地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 422-434.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.02.007
修回日期:2022-10-11
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-05-18
作者简介:张玲, 女, 1986年生, 2016年于中国地震局地质研究所获构造地质学专业博士学位, 副研究员, 主要从事活动构造、构造地貌和GPS地壳形变分析等方面研究, E-mail: zhangling4255@126.com。
基金资助:
ZHANG Ling1)( ), MIAO Shu-qing1,2), YANG Xiao-ping1)
), MIAO Shu-qing1,2), YANG Xiao-ping1)
Revised:2022-10-11
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-05-18
摘要:
数字地形分析是活动构造和构造地貌研究中的一种重要手段, 目前已被广泛应用于地表过程分析中。随着高精度数字地形数据获取的日益便捷, 精细定量化研究地貌参数已成为一个重要趋势。呼图壁断裂和独山子断裂位于天山山脉北麓, 地表迹线十分典型而显著。在这2个区域内, 前人已经完成了区域大比例尺活动断裂地质地貌填图, 并发表了大量研究成果。因此, 它们是十分理想的探索断层迹线自动化提取方法的2个区域。在实际提取过程中, 根据逆断层陡坎的倾向是否与其所在地貌面坡向一致, 文中分别定义了正向和反向逆断层陡坎。基于对这2种不同断层陡坎形态的分析, 利用ArcGIS软件平台并选择恰当的地貌参数实现了对断层地表迹线的提取。通过坡度计算、冲沟提取、数据密度分析和流程建模等步骤, 建立了2套智能化提取流程。最终提取结果与以往的地质地貌填图和遥感数据目视解译结果基本一致。除此之外, 独山子研究区的提取结果还揭露了未曾被识别的反向断层陡坎迹线。这不仅说明文中提出的方法具有很好的适用性, 同时也能够提取十分细小的逆断层地表迹线。与传统方法相比, 这种人机交互式的半自动化方法大大提高了工作效率。但是, 如何真正实现任意地质构造背景中逆断层地表迹线的完全自动化提取, 仍然是未来一个重要的研究方向。
中图分类号:
张玲, 苗树清, 杨晓平. 基于ArcGIS平台的天山北麓活动逆断层智能化提取方法的研究与实现[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 422-434.
ZHANG Ling, MIAO Shu-qing, YANG Xiao-ping. THE ANALYSIS AND IMPLEMENTATION OF THE AUTOMATIC EXTRACTING METHOD FOR ACTIVE THRUST FAULTS IN THE NORTH TIANSHAN MOUNTAINS BASED ON ARCGIS SOFTWARE PLATFORM[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(2): 422-434.
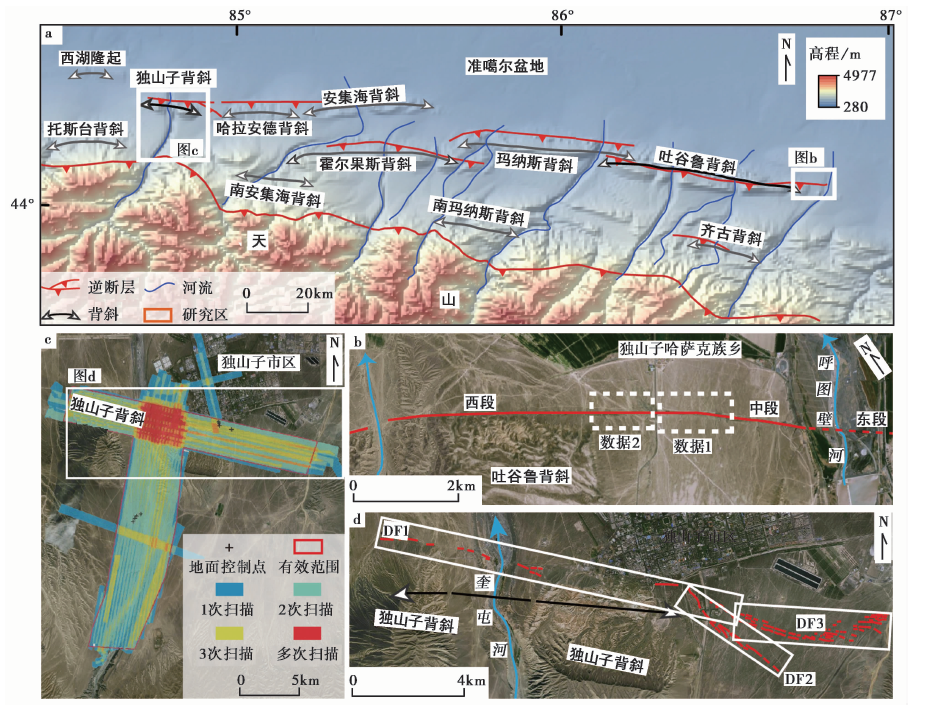
图1 北天山山前主要逆断裂-背斜褶皱带的分布简图及研究区位置 a 天山北麓逆断裂-背斜褶皱带分布图(据Su et al., 2018修改); b高精度无人机摄影测量获得的呼图壁逆断裂厘米级分辨率的数字地形数据的分布范围(即白色虚线矩形框圈定的范围); c 机载LiDAR获取的独山子逆断裂褶皱带米级分辨率的高精度数字地形数据分布; d 独山子逆断裂褶皱带的局部放大图及主要断层分布, 缩略图位置见图1c。白色矩形框圈定了独山子断裂3条次级断层的分布范围
Fig. 1 Distribution of main reverse fault-anticline fold belts in the piedmont of the North Tianshan Mountains and the location of the study area.
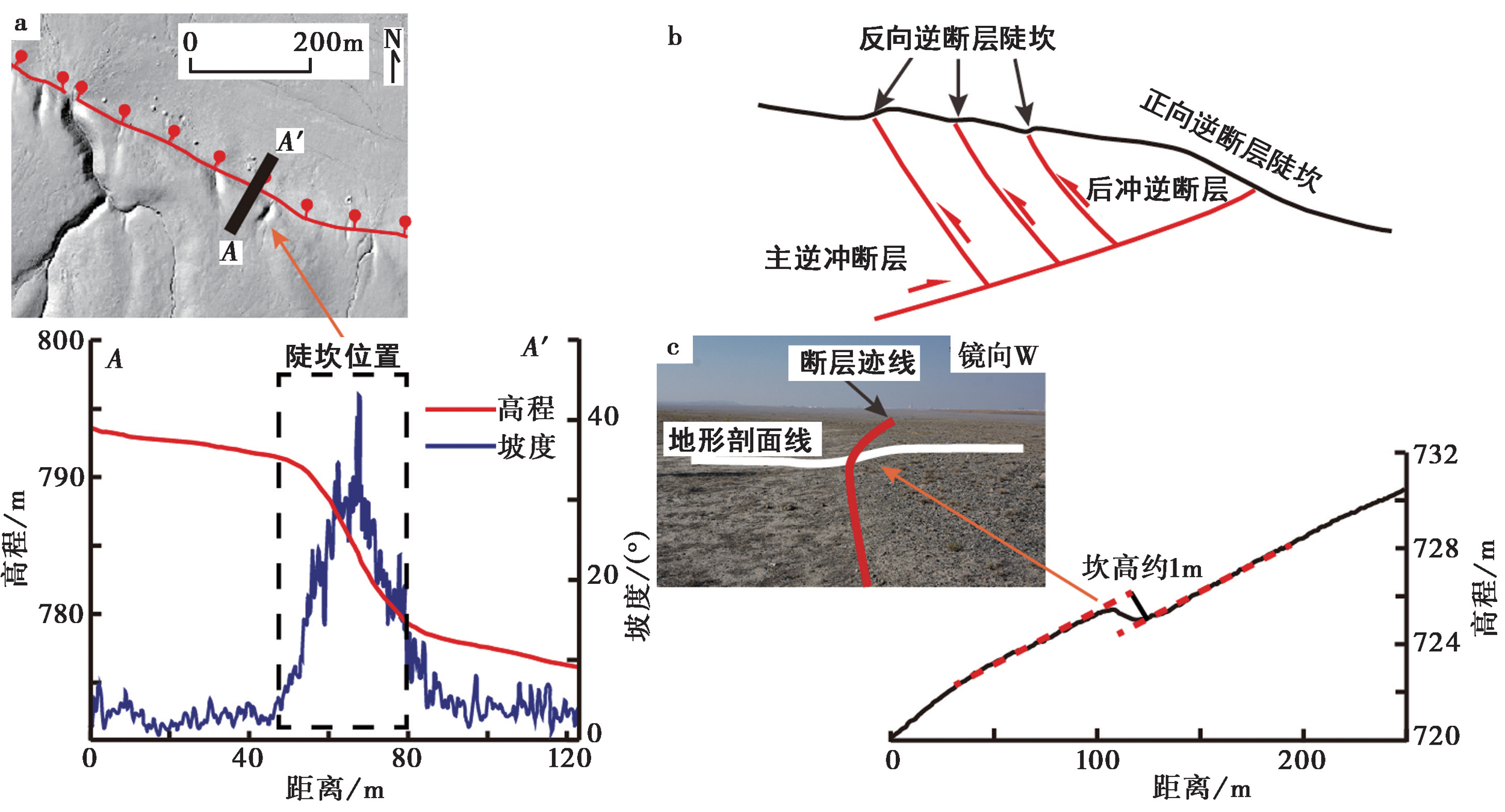
图2 正向逆断层陡坎和反向逆断层陡坎 a 正向逆断层陡坎的地表迹线分布, AA'代表高程-坡度剖面所在的位置; b 反向逆断层陡坎的发育模式及地表特征; c 反向逆断层陡坎的野外照片及实测高程-距离剖面
Fig. 2 Forward and backward thrust fault scarps.
| 控制断裂 | 断层陡坎坡度范围/(°) | 陡坎高度/m |
|---|---|---|
| 霍尔果斯背斜核部逆断裂(东段) | 9、10.5、13、17.5 | 7 |
| 20~27 | 10 | |
| 霍尔果斯背斜核部逆断裂(西段) | 6.5~17 | 0.7~1.8 |
| 14 | 8.2 | |
| 霍尔果斯背斜山前逆断裂 | 17~20.5 | 8.1 |
| 玛纳斯背斜山前断裂 | 11 | 4.3 |
| 15~21 | 4~5 | |
| 22 | 7~11.2 | |
| 吐谷鲁背斜核部逆断裂 | 12 | 2.5 |
| 10~20 | 6~10 | |
| 10~30 | 0.08~0.58 | |
| 7~20 | 0.3~0.6 | |
| 11.5 | 10.2 | |
| 10 | 11.6 | |
| 10~23 | 6.6 | |
| 23 | 3.9 | |
| 独山子背斜山前逆断裂 | 10~20 | 1.3~2.1 |
| 独山子背斜东端NW向剪切断裂带 | 5~18 | 0.9~1.4 |
表1 天山北麓逆断层陡坎的坡度值与高度统计(邓起东等, 2000)
Table1 The statistics of thrust fault scarp slope and height of the northern piedmont of the Tianshan Mountains(DENG Qi-dong et al., 2000)
| 控制断裂 | 断层陡坎坡度范围/(°) | 陡坎高度/m |
|---|---|---|
| 霍尔果斯背斜核部逆断裂(东段) | 9、10.5、13、17.5 | 7 |
| 20~27 | 10 | |
| 霍尔果斯背斜核部逆断裂(西段) | 6.5~17 | 0.7~1.8 |
| 14 | 8.2 | |
| 霍尔果斯背斜山前逆断裂 | 17~20.5 | 8.1 |
| 玛纳斯背斜山前断裂 | 11 | 4.3 |
| 15~21 | 4~5 | |
| 22 | 7~11.2 | |
| 吐谷鲁背斜核部逆断裂 | 12 | 2.5 |
| 10~20 | 6~10 | |
| 10~30 | 0.08~0.58 | |
| 7~20 | 0.3~0.6 | |
| 11.5 | 10.2 | |
| 10 | 11.6 | |
| 10~23 | 6.6 | |
| 23 | 3.9 | |
| 独山子背斜山前逆断裂 | 10~20 | 1.3~2.1 |
| 独山子背斜东端NW向剪切断裂带 | 5~18 | 0.9~1.4 |

图3 呼图壁正向逆断层地表迹线的提取流程图 a 原始DEM数据; b 提取符合实际情况的冲沟分布; c 提取符合理论坡度值5°~35°的地形范围; d 提取既剔除了冲沟影响、又符合理论坡度范围的地形范围; e 利用地貌面缓冲区重叠范围限定的陡坎范围; f 提取同时符合陡坎高程和坡度分布特征的地形范围; g 利用坡度统计和密度分布计算获取最终的精细逆断层地表迹线分布
Fig. 3 Flow diagram showing the extraction of the trace of the forward Hutubi fault scarp.
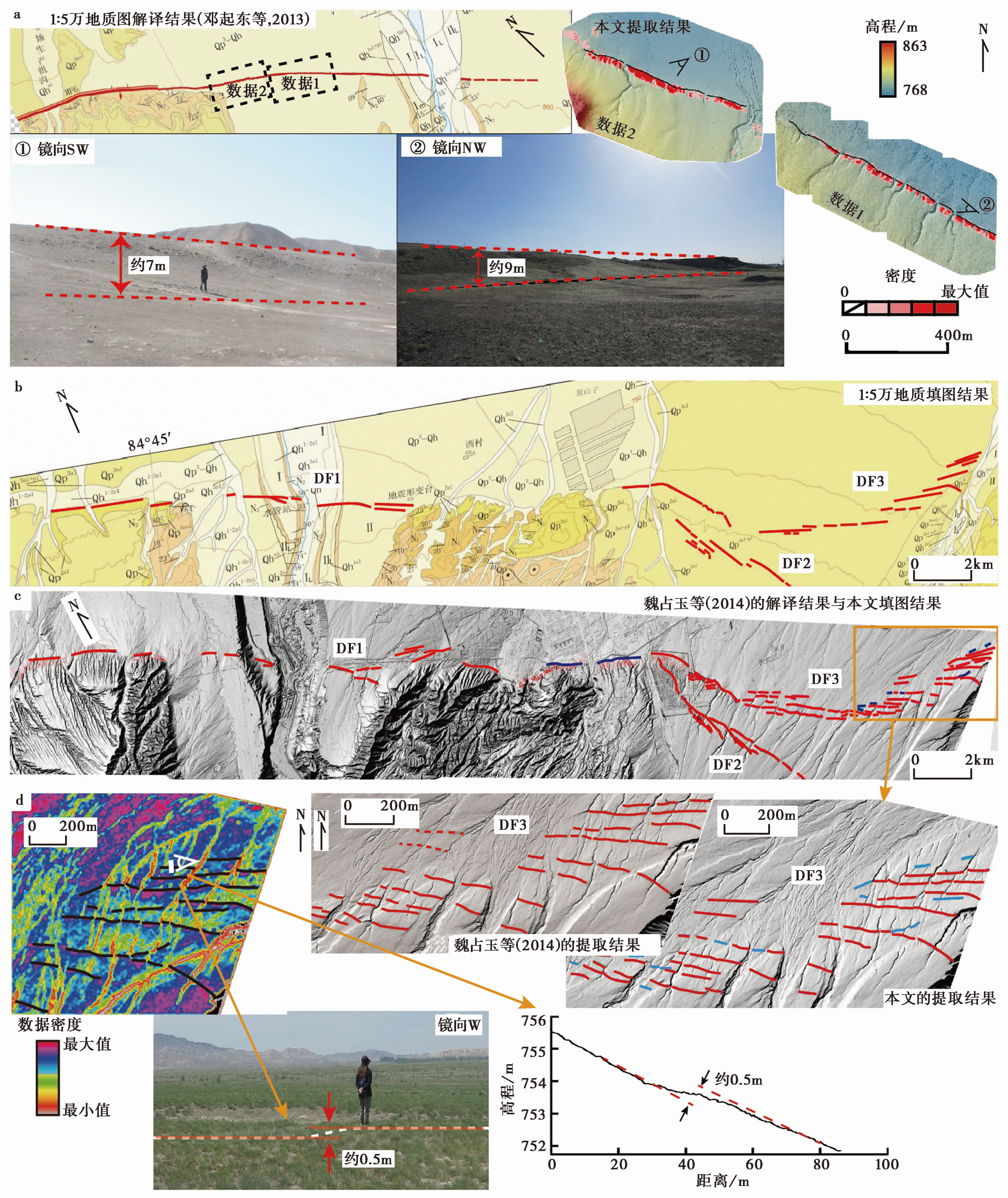
图5 不同提取结果的对比及野外验证 a 呼图壁研究区正向逆断层陡坎地表迹线的1︰5万地质图解译结果、本文提取结果和野外实际照片; b 独山子研究区内活动逆断层的1︰5万地质填图结果; c 针对独山子研究区内的活动逆断层, 魏占玉等(2014)的解译结果及本文提取结果; d 独山子研究区内反向逆断层陡坎小起伏度数据的密度分布结果(左上)、局部放大的不同解译手段获得的独山子研究区内反向逆断层陡坎的分布(右上, 展示范围见图c)、野外调查照片(左下)和实测高程剖面曲线。在数据密度分布图中, 黑线代表根据密度分布结果通过目视解译得到的断层分布, 白色线条代表野外实测的高程-距离剖面的位置。在局部放大的提取结果对比图中, 红色线条代表DF3均被解译出的迹线, 而本文提取结果中的蓝色线段为其他方法并未识别的断层地表迹线
Fig. 5 Comparison of different extraction results and field verification.
| [1] | 邓起东, 冯先岳, 张培震, 等. 2000. 天山活动构造[M]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| DENG Qi-dong, FENG Xian-yue, ZHANG Pei-zhen, et al. 2000. Active Tectonics in Tianshan Mountain[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] |
魏占玉, 何宏林, 高伟, 等. 2014. 基于LiDAR数据开展活动断层填图的实验研究: 以新疆独山子背斜-逆冲断裂带为例[J]. 地震地质, 36(3): 794-813. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.019.
DOI |
| WEI Zhan-yu, HE Hong-lin, GAO Wei, et al. 2014. Experiment study on geologic mapping of active tectonics based on LiDAR data: A case of Dushanzi anticline-reverse fault zone in Xinjiang[J]. Seismology and Geology, 36(3): 794-813. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 杨晓平. 1994. 新疆北天山活动逆断裂-褶皱带的变形、机制和大地震重复间隔研究[D]. 北京: 国家地震局地质研究所. |
| YANG Xiao-ping. 1994. Study on the deformation, kinematics and great earthquake recurrence interval of active thrust-and-fold belts in the North Tianshan Mountains[D]. Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] |
姚文倩, 刘静, Oskin M, 等. 2019. 利用R语言半自动化提取河流阶地: 以米家山黄河阶地为例[J]. 地震地质, 41(2): 363-376. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.02.007.
DOI |
| YAO Wen-qian, LIU-ZENG Jing, Oskin M, et al. 2019. Application of semiautomatic extraction of fluvial terraces based on R language: An example from the Yellow River terraces at Mijia Shan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 41(2): 363-376. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] |
张玲, 杨晓平, 魏占玉, 等. 2014. 三维数据的二维可视化方法综述[J]. 地震地质, 36(1): 275-283. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.02.023.
DOI |
| ZHANG Ling, YANG Xiao-ping, WEI Zhan-yu, et al. 2014. Overview of visualization methods of three dimensional topographic data[J]. Seismology and Geology, 36(1): 275-283. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] |
Bonetto S, Facello A, Ferrero A M, et al. 2015. A tool for semi-automatic linear feature detection based on DTM[J]. Computers and Geosciences, 75: 1-12.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
Chiba T, Hasi B. 2016. Ground surface visualization using red relief image map for a variety of map scales[J]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, XLI-B2: 393-397.
DOI URL |
| [8] | Chiba T, Kaneta S I, Suzuki Y. 2008. Red relief image map: New visualization method for three dimensional data[J]. The International Archives of the Photogrammetry, Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences, 37(B2): 1071-1076. |
| [9] |
Gannouni S, Gabtni H. 2015. Structural interpretation of lineaments by satellite image processing(Landsat TM)in the region of Zahret Medien(Northern Tunisia)[J]. Journal of Geographic Information System, 7(2): 119-127.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
Han L, Liu Z, Ning Y, et al. 2018. Extraction and analysis of geological lineaments combining a DEM and remote sensing images from the northern Baoji loess area[J]. Advances in Space Research, 62(9): 2480-2493.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
Jobe J A T, Philibosian B, Chupik C, et al. 2020. Evidence of previous faulting along the 2019 Ridgecrest, California, earthquake ruptures[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 110(4): 1427-1456.
DOI URL |
| [12] | Keller E A, Pinter N. 1996. Active Tectonics: Earthquakes, Uplift, and Landscape[M]. New Jersey, Prentice Hall. |
| [13] |
Kühni A, Pfiffner O A. 2001. The relief of the Swiss Alps and adjacent areas and its relation to lithology and structure: topographic analysis from a 250-m DEM[J]. Geomorphology, 41(4): 285-307.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Lary D J, Alavi A H, Gandomi A H, et al. 2016. Machine learning in geosciences and remote sensing[J]. Geoscience Frontiers, 7(1): 3-10.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Lin Z, Kaneda H, Mukoyama S, et al. 2013. Detection of subtle tectonic-geomorphic features in densely forested mountains by very high-resolution airborne LiDAR survey[J]. Geomorphology, 182(2): 104-115.
DOI URL |
| [16] | Liu Q, Zhang H, Li Y, et al. 2021. Effects of erosion and deposition on constraining vertical slip rates of thrust faults: A case study of the Minle-Damaying Fault in the North Qilian Shan, NE Tibetan plateau[J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 9(205): 1-20. |
| [17] |
Maggiori E, Tarabalka Y, Charpiat G, et al. 2017. High-resolution aerial image labeling with convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 55(12): 7092-7103.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Masoud A A, Koike K. 2011. Auto-detection and integration of tectonically significant lineaments from SRTM DEM and remotely-sensed geophysical data[J]. Journal of Photogrammetry and Remote Sensing, 66(6): 818-832.
DOI URL |
| [19] | Mattéo L, Manighetti I, Tarabalka Y, et al. 2021. Automatic fault mapping in remote optical images and topographic data with deep learning[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 126(4): e2020JB021269. |
| [20] |
Molnar P, Tapponnier P. 1975. Cenozoic tectonics of Asia: Effects of a continental collision: Features of recent continental tectonics in Asia can be interpreted as results of the India-Eurasia collision[J]. Science, 189(4201): 419-426.
PMID |
| [21] |
Msaddek M H, Moumni Y, Chenini I, et al. 2019. Applicability of developed algorithm for semi-automated extraction and morphotectonic interpretation of lineaments using remotely sensed data, southwestern Tunisia[J]. Remote Sensing in Earth Systems Sciences, 2(4): 292-307.
DOI |
| [22] |
Palamara D R, Dickson M E, Kennedy D M. 2007. Defining shore platform boundaries using airborne laser scan data: a preliminary investigation[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 32(6): 945-953.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Radaideh O M A, Grasemann B, Melichar R, et al. 2016. Detection and analysis of morphotectonic features utilizing satellite remote sensing and GIS: An example in SW Jordan[J]. Geomorphology, 275: 58-79.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Raj S K, Ahmed S A. 2014. Lineament extraction from Southern Chitradurga Schist Belt using Landsat TM, astergdem and geomatics techniques[J]. International Journal of Computer Applications, 93(12): 12-20. |
| [25] |
Sare R, Hilley G E, DeLong S B. 2018. Regional-scale detection of fault scarps and other tectonic landforms: Examples from Northern California[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 124: 1016-1035.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Soto-Pinto C, Arellano-Baeza A, Sánchez G. 2013. A new code for automatic detection and analysis of the lineament patterns for geophysical and geological purposes(ADALGEO)[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 57: 93-103.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Stewart I S, Hancock P L. 1988. Normal fault zone evolution and fault scarp degradation in the Aegean region[J]. Basin Research, 1(3): 139-153.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Su P, He H, Wei Z, et al. 2018. A new shortening rate across the Dushanzi anticline in the northern Tian Shan Mountains, China from lidar data and a seismic reflection profile[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 163: 131-141.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Tasar O, Tarabalka Y, Alliez P. 2019. Incremental learning for semantic segmentation of large-scale remote sensing data[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 12(9): 3524-3537.
DOI |
| [30] |
Wei Z, He H, Hao H, et al. 2017. Automated mapping of landforms through the application of supervised classification to lidAR-derived DEMs and the identification of earthquake ruptures[J]. International Journal of Remote Sensing, 38(23): 7196-7219.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Yokoyama R, Shlrasawa M, Pike R J. 2002. Visualizing topography by openness: A new application of image processing to digital elevation models[J]. Photogrammetric Engineering & Remote Sensing, 68(3): 257-265. |
| [32] |
Zielke O, Klinger Y, Arrowsmith J R. 2015. Fault slip and earthquake recurrence along strike-slip faults: Contributions of high-resolution geomorphic data[J]. Tectonophysics, 638(1): 43-62.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 郑海刚, 姚大全, 赵朋, 杨源源, 黄金水. 郯庐断裂带赤山段全新世新活动的特征[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 127-138. |
| [2] | 艾明, 毕海芸, 郑文俊, 尹金辉, 袁道阳, 任治坤, 陈干, 刘金瑞. 利用无人机摄影测量技术提取活动构造定量参数[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(6): 1276-1293. |
| [3] | 汪思妤, 艾明, 吴传勇, 雷启云, 张会平, 任光雪, 李传友, 任治坤. 高分辨率卫星影像提取DEM技术在活动构造定量研究中的应用——以库米什盆地南缘断裂陡坎为例[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(5): 999-1017. |
| [4] | 吴熙彦, 徐锡伟, 于贵华, 程佳, 陈桂华, 安艳芬, 王启欣. 国家川滇实验场地震地表破裂带分布图编制[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(1): 27-41. |
| [5] | 韩晓明, 刘芳, 张帆, 陈立峰, 李娟, 李拴虎, 杨红樱. 鄂尔多斯块体东北缘的P波速度精细结构[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(1): 215-231. |
| [6] | 徐伟, 刘志成, 袁兆德, 高战武, 杨源源. 华山山前河流地貌参数及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(6): 1316-1335. |
| [7] | 毕海芸, 郑文俊, 曾江源, 俞晶星, 任治坤. SfM摄影测量方法在活动构造定量研究中的应用[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(4): 656-674. |
| [8] | 艾晟, 张波, 樊春, 王洋. 武威盆地南缘断裂晚第四纪活动地表形迹与活动速率[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(2): 408-422. |
| [9] | 孙鑫喆, 唐声权. 光学遥感技术的发展及其在活动构造研究中的应用[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(1): 211-220. |
| [10] | 马超, 屈春燕, 孟秀军. 南水北调总干渠中线工程豫北段基础稳定性的InSAR时序分析[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(3): 749-762. |
| [11] | 李涛, 陈杰. 利用河流阶地限定活动逆断层相关褶皱晚第四纪变形机制和速率:方法与认识[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(2): 478-488. |
| [12] | 冯梅, 张纪中, 安美建. 2008年汶川地震前后震源区构造应力场变化[J]. 地震地质, 2013, 35(4): 701-720. |
| [13] | 张竹琪, 陈涛, 任治坤, 王伟涛. 数值模型显示的隐伏弯曲断层同震地表位移特征[J]. 地震地质, 2013, 35(2): 452-460. |
| [14] | 于贵华, 杜克平, 徐锡伟, 吴熙彦, 王银. 活动构造数据库建设相关问题的研究[J]. 地震地质, 2012, (4): 713-725. |
| [15] | 冉勇康, 陈立春, 陈文山, 王虎, 李安. 中国大陆古地震研究的关键技术与案例解析(2)——汶川地震地表变形特征与褶皱逆断层古地震识别[J]. 地震地质, 2012, (3): 385-400. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||