 276—298.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
张波, 何文贵, 方良好, 等. 2015. 1936年甘肃康乐 63/4级地震地表破裂带调查[J]. 地震研究, 38(2): 262—271, 333.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
张德成. 1988. 西藏当雄1951年8.0级地震烈度分布及形变特征[J]. 中国地震, 4(4): 64—69.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
张建毅. 2015. 工程场地活断层避让距离研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
张永双, 孙萍, 石菊松, 等. 2010. 汶川地震地表破裂影响带调查与建筑场地避让宽度探讨[J]. 工程地质学报, 18(3): 312—319.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
周庆, 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 等. 2008. 汶川8.0级地震地表破裂带宽度调查[J]. 地震地质, 30(3): 778—788.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
|
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
|
| [39] |
|
| [40] |
|
| [41] |
PMID |
| [42] |
|
| [43] |
|
| No related articles found! |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||