地震地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (2): 371-396.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2024.02.008
郭祥云1)( ), 房立华1), 韩立波1),*(
), 房立华1), 韩立波1),*( ), 李振月1), 李春来1), 苏珊2)
), 李振月1), 李春来1), 苏珊2)
收稿日期:2023-03-13
修回日期:2023-05-11
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-05-29
通讯作者:
*韩立波, 男, 1979年生, 研究员, 主要研究方向为地震震源参数, E-mail: 作者简介:郭祥云, 女, 1975年生, 2014年于中国地震局地球物理研究所获固体地球物理学硕士学位, 高级工程师, 主要从事震源机制及构造应力场反演方面的研究, E-mail: ldazui@sina.com。
基金资助:
GUO Xiang-yun1)( ), FANG Li-hua1), HAN Li-bo1),*(
), FANG Li-hua1), HAN Li-bo1),*( ), LI Zhen-yue1), LI Chun-lai1), SU Shan2)
), LI Zhen-yue1), LI Chun-lai1), SU Shan2)
Received:2023-03-13
Revised:2023-05-11
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-05-29
摘要:
文中利用四川、 云南、 重庆、 青海、 甘肃地震台网以及西昌密集台阵和巧家密集台阵的数字地震波形资料, 采用CAP全波形反演方法及HASH初动极性和振幅比方法, 获得了川滇菱形块体东边界区域3 951组ML≥1.0地震的震源机制。进而基于以上震源机制, 采用阻尼区域应力场反演算法(MSTASI)和Vavryčuk的迭代联合反演方法获得了研究区的构造应力场分布特征、 主要活动断裂的应力性质和摩擦系数。结果显示, 研究区震源机制P轴、 T轴以及最大主应力轴 和最小主应力轴 总体上倾角较小, 揭示了近水平的挤压或剪切应力环境。σ1以NW-SE和NWW-SEE向为主, 从北到南有顺时针旋转的趋势, 应力性质以走滑型为主, 局部兼有逆冲型和拉张型, 整体分布特征与区内走滑型边界断裂活动性质一致。R值具有明显的空间差异, 鲜水河断裂-龙门山断裂-安宁河断裂交会地区R值相对较高, 有明显的挤压特征; 鲜水河断裂带、 安宁河断裂带北段和小江断裂带的R值均在0.25~0.5之间, 表现为NE-SW向挤压和NW-SE向拉张, 拉张应力可能远小于挤压应力; 大凉山断裂带北段和则木河断裂带的R值均在0.5~1之间, 表现为NW-SE向压缩和NE-SW向拉张, 且挤压应力大于拉张应力。研究区域主要断裂的摩擦系数也有差异: 安宁河断裂带和大凉山断裂带北段的摩擦系数相对较低, 在0.75以下, 鲜水河断裂带、 则木河断裂带及大凉山断裂带南段的摩擦系数偏高, 在0.80以上。川滇菱形块体东边界活动断裂带上的构造应力相对较高, 尤其是鲜水河断裂带和小江断裂带的应力更高, 需要关注其地震危险性。
郭祥云, 房立华, 韩立波, 李振月, 李春来, 苏珊. 川滇菱形块体东边界震源机制与应力场特征[J]. 地震地质, 2024, 46(2): 371-396.
GUO Xiang-yun, FANG Li-hua, HAN Li-bo, LI Zhen-yue, LI Chun-lai, SU Shan. CHARACTERISTICS OF FOCAL MECHANISM AND STRESS FIELD IN THE EASTERN BOUNDARY OF THE SICHUAN-YUNNAN BLOCK[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2024, 46(2): 371-396.
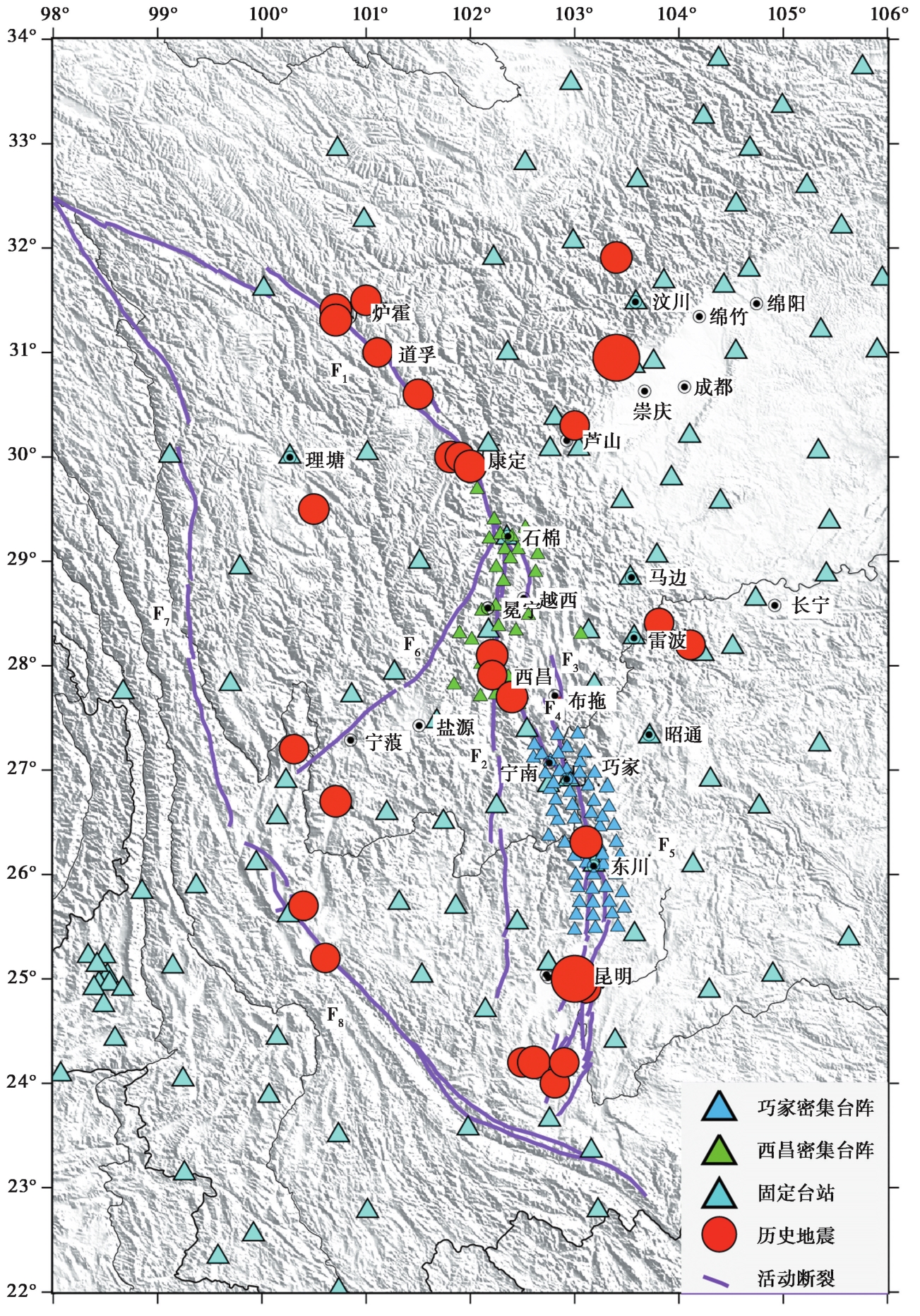
图1 研究区及其附近MS≥7.0历史地震和地震台站分布 F1鲜水河断裂带; F2安宁河断裂带; F3大凉山断裂带; F4则木河断裂带; F5小江断裂带; F6丽江-小金河断裂带; F7金沙江断裂带; F8红河断裂
Fig. 1 Seismic stations and historical earthquakes(MS≥7.0)in the study region.
| 日期范围 | 震级范围 | 地震个数 | 方法 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008-01—2020-10 | 2.5~4.0 | 2466 | HASH | 固定台网 |
| 2013-02—2021-04 | 1.0~4.0 | 745 | HASH | 西昌台阵 |
| 2012-03—2021-04 | 1.5~4.0 | 571 | HASH | 巧家台阵 |
| 2008-01—2020-10 | 4.0~7.0 | 169 | CAP | 固定台网 |
表1 不同震级档的震源机制反演方法和数据来源
Table1 Focal mechanism inversion methods for earthquakes of different magnitudes
| 日期范围 | 震级范围 | 地震个数 | 方法 | 数据来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2008-01—2020-10 | 2.5~4.0 | 2466 | HASH | 固定台网 |
| 2013-02—2021-04 | 1.0~4.0 | 745 | HASH | 西昌台阵 |
| 2012-03—2021-04 | 1.5~4.0 | 571 | HASH | 巧家台阵 |
| 2008-01—2020-10 | 4.0~7.0 | 169 | CAP | 固定台网 |
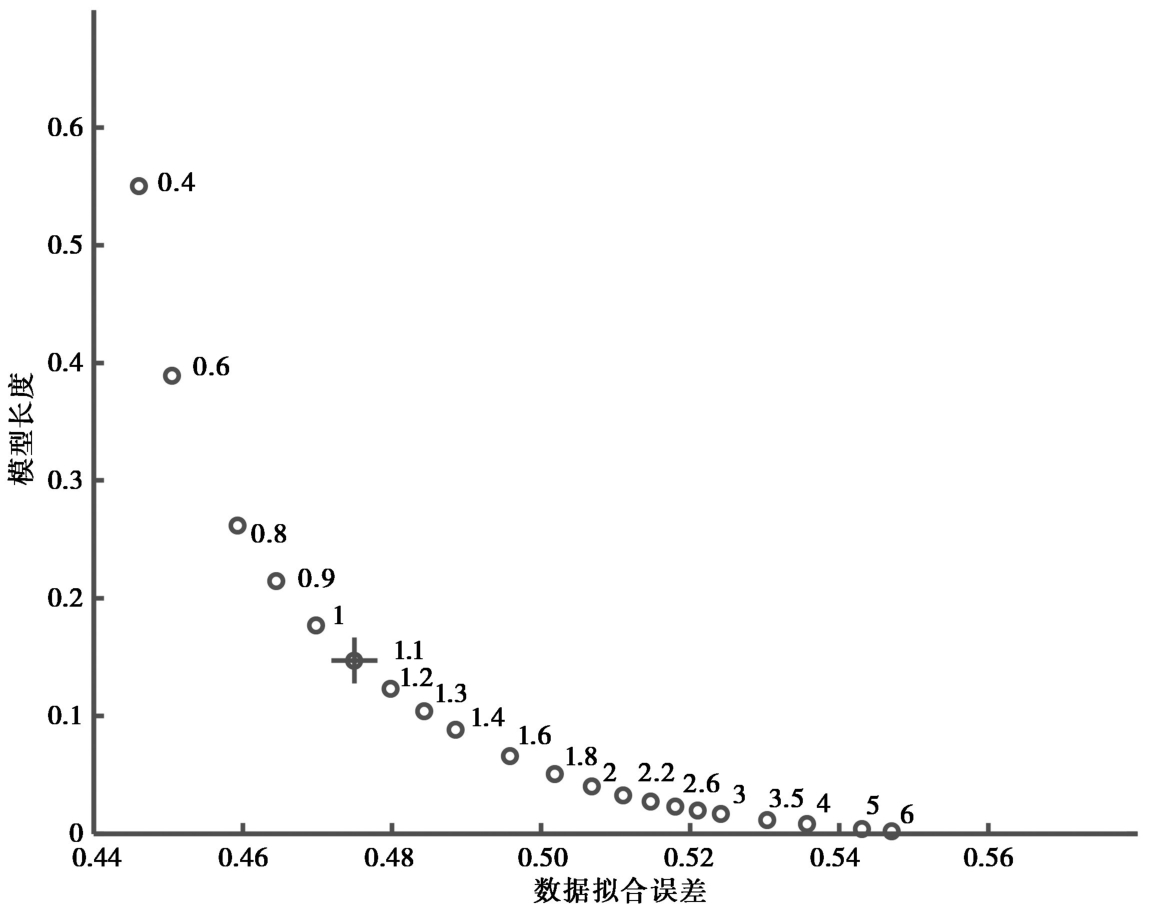
图3 模型长度与数据拟合误差之间的折衷曲线图 空心圆旁所标数字是阻尼参数, 十字表示所选择的最佳阻尼系数
Fig. 3 Trade-off curve between model length and misfit calculated from the corresponding damping parameters.
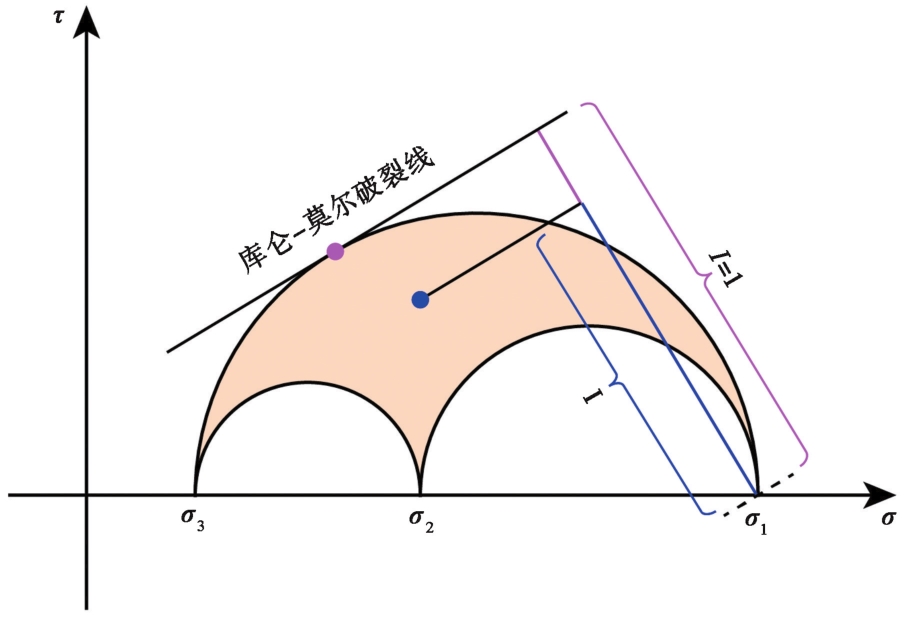
图4 失稳系数的定义(改自Vavryčuk, 2014) 紫红色的圆点是库仑-莫尔破裂线与莫尔圆的交点, 代表最易失稳的断层; 蓝黑色的点表示任意断层在莫尔圆中的位置, 蓝色实线的长度代表了断层的稳定性
Fig. 4 Definition of instability coefficient(modified from Vavryčuk, 2014).
| 类型 | P轴倾角 | B轴倾角 | T轴倾角 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 正断型(NF) | ≥52° | ≤35° | |
| 正走滑型(NS) | 40°≤倾角<52° | ≤20° | |
| 走滑型(SS) | <40° | ≥45° | ≤20° |
| ≤20° | ≥45° | <40° | |
| 逆走滑型(TS) | ≤20° | 40°≤倾角<52° | |
| 逆断型(TF) | ≤35° | ≥52° | |
| 不确定型(U) | 上述类型之外的震源机制解 | ||
表2 震源机制解分类表
Table2 Categories of tectonic stress regine for focal mechanism
| 类型 | P轴倾角 | B轴倾角 | T轴倾角 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 正断型(NF) | ≥52° | ≤35° | |
| 正走滑型(NS) | 40°≤倾角<52° | ≤20° | |
| 走滑型(SS) | <40° | ≥45° | ≤20° |
| ≤20° | ≥45° | <40° | |
| 逆走滑型(TS) | ≤20° | 40°≤倾角<52° | |
| 逆断型(TF) | ≤35° | ≥52° | |
| 不确定型(U) | 上述类型之外的震源机制解 | ||
| 断裂带 | 机制解 个数 | μ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 走向 | 倾角 | 走向 | 倾角 | 走向 | 倾角 | |||
| 鲜水河断裂带 | 213 | 0.80 | 282° | 2°±4.68° | 160° | 87°±5.25° | 12° | 2°±5.24° |
| 安宁河断裂带 | 339 | 0.65 | 313° | 10°±7.90° | 105° | 78°±8.76° | 222° | 5°±3.01° |
| 则木河断裂带 | 70 | 0.80 | 301° | 12°±6.26° | 114° | 78°±6.26° | 210° | 1°±6.80° |
| 小江断裂带 | 140 | 0.75 | 310° | 12°±7.81° | 96° | 75°±7.69° | 218° | 8°±2.96° |
| 大凉山断裂带北段 | 230 | 0.65 | 274° | 22°±4.72° | 84° | 67°±4.64° | 182° | 3°±2.17° |
| 大凉山断裂带南段 | 65 | 0.85 | 317° | 3°±9.30 | 47 | 7°±7.43° | 204° | 82°±7.3° |
表3 川滇菱形块体东边界主要活动断裂应力轴、 应力型因子(R值)、 摩擦系数(μ)
Table3 Stress axis, Shape ratio(R value), fraction(μ)of a main active fault in the eastern boundary of the Sichuan-Yunnan block
| 断裂带 | 机制解 个数 | μ | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 走向 | 倾角 | 走向 | 倾角 | 走向 | 倾角 | |||
| 鲜水河断裂带 | 213 | 0.80 | 282° | 2°±4.68° | 160° | 87°±5.25° | 12° | 2°±5.24° |
| 安宁河断裂带 | 339 | 0.65 | 313° | 10°±7.90° | 105° | 78°±8.76° | 222° | 5°±3.01° |
| 则木河断裂带 | 70 | 0.80 | 301° | 12°±6.26° | 114° | 78°±6.26° | 210° | 1°±6.80° |
| 小江断裂带 | 140 | 0.75 | 310° | 12°±7.81° | 96° | 75°±7.69° | 218° | 8°±2.96° |
| 大凉山断裂带北段 | 230 | 0.65 | 274° | 22°±4.72° | 84° | 67°±4.64° | 182° | 3°±2.17° |
| 大凉山断裂带南段 | 65 | 0.85 | 317° | 3°±9.30 | 47 | 7°±7.43° | 204° | 82°±7.3° |
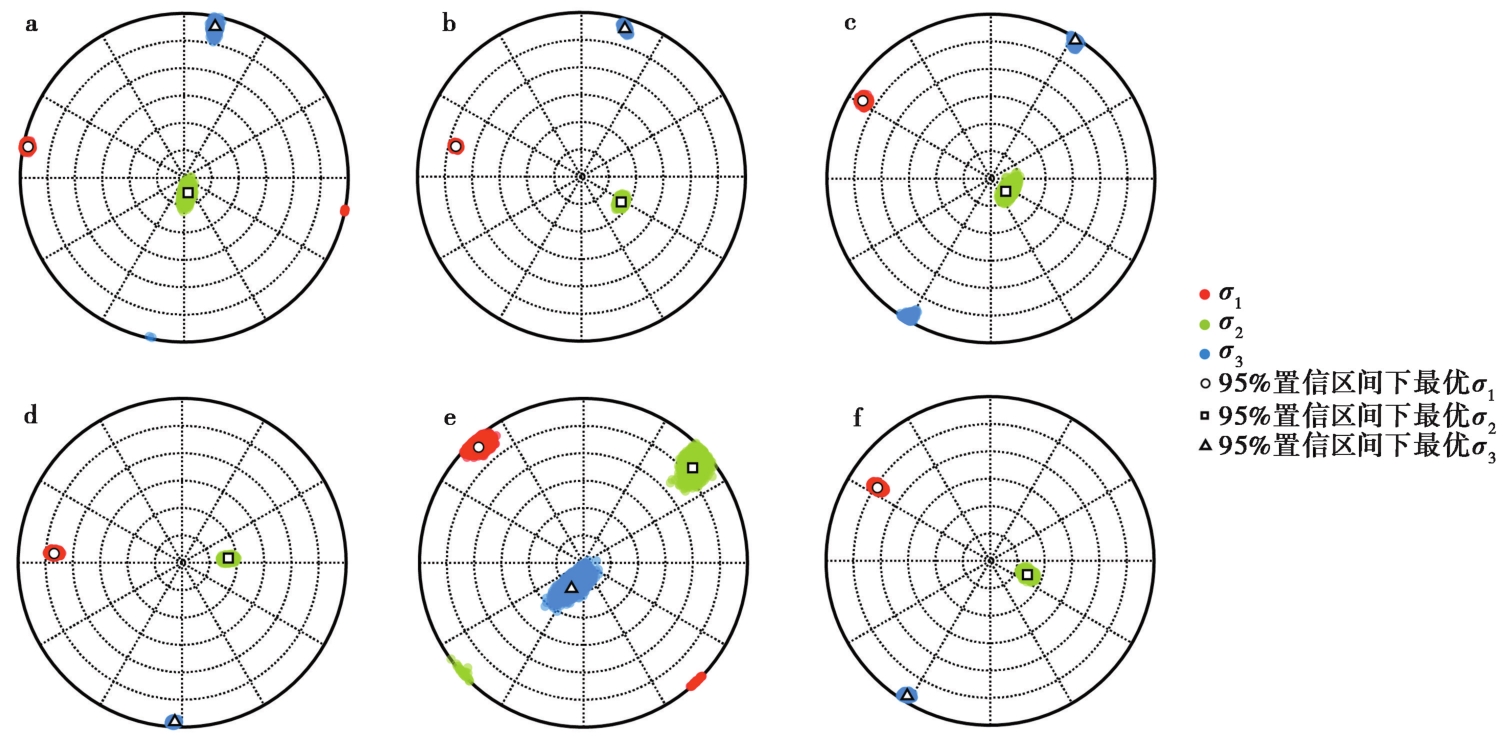
图14 川滇菱形块体东边界主要活动断裂的构造应力 a 鲜水河断裂带; b 安宁河断裂带; c 则木河断裂带; d 大凉山断裂带北段; e 大凉山断裂带南段; f 小江断裂带
Fig. 14 Stress field of the main fault zone in the eastern boundary of the Sichuan-Yunnan block.
| [1] |
陈长云, 何宏林. 2008. 大凉山地区新生代地壳缩短及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 30(2): 443—453.
DOI |
|
DOI |
|
| [2] |
陈桂华, 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 等. 2008. 川滇块体北-东边界活动构造带运动学转换与变形分解作用[J]. 地震地质, 30(1): 58—85.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
成尔林. 1981. 四川及其邻区现代构造应力场和现代构造运动特征[J]. 地震学报, 3(3): 231—241.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
程佳, 刘杰, 徐锡伟, 等. 2014. 大凉山次级块体内强震发生的构造特征与2014年鲁甸6.5级地震对周边断层的影响[J]. 地震地质, 36(4): 1229—1243. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.04.023.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
程万正, 刁桂苓, 吕弋培, 等. 2003. 川滇地块的震源力学机制、 运动速率和活动方式[J]. 地震地质, 25(1): 71—87.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
崔效锋, 谢富仁, 张红艳. 2006. 川滇地区现代构造应力场分区及动力学意义[J]. 地震学报, 28(5): 451—461.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 2002. 中国活动构造基本特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 32(12): 1020—1030.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
杜平山, 冯元保. 2000. 川滇块体东缘地壳动力学问题的讨论[J]. 四川地震, 1-2: 119—126.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
国家地震局西南烈度队. 1979. 川滇强震去地震地质汇编[M]. 北京: 地震出版社.
|
|
Southwest China Seismic Zoning Research Team, SSB. 1979. Collection Works on Seismology of Sichuan and Yunnan Strong Earthquake Areas[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing (in Chinese).
|
|
| [10] |
郭祥云, 陈学忠, 王生文, 等. 2014. 川滇地区中小地震震源机制解及构造应力场的研究[J]. 地震工程学报, 36(3): 599—607.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
何宏林, 池田安隆, 何玉林, 等. 2008. 新生的大凉山断裂带: 鲜水河-小江断裂系中段的裁弯取直[J]. 中国科学(D 辑), 38(5): 564—574.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
胡鸿翔, 林中洋, 边银菊, 等. 1996. 滇西地区壳幔过渡带性质的研究[J]. 地震学报, 18(4): 444—450.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
黄润秋. 2005. 中国西南岩石高边坡的主要特征及其演化[J]. 地球科学进展, 20(3): 292—297.
DOI |
|
DOI |
|
| [14] |
李大虎, 丁志峰, 吴萍萍, 等. 2015. 鲜水河断裂带南东段的深部孕震环境与2014年康定 MS6.3 地震[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(6): 1941—1953.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [15] |
李君, 王勤彩, 崔子健, 等. 2019. 川滇菱形块体东边界及邻区震源机制解与构造应力场空间分布特征[J]. 地震地质, 41(6): 1395—1412. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.06.006.
|
|
DOI |
|
| [16] |
李玶. 1993. 鲜水河-小江断裂带[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 74.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
林向东, 徐平, 武敏捷, 等. 2010. 小江断裂中段及邻区构造应力场分布特征[J]. 中国地震, 26(2): 192—200.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
刘辛中, 张风霜, 马伶俐, 等. 2022. 川滇菱形块体东边界现今应变积累特征及强震危险性[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 42(7): 687—693.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
龙思胜, 陈银. 2003. 安宁河-则木河断裂带近期7次地震的震源机制解[J]. 四川地震, (2): 21—25.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
吕江宁, 沈正康, 王敏. 2003. 川滇地区现代地壳运动速度场和活动块体模型研究[J]. 地震地质, 25(4): 543—554.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
罗钧, 赵翠萍, 周连庆. 2014. 川滇块体及周边区域现今震源机制和应力场特征[J]. 地震地质, 36(2): 405—421. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.02.011.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
孟文, 郭祥云, 李永华, 等. 2022. 青藏高原东北缘构造应力场及动力学特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 65(9): 3229—3251.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
潘懋, 梁海华, 蔡永恩, 等. 1994. 中国川西地区鲜水河断裂和则木河断裂几何学、 运动学特征及地震活动性对比研究[J]. 中国地震, 10(1): 28—37.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
裴玮来, 周仕勇. 2022. 基于最大顺序统计量的P波初动极性自动读取方法的小震震源机制反演及在云南小江地区的应用研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 65(3): 992—1005.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
裴锡瑜, 王新民, 张成贵. 1998. 晚第四纪安宁河活断裂分段的基本特征[J]. 四川地震, 21(4): 52—61.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
祁玉萍, 张致伟, 龙锋, 等. 2018. 大凉山次级块体及邻区震源机制解与区域应力场特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 40(2): 377—395.
DOI |
|
DOI |
|
| [27] |
钱晓东, 秦嘉政, 刘丽芳. 2011. 云南地区现代构造应力场研究[J]. 地震地质, 33(1): 91—106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.01.009.
|
|
DOI |
|
| [28] |
冉勇康, 陈建武, 宫会玲, 等. 2008. 安宁河断裂紫马跨一带晚第四纪地貌变形与断层位移速率[J]. 地震地质, 30(1): 86—98.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
单斌, 熊熊, 郑勇, 等. 2009. 2008年5月12日 MW7.9 汶川地震导致的周边断层应力变化[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 39(5): 537—545.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
宋方敏, 汪一鹏, 俞维贤, 等. 1998. 小江活动断裂带[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1—237.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
苏珊. 2019. 安宁河断裂及周边地区震源机制解与应力场分布特征[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地球物理研究所: 21—27.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
田雯, 郑勇, 刁法启. 2016. 断层闭锁区的形变过程模拟[A]//2016年中国地球科学联合学术年会论文集. 北京: 中国学术期刊电子杂志社: 1040—1041.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
王椿镛,
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
王椿镛, 吴建平, 楼海, 等. 2003. 川西藏东地区的地壳P波速度结构[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 181—189.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
王绳祖, 张流. 2002. 塑性流动网络控制下川滇菱形块体及邻区构造应力场与地震构造[J]. 地震地质, 24(3): 324—334.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
王晓山, 吕坚, 谢祖军, 等. 2015. 南北地震带震源机制解与构造应力场特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(11): 4149—4162.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
王新民, 裴锡瑜. 1998. 康定—泸定地区主要活动断层与地裂缝[J]. 四川地震, (1): 46—56.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
王阎昭, 王恩宁, 沈正康, 等. 2008. 基于GPS 资料约束反演川滇地区主要断裂现今活动速率[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 38(5): 582—597.
|
|
|
|
| [39] |
韦生吉, 倪四道, 崇加军, 等. 2009. 2003年8月16日赤峰地震: 一个可能发生在下地壳的地震?[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(1): 111—119.
|
|
|
|
| [40] |
魏文薪. 2012. 川滇块体东边界主要断裂带运动特性及动力学机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [41] |
闻学泽, 杜平山, 龙德熊. 2000. 安宁河断裂小相岭段古地震的新证据及最晚事件的年代[J]. 地震地质, 22(1): 1—8.
|
|
|
|
| [42] |
闻学泽, 范军, 易桂喜, 等. 2008. 川西安宁河断裂上的地震空区[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 38(7): 797—807.
|
|
|
|
| [43] |
吴建平, 明跃红, 王椿镛. 2004. 云南地区中小地震震源机制及构造应力场研究[J]. 地震学报, 26(5): 457—465.
|
|
|
|
| [44] |
徐纪人, 赵志新, 石川有三. 2008. 中国大陆地壳应力场与构造运动区域特征研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(3): 770—781.
|
|
|
|
| [45] |
徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 郑荣章, 等. 2003. 川滇地区活动块体最新构造变动样式及其动力来源[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 151—162.
|
|
|
|
| [46] |
许忠淮, 汪素云, 黄雨蕊, 等. 1987. 由多个小震推断的青甘和川滇地区地壳应力场的方向特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 30(5): 476—486.
|
|
|
|
| [47] |
易桂喜, 龙锋, 乔慧珍, 等. 2012. 隆昌及邻近区域小震群分析[J]. 四川地震, (2): 9—14.
|
|
|
|
| [48] |
易桂喜, 闻学泽, 苏有锦. 2008. 川滇活动地块东边界强震危险性研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(6): 1719—1725.
|
|
|
|
| [49] |
张杰, 杨光亮, 谈洪波, 等. 2020. 基于接收函数约束的川滇地区莫霍面深度反演研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(7): 2579—2591.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [50] |
张培震. 2008. 青藏高原东缘川西地区的现今构造变形, 应变分配与深部动力过程[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 38(9): 1041—1056.
|
|
|
|
| [51] |
张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等. 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12—20.
|
|
|
|
| [52] |
张培震, 王琪, 马宗晋. 2002. 中国大陆现今构造运动的GPS速度场与活动地块[J]. 地学前缘, 9(2): 430—441.
|
|
|
|
| [53] |
张世民, 谢富仁. 2001. 鲜水河-小江断裂带7级以上强震构造区的划分及其构造地貌特征[J]. 地震学报, 23(1): 36—44.
|
|
|
|
| [54] |
张岳桥, 陈文, 杨农. 2004. 川西鲜水河断裂带晚新生代剪切变形 40Ar/39Ar测年及其构造意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 34(7): 613—621.
|
|
|
|
| [55] |
周荣军, 黎小刚, 黄祖智, 等. 2003. 四川大凉山断裂带的晚第四纪平均滑动速率[J]. 地震研究, 26(2): 191—196.
|
|
|
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [60] |
|
| [61] |
|
| [62] |
|
| [63] |
|
| [64] |
|
| [65] |
|
| [66] |
|
| [67] |
|
| [68] |
|
| [69] |
|
| [70] |
|
| [71] |
|
| [72] |
|
| [73] |
|
| [74] |
|
| [75] |
PMID |
| [76] |
|
| [77] |
|
| [78] |
|
| [79] |
|
| [80] |
|
| [81] |
|
| [82] |
|
| [1] | 董春丽, 张广伟, 李欣蔚, 王跃杰, 丁大业, 宫卓宏. 基于震源机制和地震定位研究2022年山西古交ML4.1地震的发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 2024, 46(2): 414-432. |
| [2] | 陈翰林, 王勤彩, 张金川, 刘瑞丰. 四川芦山2022年6月 MS6.1 地震的发震构造及其与2013年4月 MS7.0 地震关系的探讨[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(5): 1233-1246. |
| [3] | 许英才, 郭祥云. 2022年四川马尔康MS6.0强震群重定位及发震断层探讨[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(4): 1006-1024. |
| [4] | 万永革, 王昱茹, 靳志同. 2021年云南漾濞6.4级地震震源区地壳应力不均匀性研究[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(4): 1025-1040. |
| [5] | 傅莺, 胡斌, 赵敏, 龙锋. 2022年芦山MS6.1地震序列的精确定位及发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(4): 987-1005. |
| [6] | 王喜龙, 罗银花, 金秀英, 杨梦尧, 孔祥瑞. 辽南地区断裂带的断层土壤气地球化学特征及其对区域应力调整的指示[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 710-734. |
| [7] | 樊文杰. 2021年5月21日漾濞MS6.4地震及周边的构造应力场特征和动力学意义[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 208-230. |
| [8] | 张珂, 王鑫, 杨红樱, 王玥, 徐岩, 李静. 2021年云南漾濞MS6.4地震序列特征及其发震构造分析[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 231-251. |
| [9] | 邓文泽, 刘杰, 杨志高, 孙丽, 张雪梅. 青海玛多MS7.4地震震源破裂过程反演结果的初步分析[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 1059-1070. |
| [10] | 李宗旭, 贺日政, 冀战波, 李娱兰, 牛潇. 2009年7月24日西藏尼玛MS5.6地震的震源机制及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 992-1010. |
| [11] | 王晓山, 万永革. 汶川地震前震中周围地壳应力场及应力方向集中的特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 363-377. |
| [12] | 余占洋, 沈旭章, 梁浩, 郑文俊, 刘旭宙. 基于地震活动性和震源机制解研究渭河-运城盆地主要断裂带的特征及应力场分布[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 395-413. |
| [13] | 张致伟, 龙锋, 赵小艳, 王迪. 川滇地区的震源机制解及应力场特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 170-187. |
| [14] | 孙业君, 黄耘, 刘泽民, 郑建常, 江昊琳, 李婷婷, 叶青, 方韬. 郯庐断裂带鲁苏皖段及邻区构造应力场特征及其动力学意义[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1188-1207. |
| [15] | 赵韬, 王莹, 马冀, 邵若潼, 徐一斐, 胡景. 2021年青海玛多7.4级地震序列重定位和震源机制特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 790-805. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||