地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 67-91.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.01.004
吴中海1),2)( ), 白玛多吉3),4), 叶强4),5), 韩帅1,2), 史亚然1),2),6), 尼玛次仁4), 高扬1),2),7)
), 白玛多吉3),4), 叶强4),5), 韩帅1,2), 史亚然1),2),6), 尼玛次仁4), 高扬1),2),7)
收稿日期:2022-05-04
修回日期:2022-10-11
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2023-03-24
作者简介:吴中海, 男, 1974年生, 博士, 研究员, 现主要研究方向为板内新构造变形、 活断层与地震等, E-mail: wuzhonghai8848@foxmail.com。
基金资助:
WU Zhong-hai1),2)( ), Baima Duoji3),4), YE Qiang4),5), HAN Shuai1,2), SHI Ya-ran1),2),6), Nima Ciren4), GAO Yang1),2),7)
), Baima Duoji3),4), YE Qiang4),5), HAN Shuai1,2), SHI Ya-ran1),2),6), Nima Ciren4), GAO Yang1),2),7)
Received:2022-05-04
Revised:2022-10-11
Online:2023-02-20
Published:2023-03-24
摘要:
藏北高原非常薄弱的活断层调查程度和不完整的历史地震资料等, 限制了对青藏高原内部活动构造的变形机制及强震活动特征等问题的深入认识。文中通过综合地质、 遥感和地震等资料对阿里北部进行详细的活断层解译, 重点对阿鲁错地堑系南段昆楚克错地堑西侧边界正断层的第四纪活动性、 新发现的最新同震地表破裂及其震级与形成时间等进行了深入分析。研究结果表明, 阿里北部第四纪期间以近EW向伸展变形为主, 发育了以近SN向正断层和由NW向与NE向走滑断层构成的共轭走滑断层为主的高密度活断层系统。沿昆楚克错地堑西缘主边界正断层新发现的最新同震地表破裂整体沿NNW向雁列展布, 总长约400m, 最大垂直位移约0.8m, 平均垂直位移为0.3~0.4m。结合历史地震记录和经典的“地表破裂位移与震级”统计关系式推断, 该破裂应是震源深度为35km的1955年革吉县纳屋错东 MW6.5 强震事件的结果。综合该地表破裂的发育特点推断, 震源深度对地表破裂参数存在显著影响, 震源偏深时的地表破裂长度可远小于震源破裂的最大长度, 表明在活断层的地震复发模式研究中应注意随机性较强的断层局部破裂行为或小位移破裂事件。
中图分类号:
吴中海, 白玛多吉, 叶强, 韩帅, 史亚然, 尼玛次仁, 高扬. 西藏阿里阿鲁错地堑系的第四纪活动性、最新同震地表破裂及其地震地质意义[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 67-91.
WU Zhong-hai, Baima Duoji, YE Qiang, HAN Shuai, SHI Ya-ran, Nima Ciren, GAO Yang. THE QUATERNARY NORMAL FAULTING AND RECENT CO-SEISMIC SURFACE RUPTURE AND RELATED SEISMOLOGICAL SIGNIFICANCE ALONG THE ARU CO GRABEN SYSTEM IN NORTHERN NGARI, TIBET[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(1): 67-91.
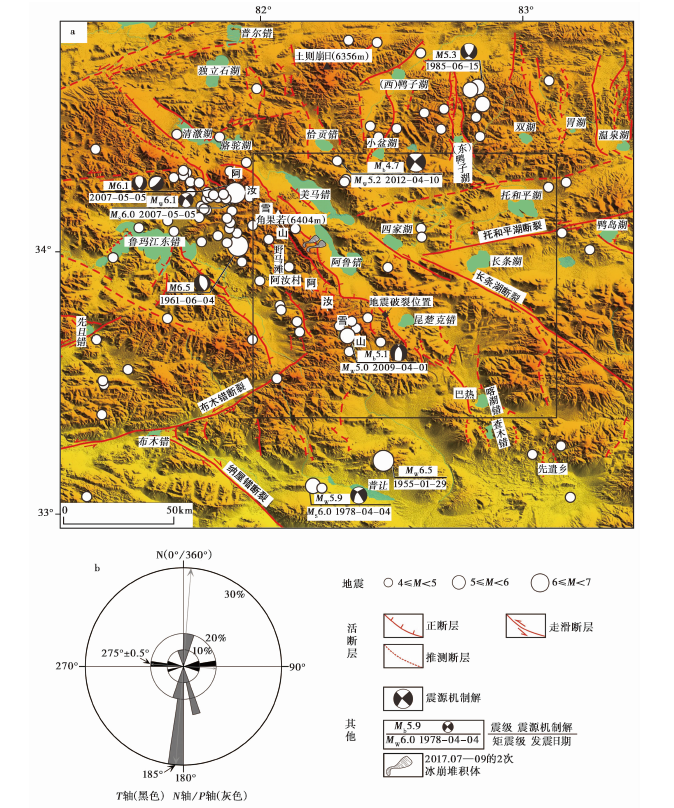
图2 阿里北部地区的主要活动断裂与地震 a 研究区内主要的第四纪活断层、 M≥4.0地震和震源机制解(图中框线为图3的范围); b 根据研究区的震源机制解资料统计得到的现今水平挤压方向(N/P轴)和伸展方向(T轴)。震源机制解数据见表1, 地震数据源自美国地质调查局(USGS)的地震目录
Fig. 2 Major active faults and earthquakes around northern Ngari in Tibet.
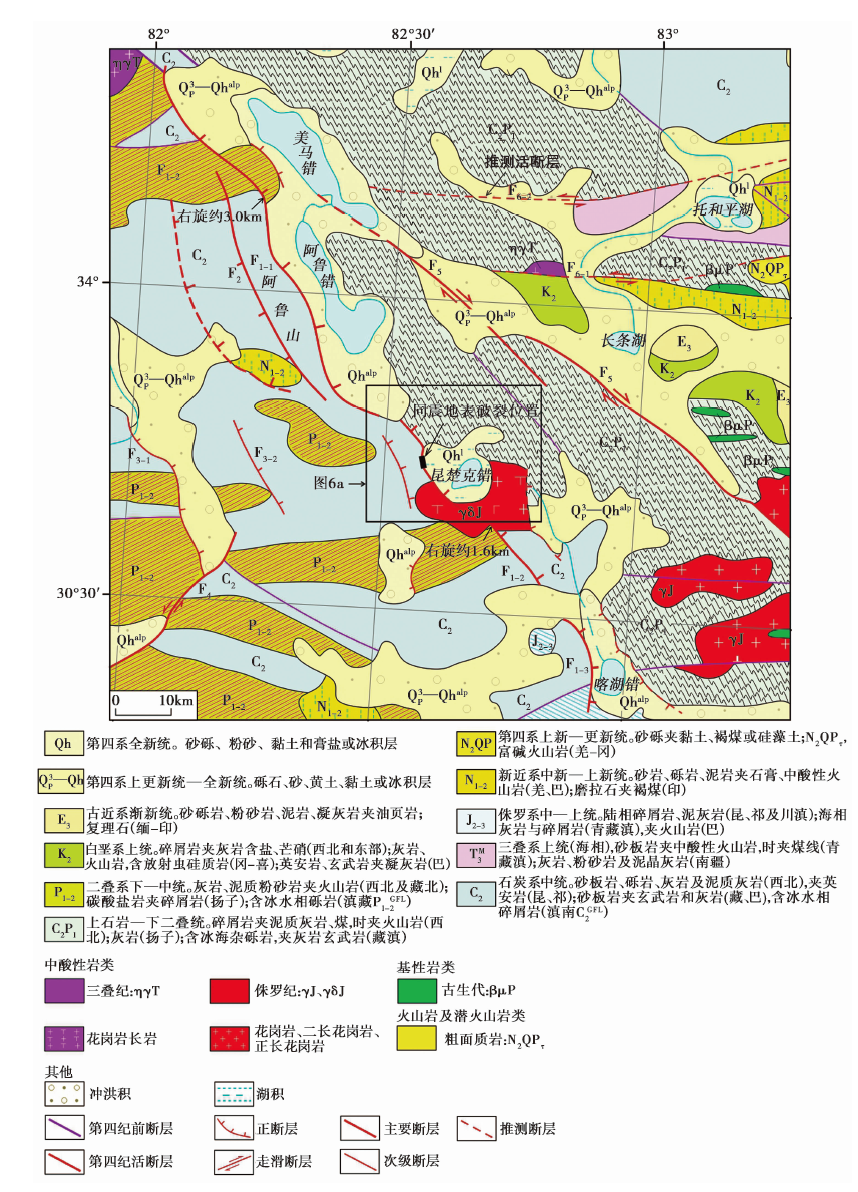
图3 阿鲁错地堑系中南段及邻区的地质构造图 地质资料引自文献(潘桂棠等, 2004), 活断层为本文解译结果。F1阿鲁错地堑系的主边界正断层(F1-1阿鲁错-美马错地堑西缘正断层, F1-2昆楚克错地堑西缘正断层, F1-3喀湖错地堑西缘正断层); F2阿鲁山西麓正断层; F3 阿汝地堑正断层 (F3-1西支, F3-2东支); F4布木错断裂; F5长条湖断裂; F6托和平湖断裂(F6-1北支, F6-2南支)
Fig. 3 A geological structure map of the middle-southern Aru Co graben system and its adjacent areas.
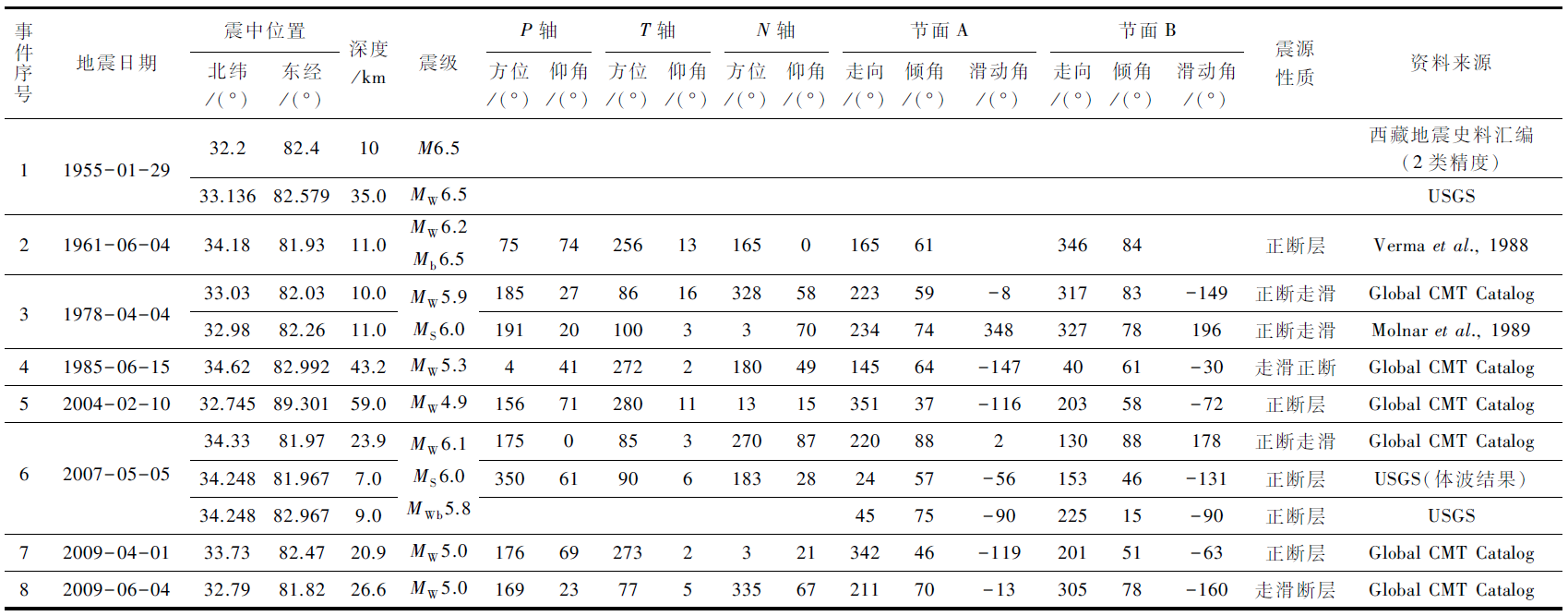 |
表1 阿里北部阿鲁错地堑系及邻区自公元1900年以来记录的M≥6.0地震及有关的震源机制数据
Table1 The M≥6.0 earthquakes and related focal mechanism recorded in the Aru Co graben and its adjacent areas since 1900 AD
 |
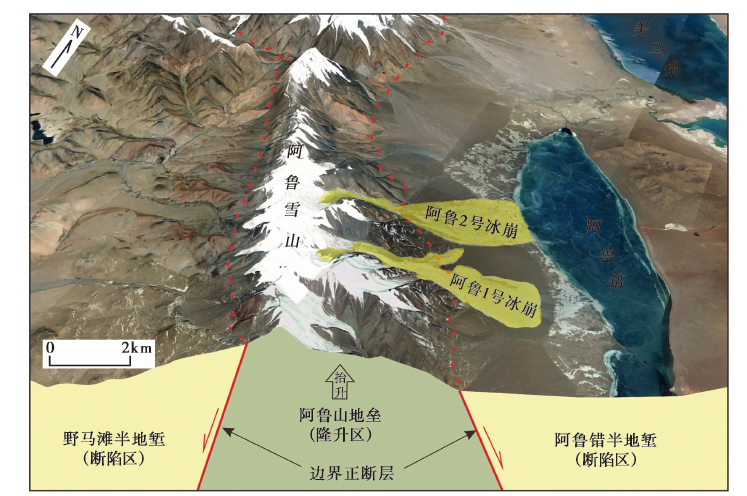
图4 阿鲁错地堑系西侧的阿鲁山地垒构造及冰崩灾害影像特征 遥感影像位置为(34°00'37.5″N, 2°14'34.7″E)
Fig. 4 The image characteristics of Aru Mountain horst structure and ice avalanche disaster on the west side of Aru Co graben system.
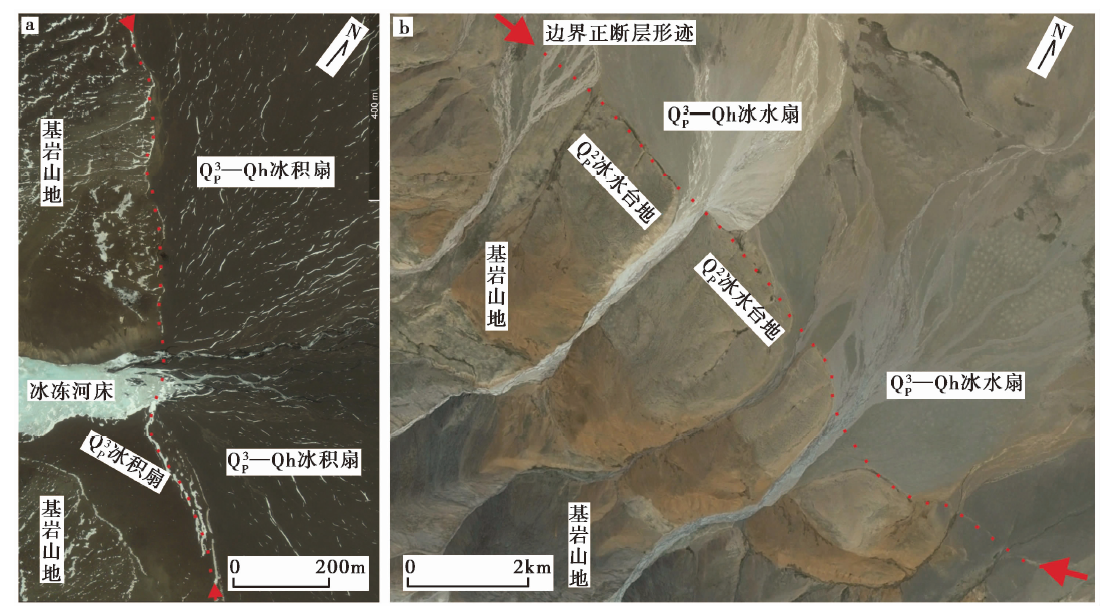

图5 阿鲁错地堑系西缘主边界正断层上的晚第四纪活动影像标志 a 阿鲁错西南山前穿过盆山边界和晚更新世( Q P 3)扇体的断坎地貌, 其中沿断坎的积雪很好地勾勒出了断层形迹, 影像位置为(33°54'49.7″N, 82°22'22.0″E); b 清澈湖西南山前穿过盆山边界和中更新世( Q P 2)冰水台地及晚更新世全新世 ( Q P 3Qh)冰水扇的断层崖与断坎地貌, 影像位置为(34°21'54.9″N, 81°46'45.4″E)
Fig. 5 The image markers of late Quaternary normal faulting along the western boundary of the Aru Co graben system.
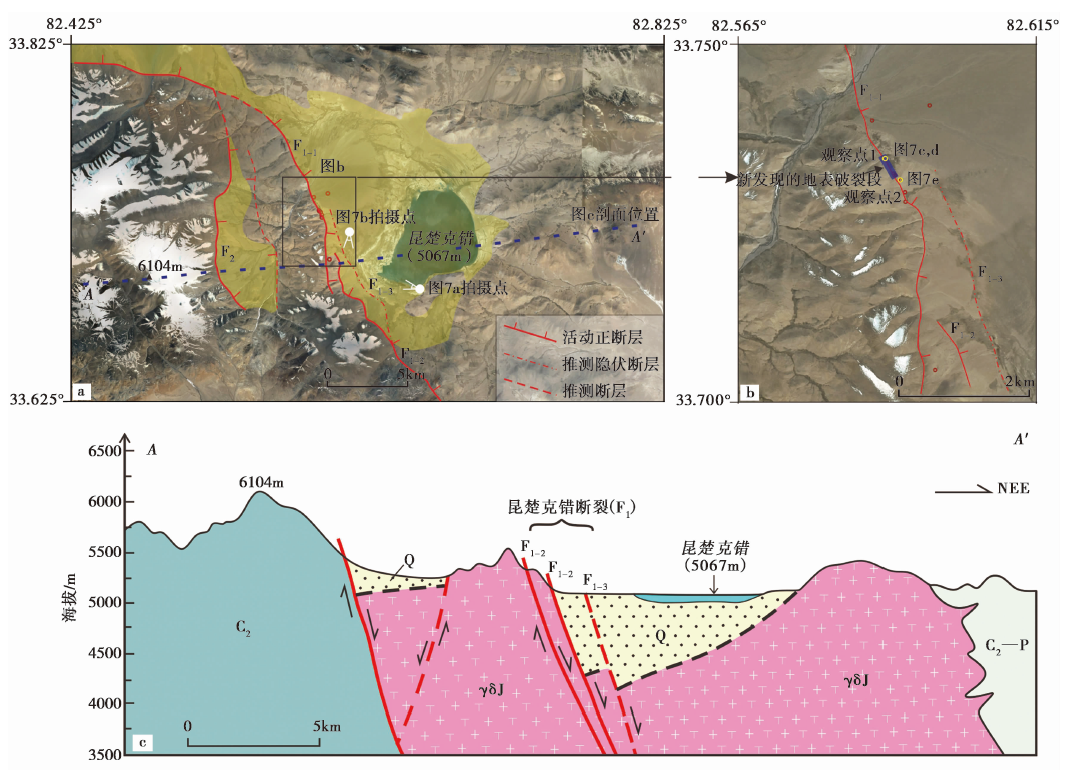
图6 昆楚克错地堑及主要活断层的影像特征与构造剖面图 a 昆楚克错地堑及周边的主要活断层。F1昆楚克错西缘正断层带(F1-1主边界正断层北支, F1-2主边界正断层南支, F1-3盆地内部的推测隐伏正断层); F2昆楚克错西的分支正断层。b 昆楚克错地堑西侧山前山麓地带的正断层活动影像标志。 c 跨昆楚克错地堑的地质剖面(岩石地层单元与图3对应)
Fig. 6 The active faults image around the Kunchuke Co and structural sections across Kunchuke Co graben.

图7 昆楚克错断裂第四纪和晚第四纪活动的地表证据 a 昆楚克错断裂中段第四纪正断层作用形成的断层三角面与阶梯状地貌现象; b 昆楚克错地堑南段的西侧山前边界正断层(F1-2); c F1-1正断层中段下盘侧花岗岩中R剪切变形指示的正断层活动性质; d F1-1正断层中段的阶梯状晚第四纪断坎 (图11b中的观察点1); e F1-1正断层中段的晚第四纪断坎(图11b中的观察点2)
Fig. 7 The surface evidence of Quaternary and late Quaternary normal faulting along the Kunchuke Co fault.

图8 昆楚克错断裂中F1-1 正断层中段的最新同震地表破裂带及其几何学与运动学特征
Fig. 8 The latest co-seismic surface rupture zone and its geometric and kinematic characteristics along the middle of F1-1 in the Kunchuke Co fault.
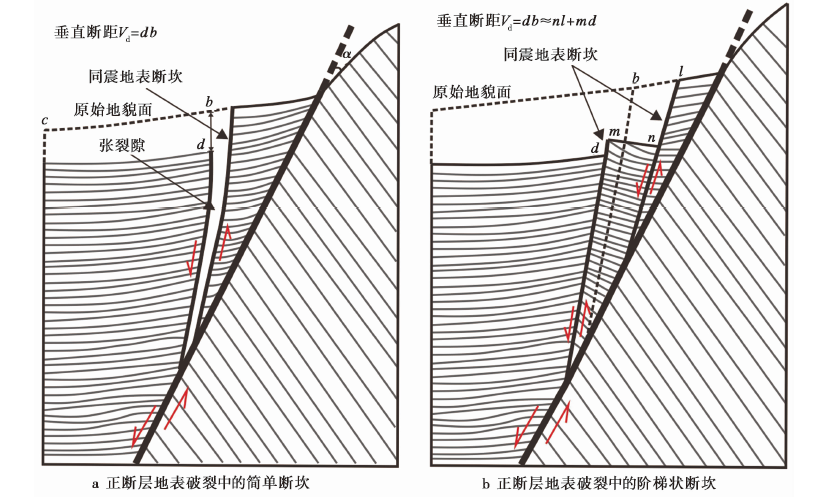
图10 昆楚克错地震破裂中正断层断坎的2种基本形态及其垂直位移测量方法(改自Slemmons, 1957)
Fig. 10 Two basic forms and relevant measurement methods of vertical displacement of normal fault scarp applied to the Kunchuke Co co-seismic rupture(modified from Slemmons, 1957).
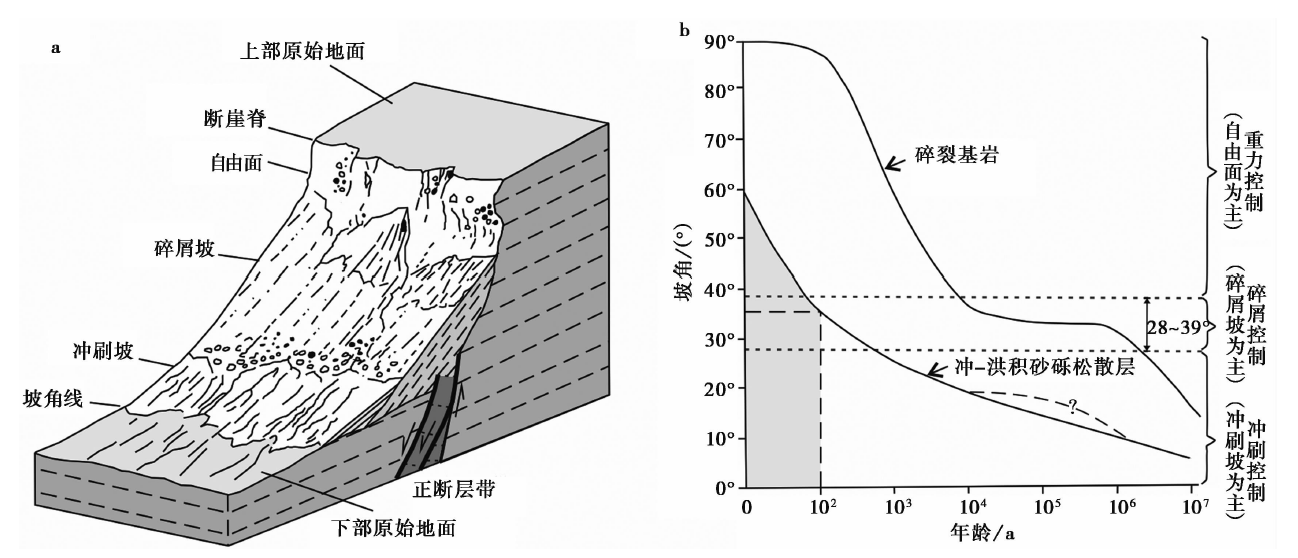
图12 a 正断层的断崖斜坡结构分类; b 断崖随时间的演化曲线(引自Wallace, 1977)
Fig. 12 The slope composition and classification of normal fault scarp(a)and the diagram of fault scarp age and slope angle(b)(from Wallace, 1977).
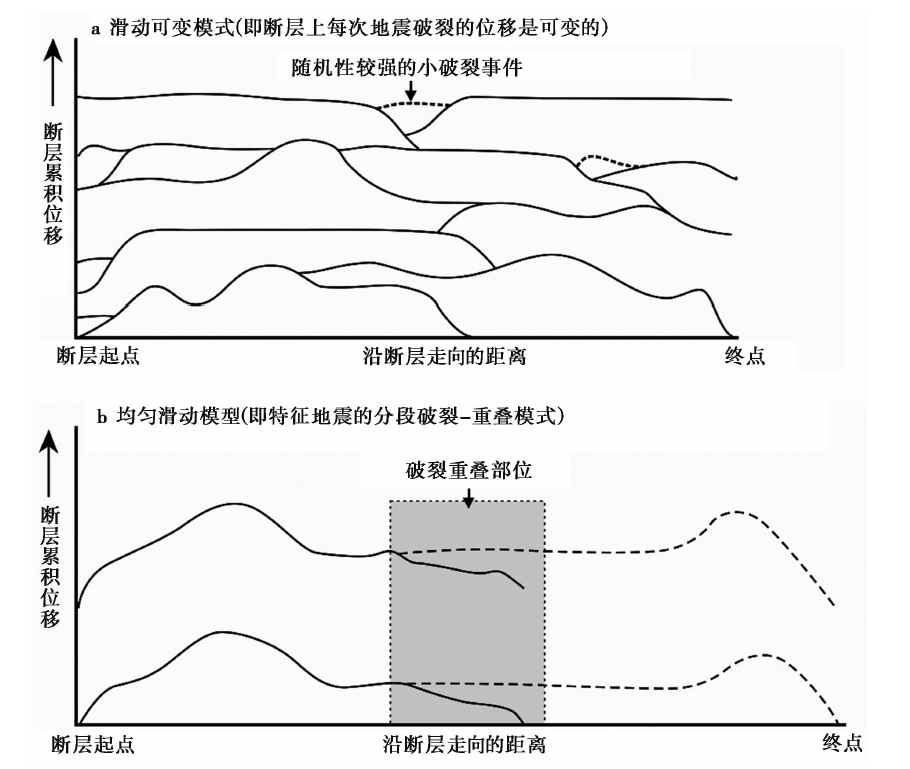
图13 活动断裂带上大地震地表破裂的复发模式(修改自Berryman et al., 1991; 吴中海等, 2014)
Fig. 13 Diagrams showing two basic patterns along-strike slip behavior of repeated surface rupture on an active fault(modified from Berryman et al., 1991; Wu et al., 2014).
| [1] | 卞爽, 于志泉, 龚俊峰, 等. 2021. 青藏高原近SN向裂谷的时空分布特征及动力学机制[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 178194. |
| BIAN Shuang, YU Zhi-quan, GONG Jun-feng, et al. 2021. Spatiotemporal distribution and geodynamic mechanism of the nearly NS-trending rifts in the Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 178194. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 邓起东. 2007. 中国活动构造图(1︰400万)[CM]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| DENG Qi-dong. 2007. China’s Active Tectonic Map(1:4000000)[CM]. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 邓起东, 程绍平, 马冀, 等. 2014. 青藏高原地震活动特征及当前地震活动形势[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(7): 20252042. |
| DENG Qi-dong, CHENG Shao-ping, MA Ji, et al. 2014. Seismic activities and earthquake potential in the Tibetan plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(7): 20252042. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 邓起东, 刘百篪, 张培震, 等. 1992. 活动断裂工程安全评价和位错量的定量评估[G]邓起东主编. 活动断裂研究(2). 北京: 地震出版社: 236246. |
| DENG Qi-dong, LIU Bai-chi, ZHANG Pei-zhen, et al. 1992. Research of active fault in evaluating engineering safety and assessing amount of displacement[G]∥DENG Qi-dong(ed). Research of Active Fault (2). Beijing: Seismological Press: 236246. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 2003. 中国活动构造与地震活动[J]. 地学前缘, 10(S1): 6673. |
| DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Pei-zhen, RAN Yong-kang, et al. 2003. Active tectonics and earthquake activities in China[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 10(S1): 6673. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 哈广浩, 吴中海. 2021. 西藏尼木1901年M63/4地震的发震构造探讨[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(2): 218229. |
| HA Guang-hao, WU Zhong-hai. 2021. Discussion of the seismogenic structure of the 1901 M63/4 Nyemo earthquake[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(2): 218229. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] |
哈广浩, 吴中海, 马凤山, 等. 2019. 藏北改则县别若则错活动断裂的发现及其地质意义[J]. 地震地质, 41(2): 436446. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.02.011.
DOI |
| HA Guang-hao, WU Zhong-hai, MA Feng-shan, et al. 2019. First report of Bero Zeco active fault in Gêrzê, northern Tibet[J]. Seismology and Geology, 41(2): 436446. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 韩帅, 吴中海, 高扬, 等. 2022. 2022年1月8日青海门源 MS6.9 地震地表破裂考察的初步结果及对冷龙岭断裂活动行为和区域强震危险性的启示[J]. 地质力学学报, 28(2): 155168. |
| HAN Shuai, WU Zhong-hai, GAO Yang, et al. 2022. Surface rupture investigation of the 2022 Menyuan MS6.9 earthquake, Qinghai, China: Implications for the fault behavior of the Lenglongling fault and regional intense earthquake risk[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 28(2): 155168. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 李海兵, 潘家伟, 孙知明, 等. 2021. 大陆构造变形与地震活动: 以青藏高原为例[J]. 地质学报, 95(1): 194213. |
| LI Hai-bing, PAN Jia-wei, SUN Zhi-ming, et al. 2021. Continental tectonic deformation and seismic activity: A case study from the Tibetan plateau[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(1): 194213. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 李康, 王躲, 邵庆丰, 等. 2018. 青藏高原中部NE向其香错断裂全新世左旋走滑速率及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 40(6): 12041215. |
| LI Kang, WANG Duo, SHAO Qing-feng, et al. 2018. Holocene slip rate along the NE-trending Qixiang Co Fault in the central Tibetan plateau and its tectonic implications[J]. Seismology and Geology, 40(6): 12041215. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 刘富财, 潘家伟, 李海兵, 等. 2022. 青藏高原中部日干配错断裂第四纪活动特征及2020年7月23日西藏尼玛 MW6.4 地震发震构造分析[J]. 地球学报, 43(2): 173188. |
| LIU Fu-cai, PAN Jia-wei, LI Hai-bing, et al. 2022. Characteristics of Quaternary activities along the Riganpei Co Fault and seismogenic structure of the July 23, 2020 MW6.4 Nima earthquake, central Tibet[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 43(2): 173188. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 潘桂棠, 丁俊. 2004. 青藏高原及邻区地质图及说明书(1︰1500000)[M]. 成都: 成都地图出版社:1140. |
| PAN Gui-tang, DING Jun. 2004. Geological map of the Qinghai-Xizang(Tibet)Plateau and adjacent areas(scale 1︰1 500 000)(attached explanation)[M]. Chengdu: Chengdu Cartographic Publishing House:1140. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 施雅风主编. 2005. 简明中国冰川目录[M]. 上海: 上海科学普及出版社:89100. |
| SHI Ya-fenged. 2005. Concise Catalogue of Glaciers in China[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science Popularization Press:89100. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 王光明, 吴中海, 彭关灵, 等. 2021. 2021年5月21日漾濞 MS6.4 地震的发震断层及其破裂特征: 地震序列的重定位分析结果[J]. 地质力学学报, 27(4): 662678. |
| WANG Guang-ming, WU Zhong-hai, PENG Guan-ling, et al. 2021. Seismogenic fault and its rupture characteristics of the 21 May, 2021 Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake: Analysis results from the relocation of the earthquake sequence[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 27(4): 662678. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 魏云杰, 王婷, 杨成生, 等. 2022. 2021年云南漾濞 MW6.4 地震的InSAR监测与反演[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 44(3): 558567. |
| WEI Yun-jie, WANG Ting, YANG Cheng-sheng, et al. 2022. InSAR Monitoring and Inversion of 2021 Yangbi MW6.4 Earthquake in Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 44(3): 558567. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 吴中海. 2019. 活断层的定义与分类: 历史、 现状和进展[J]. 地球学报, 40(5): 661697. |
| WU Zhong-hai. 2019. The definition and classification of active faults: history, current status and progress[J]. Acta Geoscientica Sinica, 40(5): 661697. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 吴中海, 吴珍汉, 胡道功, 等. 2006. 青藏铁路唐古拉山拉萨段全新世控震断裂研究[J]. 地质通报, 25(12): 13871401. |
| WU Zhong-hai, WU Zhen-han, HU Dao-gong, et al. 2006. Holocene seismogenic faults along the Tanggula Lhasa section of the Qinghai-Tibet Railway, China[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 25(12): 13871401. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 吴中海, 叶培盛, 王成敏, 等. 2009. 西藏安多最新史前大地震的地质证据及其年龄[J]. 第四纪研究, 29(3): 608615. |
| WU Zhong-hai, YE Pei-sheng, WANG Cheng-min, et al. 2009. The most recent surface normal faulting and its age along the northern margin of Tsona-amdo graben in central Tibet[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 29(3): 608615. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 吴中海, 叶培盛, 王成敏, 等. 2015. 藏南安岗地堑的史前大地震遗迹、 年龄及其地质意义[J]. 地球科学, 40(10): 16211642. |
| WU Zhong-hai, YE Pei-sheng, WANG Cheng-min, et al. 2015. The relics, ages and significance of prehistoric large earthquakes in the Angang Graben in South Tibet[J]. Earth Science, 40(10): 16211642. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 吴中海, 周春景. 2018. 中国及毗邻海区活动断裂分布图(1︰500万)(附说明书)[CM]∥郝爱兵, 李瑞敏(主编). 中国地质环境图系(图件编号00-01-05). 北京: 地质出版社. |
| WU Zhong-hai, ZHOU Chun-jing. 2018. Distribution map of active faults in China and its adjacent sea area(1︰5000000)(attached explanation)[CM]//HAO Ai-bing, LI Rui-mineds. Atlas Sets of Geological Environment of China(Map Number 00-01-05). Beijing: Geological Publishing House(in Chinese). | |
| [21] | 吴中海, 周春景, 冯卉, 等. 2014. 青海玉树地区活动断裂与地震[J]. 地质通报, 33(4): 419469. |
| WU Zhong-hai, ZHOU Chun-jing, FENG Hui, et al. 2014. Active faults and earthquake around Yushu in eastern Tibetan plateau[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 33(4): 419469. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 西藏自治区科学技术委员会, 西藏自治区档案馆编译. 1982. 西藏地震史料汇编(第一卷)[M]. 拉萨: 西藏人民出版社:1583. |
| The Science and Technology Committee and the Archives of Xizang Autonomous Region. 1982. A Compilation on Historical Earthquakes Data in Tibet(the First Volume)[M]. Lasa: Xizang People’ s Publishing House: 1583. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 徐锡伟, 韩竹军, 杨晓平, 等. 2016. 中国及邻近地区地震构造图[CM]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| XU Xi-wei, HAN Zhu-jun, YANG Xiao-ping, et al. 2016. The seismotectonic map of China and its vicinity[CM]. Beijing: Seismological Press. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] |
叶雨晖, 吴磊, 王依平, 等. 2022. 北阿尔金断裂晚第四纪活动构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 44(2): 297312. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.02.002
DOI |
| YE Yu-hui, WU Lei, WANG Yi-ping, et al. 2022. Late Quaternary active tectonics of the North Altyn fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 44(2): 297312. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 张培震, 邓起东, 张竹琪, 等. 2013. 中国大陆的活动断裂、 地震灾害及其动力过程[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 43(10): 16071620. |
| ZHANG Pei-zhen, DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Zhu-qi, et al. 2013. Active faults, earthquake hazards and associated geodynamic processes in continental China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 43(10): 16071620. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 钟岩, 田立德. 2018. 阿里极大陆性冰川崩塌“超稳定”冰巨人倒下的背后[J]. 中国国家地理, (4): 116125. |
| ZHONG Yan, TIAN Li-de. 2018. The super-continental glacier of Ngari collapse behind the collapse of the giant “super-stable” ice[J]. China National Geography, (4): 116125. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] |
Armijo R, Tapponnier P, Mercier J L, et al. 1986. Quaternary extension in southern Tibet: field observations and tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 91(B14): 1380313872.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Armijo R, Tapponnier P, Tonglin H. 1989. Late Cenozoic right-lateral strike-slip faulting in southern Tibet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 94(B3): 27872838.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
Berryman K, Beanland S. 1991. Variation in fault behaviour in different tectonic provinces of New Zealand[J]. Journal Structure Geology, 13(2): 177189.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Blisniuk P M, Sharp W D. 2003. Rates of late Quaternary normal faulting in central Tibet from U-series dating of pedogenic carbonate in displaced fluvial gravel deposits[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 215(1-2), 169186.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Caputo R, Pavlides S B. 2008. Earthquake geology: methods and applications[J]. Tectonophysics, 453(1-4): 16.
DOI URL |
| [32] | dePolo C M. 1994. The maximum background earthquake for the Basin and Range Province, western North America[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 84(2): 466472. |
| [33] |
Dewey J F, Shackelton R M, Chang C, et al. 1988. The tectonic evolution of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 327(1594): 379413.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Gao H, Liao M, Liang X, et al. 2022. Coseismic and postseismic fault kinematics of the July 22, 2020, Nima(Tibet) MS6.6 earthquake: Implications of the forming mechanism of the active N-S-trending grabens in Qiangtang, Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 41(3): e2021TC006949. |
| [35] | Gilbert A, Leinss S, Kargel J S, et al. 2018. Mechanisms leading to the 2016 giant twin glacier collapses, Aru range, Tibet[J]. Cryosphere Discussions, 12(9): 28832900. |
| [36] |
Han S, Li H B, Pan J W, et al. 2019. Co-seismic surface ruptures in Qiangtang Terrane: Insight into Late Cenozoic deformation of central Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 750(5): 359378.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
Kääb A, Leinss S, Gilbert A, et al. 2018. Massive collapse of two glaciers in western Tibet in 2016 after surge-like instability[J]. Nature Geoscience, 11(2): 114120.
DOI |
| [38] | Keller E A, Pinter N. 2002. Active Tectonics:Earthquake, Uplift, and Landscape[M]. New York: Prentice-hall. |
| [39] | Kidd W S F, Molnar P. 1988. Quaternary and active faulting observed on the 1985 Academia Sinica-Royal Society Geotraverse of Tibet[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A, Mathematical and Physical Sciences, 1594: 337363. |
| [40] | Langridge R M, Ries W F. 2014. Active fault mapping and fault avoidance zones for central Hawkes Bay district: 2013 update[R]. GNS Science Consultancy Report:48. |
| [41] | McCalpin J PEd. 1996. Paleoseismology[M]. Academic Press, San Diego: 588. |
| [42] |
Molnar P, Lyon-Caen H. 1989. Fault-plane solutions of earthquakes and active tectonics of the Tibetan plateau and its margins[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 99(1): 123153.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Molnar P, Tapponnier P. 1978. Active tectonics of Tibet[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research.: Solid Earth, 83(B11): 53615375. |
| [44] | Ni J, York J E. 1978. Late Cenozoic tectonics of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research.: Solid Earth, 83(B11): 53775384. |
| [45] |
Ratschbacher L, Krumrei I, Blumenwitz M, et al. 2011. Rifting and strike-slip shear in central Tibet and the geometry, age and kinematics of upper crustal extension in Tibet[J]. Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 353(1): 127163.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Rothery D A, Drury S A. 1984. The neotectonics of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonics, 3(1): 1926.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Schwartz D P, Coppersmith K J. 1984. Fault behavior and characteristic earthquakes: Examples from the Wasatch and San Andreas fault zones[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 89: 56815698. |
| [48] |
Schwartz D P, Lund W R. 1991. The Wasatch fault zone, Utah-segmentation and history of Holocene earthquake[J]. Journal Structure Geology, 13(2): 137149.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Slemmons D B. 1957. Geological effects of the Dixie Valley-Fairview Peak, Nevada, earthquakes of December 16, 1954[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 47(4): 353375.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Tapponnier P, Molnar P. 1977. Active faulting and tectonics of China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 82(20): 29052930.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Taylor M H, Yin A. 2009. Active structures of the Himalayan-Tibet orogen and their relationships to earthquake distribution, contemporary strain field, and Cenozoic volcanism[J]. Geosphere, 5(3): 199214.
DOI URL |
| [52] | Taylor M, Yin A, Ryerson F J, et al. 2003. Conjugate strike-slip faulting along the Bangong-Nujiang suture zone accommodates coeval east-west extension and north-south shortening in the interior of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonics, 22(4): 1044. |
| [53] | The Research Group for Active Faults of Japan. 1980. Active faults in and around Japan: the distribution and the degree of activity[J]. Journal of Natural Disaster Science, 2(2): 6199. |
| [54] |
Tian L, Yao T, Gao Y, et al. 2017. Two glaciers collapse in western Tibet[J]. Journal of Glaciology, 63(237): 194197.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Verma R K, Reddy Y S K. 1988. Seismicity, focal mechanisms and their correlation with the geological/tectonic history of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 156(1-2): 107131.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
Wallace R E. 1977. Profiles and ages of young fault scarps, north-central Nevada[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 88(9): 12671281.
DOI URL |
| [57] | Wells D L, Coppersmith K J. 1994. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 84(4): 9741002. |
| [58] |
Wu Z, Ye P, Barosh P, et al. 2011. The October 6, 2008 MW6.3 magnitude Damxung earthquake, Yadong-Gulu rift, Tibet, and implications for present-day crustal deformation[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 40(4): 943957.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
Yin A. 2000. Mode of Cenozoic east-west extension in Tibet suggesting a common origin of rifts in Asia during the Indo-Asian collision[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 105(B9): 2174521759.
DOI URL |
| [60] | Yin A, Taylor M H. 2011. Mechanics of v-shaped conjugate strike-slip faults and the corresponding continuum mode of continental deformation[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 123(9-10): 17981821. |
| [1] | 于书媛, 黄显良, 郑海刚, 李玲利, 骆佳骥, 丁娟, 范晓冉. 2022年门源MW6.7地震的同震破裂模型及应力研究[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 286-303. |
| [2] | 宋婷, 沈旭章, 梅秀苹, 焦煜媛, 李敏娟, 苏小芸, 季婉婧. 利用接收函数频率特征研究青藏高原东北缘地区的莫霍面性质[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(5): 1290-1312. |
| [3] | 李宗旭, 贺日政, 冀战波, 李娱兰, 牛潇. 2009年7月24日西藏尼玛MS5.6地震的震源机制及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 992-1010. |
| [4] | 张驰, 李智敏, 任治坤, 刘金瑞, 张志亮, 武登云. 日月山断裂南段晚第四纪活动特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 1-19. |
| [5] | 盖海龙, 李智敏, 姚生海, 李鑫. 2022年青海门源MS6.9地震地表破裂特征的初步调查研究[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 238-255. |
| [6] | 何翔, 杜星星, 刘健, 李艺豪, 李群. 武威盆地第四纪沉积过程及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 76-97. |
| [7] | 臧阳, 俞言祥, 孟令媛, 韩颜颜. 青藏高原东北缘地震波衰减特征及地震震源参数研究[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1638-1656. |
| [8] | 方东, 胡敏章, 郝洪涛. 青藏高原东南缘重力场多尺度分析及其构造含义[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1208-1232. |
| [9] | 唐茂云, 刘静, 李翠平, 王伟, 张金玉, 许强. 青藏高原东南缘的新生代盆地古高度重建研究与进展[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(3): 576-599. |
| [10] | 哈广浩, 任治坤, 刘金瑞, 李智敏, 李正芳, 闵伟, 周本刚. 青海都兰地区夏日哈活动断裂带的发现及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(3): 614-629. |
| [11] | 李智敏, 李文巧, 李涛, 徐岳仁, 苏鹏, 郭鹏, 孙浩越, 哈广浩, 陈桂华, 袁兆德, 李忠武, 李鑫, 杨理臣, 马震, 姚生海, 熊仁伟, 张彦博, 盖海龙, 殷翔, 徐玮阳, 董金元. 2021年5月22日青海玛多MS7.4地震的发震构造和地表破裂初步调查[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(3): 722-737. |
| [12] | 李启雷, 李玉丽, 屠泓为, 刘文邦. 丁青地区地震重定位、 震源机制及其发震构造初步分析[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(1): 209-231. |
| [13] | 马骏, 周本刚, 王明明, 安力科. 鲜水河断裂带折多塘断裂西北段全新世活动的地质地貌依据[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(5): 1021-1038. |
| [14] | 罗全星, 李传友, 任光雪, 李新男, 马字发, 董金元. 阳高-天镇断裂晚第四纪活动特征及滑动速率[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(2): 399-413. |
| [15] | 张波, 何文贵, 刘炳旭, 高效东, 庞炜, 王爱国, 袁道阳. 甘肃北山南缘俄博庙断裂的新活动特征及活动速率[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(2): 455-471. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||