地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (1): 231-251.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.01.013
张珂1)( ), 王鑫1),*(
), 王鑫1),*( ), 杨红樱1), 王玥1), 徐岩1), 李静2)
), 杨红樱1), 王玥1), 徐岩1), 李静2)
收稿日期:2022-04-19
修回日期:2022-09-26
出版日期:2023-02-20
发布日期:2023-03-24
通讯作者:
* 王鑫, 男, 1982年生, 高级工程师, 主要从事地震活动性、 震源物理与数字地震学等方面研究, E-mail: wangxin0111@163.com。
作者简介:张珂, 女, 1993年生, 2018年于中国海洋大学获矿产普查与勘探专业工学硕士学位, 工程师, 现主要从事地震活动性、 震源物理与数字地震学等方面研究, 开展地震监测分析方法与预警技术分析等, E-mail: zkee0928@163.com。
基金资助:
ZHANG Ke1)( ), WANG Xin1),*(
), WANG Xin1),*( ), YANG Hong-ying1), WANG Yue1), XU Yan1), LI Jing2)
), YANG Hong-ying1), WANG Yue1), XU Yan1), LI Jing2)
Received:2022-04-19
Revised:2022-09-26
Online:2023-02-20
Published:2023-03-24
摘要:
2021年5月21日21时, 云南大理白族自治州漾濞县发生 MS6.4 地震。该地震的震中位于川滇块体的西南边界, 是该区40多年来震级最大的一次地震。地震未产生地表破裂, 余震也未沿震区附近已知的断裂分布。研究者针对这次地震的发震构造已有若干研究结果, 但采用不同数据、 方法和思考角度对这些结果进行验证并同时补充新认识是必要的。文中利用云南地震台网观测资料分析了漾濞地震序列的时空分布特征, 进行重新定位, 并通过CAP(Cut and Paste)方法获取序列中较大地震的震源机制解与矩心深度。结果表明, 漾濞地震的余震震源深度主要集中在4~13km, 余震带总体呈NW-SE走向, 空间分段性明显: 主震震中北西侧余震稀少且分布相对集中, 东南侧余震密集且余震带宽度变大; 前震序列发生在主震震中的东南侧, 与余震密集段的位置基本重叠, 反映主震震中北西侧的稀疏余震应属于触发型, 而主震破裂可能属于由震中向SE扩展的单侧破裂型。余震带的深度横剖面显示主震破裂具有明显的分段性, 序列北西段的结构较为简单, 显示出一个地震丛集, 而南东段则相对复杂, 很可能由2条倾向SW的高倾角断层组成。漾濞地震序列中29个MS≥3.0地震的矩心深度主要分布于3~13km, 震源机制解以右旋走滑型为主, 大多存在一个NW-SE走向的高倾角节面, 且具有一定的正断倾滑分量。主震是以右旋走滑为主的破裂所引发的, 矩心深度为5.2km, 与重定位所得的震源初始破裂深度8.9km较为接近, 反映该地震发生在上地壳, 也反映震区的地震活动深度偏浅。文中对2021年5月云南漾濞序列的时-空分布特征与震源机制解的分析, 反映此次地震的发震断层产状及力学性质与NW走向的维西-乔后-巍山断裂较为一致, 但位置不同, 证实这次地震的发震构造是该断裂南段西侧一条SW陡倾的右旋走滑次级断裂。
中图分类号:
张珂, 王鑫, 杨红樱, 王玥, 徐岩, 李静. 2021年云南漾濞MS6.4地震序列特征及其发震构造分析[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 231-251.
ZHANG Ke, WANG Xin, YANG Hong-ying, WANG Yue, XU Yan, LI Jing. THE CHARACTERISTICS AND SEISMOGENIC STRUCTURE ANALYSIS OF THE 2021 YANGBI MS6.4 EARTHQUAKE SEQUENCE, YUNNAN[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(1): 231-251.
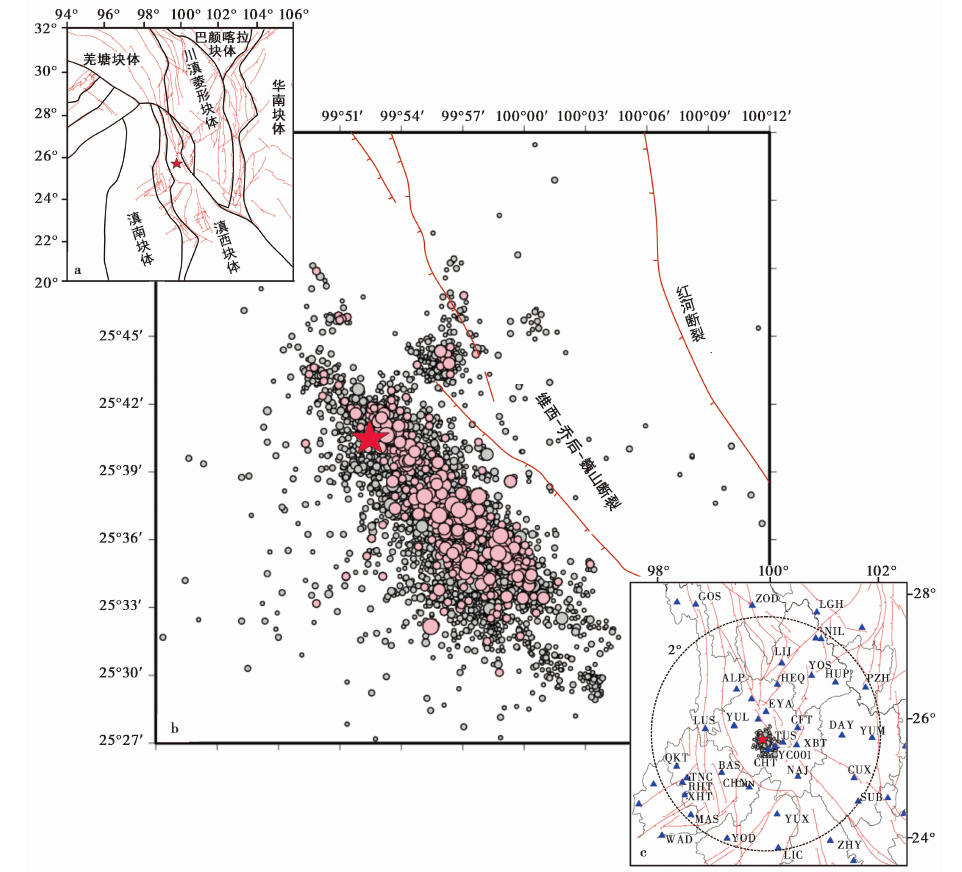
图1 云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震附近区域的构造(a)、 地震序列(ML≥0.0)震中分布(b)与台站分布(c) 红色直线代表震区断裂(断层数据来自中国地震局地质研究所 ), 灰色圆点代表漾濞序列ML≥0.0地震震中, 粉色圆点代表漾濞地震序列ML≥2.0地震震中, 红色五角星代表2021年5月21日漾濞 MS6.4 主震震中, 蓝色三角形代表所用的测震台站, 黑色空心圆代表震中2°范围
Fig. 1 The distribution of active tectonics in the Yangbi MS6.4 earthquakes(a), and epicenter of the earthquake sequence(ML≥0.0)(b), and seismic stations of the research area(c).
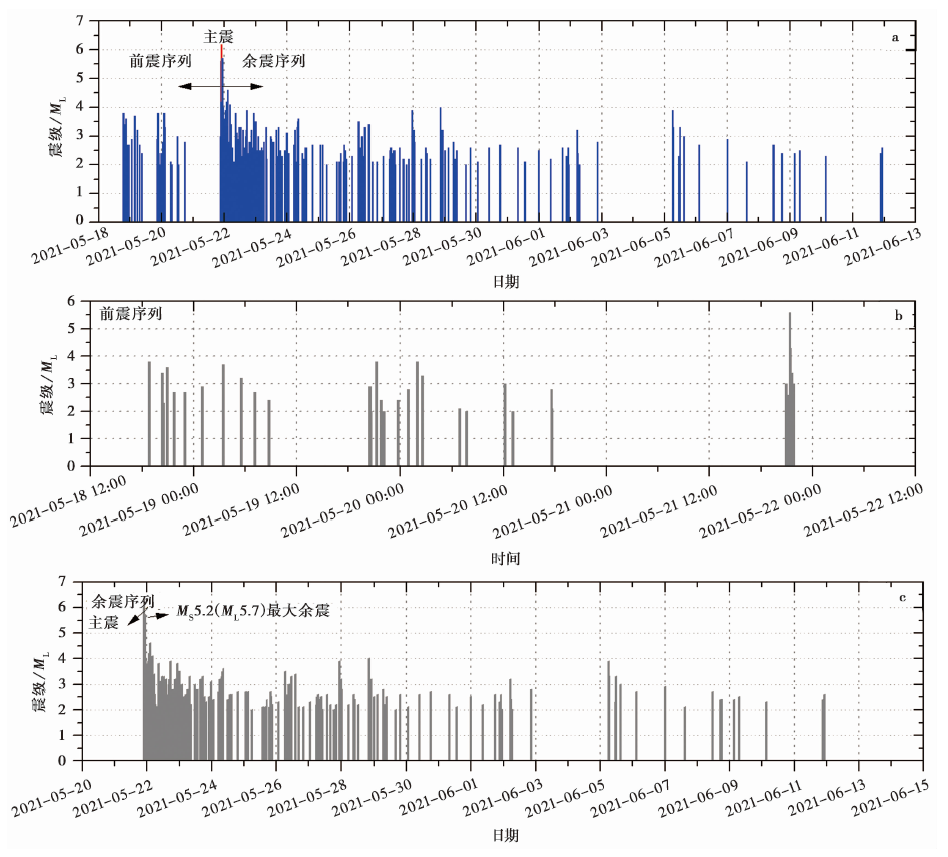
图2 云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列内全部地震(a)、 前震(b)及余震(c)的震级-时间分布特征
Fig. 2 The distribution of amplitude-time of all earthquakes(a), foreshocks(b), and aftershocks(c)in the Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake sequence.
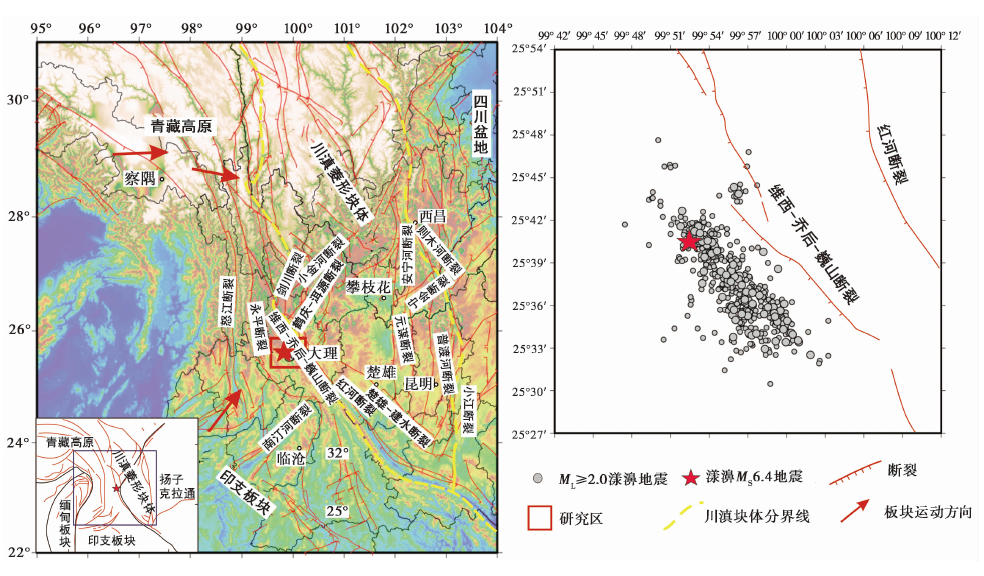
图3 研究区域构造特征及漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列ML≥2.0地震震中分布图
Fig. 3 The distribution of active tectonics in research area and epicenter distribution of ML≥2.0 earthquakes in Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake sequences.
| 层厚/km | VP/km·s-1 | VS/km·s-1 |
|---|---|---|
| 4.0 | 4.85 | 2.80 |
| 16.0 | 6.25 | 3.61 |
| 22.0 | 6.40 | 3.70 |
| 0.0 | 7.75 | 4.47 |
表1 云南地区的地壳速度模型
Table1 Crustal velocity model in Yunnan region
| 层厚/km | VP/km·s-1 | VS/km·s-1 |
|---|---|---|
| 4.0 | 4.85 | 2.80 |
| 16.0 | 6.25 | 3.61 |
| 22.0 | 6.40 | 3.70 |
| 0.0 | 7.75 | 4.47 |
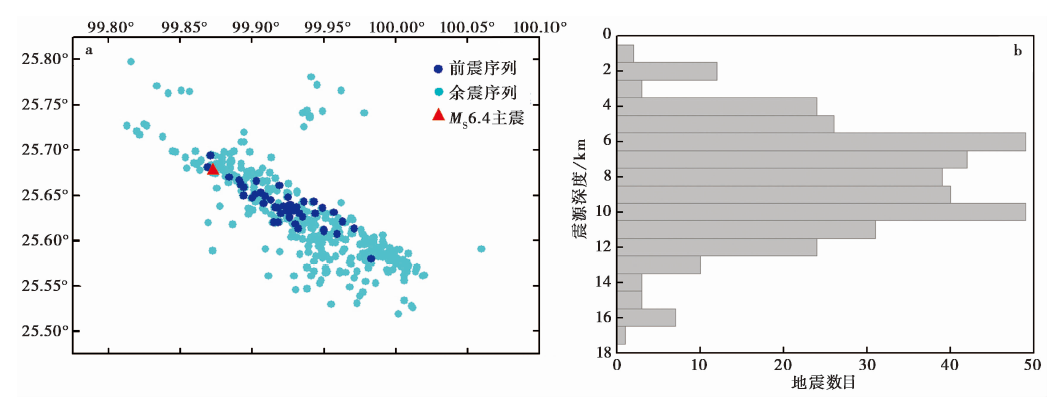
图4 a 双差精定位后的地震序列震中分布特征; b 震源深度统计
Fig. 4 Epicenter distribution characteristics(a)and focal depth statistics(b) of earthquake sequence after double difference relocation.
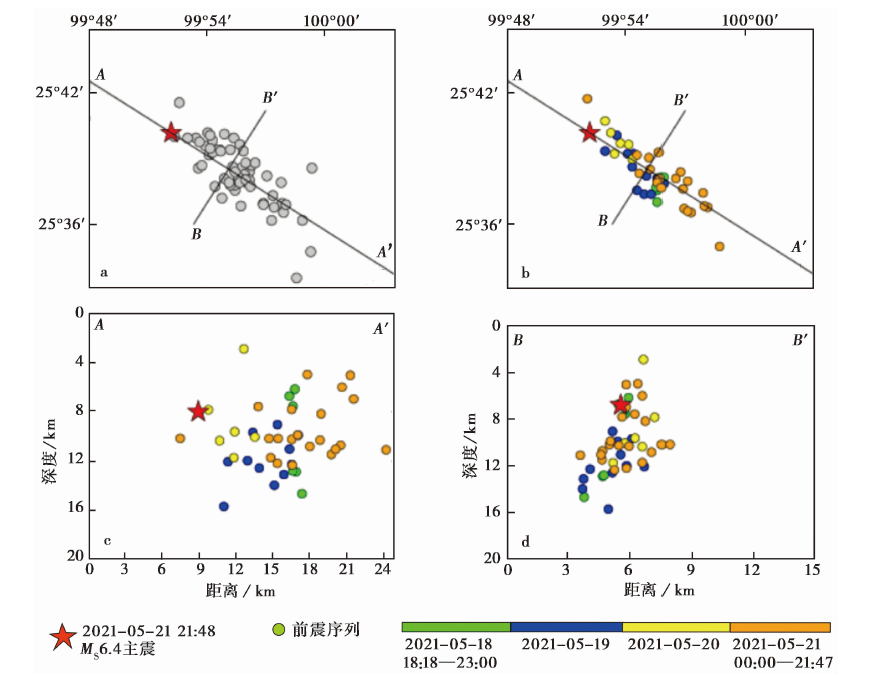
图7 双差精定位前后前震序列的震中分布及精定位后各剖面的地震深度分布图
Fig. 7 Distribution of foreshock sequence and the seismic depth distribution on different sections after double difference relocation.
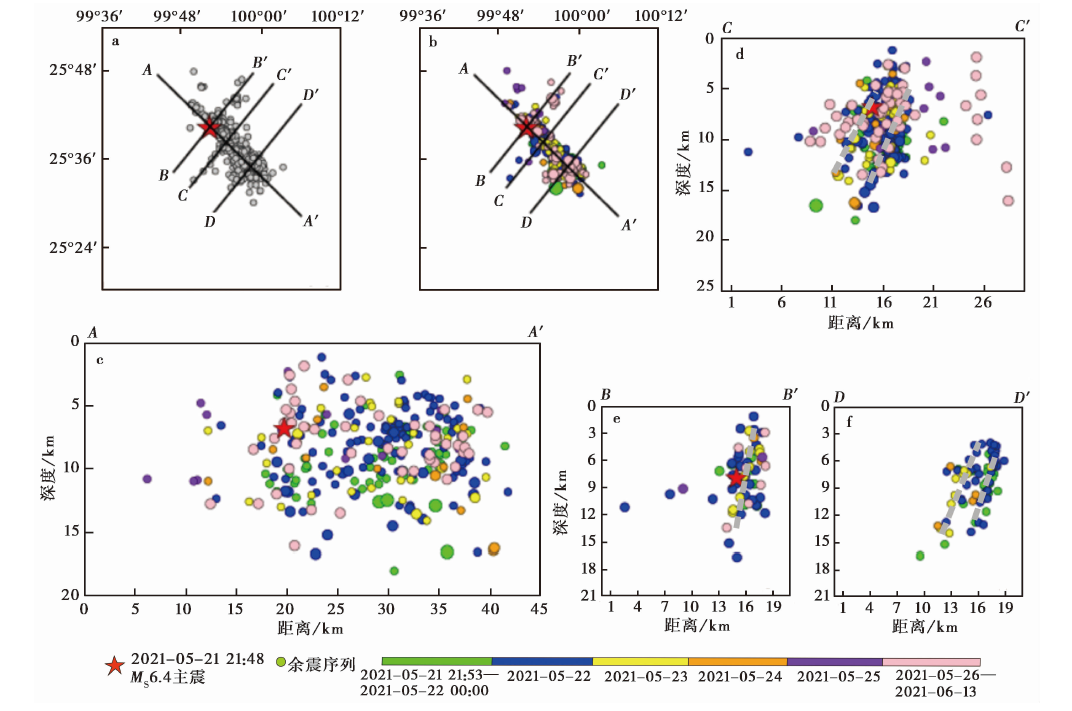
图8 双差精定位前后余震序列的震中分布及精定位后各剖面的地震深度分布
Fig. 8 Distribution of aftershock sequence and the seismic depth distribution on different sections after double difference relocation.
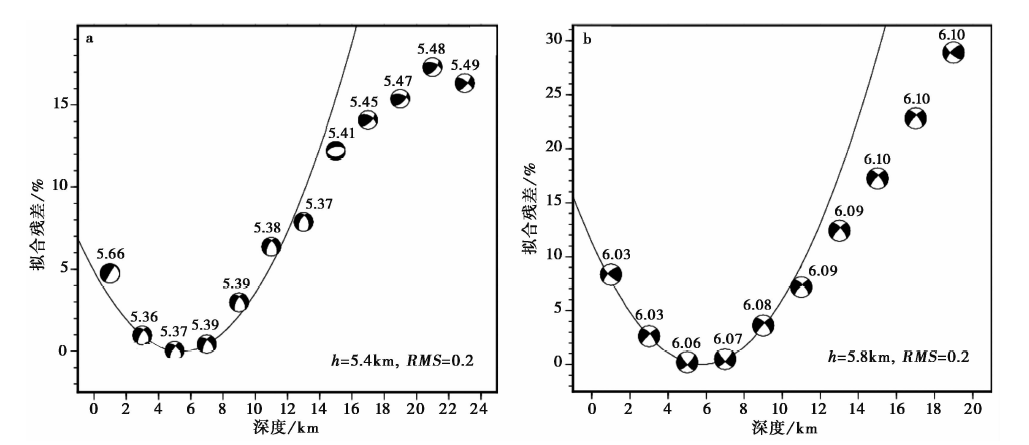
图9 2021年5月21日漾濞 MS5.6 (a)与 MS6.4 (b)地震的震源机制解波形反演残差随深度的变化
Fig. 9 Variations of inversion error of focal mechanism solution with the depth of the Yangbi MS5.6 earthquake(a) and the Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake respectively(b).
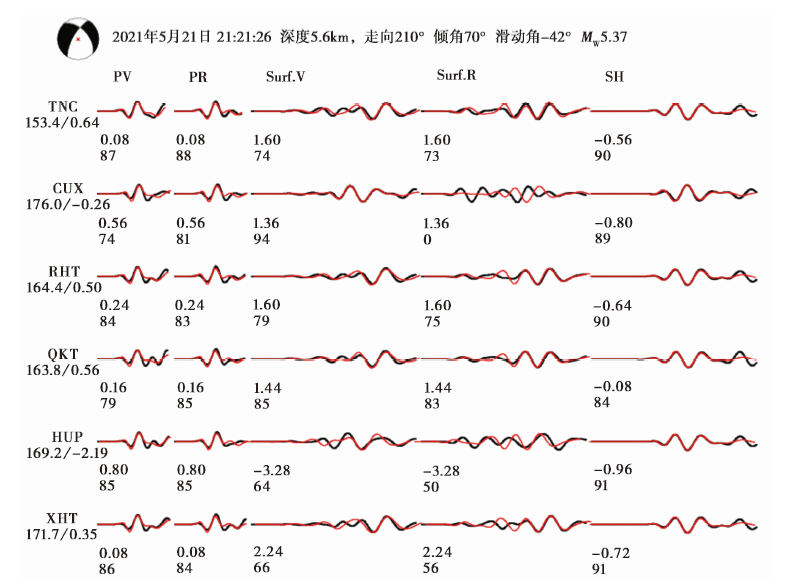
图10 2021年5月21日漾濞 MS5.6 地震在最佳拟合深度5.4km处的波形拟合
Fig. 10 Waveform fitting diagram under the optimal inversion depth of 5.4km of the Yangbi MS5.6 earthquake.
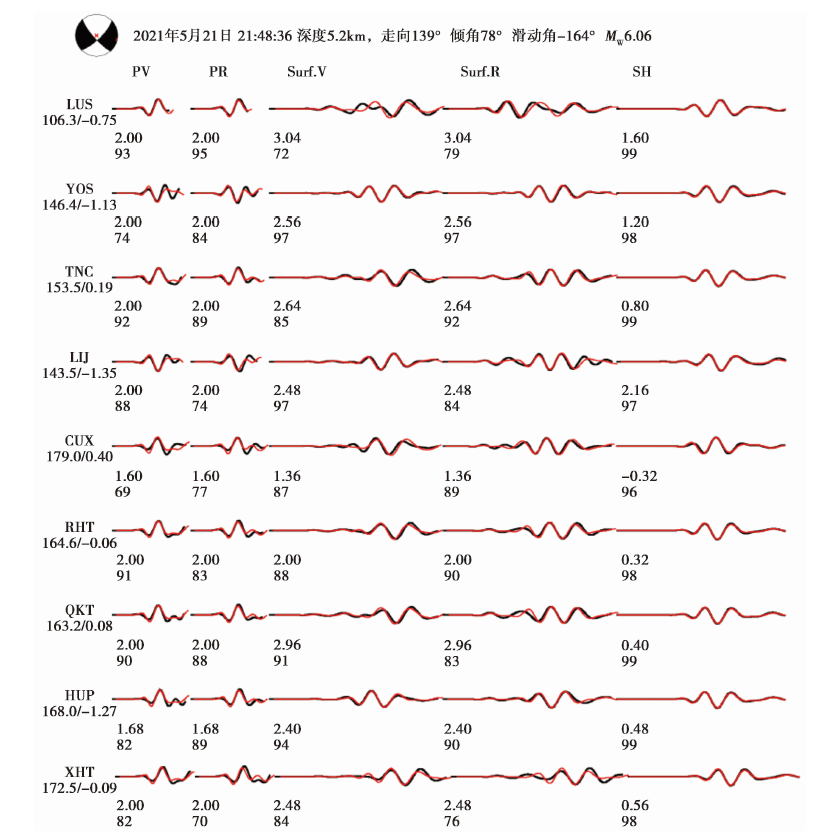
图11 2021年5月21日漾濞 MS6.4 地震在最佳拟合深度5.8km处的波形拟合
Fig. 11 Waveform fitting diagram under the optimal inversion depth of 5.8km of the Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake.
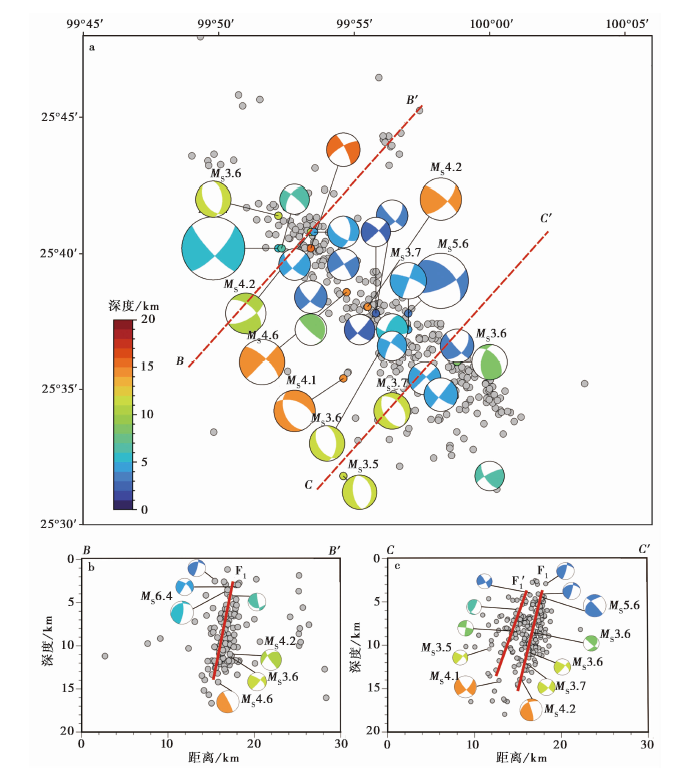
图12 a 漾濞地震序列主震及其他28个MS≥3.0地震的震源机制解平面分布图; b,c 剖面投影图 F1和F'1 是根据地震丛集与震源机制解结果推断的未知断裂
Fig. 12 Plane map(a) and profile map(b,c) of the focal mechanism solutions of the main shock and the other 28 MS≥3.0 events in the sequence.
| [1] | 常祖峰, 常昊, 臧阳, 等. 2016. 维西-乔后断裂新活动特征及其与红河断裂的关系[J]. 地质力学学报, 22(3): 517530. |
| CHANG Zu-feng, CHANG Hao, ZANG Yang, et al. 2016. Recent active features of Weixi-Qiaohou fault and its relationship with the Honghe fault[J]. Journal of Geomechanics, 22(3): 517530. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 陈晨, 胥颐. 2013. 芦山 MS7.0 地震余震序列重新定位及构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(12): 40284036. |
| CHEN Chen, XU Yi. 2013. Relocation of the Lushan MS7.0 earthquake sequence and its tectonic implication[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(12): 40284036. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 陈九辉, 刘启元, 李顺成, 等. 2009. 汶川 MS8.0 地震余震序列重新定位及其地震构造研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(2): 390397. |
|
CHEN Jiu-hui, LIU Qi-yuan, LI Shun-cheng, et al. 2019. Seismotectonic study by relocation of the Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake sequence. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(2): 390397. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [4] | 段梦乔, 赵翠萍, 周连庆, 等. 2021. 2021年5月21日云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列发震构造[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(9): 31113125. |
| DUAN Meng-qiao, ZHAO Cui-ping, ZHOU Lian-qing, et al. 2021. Seismogenic structure of the 21 May 2021 MS6.4 Yunnan Yangbi earthquake sequence[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(9): 31113125. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 房立华, 吴建平, 张天中, 等. 2011. 2011年云南盈江 MS5.8 地震及其余震序列重定位[J]. 地震学报, 33(2): 262267. |
| FANG Li-hua, WU Jian-ping, ZHANG Tian-zhong, et al. 2011. Relocation of mainshock and aftershocks of the 2011 Yingjiang MS5.8 earthquake in Yunnan[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 33(2): 262267. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 韩立波, 蒋长胜, 包丰. 2012. 2010年河南太康 MS4.6 地震序列震源参数的精确确定[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(9): 29732981. |
| HAN Li-bo, JIANG Chang-sheng, BAO Feng. 2012. Source parameter determination of 2010 Taikang MS4.6 earthquake sequences[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(9): 29732981. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 阚荣举, 张四昌, 晏凤桐, 等. 1977. 我国西南地区现代构造应力场与现代构造活动特征的探讨[J]. 地球物理学报, 20(2): 96109. |
| KAN Rong-ju, ZHANG Si-chang, YAN Feng-tong, et al. 1977. Prensent tectonic stress field and its relation to the characteristics of recent tectonic activity in southwestern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 20(2): 96109. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 雷兴林, 王志伟, 马胜利, 等. 2021. 关于2021年5月滇西漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列特征及成因的初步研究[J]. 地震学报, 43(3): 261286. |
| LEI Xing-lin, WANG Zhi-wei, MA Sheng-li, et al. 2021. A preliminary study on the characteristics and mechanism of the May 2021 MS6.4 Yangbi earthquake sequence, Yunnan, China[J]. Journal of seismological research, 43(3): 261286. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] |
李传友, 张金玉, 王伟, 等. 2021. 2021年云南漾濞6.4级地震发震构造分析[J]. 地震地质, 43(3): 706721. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.03.015.
DOI |
| LI Chuan-you, ZHANG Jin-yu, WANG Wei, et al. 2021. The seismogenic fault of the 2021 Yunnan Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(3): 706721. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 李大虎, 丁志峰, 吴萍萍, 等. 2021. 2021年5月21日云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震震区地壳结构特征与孕震背景[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(9): 30833100. |
| LI Da-hu, DING Zhi-feng, WU Ping-ping, et al. 2021. The characteristics of crustal structure and seismogenic background of Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake on May 21, 2021 in Yunnan Province, Chinese[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(9): 30833100. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 李西. 2015. 川滇地块云南地区不同发育阶段边界断裂破裂特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. |
| LI Xi. 2015. Study on boundary fault rupture characteristics of the Sichuan-Yunnan block at different development stages in Yunnan Province[D]. Beijing: Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 刘劲松, Chun K Y, Henderson G A, 等. 2007. 双差定位法在地震丛集精确定位中的应用[J]. 地球物理学进展, 22(1): 137141. |
| LIU Jin-song, Chun K Y, Henderson G A, et al. 2007. Relocation of earthquake clusters using the double difference technique[J]. Progress in Geophysics, 22(1): 137141. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 龙锋, 祁玉萍, 易桂喜, 等. 2021. 2021年5月21日云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列重新定位与发震构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(8): 26312646. |
| LONG Feng, QI Yu-ping, YI Gui-xi, et al. 2021. Relocation of the MS6.4 Yangbi earthquake sequence on May 21, 2021 in Yunnan Province and its seismogenic structure analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(8): 26312646. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 吕坚, 王晓山, 苏金蓉, 等. 2013. 芦山7.0级地震序列的震源位置与震源机制解特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(5): 17531763. |
| LÜ Jian, WANG Xiao-shan, SU Jin-rong, et al. 2013. Hypocentral location and source mechanism of the MS7.0 Lushan earthquake sequence[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(5): 17531763. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 潘睿, 姜金钟, 付虹, 等. 2019. 2017年云南漾濞 MS5.1 及 MS4.8 地震震源机制解和震源深度测定[J]. 地震研究, 42(3): 338348. |
| PAN Rui, JIANG Jin-zhong, FU Hong, et al. 2019. Focal mechanism and focal depth determination of Yunnan Yangbi MS5.1 and MS4.8 earthquakes in 2017[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 42(3): 338348. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 邵兆刚. 2003. 云南兰坪维西地区构造动力学分析[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学. |
| SHAO Zhao-gang. 2003. Tectonic dynamics analysis of Lanping-Weixi area in Yunnan Province[D]. China University of Geosciences, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] |
王绍俊, 刘云华, 单新建, 等. 2021. 2021年云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震同震地表形变与断层滑动分布[J]. 地震地质, 43(3): 692705. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.03.014.
DOI |
| WANG Shao-jun, LIU Yun-hua, SHAN Xin-jian, et al. 2021. Coseismic surface deformation and slip models of the 2021 MS6.4 Yangbi(Yunnan, China)earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(3): 692705. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] |
王莹, 赵韬, 胡景, 等. 2021. 2021年云南漾濞6.4级地震序列重定位及震源机制解特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 43(4): 847863. doi: 10.3969 /j.issn.0253-4967.2021.04.007.
DOI |
| WANG Ying, ZHAO Tao, HU Jing, et al. 2021. Relocation and focal mechanism solutions of the 2021 Yangbi, Yunnan MS6.4 earthquake sequence[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(4): 847863. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 吴建平, 明跃红, 王椿镛. 2004. 云南地区中小地震震源机制及构造应力场研究[J]. 地震学报, 26(5): 457465. |
| WU Jian-ping, MING Yue-hong, WANG Chun-yong. 2004. Source mechanism of small-to-moderate earthquakes and tectonic stress field in Yunnan Province[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 26(5): 457465. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 杨九元, 温扬茂, 许才军. 2021. 2021年5月21日云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震: 一次破裂在隐伏断层上的浅源走滑事件[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(9): 31013110. |
| YANG Jiu-yuan, WEN Yang-mao, XU Cai-jun. 2021. The 21 May 2021 MS6.4 Yangbi(Yunnan)earthquake: A shallow strike-slip event rupturing in a blind fault[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(9): 31013110. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 易桂喜, 龙锋, 梁明剑, 等. 2017. 2017年8月8日九寨沟 MS7.0 地震及余震震源机制解与发震构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(10): 40834097. |
| YI Gui-xi, LONG Feng, LIANG Ming-jian, et al. 2017. Focal mechanism solutions and seismogenic structure of the 8 August 2017 M7.0 Jiuzhaigou earthquake and its aftershocks, northern Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(10): 40834097. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 易桂喜, 龙锋, 梁明剑, 等. 2019. 2019年6月17日四川长宁 MS6.0 地震序列震源机制解与发震构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 62(9): 34323447. |
| YI Gui-xi, LONG Feng, LIANG Ming-jian, et al. 2019. Focal mechanism solutions and seismogenic structure of the 17 June 2019 MS6.0 Sichuan Changning earthquake sequence[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 62(9): 34323447. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 易桂喜, 龙锋, 梁明剑, 等. 2020. 四川盆地荣县威远资中地区发震构造几何结构与构造变形特征: 基于震源机制解的认识和启示[J]. 地球物理学报, 63(9): 32753291. |
| YI Gui-xi, LONG Feng, LIANG Ming-jian, et al. 2020. Geometry and tectonic deformation of seismogenic structures in the Rongxian-Weiyuan-Zizhong region, Sichuan Basin: insights from focal mechanism solutions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 63(9): 32753291. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 张建国. 2009. 中越红河断裂活动性研究[D]. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学. |
| ZHANG Jian-guo. 2009. Study on the activity of Zhongyue Honghe fault[D]. Beijing: University of Science and Technology of China. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 张克亮, 甘卫军, 梁诗明, 等. 2021. 2021年5月21日 MS6.4 漾濞地震GNSS同震变形场及其约束反演的破裂滑动分布[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(7): 22532266. |
| ZHANG Ke-liang, GAN Wei-jun, LIANG Shi-ming, et al. 2021. Coseismic displacement and slip distribution of the 2021 May 21, MS6.4, Yangbi earthquake derived from GNSS observations[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(7): 22532266. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 赵博, 高原, 马延路. 2022. 2021年5月21日云南漾濞 MS6.4 地震序列重新定位, 震源机制及应力场反演[J]. 地球物理学报, 65(3): 10061020. |
| ZHAO Bo, GAO Yuan, MA Yan-lu. 2022. Relocations, focal mechanisms and stress inversion of the May 21th 2021 Yangbi MS6.4 earthquake sequence in Yunnan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 65(3): 10061020. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 郑勇, 马宏生, 吕坚, 等. 2009. 汶川地震强余震(MS≥5.6)的震源机制解及其与发震构造的关系[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 39(4): 413426. |
| ZHENG Yong, MA Hong-sheng, LÜ Jian, et al. 2009. Focal mechanism solutions of the strong aftershock(MS≥5.6)of the Wenchuan earthquake and their relationship with seismogenic structures[J]. Science China Press(D), 39(4): 413426. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 朱俊江, 詹文欢, 唐诚, 等. 2003. 红河断裂带活动性研究[J]. 华南地震, 23(2): 1319. |
| ZHU Jun-jiang, ZHAN Wen-huan, TANG Cheng, et al. 2003. Study on the activity of the Red River fault zone[J]. South China earthquake, 23(2): 1319. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | Got J L, Freche T J, Klein F W. 1994. Deep fault plane geometry inferred from multiplet relative relocation beneath the south flank of Kilauca[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 99(B8): 1537515386. |
| [30] |
Luo Y, Zhao L, Zeng X F, et al. 2015. Focal mechanisms of the Lushan earthquake sequence and spatial variation of the stress field[J]. Science China: Earth Sciences, 58: 11481158.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Waldhauser F, Ellsworth W. 2000. A double-difference earthquake location algorithm: method and application to the Northern Hayward fault, California[J]. Translated World Seismology, 90(6): 13531368. |
| [32] | Wang M, Shen Z K. 2020. Present day crustal deformation of continental China derived from GPS and its tectonic implications[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 125(2): e2019JB018774. |
| [33] | Wells B D L, Coppersmith K J. 1994. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 84(4): 9741002. |
| [34] | Wessel P, Smith H F. 1995. New version of the generic mapping tools[J]. Earth & Space Science News, 76(33): 329329. |
| [35] |
Zhang P Z. 2013. Beware of slowly slipping faults[J]. Nature Geoscience, 6(5): 323324.
DOI |
| [36] | Zhao L S, Helmberger D V. 1994. Source estimation from broadband regional seismograms[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 84(1): 91104. |
| [37] |
Zhu L, Helmberger D V. 1996. Advancement in source estimation techniques using broadband regional seismograms[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 86(5): 16341641.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 刘白云, 赵莉, 刘云云, 王文才, 张卫东. 2021年5月22日青海玛多M7.4地震余震重新定位与断层面参数拟合[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 500-516. |
| [2] | 赵德政, 屈春燕, 张桂芳, 龚文瑜, 单新建, 朱传华, 张国宏, 宋小刚. 基于InSAR技术的同震形变获取、地震应急监测和发震构造研究应用进展[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 570-592. |
| [3] | 樊文杰. 2021年5月21日漾濞MS6.4地震及周边的构造应力场特征和动力学意义[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 208-230. |
| [4] | 李传友, 孙凯, 马骏, 李俊杰, 梁明剑, 房立华. 四川泸定6.8级地震--鲜水河断裂带磨西段局部发起、 全段参与的一次复杂事件[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1648-1666. |
| [5] | 张博譞, 郑文俊, 陈杰, 何骁慧, 李启雷, 张冬丽, 段磊, 陈干. 柴达木盆地北部2021年6月16日青海茫崖MS5.8地震发震构造分析[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(5): 1313-1332. |
| [6] | 邓文泽, 刘杰, 杨志高, 孙丽, 张雪梅. 青海玛多MS7.4地震震源破裂过程反演结果的初步分析[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 1059-1070. |
| [7] | 姚生海, 盖海龙, 殷翔, 刘炜, 张加庆, 袁建新. 阿木尼克山山前地表破裂带与1962年6.8级地震关系的讨论[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 976-991. |
| [8] | 李宗旭, 贺日政, 冀战波, 李娱兰, 牛潇. 2009年7月24日西藏尼玛MS5.6地震的震源机制及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 992-1010. |
| [9] | 王晓山, 万永革. 汶川地震前震中周围地壳应力场及应力方向集中的特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 363-377. |
| [10] | 余占洋, 沈旭章, 梁浩, 郑文俊, 刘旭宙. 基于地震活动性和震源机制解研究渭河-运城盆地主要断裂带的特征及应力场分布[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 395-413. |
| [11] | 张致伟, 龙锋, 赵小艳, 王迪. 川滇地区的震源机制解及应力场特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 170-187. |
| [12] | 梁宽, 何仲太, 姜文亮, 李永生, 刘泽民. 2022年1月8日青海门源MS6.9地震的同震地表破裂特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 256-278. |
| [13] | 高帆, 韩竹军, 袁仁茂, 董绍鹏, 郭鹏. 滇东南地区小江断裂南段历史滑坡特征及其地震地质意义[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1412-1434. |
| [14] | 姚生海, 盖海龙, 殷翔, 李鑫. 青海玛多MS7.4地震地表破裂带的基本特征和典型现象[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1060-1072. |
| [15] | 孙业君, 黄耘, 刘泽民, 郑建常, 江昊琳, 李婷婷, 叶青, 方韬. 郯庐断裂带鲁苏皖段及邻区构造应力场特征及其动力学意义[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1188-1207. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||