地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 355-376.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.02.004
左玉琦( ), 杨海波, 杨晓平*(
), 杨海波, 杨晓平*( ), 詹艳, 李安, 孙翔宇, 胡宗凯
), 詹艳, 李安, 孙翔宇, 胡宗凯
修回日期:2023-01-20
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-05-18
通讯作者:
*杨晓平, 男, 1962年生, 研究员, 主要研究方向为活动构造及地震危险性评价, E-mail: 作者简介:左玉琦, 男, 1996年生, 2018年于湖南师范大学获地理科学专业学士学位, 现为中国地震局地质研究所构造地质学专业在读硕士研究生, 研究方向为活动构造与构造地貌, E-mail: zuoyuqi1996@163.com。
基金资助:
ZUO Yu-qi( ), YANG Hai-bo, YANG Xiao-ping*(
), YANG Hai-bo, YANG Xiao-ping*( ), ZHAN Yan, LI An, SUN Xiang-yu, HU Zong-kai
), ZHAN Yan, LI An, SUN Xiang-yu, HU Zong-kai
Revised:2023-01-20
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-05-18
摘要:
阿拉善地块南缘地处青藏高原东北缘地壳扩展前锋带的北侧, 对该地区活动断裂晚第四纪的运动性质、滑动速率等开展研究, 有助于理解阿拉善地块的晚第四纪构造变形特征及其对青藏高原向N扩展的响应。文中结合遥感影像解译与野外地质地貌考察, 对阿拉善地块南缘的北大山断裂进行了分段和活动性研究。结果表明, 北大山断裂左旋走滑断错晚第四纪洪积扇和阶地等地貌, 形成显著的位错阶地坎、冲沟以及断层陡坎。通过对断错地貌线等标志的测量、复原、统计分析等, 发现断裂的地貌位移值分布于3~20m, 发育新鲜断层自由面的断层陡坎和左旋错动的纹沟指示了断层的最新一次活动。基于同期洪积扇年龄估算得到北大山断裂晚更新世以来的左旋滑动速率为0.3~0.6mm/a。北大山断裂的运动学特征与区域NE向应力场一致, 可能受到了青藏高原NE向扩展的影响。
中图分类号:
左玉琦, 杨海波, 杨晓平, 詹艳, 李安, 孙翔宇, 胡宗凯. 阿拉善地块南缘北大山断裂的晚第四纪构造活动证据[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 355-376.
ZUO Yu-qi, YANG Hai-bo, YANG Xiao-ping, ZHAN Yan, LI An, SUN Xiang-yu, HU Zong-kai. EVIDENCE OF LATE QUATERNARY TECTONIC ACTIVITY OF THE BEIDA SHAN FAULT, SOUTHERN MARGIN OF THE ALASHAN BLOCK[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(2): 355-376.

图1 祁连山-阿拉善南部的活动断裂分布 图中活动断裂特征据陈文彬(2003)、俞晶星(2016)和Yang等(2019)修改。 HSF 黑山断裂; JYGF 嘉峪关断裂; BHWF 北河湾断裂; JTNSF 金塔南山断裂; HLSF 合黎山南缘断裂; YMSF 榆木山断裂; MSLF 慕少梁断裂; PYF 盘头山-羊圈沟断裂; BDSF 北大山断裂; THF 桃花拉山断裂; AYQF 阿右旗断裂; SLSF 龙首山南缘断裂; YRF 雅布赖断裂; WHF 贺兰山西麓断裂
Fig. 1 Active faults in the Qilian Shan and southern Alashan block.
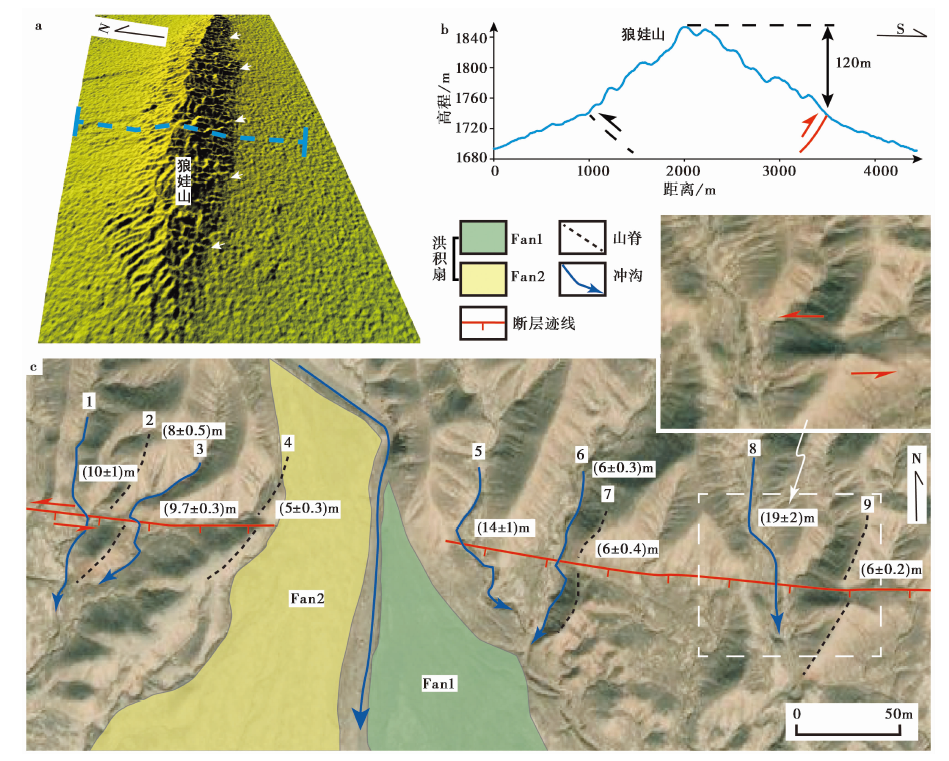
图3 狼娃山段点位1的断错地貌 a 狼娃山段点位1处的DEM影像; b 狼娃山的地形剖面, 剖面线位置见图a; c 多条冲沟与山脊被左旋位错, 图中Fan1、Fan2表示不同的洪积扇。影像来源于Google Earth
Fig. 3 Offset landforms along the Langwa Shan segment at site 1.

图5 夹批泉山段北支点位3的断错地貌 a 夹批泉山段北支点位3处的山影图, 红色三角形指示断层陡坎的位置; b 左旋位错的洪积台地边缘; c 坡向S的断层陡坎; d 强褶皱变形的白垩纪砂岩; e 从DEM影像中提取的地形剖面, 地形剖面线P1、P2的位置见图a
Fig. 5 Offset landforms along the north branch of the Jiapiquan Shan segment at site 3.

图6 夹批泉山段北支点位4的断错地貌 a 夹批泉山段北支断层点位4处的山影图; b 点位4的地貌解译图, 图中Fan1为洪积扇, T1、T2为河流阶地; c、d 多个洪积扇边缘被断层同步左旋位错; e 回滑约5m的位错恢复图; f 从DEM影像中提取的地形剖面, 地形剖面线P3、P4的位置见图a
Fig. 6 Offset landforms along the north branch of the Jiapiquan Shan segment at site 4.

图7 夹批泉山段北支点位5的断错地貌 a 线性发育于基岩山体中的断层, 可见一系列冲沟与山脊被左旋错断; b、c 冲沟与山脊的位错解译。蓝色实线代表位错冲沟, 黑色虚线代表位错山脊
Fig. 7 Offset landforms along the north branch of the Jiapiquan Shan segment at site 5.

图8 夹批泉山段南支断层点位6的断错地貌 a 大红山南支断层点位6处的山影图; b 点位6的地貌解译图; c 多条冲沟被同步左旋位错; d 冲沟与阶地坎被断层左旋位错(18±2)m; e 从DEM影像中提取的地形剖面, 地形剖面线P5、P6的位置见图a
Fig. 8 Offset landforms along the south branch of the Jiapiquan Shan segment at site 6.

图9 夹批泉山段南支点位7的断错地貌 a 夹批泉山段南支断层的局部山影图; b 山前洪积扇的分布解译, 图中Fan1、Fan2、Fan3代表不同期次的洪积扇; c 断层陡坎与位错冲沟; d 从DEM影像中提取的地形剖面, 地形剖面线P7、P8的位置见图a; e 一冲沟西壁出露的断层剖面, 剖面位置见图a
Fig. 9 Offset landforms along the south branch of the Jiapiquan Shan segment at site 7.

图10 夹批泉山段南支的断错地貌 a夹批泉山段南支断层的局部山影图;b山前洪积扇的分布解译;c、d一冲沟东壁的断层露头及素描图,剖面位置见图a;e多级阶地上的断层陡坎;f地表破裂带,可见断层自由面发育
Fig.10 Offset landforms along the south branch of the Jiapiquan Shan segment.

图11 夹批泉山段南支点位10的断错地貌 a 夹批泉山段南支点位10处的山影图; b 点位10的地貌解译图; c T1/T2阶地陡坎的左旋位错; d 从DEM影像中提取的地形剖面, 地形剖面线P9、P10的位置见图a
Fig. 11 Offset landforms along the south branch of the Jiapiquan Shan segment at site 10.

图12 地表破裂带的分布 a 地表破裂带的分布范围; b-e 最新地震产生的地表破裂与纹沟位错, 红色箭头指示破裂带陡坎的位置; d 断层自由面处纹沟上的裂点和跌水, 箭头指示裂点的位置; e 断层陡坎上的新鲜断层自由面; f、g 露头揭示断层上断至近地表
Fig. 12 Distribution of the surface rupture.
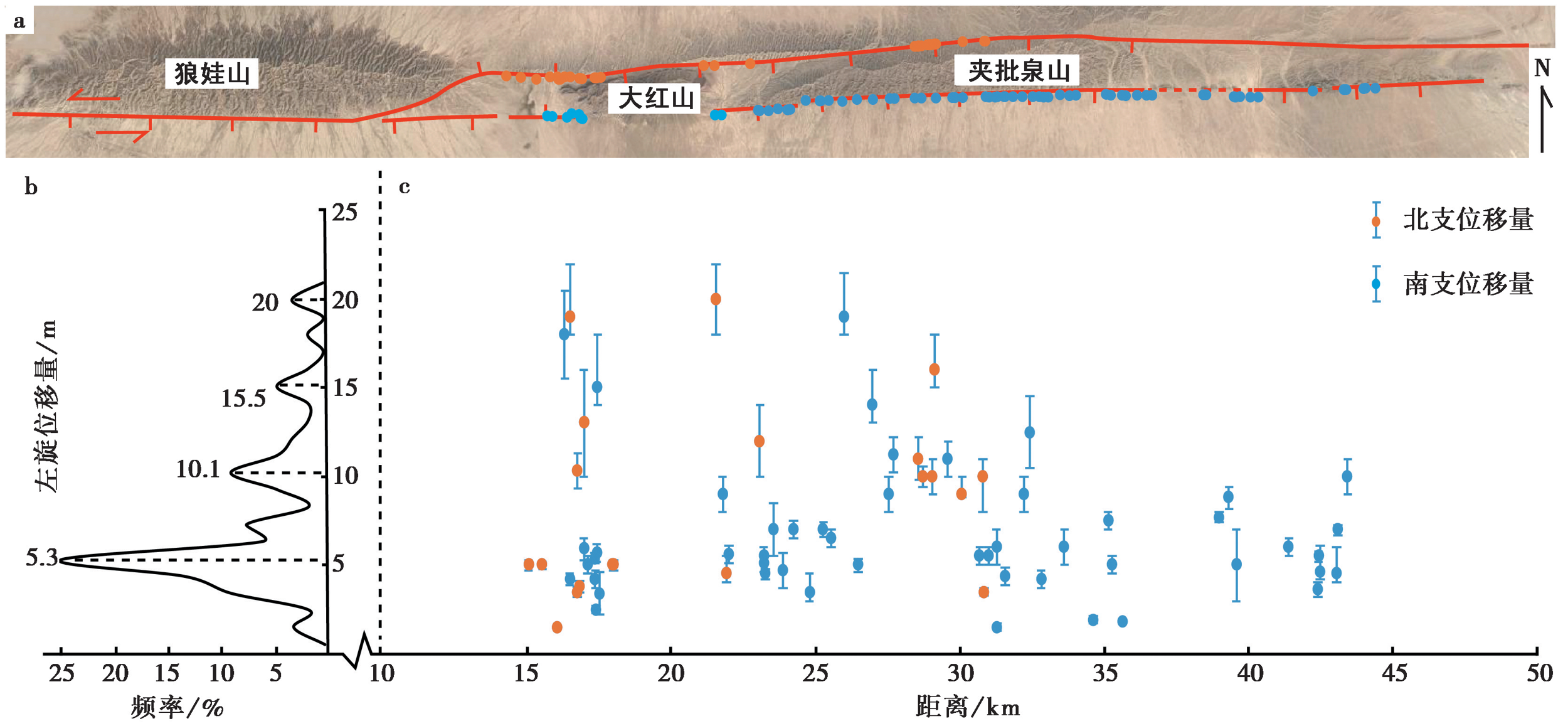
图13 断裂沿线的左旋位错量分布特征 a 位移量测量点位的分布; b 以1m为单位的左旋位移量频率分布曲线; c 左旋位移量沿断裂的分布图
Fig. 13 Distribution of the left-lateral strike-slip displacement along the Beida shan Fault.
| [1] |
艾晟, 张波, 樊春, 等. 2017. 武威盆地南缘断裂晚第四纪活动地表形迹与活动速率[J]. 地震地质, 39(2): 408-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.02.010.
DOI |
| AI Sheng, ZHANG Bo, FAN Chun, et al. 2017. Surface traces and slip rate of the fault along the southern margin of the Wuwei Basin in the late Quaternary[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(2): 408-422. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 陈文彬. 2003. 河西走廊及邻近地区最新构造变形基本特征及构造成因分析[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. |
| CHEN Wen-bin. 2003. Principal features of tectonic of deformation and their generation mechanism in the Hexi Corridor and its adjacent regions since late Quaternary[D]. Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 陈文彬, 徐锡伟. 2006. 阿拉善地块南缘的左旋走滑断裂与阿尔金断裂带的东延[J]. 地震地质, 28(2): 319-324. |
| CHEN Wen-bin, XU Xi-wei. 2006. Sinistral strike-slip faults along the southern Alashan margin and eastwards extending of the Altun Fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 28(2): 319-324. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] |
李佳昱, 郑文俊, 王伟涛, 等. 2020. 青藏高原东北部龙首山晚新生代剥露历史: 来自磷灰石(U-Th)/He的证据[J]. 地震地质, 42(2): 472-491. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.02.014.
DOI |
| LI Jia-yu, ZHENG Wen-jun, WANG Wei-tao, et al. 2020. The northward growth of the northeastern Tibetan plateau in late Cenozoic: Implications from apatite(U-Th)/He ages of Longshou Shan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(2): 472-491. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 刘睿. 2020. 河西走廊西端晚第四纪构造变形与断裂相互作用[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. |
| LIU Rui. 2020. Tectonic deformation and faults interaction since late Quaternary in the west end of Hexi Corridor[D]. Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 潘保田, 蔡顺, 耿豪鹏. 2021. 山体隆升历史与地貌演化过程的数值模拟约束: 以青藏高原东北缘河西走廊中段的周边年轻上升山地为例[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 51(4): 523-536. |
|
PAN Bao-tian, CAI Shun, GENG Hao-peng. 2021. Numerical simulation of landscape evolution and mountain uplift history constrain: A case study from the youthful stage mountains around the central Hexi Corridor, NE Tibetan plateau[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 64(3): 412-424.
DOI |
|
| [7] | 徐锡伟, Tapponnier P, van der Woerd J, 等. 2003. 阿尔金断裂带晚第四纪左旋走滑速率及其构造运动转换模式讨论[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(10): 967-974. |
| XU Xi-wei, Tapponnier P, van der Woerd J, et al. 2003. Slip of the Altun fault zone since the late Quaternary and tectonic transformation style[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 33(10): 957-974. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] |
杨海波, 杨晓平, 黄雄南. 2017. 祁连山北缘断裂带中段晚第四纪活动速率初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 39(1): 20-42. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.01.002.
DOI |
| YANG Hai-bo, YANG Xiao-ping, HUANG Xiong-nan. 2017. A preliminary study about slip rate of middle segment of the northern Qilian thrust fault zone since late Quaternary[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(1): 20-42. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 俞晶星. 2016. 阿拉善地块南部构造活动及其对周边地块相互作用的响应[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. |
| YU Jing-xing. 2016. Active tectonics in the southern Gobi-Alashan block and its response to the interactions of the adjacent crustal blocks[D]. Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] |
张波, 何文贵, 庞炜, 等. 2016. 青藏块体北部金塔南山断裂晚第四纪走滑活动的地质地貌特征[J]. 地震地质, 38(1): 1-21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.01.001.
DOI |
| ZHANG Bo, HE Wen-gui, PANG Wei, et al. 2016. Geological and geomorphic expressions of late Quaternary strike-slip activity on Jintananshan Fault in northern edge of Qing-Zang block[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(1): 1-21. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 郑文俊, 张博譞, 袁道阳, 等. 2021. 阿拉善地块南缘构造活动特征与青藏高原东北缘向外扩展的最新边界[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 43(2): 224-236. |
| ZHENG Wen-jun, ZHANG Bo-xuan, YUAN Dao-yang, et al. 2021. Tectonic activity in the southern Alashan Block and the latest boundary of outward expansion on the northeastern Tibetan plateau, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 43(2): 224-236. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] |
Bi H Y, Zheng W J, Ge W P, et al. 2018. Constraining the distribution of vertical slip on the south Heli Shan Fault(northeastern Tibet)from high-resolution topographic data[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 123(3): 2484-2501.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
Darby B J, Ritts B D, Yue Y J, et al. 2005. Did the Altyn Tagh Fault extend beyond the Tibetan plateau?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 240(2): 425-435.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Du J X, Fu B H, Shi P L, et al. 2021. Cenozoic tectono-geomorphic evolution of Yabrai Mountain and the Badain Jaran Desert(NE Tibetan plateau margin)[J]. Geomorphology, 389:107857.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Haddon E K, Amos C B, Zielke O, et al. 2016. Surface slip during large Owens Valley earthquakes[J]. Geochemistry Geophysics Geosystems, 17(6): 2239-2269.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Hetzel R, Tao M X, Niedermann S, et al. 2004a. Implications of the fault scaling law for the growth of topography: Mountain ranges in the broken foreland of northeast Tibet[J]. Terra Nova, 16(3): 157-162.
DOI URL |
| [17] | Hetzel R, Tao M X, Stokes S, et al. 2004b. Late Pleistocene/Holocene slip rate of the Zhangye thrust(Qilian Shan, China)and implications for the active growth of the northeastern Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonics, 23(6): TC6006. |
| [18] |
Hilley G E, Arrowsmith J R. 2008. Geomorphic response to uplift along the Dragon’s Back pressure ridge, Carrizo Plain, California[J]. Geology, 36(5): 367-370.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Klinger Y, Etchebes M, Tapponnier P, et al. 2011. Characteristic slip for five great earthquakes along the Fuyun Fault in China[J]. Nature Geoscience, 4(6): 389-392.
DOI |
| [20] |
Meyer B, Tapponnier P, Bourjot L, et al. 1998. Crustal thickening in Gansu-Qinghai, lithospheric mantle subduction, and oblique, strike-slip controlled growth of the Tibet plateau[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 135(1): 1-47.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Palumbo L, Hetzel R, Tao M, et al. 2009. Deciphering the rate of mountain growth during topographic presteady state: An example from the NE margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonics, 28: TC4017. |
| [22] |
Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Le Dain A Y, et al. 1982. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: New insights from simple experiments with plasticine[J]. Geology, 10(12): 611-616.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
Vincent S J, Allen M B. 1999. Evolution of the Minle and Chaoshui Basins, China: Implications for Mesozoic strike-slip basin formation in central Asia[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 111(5): 725-742.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
Yang H B, Yang X P, Zhan Y, et al. 2019. Quaternary activity of the Beihewan Fault in the southeastern Beishan wrench belt, western China: Implications for crustal stability and intraplate earthquake hazards north of Tibet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 124(12): 13286-13309.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
Yu J X, Zheng W J, Kirby E, et al. 2016. Kinematics of late Quaternary slip along the Yabrai Fault: Implications for Cenozoic tectonics across the Gobi Alashan block, China[J]. Lithosphere, 8(3): 199-218.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
Yu J X, Zheng W J, Zhang P Z, et al. 2017. Late Quaternary strike-slip along the Taohuala Shan-Ayouqi fault zone and its tectonic implications in the Hexi Corridor and the southern Gobi Alashan, China[J]. Tectonophysics, 721: 28-44.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Zhang J, Cunningham D, Yun L, et al. 2021. Kinematic variability of late Cenozoic fault systems and contrasting mountain building processes in the Alxa block, western China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 205:104597.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Zhang P Z, Molnar P, Xu X W. 2007. Late Quaternary and present-day rates of slip along the Altyn Tagh Fault, northern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonics, 26(5): TC5010. |
| [29] |
Zhang P Z, Shen Z K, Wang M, et al. 2004. Continuous deformation of the Tibetan plateau from global positioning system data[J]. Geology, 32(9): 809-812.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Zheng D W, Clark M K, Zhang P Z, et al. 2010. Erosion, fault initiation and topographic growth of the North Qilian Shan(northern Tibetan plateau)[J]. Geosphere, 6(6): 937-941.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Zheng D W, Wang W T, Wan J L, et al. 2017. Progressive northward growth of the northern Qilian Shan-Hexi Corridor(northeastern Tibet)during the Cenozoic[J]. Lithosphere, 9(3): 408-416.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Zheng W J, Zhang H P, Zhang P Z, et al. 2013a. Late Quaternary slip rates of the thrust faults in western Hexi Corridor(northern Qilian Shan, China)and their implications for northeastward growth of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Geosphere, 9(2): 342-354.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
Zheng W J, Zhang P Z, Ge W P, et al. 2013b. Late Quaternary slip rate of the south Heli Shan Fault(northern Hexi Corridor, NW China)and its implications for northeastward growth of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonics, 32(2): 271-293.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
Zheng W J, Zhang P Z, He W G, et al. 2013c. Transformation of displacement between strike-slip and crustal shortening in the northern margin of the Tibetan plateau: Evidence from decadal GPS measurements and late Quaternary slip rates on faults[J]. Tectonophysics, 584: 267-280.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Zhong Y Z, Xiong J G, Li Y L, et al. 2020. Constraining late Quaternary crustal shortening in the eastern Qilian Shan from deformed river terraces[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 125(9): e2020JB020631. |
| [36] |
Zielke O, Arrowsmith J R. 2012. LaDiCaoz and LiDARimager: MATLAB GUIs for LiDAR data handling and lateral displacement measurement[J]. Geosphere, 8(1): 206-221.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Zielke O, Arrowsmith J R, Ludwig L G, et al. 2010. Slip in the 1857 and earlier large earthquakes along the Carrizo plain, San Andreas Fault[J]. Science, 327(5969): 1119-1122.
DOI PMID |
| [1] | 沈军, 戴训也, 肖淳, 焦轩凯, 白其乐格尔, 邓梅, 刘泽众, 夏方华, 刘玉, 刘明. 夏垫西断裂的晚第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 909-924. |
| [2] | 张驰, 李智敏, 任治坤, 刘金瑞, 张志亮, 武登云. 日月山断裂南段晚第四纪活动特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 1-19. |
| [3] | 盖海龙, 李智敏, 姚生海, 李鑫. 2022年青海门源MS6.9地震地表破裂特征的初步调查研究[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 238-255. |
| [4] | 常昊, 常祖峰, 刘昌伟. 金沙江断裂带活动与大型滑坡群的关系研究:以金沙江拿荣—绒学段为例[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1435-1458. |
| [5] | 姚生海, 盖海龙, 殷翔, 李鑫. 青海玛多MS7.4地震地表破裂带的基本特征和典型现象[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1060-1072. |
| [6] | 姚生海, 盖海龙, 殷翔, 刘炜, 张加庆, 袁建新. 柴达木盆地北缘断裂(锡铁山段)的构造地貌特征与晚第四纪活动速率[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(6): 1385-1400. |
| [7] | 张波, 何文贵, 刘炳旭, 高效东, 庞炜, 王爱国, 袁道阳. 甘肃北山南缘俄博庙断裂的新活动特征及活动速率[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(2): 455-471. |
| [8] | 李佳昱, 郑文俊, 王伟涛, 王英, 张培震, 王洋. 青藏高原东北部龙首山晚新生代剥露历史:来自磷灰石(U-Th)/He的证据[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(2): 472-491. |
| [9] | 梁明剑, 陈立春, 冉勇康, 李彦宝, 王栋, 高帅坡, 韩明明, 曾蒂. 鲜水河断裂带雅拉河段晚第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(2): 513-525. |
| [10] | 陈阜超, 郭良迁, 郑智江. 基于GPS观测的张家口-渤海断裂带活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(1): 95-108. |
| [11] | 李康, 王躲, 邵庆丰, 徐锡伟. 青藏高原中部NE向其香错断裂全新世左旋走滑速率及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(6): 1204-1215. |
| [12] | 王明明, 何玉林, 刘韶, 王世元, 马超, 张威, 贾召亮. 甘孜-玉树断裂东南段晚第四纪活动特征及古地震破裂行为[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(4): 738-752. |
| [13] | 陈干, 郑文俊, 王旭龙, 张培震, 熊建国, 俞晶星, 刘兴旺, 毕海芸, 刘金瑞, 艾明. 榆木山北缘断裂现今构造活动特征及其对青藏高原北东扩展的构造地貌响应[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(5): 871-888. |
| [14] | 吴富峣, 冉勇康, 李安, 徐良鑫, 曹筠. 东天山东段碱泉子-巴里坤断裂系晚第四纪左旋走滑的地质证据[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(3): 617-630. |
| [15] | 云龙, 杨晓平, 宋方敏, 王驹. 青藏高原北缘三危山断裂晚第四纪以来的左旋走滑活动[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(2): 434-446. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||