地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 1025-1040.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.04.013
• 研究论文 • 上一篇
收稿日期:2022-10-08
修回日期:2023-01-02
出版日期:2023-08-20
发布日期:2023-09-20
作者简介:万永革, 男, 1967年生, 研究员, 主要从事构造应力场、 地震应力触发等方面研究工作, E-mail: wanyg217217@vip.sina.com。
基金资助:
WAN Yong-ge1,2,3)( ), WANG Yu-ru1), JIN Zhi-tong1,2,3)
), WANG Yu-ru1), JIN Zhi-tong1,2,3)
Received:2022-10-08
Revised:2023-01-02
Online:2023-08-20
Published:2023-09-20
摘要:
精细地壳应力场在地球动力学研究中具有至关重要的作用。2021年云南漾濞地震序列发生在地震观测台站密集分布的地区, 丰富的漾濞地震序列资料为该地区的精细应力场分析提供了大量地震震源机制解数据。为分析漾濞地震震源区的应力状态、 断层构造和地震动力学关系, 首先选择震源机制中心解算法对搜集到的漾濞地震序列震源机制解进行中心解求解, 以保证震源机制数据的准确性; 其次基于地震序列发生的位置, 采用移动窗方法将震源机制解划分为6个区域, 分别求解了6个区域的应力张量数据; 最后分析了非均匀应力场所揭示的动力学问题。研究结果表明: 漾濞地震震源区西北部和东南部的压应力轴方向由NNW-SSE向转换为NNE-SSW向, 偏转角度达23°, 且西北部的应力形因子大于东南部。推测西北部和东南部明显的应力场变化是由破裂区北部物质南移受阻和印缅弧深部NNE向低角度俯冲导致研究区浅部出现NNE向拉张联合作用所致。漾濞地震序列破裂东南区呈现马尾状散开的断层分布及山脉和水系走向在周围的分布均与本研究推测的应力偏转和应力形因子改变相符。这些研究对认识该地区的断裂活动特性和地震动力学具有一定意义。
万永革, 王昱茹, 靳志同. 2021年云南漾濞6.4级地震震源区地壳应力不均匀性研究[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(4): 1025-1040.
WAN Yong-ge, WANG Yu-ru, JIN Zhi-tong. STUDY ON HETEROGENEITY OF THE STRESS FIELD IN THE YANGBI EARTHQUAKE FAULT ZONE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(4): 1025-1040.
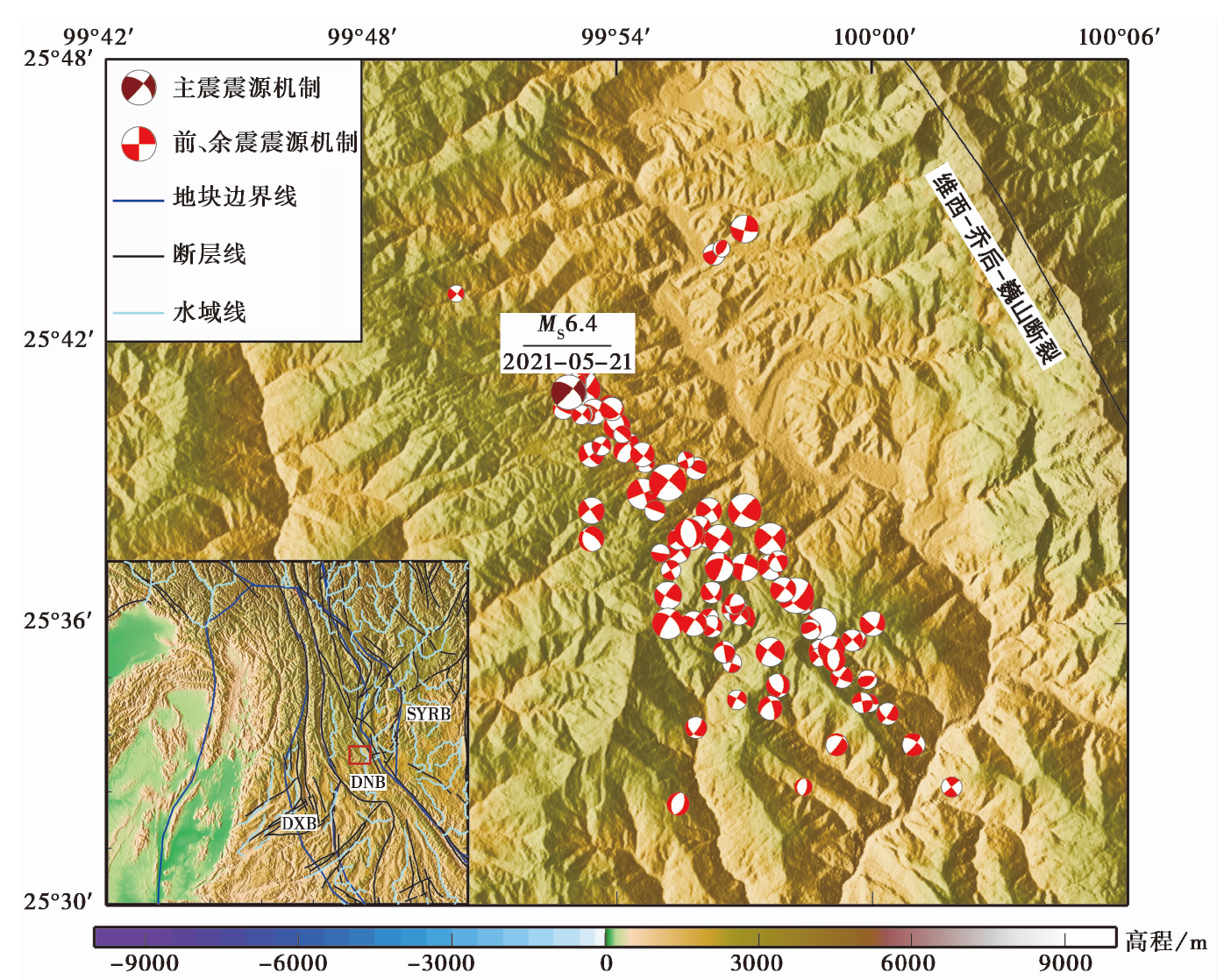
图1 本研究所用的漾濞地震序列的震源机制分布 黑线为断层,震源机制采用下半球施密特投影的海滩球表示,带有颜色的卦限为压缩区。左下图给出了研究区域的位置,其中蓝色线条为地块边界线,浅蓝色为水域线。SYRB川滇菱形块体; DNB滇南地块; DXB滇西地块。块体边界数据来自文献(张培震等, 2003)
Fig. 1 Focal mechanisms of the Yangbi earthquake sequence in this study.
| 发震日期 | 发震时刻 | 北纬/(°) | 东经/(°) | 震级(ML) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 滑动角/(°) | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-05-18 | 18:49:30 | 25.64 | 99.936 | 3.8 | 316.41 | 72.26 | 170.17 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-18 | 20:20:28 | 25.631 | 99.935 | 3.4 | 145.37 | 65.08 | -147.37 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-18 | 20:56:46 | 25.634 | 99.932 | 3.6 | 46.63 | 67.84 | 14.19 | ①②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-18 | 21:39:35 | 25.631 | 99.929 | 4.2 | 40.03 | 85.65 | 7.89 | ①②③④⑥ |
| 2021-05-19 | 3:27:56 | 25.626 | 99.924 | 3.7 | 45.66 | 80.37 | 9.26 | ①②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-18 | 22:57:59 | 25.632 | 99.926 | 2.7 | 120 | 30 | 180 | ① |
| 2021-05-19 | 5:33:24 | 25.63 | 99.924 | 3.2 | 317 | 51 | 172 | ① |
| 2021-05-19 | 20:05:56 | 25.646 | 99.91 | 4.6 | 69.43 | 89.73 | 9.24 | ①②④⑥ |
| 2021-05-19 | 20:28:45 | 25.657 | 99.911 | 2.9 | 311 | 85 | -150 | ① |
| 2021-05-19 | 21:13:07 | 25.67 | 99.9 | 3.8 | 313 | 59.86 | 173 | ①②③ |
| 2021-05-20 | 0:54:22 | 25.664 | 99.905 | 2.8 | 130 | 90 | 140 | ① |
| 2021-05-20 | 1:58:59 | 25.66 | 99.89 | 3.8 | 51.68 | 87.39 | -21.96 | ②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-20 | 2:32:10 | 25.661 | 99.903 | 3.3 | 359 | 36 | -126 | ① |
| 2021-05-20 | 12:08:41 | 25.64 | 99.915 | 3 | 110 | 90 | 90 | ① |
| 2021-05-20 | 17:35:22 | 25.663 | 99.894 | 2.8 | 300 | 80 | 180 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 20:55:43 | 25.632 | 99.928 | 4.3 | 348.41 | 45.14 | -93.81 | ①③④⑥ |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:21:24 | 25.65 | 99.92 | 5.5 | 59.09 | 88.76 | 5.28 | ②③④ |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:21:57 | 25.63 | 99.96 | 4.7 | 315 | 78 | 176 | ③ |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:22:35 | 25.6 | 99.98 | 4.3 | 121 | 59 | 133 | ③ |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:37:33 | 25.62 | 99.96 | 3.7 | 315 | 74 | 178 | ② |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:48:34 | 25.7 | 99.88 | 6.5 | 134.69 | 82.74 | -178.04 | ②③④⑤ |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:55:29 | 25.683 | 99.887 | 5 | 310 | 87 | 171 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:56:00 | 25.64 | 99.95 | 4.9 | 220 | 84 | 20 | ④ |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:13:46 | 25.677 | 99.897 | 3.2 | 360 | 10 | 180 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:15:16 | 25.59 | 99.96 | 4.3 | 127.36 | 88.5 | 162.64 | ①②③④ |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:19:48 | 25.605 | 99.946 | 3.8 | 337 | 62 | 169 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:27:11 | 25.607 | 99.973 | 2.9 | 130 | 90 | 100 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:30:27 | 25.675 | 99.891 | 3.8 | 306 | 64 | 164 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:31:10 | 25.61 | 99.97 | 5.3 | 145.65 | 60.14 | -157.72 | ②③④⑤ |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:52:08 | 25.59 | 99.98 | 3.8 | 28.06 | 62 | -22.61 | ②⑤ |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:59:37 | 25.61 | 99.92 | 4 | 212.46 | 76.75 | 10.81 | ②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-21 | 23:08:57 | 25.6 | 99.979 | 3.7 | 305.41 | 78.19 | -170.74 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-21 | 23:13:54 | 25.63 | 99.94 | 4.2 | 32.7 | 85.64 | -0.35 | ②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-21 | 23:18:09 | 25.6 | 100 | 3.8 | 33.48 | 60.5 | -8.4 | ②⑥ |
| 2021-05-21 | 23:23:34 | 25.6 | 99.98 | 4.5 | 216.39 | 84.98 | 4.68 | ②③④ |
| 2021-05-22 | 0:21:06 | 25.594 | 99.994 | 2.8 | 166 | 71 | -144 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 0:27:51 | 25.676 | 99.899 | 2.9 | 144 | 36 | 149 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 0:51:41 | 25.7 | 99.88 | 4.3 | 34.32 | 84.67 | -12.03 | ②③④ |
| 2021-05-22 | 0:56:07 | 25.63 | 99.89 | 3.8 | 307.78 | 67.81 | -112.66 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 1:36:06 | 25.62 | 99.95 | 4.1 | 193.58 | 82.76 | -14.64 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 1:50:18 | 25.612 | 99.965 | 3.8 | 304.87 | 73.96 | 174.94 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 2:00:58 | 25.553 | 99.831 | 2.6 | 133 | 80 | -152 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 4:10:57 | 25.62 | 99.94 | 4.2 | 272 | 40 | 159 | ② |
| 2021-05-22 | 5:54:14 | 25.572 | 99.999 | 2.7 | 280 | 10 | 90 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 8:36:47 | 25.67 | 99.9 | 3.9 | 3.77 | 48.5 | -42.44 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 9:48:00 | 25.7 | 99.89 | 4.2 | 40.23 | 85.29 | -0.84 | ②③④⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 10:23:05 | 25.573 | 99.947 | 2.9 | 300 | 82 | -174 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 10:45:04 | 25.58 | 99.998 | 2.9 | 266 | 53 | 115 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 11:05:23 | 25.572 | 99.996 | 3.1 | 170 | 90 | 170 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 11:17:03 | 25.568 | 100.006 | 3.2 | 24.99 | 79.98 | -28.78 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 12:40:17 | 25.676 | 99.898 | 3.4 | 1.5 | 55.55 | -46.58 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 16:19:02 | 25.622 | 99.963 | 3 | 332 | 84 | -140 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 16:50:56 | 25.655 | 99.931 | 3.2 | 120 | 73 | 122 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 17:09:18 | 25.674 | 99.888 | 2.5 | 143 | 71 | -111 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 17:24:16 | 25.64 | 99.89 | 3.9 | 320.62 | 88 | -173.63 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 20:14:36 | 25.6 | 99.92 | 4.6 | 311.76 | 54.15 | -163.29 | ②③④⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 20:21:04 | 25.602 | 99.936 | 2.8 | 300 | 87 | 17 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 20:40:40 | 25.599 | 99.937 | 3.2 | 122 | 84 | -140 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 22:30:05 | 25.6 | 99.93 | 3.8 | 307.58 | 64.46 | -171.25 | ①②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 22:49:30 | 25.611 | 99.937 | 3.2 | 142 | 84 | -140 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 23:30:16 | 25.578 | 99.963 | 3.5 | 129.82 | 55.02 | -127.11 | ①②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-23 | 0:17:20 | 25.57 | 99.96 | 3.6 | 339.88 | 70.37 | -142.37 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-23 | 11:44:01 | 25.619 | 99.921 | 2.9 | 150 | 90 | 0 | ① |
| 2021-05-23 | 12:04:30 | 25.603 | 99.948 | 2.8 | 310 | 80 | 180 | ① |
| 2021-05-23 | 13:28:37 | 25.586 | 99.945 | 2.8 | 110 | 90 | 0 | ① |
| 2021-05-23 | 15:39:21 | 25.59 | 99.942 | 3.2 | 170 | 90 | 130 | ① |
| 2021-05-23 | 17:26:13 | 25.557 | 100.016 | 3.4 | 40.36 | 78.72 | -149.78 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-25 | 1:20:28 | 25.591 | 99.985 | 2.7 | 330 | 81 | -177 | ① |
| 2021-05-25 | 3:10:29 | 25.588 | 99.979 | 2.7 | 320 | 80 | 180 | ① |
| 2021-05-25 | 10:53:27 | 25.542 | 100.031 | 3 | 140 | 90 | 0 | ① |
| 2021-05-26 | 6:37:34 | 25.66 | 99.91 | 3.6 | 38.63 | 75.52 | -3.5 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-26 | 9:05:42 | 25.607 | 99.946 | 3 | 187 | 56 | -158 | ① |
| 2021-05-26 | 9:22:59 | 25.676 | 99.879 | 3 | 120 | 73 | 122 | ① |
| 2021-05-26 | 11:18:57 | 25.557 | 99.986 | 3.3 | 37 | 81 | -110 | ① |
| 2021-05-26 | 14:20:32 | 25.731 | 99.938 | 3.3 | 12.54 | 61.24 | 32.53 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-27 | 8:56:52 | 25.658 | 99.927 | 2.5 | 250 | 88 | 170 | ① |
| 2021-05-27 | 13:36:47 | 25.733 | 99.941 | 2.6 | 36 | 61 | 102 | ① |
| 2021-05-27 | 19:52:46 | 25.74 | 99.95 | 4.1 | 102.42 | 78.18 | -179.61 | ①③④⑥ |
| 2021-05-27 | 23:03:57 | 25.69 | 99.884 | 3.9 | 133.16 | 64.76 | -175.06 | ①③⑥ |
| 2021-05-28 | 0:03:08 | 25.594 | 99.992 | 3.2 | 44.78 | 89.41 | 5.42 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-28 | 0:27:05 | 25.674 | 99.886 | 2.8 | 310 | 81 | 177 | ① |
| 2021-05-28 | 20:43:18 | 25.536 | 99.924 | 3.4 | 194.69 | 40.23 | -97.64 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-28 | 22:05:08 | 25.693 | 99.863 | 3.2 | 316 | 82 | 130 | ① |
| 2021-05-29 | 0:09:24 | 25.717 | 99.837 | 2.5 | 310 | 84 | 172 | ① |
| 2021-05-29 | 2:39:27 | 25.667 | 99.902 | 2.6 | 130 | 90 | 90 | ① |
| 2021-05-29 | 19:30:57 | 25.542 | 99.973 | 2.6 | 10 | 60 | -90 | ① |
| 2021-06-02 | 5:12:05 | 25.563 | 99.931 | 3.2 | 140 | 44 | -158 | ① |
| 2021-06-02 | 20:37:29 | 25.686 | 99.884 | 2.8 | 123 | 56 | 157 | ① |
| 2021-06-05 | 6:12:22 | 25.591 | 99.984 | 3.9 | 120 | 85 | -171 | ① |
| 2021-06-05 | 6:31:27 | 25.581 | 99.988 | 3.3 | 118 | 73 | 170 | ① |
| 2021-06-05 | 6:39:19 | 25.587 | 99.985 | 3.3 | 168 | 41 | -105 | ① |
| 2021-06-05 | 14:53:38 | 25.598 | 99.976 | 3 | 304 | 36 | 149 | ① |
| 2021-06-06 | 2:35:26 | 25.625 | 99.917 | 2.7 | 280 | 90 | 90 | ① |
表 1 漾濞6.4级震源区地震序列中93次地震的震源机制解
Table 1 The focal mechanism solutions of the 93 earthquakes of the Yangbi earthquake sequence
| 发震日期 | 发震时刻 | 北纬/(°) | 东经/(°) | 震级(ML) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 滑动角/(°) | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2021-05-18 | 18:49:30 | 25.64 | 99.936 | 3.8 | 316.41 | 72.26 | 170.17 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-18 | 20:20:28 | 25.631 | 99.935 | 3.4 | 145.37 | 65.08 | -147.37 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-18 | 20:56:46 | 25.634 | 99.932 | 3.6 | 46.63 | 67.84 | 14.19 | ①②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-18 | 21:39:35 | 25.631 | 99.929 | 4.2 | 40.03 | 85.65 | 7.89 | ①②③④⑥ |
| 2021-05-19 | 3:27:56 | 25.626 | 99.924 | 3.7 | 45.66 | 80.37 | 9.26 | ①②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-18 | 22:57:59 | 25.632 | 99.926 | 2.7 | 120 | 30 | 180 | ① |
| 2021-05-19 | 5:33:24 | 25.63 | 99.924 | 3.2 | 317 | 51 | 172 | ① |
| 2021-05-19 | 20:05:56 | 25.646 | 99.91 | 4.6 | 69.43 | 89.73 | 9.24 | ①②④⑥ |
| 2021-05-19 | 20:28:45 | 25.657 | 99.911 | 2.9 | 311 | 85 | -150 | ① |
| 2021-05-19 | 21:13:07 | 25.67 | 99.9 | 3.8 | 313 | 59.86 | 173 | ①②③ |
| 2021-05-20 | 0:54:22 | 25.664 | 99.905 | 2.8 | 130 | 90 | 140 | ① |
| 2021-05-20 | 1:58:59 | 25.66 | 99.89 | 3.8 | 51.68 | 87.39 | -21.96 | ②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-20 | 2:32:10 | 25.661 | 99.903 | 3.3 | 359 | 36 | -126 | ① |
| 2021-05-20 | 12:08:41 | 25.64 | 99.915 | 3 | 110 | 90 | 90 | ① |
| 2021-05-20 | 17:35:22 | 25.663 | 99.894 | 2.8 | 300 | 80 | 180 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 20:55:43 | 25.632 | 99.928 | 4.3 | 348.41 | 45.14 | -93.81 | ①③④⑥ |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:21:24 | 25.65 | 99.92 | 5.5 | 59.09 | 88.76 | 5.28 | ②③④ |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:21:57 | 25.63 | 99.96 | 4.7 | 315 | 78 | 176 | ③ |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:22:35 | 25.6 | 99.98 | 4.3 | 121 | 59 | 133 | ③ |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:37:33 | 25.62 | 99.96 | 3.7 | 315 | 74 | 178 | ② |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:48:34 | 25.7 | 99.88 | 6.5 | 134.69 | 82.74 | -178.04 | ②③④⑤ |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:55:29 | 25.683 | 99.887 | 5 | 310 | 87 | 171 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 21:56:00 | 25.64 | 99.95 | 4.9 | 220 | 84 | 20 | ④ |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:13:46 | 25.677 | 99.897 | 3.2 | 360 | 10 | 180 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:15:16 | 25.59 | 99.96 | 4.3 | 127.36 | 88.5 | 162.64 | ①②③④ |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:19:48 | 25.605 | 99.946 | 3.8 | 337 | 62 | 169 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:27:11 | 25.607 | 99.973 | 2.9 | 130 | 90 | 100 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:30:27 | 25.675 | 99.891 | 3.8 | 306 | 64 | 164 | ① |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:31:10 | 25.61 | 99.97 | 5.3 | 145.65 | 60.14 | -157.72 | ②③④⑤ |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:52:08 | 25.59 | 99.98 | 3.8 | 28.06 | 62 | -22.61 | ②⑤ |
| 2021-05-21 | 22:59:37 | 25.61 | 99.92 | 4 | 212.46 | 76.75 | 10.81 | ②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-21 | 23:08:57 | 25.6 | 99.979 | 3.7 | 305.41 | 78.19 | -170.74 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-21 | 23:13:54 | 25.63 | 99.94 | 4.2 | 32.7 | 85.64 | -0.35 | ②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-21 | 23:18:09 | 25.6 | 100 | 3.8 | 33.48 | 60.5 | -8.4 | ②⑥ |
| 2021-05-21 | 23:23:34 | 25.6 | 99.98 | 4.5 | 216.39 | 84.98 | 4.68 | ②③④ |
| 2021-05-22 | 0:21:06 | 25.594 | 99.994 | 2.8 | 166 | 71 | -144 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 0:27:51 | 25.676 | 99.899 | 2.9 | 144 | 36 | 149 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 0:51:41 | 25.7 | 99.88 | 4.3 | 34.32 | 84.67 | -12.03 | ②③④ |
| 2021-05-22 | 0:56:07 | 25.63 | 99.89 | 3.8 | 307.78 | 67.81 | -112.66 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 1:36:06 | 25.62 | 99.95 | 4.1 | 193.58 | 82.76 | -14.64 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 1:50:18 | 25.612 | 99.965 | 3.8 | 304.87 | 73.96 | 174.94 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 2:00:58 | 25.553 | 99.831 | 2.6 | 133 | 80 | -152 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 4:10:57 | 25.62 | 99.94 | 4.2 | 272 | 40 | 159 | ② |
| 2021-05-22 | 5:54:14 | 25.572 | 99.999 | 2.7 | 280 | 10 | 90 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 8:36:47 | 25.67 | 99.9 | 3.9 | 3.77 | 48.5 | -42.44 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 9:48:00 | 25.7 | 99.89 | 4.2 | 40.23 | 85.29 | -0.84 | ②③④⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 10:23:05 | 25.573 | 99.947 | 2.9 | 300 | 82 | -174 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 10:45:04 | 25.58 | 99.998 | 2.9 | 266 | 53 | 115 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 11:05:23 | 25.572 | 99.996 | 3.1 | 170 | 90 | 170 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 11:17:03 | 25.568 | 100.006 | 3.2 | 24.99 | 79.98 | -28.78 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 12:40:17 | 25.676 | 99.898 | 3.4 | 1.5 | 55.55 | -46.58 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 16:19:02 | 25.622 | 99.963 | 3 | 332 | 84 | -140 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 16:50:56 | 25.655 | 99.931 | 3.2 | 120 | 73 | 122 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 17:09:18 | 25.674 | 99.888 | 2.5 | 143 | 71 | -111 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 17:24:16 | 25.64 | 99.89 | 3.9 | 320.62 | 88 | -173.63 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 20:14:36 | 25.6 | 99.92 | 4.6 | 311.76 | 54.15 | -163.29 | ②③④⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 20:21:04 | 25.602 | 99.936 | 2.8 | 300 | 87 | 17 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 20:40:40 | 25.599 | 99.937 | 3.2 | 122 | 84 | -140 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 22:30:05 | 25.6 | 99.93 | 3.8 | 307.58 | 64.46 | -171.25 | ①②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-22 | 22:49:30 | 25.611 | 99.937 | 3.2 | 142 | 84 | -140 | ① |
| 2021-05-22 | 23:30:16 | 25.578 | 99.963 | 3.5 | 129.82 | 55.02 | -127.11 | ①②③⑥ |
| 2021-05-23 | 0:17:20 | 25.57 | 99.96 | 3.6 | 339.88 | 70.37 | -142.37 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-23 | 11:44:01 | 25.619 | 99.921 | 2.9 | 150 | 90 | 0 | ① |
| 2021-05-23 | 12:04:30 | 25.603 | 99.948 | 2.8 | 310 | 80 | 180 | ① |
| 2021-05-23 | 13:28:37 | 25.586 | 99.945 | 2.8 | 110 | 90 | 0 | ① |
| 2021-05-23 | 15:39:21 | 25.59 | 99.942 | 3.2 | 170 | 90 | 130 | ① |
| 2021-05-23 | 17:26:13 | 25.557 | 100.016 | 3.4 | 40.36 | 78.72 | -149.78 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-25 | 1:20:28 | 25.591 | 99.985 | 2.7 | 330 | 81 | -177 | ① |
| 2021-05-25 | 3:10:29 | 25.588 | 99.979 | 2.7 | 320 | 80 | 180 | ① |
| 2021-05-25 | 10:53:27 | 25.542 | 100.031 | 3 | 140 | 90 | 0 | ① |
| 2021-05-26 | 6:37:34 | 25.66 | 99.91 | 3.6 | 38.63 | 75.52 | -3.5 | ①②⑥ |
| 2021-05-26 | 9:05:42 | 25.607 | 99.946 | 3 | 187 | 56 | -158 | ① |
| 2021-05-26 | 9:22:59 | 25.676 | 99.879 | 3 | 120 | 73 | 122 | ① |
| 2021-05-26 | 11:18:57 | 25.557 | 99.986 | 3.3 | 37 | 81 | -110 | ① |
| 2021-05-26 | 14:20:32 | 25.731 | 99.938 | 3.3 | 12.54 | 61.24 | 32.53 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-27 | 8:56:52 | 25.658 | 99.927 | 2.5 | 250 | 88 | 170 | ① |
| 2021-05-27 | 13:36:47 | 25.733 | 99.941 | 2.6 | 36 | 61 | 102 | ① |
| 2021-05-27 | 19:52:46 | 25.74 | 99.95 | 4.1 | 102.42 | 78.18 | -179.61 | ①③④⑥ |
| 2021-05-27 | 23:03:57 | 25.69 | 99.884 | 3.9 | 133.16 | 64.76 | -175.06 | ①③⑥ |
| 2021-05-28 | 0:03:08 | 25.594 | 99.992 | 3.2 | 44.78 | 89.41 | 5.42 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-28 | 0:27:05 | 25.674 | 99.886 | 2.8 | 310 | 81 | 177 | ① |
| 2021-05-28 | 20:43:18 | 25.536 | 99.924 | 3.4 | 194.69 | 40.23 | -97.64 | ①⑥ |
| 2021-05-28 | 22:05:08 | 25.693 | 99.863 | 3.2 | 316 | 82 | 130 | ① |
| 2021-05-29 | 0:09:24 | 25.717 | 99.837 | 2.5 | 310 | 84 | 172 | ① |
| 2021-05-29 | 2:39:27 | 25.667 | 99.902 | 2.6 | 130 | 90 | 90 | ① |
| 2021-05-29 | 19:30:57 | 25.542 | 99.973 | 2.6 | 10 | 60 | -90 | ① |
| 2021-06-02 | 5:12:05 | 25.563 | 99.931 | 3.2 | 140 | 44 | -158 | ① |
| 2021-06-02 | 20:37:29 | 25.686 | 99.884 | 2.8 | 123 | 56 | 157 | ① |
| 2021-06-05 | 6:12:22 | 25.591 | 99.984 | 3.9 | 120 | 85 | -171 | ① |
| 2021-06-05 | 6:31:27 | 25.581 | 99.988 | 3.3 | 118 | 73 | 170 | ① |
| 2021-06-05 | 6:39:19 | 25.587 | 99.985 | 3.3 | 168 | 41 | -105 | ① |
| 2021-06-05 | 14:53:38 | 25.598 | 99.976 | 3 | 304 | 36 | 149 | ① |
| 2021-06-06 | 2:35:26 | 25.625 | 99.917 | 2.7 | 280 | 90 | 90 | ① |
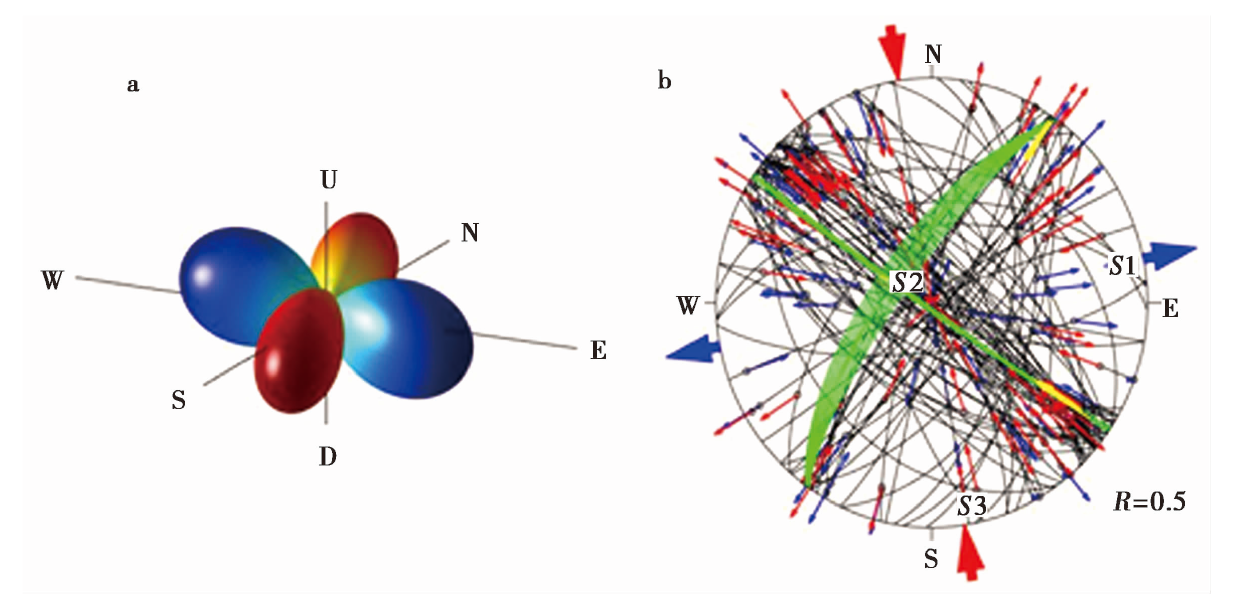
图2 a漾濞地震序列整体应力场的三维示意图; b应力场反演结果 a应力状态的立体表示图。红色表示压缩区,蓝色表示膨胀区。b应力场反演结果及数据拟合情况的下半球施密特投影图;黑色弧线表示所选“可能断层面”的施密特投影;蓝色大箭头为S1轴的水平最优方向,蓝色小剪头表示“可能断层面”的观测滑动方向;红色大箭头为S3轴的水平最优方向,红色小箭头表示“可能断层面”的理论滑动方向;绿色弧线表示置信度为95%的应力场最大剪应力节面;黄色箭头表示该节面的最优滑动方向;红色、黄色和蓝色闭合曲线分别表示主压应力轴、中间应力轴和主张应力轴95%置信水平下的置信范围
Fig. 2 3D diagram(a)and results of the overall stress field inversion(b)in the Yangbi earthquake sequence.
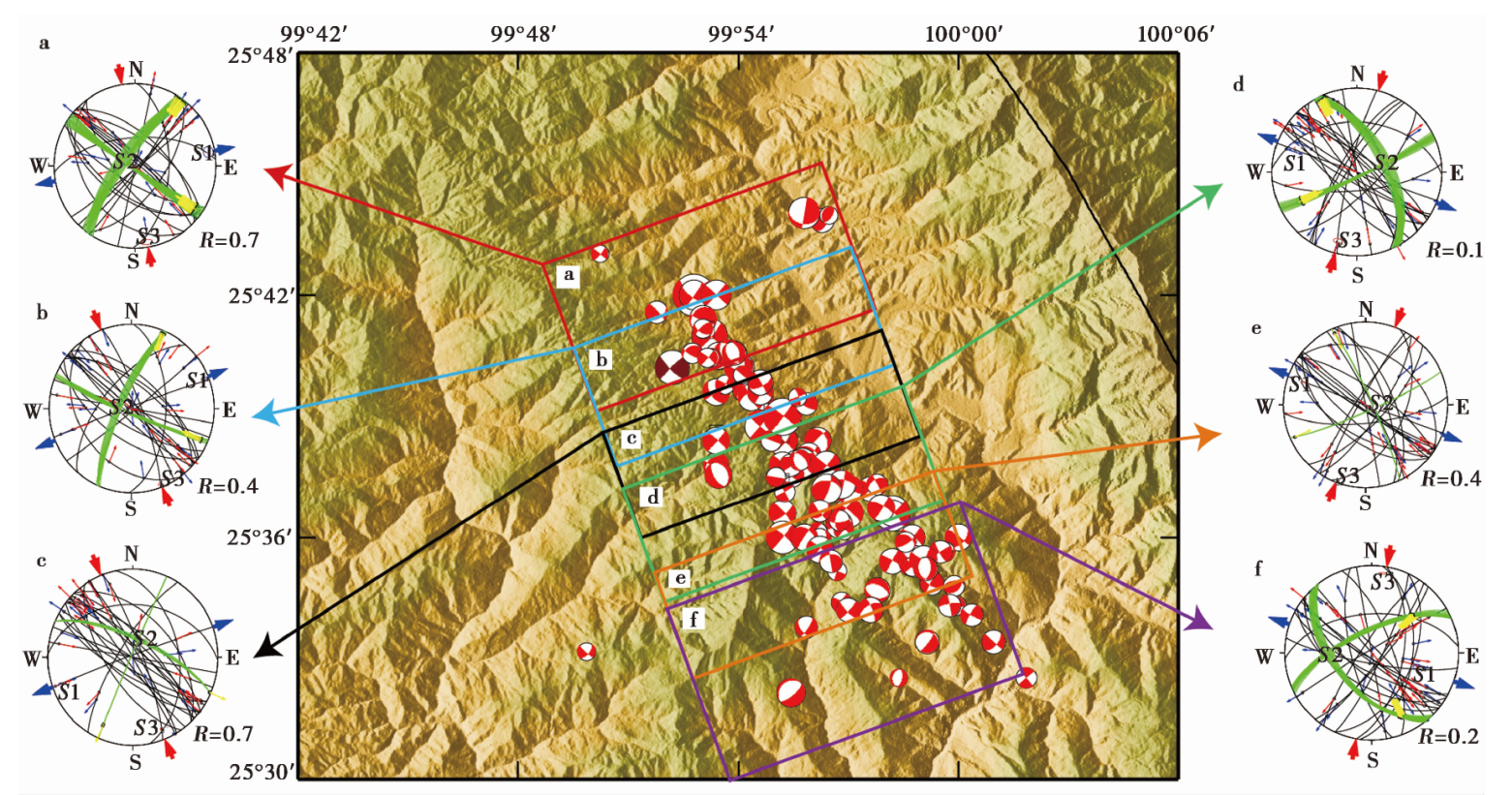
图3 应力场分区反演结果 海滩球为震源机制数据(含义同图1)。方框为划分区域:深红色框表示区域a,天蓝色框表示区域b,黑色框表示区域c, 绿色框表示区域d,橙色框表示区域e,紫色框表示区域f。大图两侧给出了各区的应力反演结果,其表示符号与图2b相同
Fig. 3 Results of stress field inversion in different sub-areas.
| 分 区 | 数 目 | 应力张量参数 | R | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | ||||||
| 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | |||
| a | 23 | 79.43 | 10.16 | 292 | 78 | 170.57 | 6.33 | 0.7 |
| (75.43~83.43) | (2.16~15.16) | (288.00~296.00) | (70.00~83.00) | (166.57~175.51) | (3.7~10.44) | (0.5~0.8) | ||
| b | 23 | 67.69 | 9.27 | 270 | 80 | 158.3 | 3.73 | 0.4 |
| (67.19~69.69) | (2.27~9.77) | (269.50~272.00) | (73.00~80.50) | (157.31~160.30) | (3.40~6.29) | (0.2~0.4) | ||
| c | 23 | 250.1 | 9.99 | 18 | 74 | 157.89 | 12.37 | 0.7 |
| (249.60~250.60) | (6.99~10.49) | (17.50~18.50) | (71.00~74.50) | (157.42~158.39) | (11.87~14.66) | (0.4~0.9) | ||
| d | 23 | 291.42 | 22.62 | 73 | 62 | 194.73 | 15.62 | 0.1 |
| (288.42~295.42) | (15.62~27.62) | (70.00~77.00) | (55.00~67.00) | (191.73~198.73) | (12.95~19.21) | (0.1~0.2) | ||
| e | 23 | 291 | 9 | 111 | 81 | 201 | 0 | 0.3 |
| (290.50~291.50) | (8.00~9.50) | (110.50~111.50) | (80.00~81.50) | (200.50~201.50) | (-0.50~0.50) | (0.30~0.40) | ||
| f | 23 | 109.12 | 42.38 | 270 | 46 | 10.17 | 9.67 | 0.2 |
| (104.12~109.62) | (40.38~48.38) | (265.00~270.50) | (44.00~52.00) | (5.17~11.12) | (6.93~10.02) | (0.20~0.5) | ||
表 2 震源机制数据反演应力张量数值结果
Table 2 The inversed stress tensor from focal mechanism data
| 分 区 | 数 目 | 应力张量参数 | R | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | ||||||
| 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | |||
| a | 23 | 79.43 | 10.16 | 292 | 78 | 170.57 | 6.33 | 0.7 |
| (75.43~83.43) | (2.16~15.16) | (288.00~296.00) | (70.00~83.00) | (166.57~175.51) | (3.7~10.44) | (0.5~0.8) | ||
| b | 23 | 67.69 | 9.27 | 270 | 80 | 158.3 | 3.73 | 0.4 |
| (67.19~69.69) | (2.27~9.77) | (269.50~272.00) | (73.00~80.50) | (157.31~160.30) | (3.40~6.29) | (0.2~0.4) | ||
| c | 23 | 250.1 | 9.99 | 18 | 74 | 157.89 | 12.37 | 0.7 |
| (249.60~250.60) | (6.99~10.49) | (17.50~18.50) | (71.00~74.50) | (157.42~158.39) | (11.87~14.66) | (0.4~0.9) | ||
| d | 23 | 291.42 | 22.62 | 73 | 62 | 194.73 | 15.62 | 0.1 |
| (288.42~295.42) | (15.62~27.62) | (70.00~77.00) | (55.00~67.00) | (191.73~198.73) | (12.95~19.21) | (0.1~0.2) | ||
| e | 23 | 291 | 9 | 111 | 81 | 201 | 0 | 0.3 |
| (290.50~291.50) | (8.00~9.50) | (110.50~111.50) | (80.00~81.50) | (200.50~201.50) | (-0.50~0.50) | (0.30~0.40) | ||
| f | 23 | 109.12 | 42.38 | 270 | 46 | 10.17 | 9.67 | 0.2 |
| (104.12~109.62) | (40.38~48.38) | (265.00~270.50) | (44.00~52.00) | (5.17~11.12) | (6.93~10.02) | (0.20~0.5) | ||
| 分 区 | 数 目 | 应力张量参数 | R | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | ||||||
| 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | |||
| a | 23 | 79.43 | 10.16 | 292 | 78 | 170.57 | 6.33 | 0.7 |
| (75.43~83.43) | (2.16~15.16) | (288.00~296.00) | (70.00~83.00) | (166.57~175.51) | (3.7~10.44) | (0.5~0.8) | ||
| b | 23 | 67.69 | 9.27 | 270 | 80 | 158.3 | 3.73 | 0.4 |
| (67.19~69.69) | (2.27~9.77) | (269.50~272.00) | (73.00~80.50) | (157.31~160.30) | (3.40~6.29) | (0.2~0.4) | ||
| c | 23 | 250.1 | 9.99 | 18 | 74 | 157.89 | 12.37 | 0.7 |
| (249.60~250.60) | (6.99~10.49) | (17.50~18.50) | (71.00~74.50) | (157.42~158.39) | (11.87~14.66) | (0.4~0.9) | ||
| d | 23 | 238.87 | 11.93 | 65 | 78 | 329.13 | 1.25 | 0.5 |
| (238.37~239.37) | (11.43~12.93) | (64.50~65.50) | (77.50~79.00) | (329.11~329.63) | (1.14~1.75) | (0.40~0.50) | ||
| e | 23 | 290.3 | 22.9 | 35 | 31 | 170.31 | 49.8 | 0.1 |
| (289.80~290.80) | (22.40~49.90) | (34.50~35.50) | (30.50~58.00) | (169.81~184.00) | (28.17~50.30) | (0.1~0.3) | ||
| f | 23 | 290 | 9 | 111 | 81 | 201 | 0 | 0.3 |
| (290.50~291.50) | (6.00~9.50) | (110.50~111.50) | (78.00~81.50) | (200.50~201.50) | (-0.50~0.50) | (0.3~0.5) | ||
| g | 23 | 292.3 | 9.33 | 91 | 80 | 201.71 | 3.57 | 0.1 |
| (291.30~292.80) | (8.83~9.83) | (90.00~91.50) | (79.50~80.50) | (200.71~202.21) | (3.40~4.07) | (0.1~0.1) | ||
| h | 23 | 109.12 | 42.38 | 270 | 46 | 10.17 | 9.67 | 0.2 |
| (104.12~109.62) | (41.38~48.38) | (265.00~270.50) | (45.00~52.00) | (5.17~11.12) | (7.62~9.85) | (0.1~0.5) | ||
表 3 8个分区应力张量反演结果
Table 3 Stress tensor inversion results in eight sub-regions
| 分 区 | 数 目 | 应力张量参数 | R | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | ||||||
| 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | |||
| a | 23 | 79.43 | 10.16 | 292 | 78 | 170.57 | 6.33 | 0.7 |
| (75.43~83.43) | (2.16~15.16) | (288.00~296.00) | (70.00~83.00) | (166.57~175.51) | (3.7~10.44) | (0.5~0.8) | ||
| b | 23 | 67.69 | 9.27 | 270 | 80 | 158.3 | 3.73 | 0.4 |
| (67.19~69.69) | (2.27~9.77) | (269.50~272.00) | (73.00~80.50) | (157.31~160.30) | (3.40~6.29) | (0.2~0.4) | ||
| c | 23 | 250.1 | 9.99 | 18 | 74 | 157.89 | 12.37 | 0.7 |
| (249.60~250.60) | (6.99~10.49) | (17.50~18.50) | (71.00~74.50) | (157.42~158.39) | (11.87~14.66) | (0.4~0.9) | ||
| d | 23 | 238.87 | 11.93 | 65 | 78 | 329.13 | 1.25 | 0.5 |
| (238.37~239.37) | (11.43~12.93) | (64.50~65.50) | (77.50~79.00) | (329.11~329.63) | (1.14~1.75) | (0.40~0.50) | ||
| e | 23 | 290.3 | 22.9 | 35 | 31 | 170.31 | 49.8 | 0.1 |
| (289.80~290.80) | (22.40~49.90) | (34.50~35.50) | (30.50~58.00) | (169.81~184.00) | (28.17~50.30) | (0.1~0.3) | ||
| f | 23 | 290 | 9 | 111 | 81 | 201 | 0 | 0.3 |
| (290.50~291.50) | (6.00~9.50) | (110.50~111.50) | (78.00~81.50) | (200.50~201.50) | (-0.50~0.50) | (0.3~0.5) | ||
| g | 23 | 292.3 | 9.33 | 91 | 80 | 201.71 | 3.57 | 0.1 |
| (291.30~292.80) | (8.83~9.83) | (90.00~91.50) | (79.50~80.50) | (200.71~202.21) | (3.40~4.07) | (0.1~0.1) | ||
| h | 23 | 109.12 | 42.38 | 270 | 46 | 10.17 | 9.67 | 0.2 |
| (104.12~109.62) | (41.38~48.38) | (265.00~270.50) | (45.00~52.00) | (5.17~11.12) | (7.62~9.85) | (0.1~0.5) | ||
| 分 区 | 数 目 | 应力张量参数 | R | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | ||||||
| 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | |||
| a | 28 | 83.66 | 5.53 | 316 | 81 | 174.34 | 7.08 | 0.9 |
| (81.66~84.66) | (3.53~8.53) | (314.00~317.00) | (79.00~84.00) | (171.33~175.35) | (4.72~8.65) | (0.9~0.9) | ||
| b | 28 | 67.69 | 9.27 | 270 | 80 | 158.3 | 3.73 | 0.4 |
| (67.19~68.69) | (5.27~9.77) | (269.50~271.00) | (76.00~80.50) | (157.80~160.28) | (3.40~5.20) | (0.3~0.4) | ||
| c | 28 | 250.1 | 9.99 | 18 | 74 | 157.89 | 12.37 | 0.7 |
| (249.60~250.60) | (7.99~10.49) | (17.50~18.50) | (72.00~74.50) | (157.59~158.39) | (11.89~13.90) | (0.4~0.9) | ||
| d | 28 | 291.42 | 22.62 | 73 | 62 | 194.73 | 15.62 | 0.1 |
| (289.42~295.42) | (16.62~27.62) | (71.00~77.00) | (56.00~67.00) | (192.73~198.73) | (12.95~18.71) | (0.1~0.3) | ||
| e | 28 | 292.3 | 9.33 | 91 | 80 | 201.71 | 3.57 | 0.1 |
| (290.30~292.80) | (8.33~9.33) | (89.00~91.50) | (79.00~80.50) | (199.71~202.21) | (3.24~3.92) | (0.1~0.2) | ||
| f | 28 | 108.82 | 41.43 | 270 | 47 | 10.33 | 9.5 | 0.2 |
| (100.82~109.32) | (39.43~46.43) | (262.00~270.50) | (45.00~52.00) | (2.33~11.12) | (6.12~9.85) | (0.1~0.5) | ||
表 4 子区内的震源机制解数目变为28个后的应力张量反演结果
Table 4 The stress tensor inversion results with the number of focal mechanisms of 28
| 分 区 | 数 目 | 应力张量参数 | R | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | S2 | S3 | ||||||
| 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | 走向/(°) | 倾向/(°) | |||
| a | 28 | 83.66 | 5.53 | 316 | 81 | 174.34 | 7.08 | 0.9 |
| (81.66~84.66) | (3.53~8.53) | (314.00~317.00) | (79.00~84.00) | (171.33~175.35) | (4.72~8.65) | (0.9~0.9) | ||
| b | 28 | 67.69 | 9.27 | 270 | 80 | 158.3 | 3.73 | 0.4 |
| (67.19~68.69) | (5.27~9.77) | (269.50~271.00) | (76.00~80.50) | (157.80~160.28) | (3.40~5.20) | (0.3~0.4) | ||
| c | 28 | 250.1 | 9.99 | 18 | 74 | 157.89 | 12.37 | 0.7 |
| (249.60~250.60) | (7.99~10.49) | (17.50~18.50) | (72.00~74.50) | (157.59~158.39) | (11.89~13.90) | (0.4~0.9) | ||
| d | 28 | 291.42 | 22.62 | 73 | 62 | 194.73 | 15.62 | 0.1 |
| (289.42~295.42) | (16.62~27.62) | (71.00~77.00) | (56.00~67.00) | (192.73~198.73) | (12.95~18.71) | (0.1~0.3) | ||
| e | 28 | 292.3 | 9.33 | 91 | 80 | 201.71 | 3.57 | 0.1 |
| (290.30~292.80) | (8.33~9.33) | (89.00~91.50) | (79.00~80.50) | (199.71~202.21) | (3.24~3.92) | (0.1~0.2) | ||
| f | 28 | 108.82 | 41.43 | 270 | 47 | 10.33 | 9.5 | 0.2 |
| (100.82~109.32) | (39.43~46.43) | (262.00~270.50) | (45.00~52.00) | (2.33~11.12) | (6.12~9.85) | (0.1~0.5) | ||
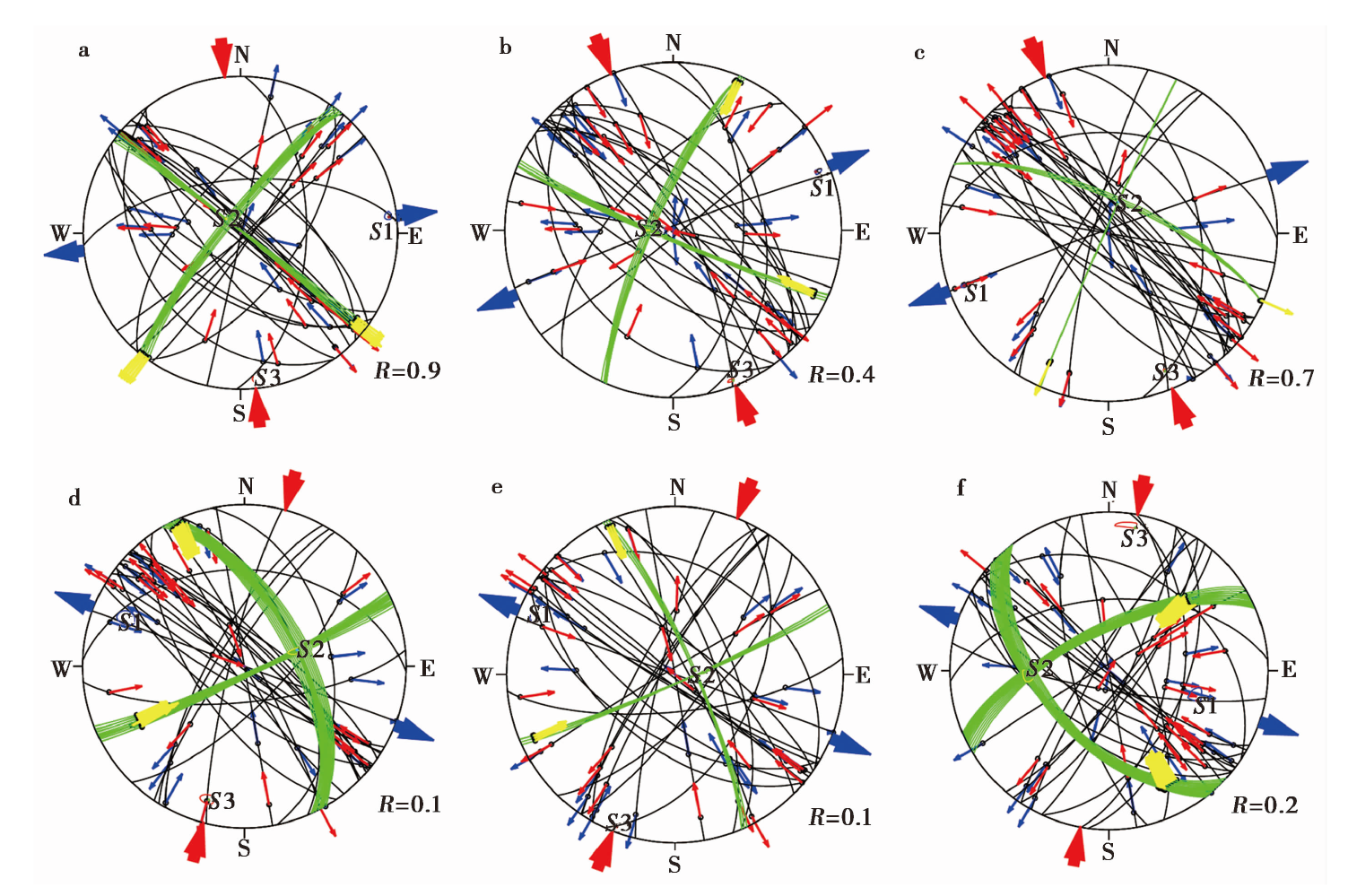
图5 子区内震源机制解数目变为28的应力反演结果 a-f为6个子区间应力场反演结果的下半球施密特投影图,其表示符号与图2b相同
Fig. 5 The stress tensor inversion results with the number of focal mechanisms of 28 in each sub-region.
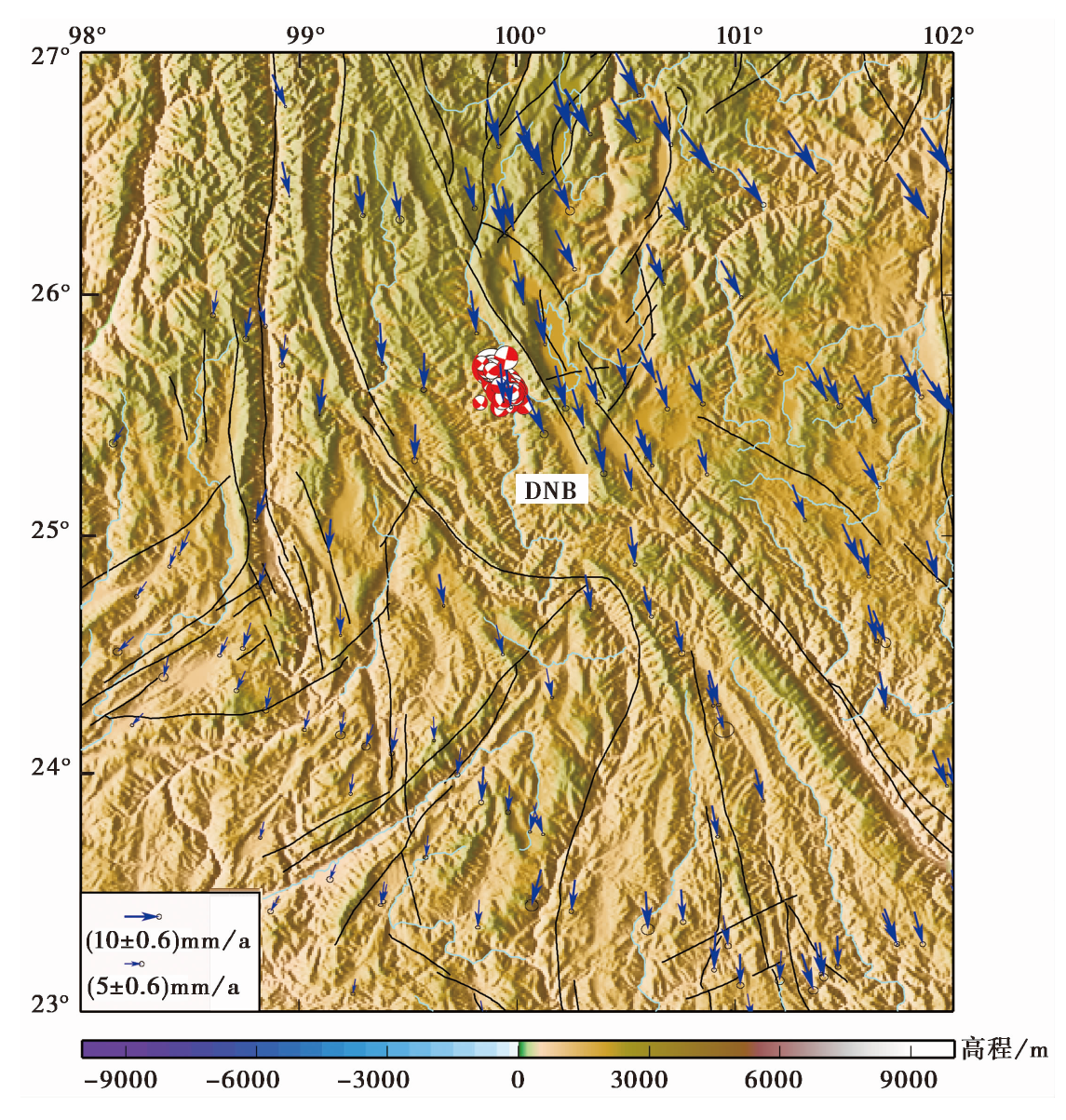
图6 漾濞震源区的位移场分布 蓝色箭头表示该区域的地壳运动,其上的椭圆表示误差范围。地壳运动数据来源于Wang等(2020)
Fig. 6 The displacement field in the Yangbi earthquake fault zone and its adjacent areas.
| [1] |
崔华伟, 郑建常, 万永革, 等. 2022. 2021年云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列发震构造及其与2013年洱源、 2017年漾濞地震的异同[J]. 地球物理学报, 65(2): 620-636.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
郭祥云, 尹海权, 汪贞杰, 等. 2021. 2021年5月21日云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列的矩心矩张量解及动力环境分析[J]. 地震地质, 43(4): 806-826. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.04.005.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [3] |
胡景, 赵韬, 白超英, 等. 2021. 2021年5月21日漾濞 MS6.4 地震震源区三维P和S波速度结构与地震重定位研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(12): 4488-4509.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
龙锋, 祁玉萍, 易桂喜, 等. 2021. 2021年5月21日云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列重新定位与发震构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(8): 2631-2646.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
苏金波, 刘敏, 张云鹏, 等. 2021. 基于深度学习构建2021年5月21日云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列高分辨率地震目录[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(8): 2647-2656.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
万永革. 2019. 同一地震多个震源机制中心解的确定[J]. 地球物理学报, 62(12): 4718-4728.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
万永革. 2022. 断裂带震源机制节面聚类确定断裂带产状方法及在2021年漾濞地震序列中的应用[J]. 地球物理学报, 65(2): 637-648.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
王光明, 吴中海, 彭关灵, 等. 2021. 2021年5月21日漾濞 MS6.4 地震的发震断层及其破裂特征: 地震序列的重定位分析结果[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(4): 662-678.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
王莹, 赵韬, 胡景, 等. 2021. 2021年云南漾濞6.4级地震序列重定位及震源机制解特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 43(4): 847-863. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.04.007.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [10] |
王月, 胡少乾, 何骁慧, 等. 2021. 2021年5月21日云南漾濞6.4级地震序列重定位及震源机制研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(12): 4510-4525.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
余海琳, 万永革, 黄少华, 等. 2021. 利用P波初动数据研究2021年云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列震源机制解及应力场[J]. 地震研究, 44(3): 338-347.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
张丽娟, 万永革, 王福昌, 等. 2022. 采用模糊聚类算法确定2021年漾濞地震序列的断层结构[J]. 地震地质, 44(6): 1634-1647. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.06.016.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [13] |
张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等. 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12-20.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
DOI URL |
| [15] |
DOI URL |
| [16] |
DOI URL |
| [17] |
|
| [18] |
DOI |
| [19] |
DOI |
| [20] |
DOI |
| [1] | 傅莺, 胡斌, 赵敏, 龙锋. 2022年芦山MS6.1地震序列的精确定位及发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(4): 987-1005. |
| [2] | 樊文杰. 2021年5月21日漾濞MS6.4地震及周边的构造应力场特征和动力学意义[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 208-230. |
| [3] | 邓文泽, 刘杰, 杨志高, 孙丽, 张雪梅. 青海玛多MS7.4地震震源破裂过程反演结果的初步分析[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 1059-1070. |
| [4] | 余占洋, 沈旭章, 梁浩, 郑文俊, 刘旭宙. 基于地震活动性和震源机制解研究渭河-运城盆地主要断裂带的特征及应力场分布[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 395-413. |
| [5] | 张致伟, 龙锋, 赵小艳, 王迪. 川滇地区的震源机制解及应力场特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 170-187. |
| [6] | 杜浩国, 林旭川, 张建国, 杜浩标, 张方浩, 杜竹泉, 卢永坤, 代博洋. 基于改进蚁群算法与无人机影像的震害识别方法及其在漾濞地震中的应用[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 1013-1029. |
| [7] | 王凯英, 金明培, 黄雅, 党文杰, 李文涛, 卓燕群, 何昌荣. 2021年5月21日云南漾濞MS6.4地震序列的时空演化[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 1030-1039. |
| [8] | 赵韬, 王莹, 马冀, 邵若潼, 徐一斐, 胡景. 2021年青海玛多7.4级地震序列重定位和震源机制特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 790-805. |
| [9] | 王莹, 赵韬, 胡景, 刘春. 2021年云南漾濞6.4级地震序列重定位及震源机制解特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 847-863. |
| [10] | 李传友, 张金玉, 王伟, 孙凯, 单新建. 2021年云南漾濞6.4级地震发震构造分析[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(3): 706-721. |
| [11] | 崔仁胜, 赵翠萍, 周连庆, 陈阳. 2020年1月19日新疆伽师MS6.4地震序列的活动特征和发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(2): 329-344. |
| [12] | 李金, 蒋海昆, 魏芸芸, 孙昭杰. 2020年1月19日伽师6.4级地震发震构造的初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(2): 357-376. |
| [13] | 刘旭宙, 沈旭章, 何骁慧, 蒲举. 2019年夏河M5.7地震的余震序列重定位及发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(1): 197-208. |
| [14] | 崔华伟, 郑建常, 张正帅, 李冬梅, 柴光斌. 长岛地区小地震断层面参数拟合及应力场特征[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(6): 1432-1445. |
| [15] | 梁姗姗, 徐志国, 盛书中, 张广伟, 赵博, 邹立晔. 2019年四川长宁6.0级地震主震及中强余震(MS≥4.0)的震源机制及其应力场[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(3): 547-561. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||