地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 961-975.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.04.009
收稿日期:2021-05-06
修回日期:2021-06-09
出版日期:2022-08-20
发布日期:2022-09-23
通讯作者:
梁浩
作者简介:卢本添, 男, 1994年生, 2021年于中山大学地球科学与工程学院获构造地质学硕士学位, 主要从事河流地貌研究和水文测报等工作, E-mail: 991098578@qq.com。
基金资助:
LU Ben-tian( ), LI Zhi-gang, LIANG Hao*(
), LI Zhi-gang, LIANG Hao*( ), YANG Jing-jun, ZHENG Wen-jun
), YANG Jing-jun, ZHENG Wen-jun
Received:2021-05-06
Revised:2021-06-09
Online:2022-08-20
Published:2022-09-23
Contact:
LIANG Hao
摘要:
河流地貌发育特征对构造活动异常敏感, 因此能够有效揭示活动断裂的分段性差异。通过提取地形信息, 综合分析河流地貌参数的空间分布, 筛分构造、 气候、 岩性特征等影响因素, 量化构造活动强度, 是活动断裂分段性的重要研究切入点之一。中条山北麓断裂是控制中条山与运城盆地差异升降的活动断裂, 由南向北可划分为韩阳段、 永济段、 盐湖段和夏县段, 断裂各段的活动性与现今中条山地形地貌的塑造密切相关, 是应用河流地貌研究断裂分段性的理想地区。文中通过提取中条山北坡基岩山区流域水系的河道地形信息, 获取了河道标准化陡峭指数ksn、 坡度S、 水系高程剖面的几何特征、 河流裂点位置及裂点上、 下游下切量等参数。结果显示, 纵向上中条山北坡基岩河道记录了1期加速下切事件, 在横向上, 河道标准化陡峭指数ksn、 坡度与河道下切量等地貌参数存在明显的空间变化, 高值区位于韩阳段-永济段, 向W分段性递减, 与中条山西高东低的地形起伏相符, 但与活动速率高值区及盆地新生界沉积中心(盐湖段)的位置不一致。不一致的主因可能与华山山前断裂部分活动性沿中条山北麓断裂韩阳段西延隐伏断裂的迁移有关, 二者活动性在韩阳段-永济段叠加, 并被河流地貌敏感记录, 形成地貌参数的高值异常区, 暗示中条山北麓断裂的构造活动中心已经向W迁移。
中图分类号:
卢本添, 李志刚, 梁浩, 杨敬钧, 郑文俊. 中条山北麓河流地貌特征及其对断裂构造演化的响应[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 961-975.
LU Ben-tian, LI Zhi-gang, LIANG Hao, YANG Jing-jun, ZHENG Wen-jun. THE RESPONSE OF FLUVIAL LANDFORM TO THE EVOLU-TION OF FAULT STRUCTURE IN THE NORTHERN ZHONGTIAO MOUNTAINS FAULT[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(4): 961-975.
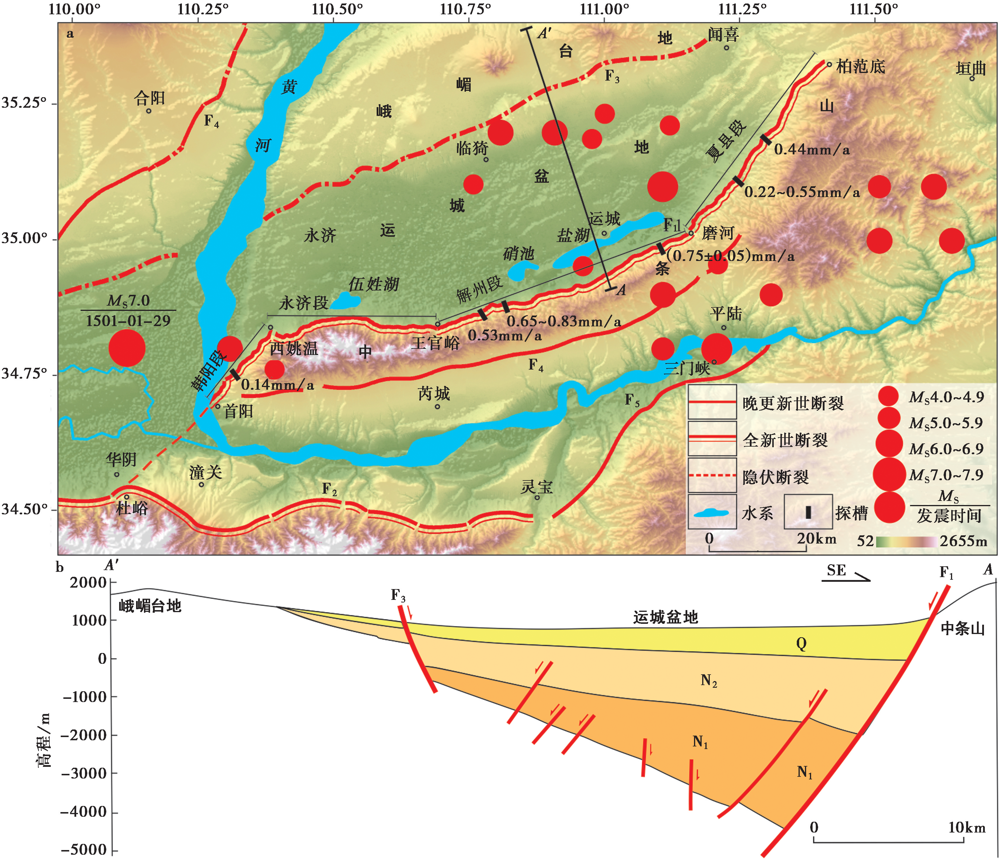
图1 运城盆地周缘区域的构造简图 a F1中条山北麓断裂; F2华山山前断裂; F3双泉-临猗隐伏断裂; F4韩城断裂; F5温塘断裂; b N1中新统; N2上新统; Q 第四系; 剖面AA'据Su等(2020)修改; 活动速率据文献(程绍平等, 2002; 苗德雨等, 2014; 司苏沛等, 2014; 郭春杉等, 2019)
Fig. 1 Topographic and tectonic map of the Zhongtiao Mountains and adjacent basin areas.
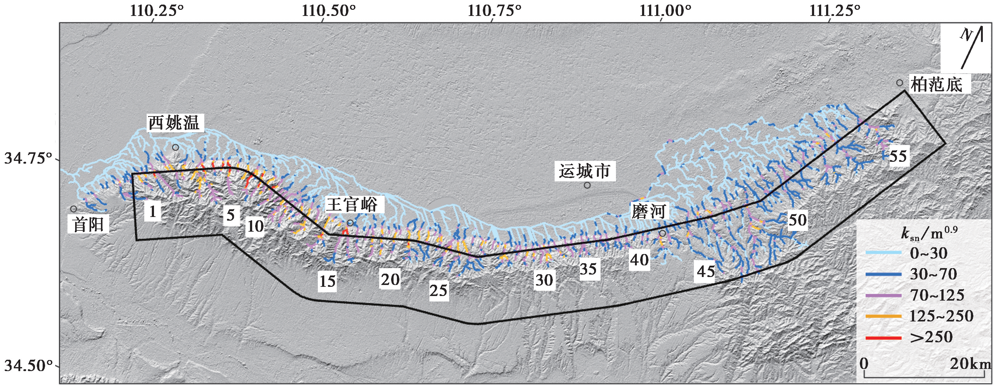
图2 中条山北坡基岩河道标准化陡峭系数ksn的空间分布图 黑色方框为条带剖面的提取范围
Fig. 2 Normalized steepness index ksn of the bedrock channels in the north flank of the Zhongtiao Mountains.
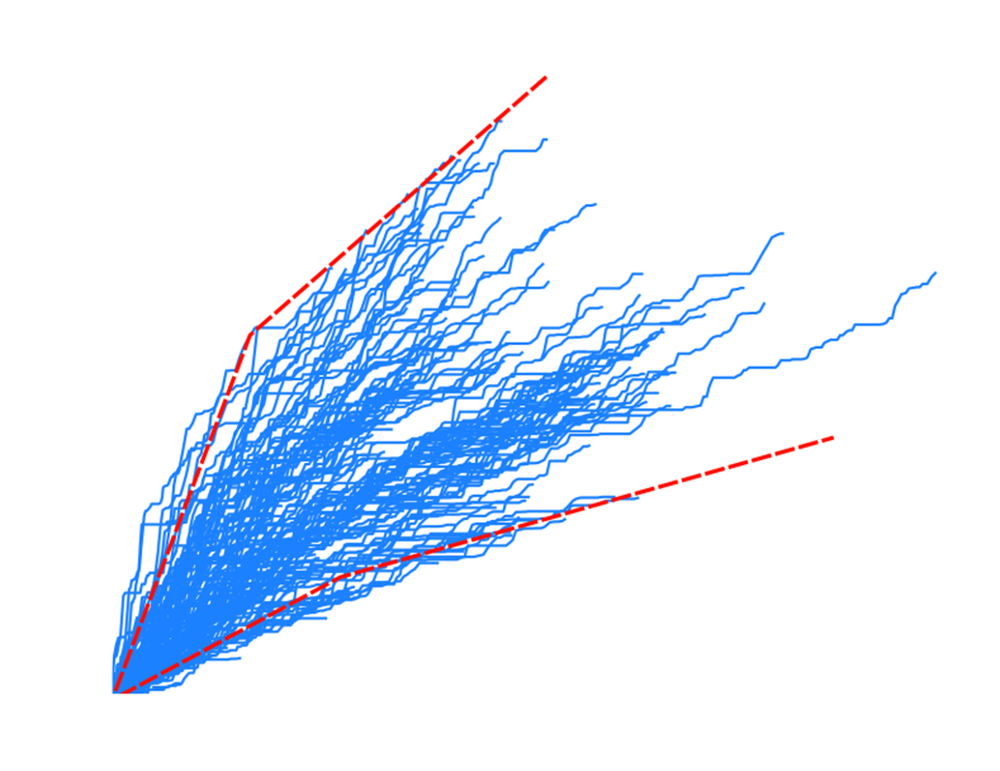
图3 中条山北坡基岩山区水系高程剖面的几何特征图 对图2中黑色方框内的条带区域使用积分法提取中条山ksn值为0~500m0.9 的主干流高程剖面图, 蓝色实线为河流干流纵剖面形态, 红色虚线为河流干流纵剖面形态的整体趋势
Fig. 3 χ-plot of the bedrock channels in the north flank of Zhongtiao Mountains.
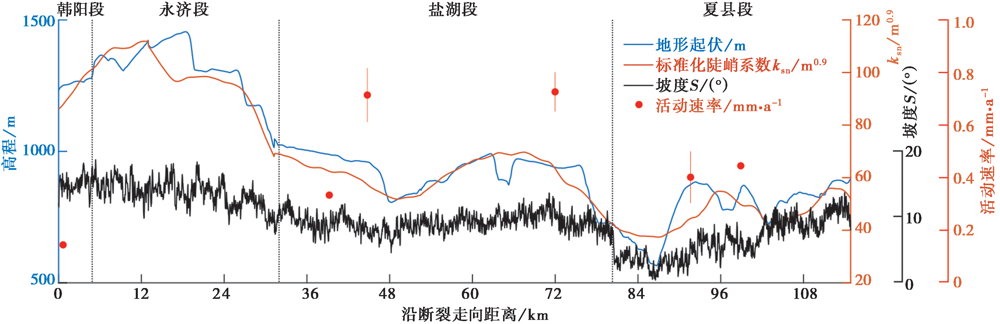
图4 沿中条山走向的地形起伏、 河道标准化陡峭系数ksn和坡度S的空间分布图 对图2中黑色方框内的条带区域进行地貌参数提取; 蓝色实线为地形起伏, 橙色实线为河流标准化陡峭系数ksn, 黑色实线为坡度S, 红点为活动速率(程绍平等, 2002; 苗德雨等, 2014; 司苏沛等, 2014; 郭春杉等, 2019)
Fig. 4 Spatial distribution of relief, normalized steepness index ksn and slope along the north flank of Zhongtiao Mountains.
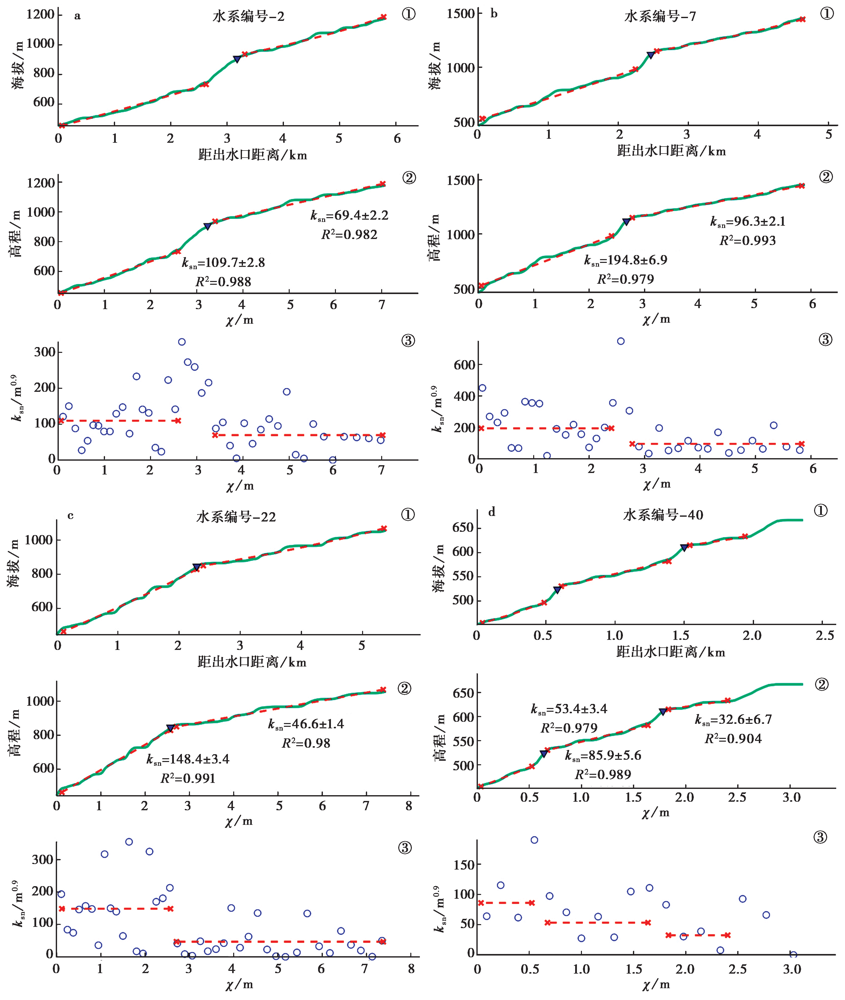
图5 河流纵剖面分析结果及其裂点图 a-d表示不同段的河流纵剖面: a 2号裂点水系; b 7号裂点水系; c 22号裂点水系; d 40号裂点水系。各水系纵剖面图内: ①距离出水口位置-海拔关系图, 蓝色实线表示原始的河流纵剖面形态; ②χ-海拔关系图, 蓝色实线表示χ(chi)值; ③χ-ksn关系图, 表示沿①中河流纵剖面形态的ksn分布特征, 红色虚线均表示拟合。深蓝色三角形为纵剖面坡折点, 即为裂点
Fig. 5 Log-log analysis of longitudinal profiles and knickpoints.
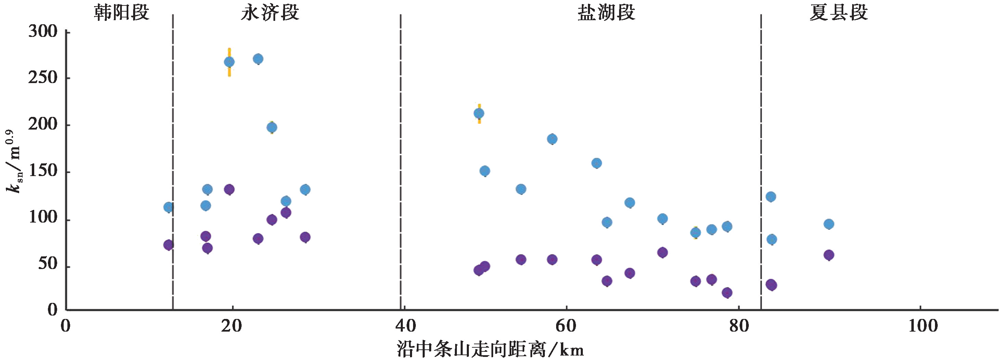
图6 河流裂点处上、 下游河道标准化陡峭指数ksn分布图 蓝色点表示裂点处下游的ksn值; 紫色点表示裂点处上游的ksn值; 黄色线为误差值
Fig. 6 The spatial distribution of normalized steepness index ksn in the upstream and downstream drainage areas of individual knickpoint.
| [1] | 程绍平, 杨桂枝. 2002. 山西中条山断裂带的晚第四纪分段模型[J]. 地震地质, 24(3): 289-302. |
| CHENG Shao-ping, YANG Gui-zhi. 2002. Late Quaternary segmentation model of the Zhongtiaoshan Fault, Shanxi Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 24(3): 289-302. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 慈洪娟, 闫冬冬, 李有利, 等. 2016. 中条山北麓韩阳段冲沟发育及其新构造意义[J]. 水土保持研究, 23(4): 363-367. |
| CI Hong-juan, YAN Dong-dong, LI You-li, et al. 2016. Geomorphic indices in the Hanyang segment of Zhongtiaoshan Mountains, Shanxi and its implication for neotectonics[J]. Research of Soil and Water Conservation, 23(4): 363-367. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 郭春杉. 2019. 运城盆地主要断裂活动性及其相关块体变形特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地震预测研究所. |
| GUO Chun-shan. 2019. Study on main fault activity and deformation characteristics of related blocks in Yuncheng Basin[D]. Institute of Earthquake Forecasting, CEA, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 郭春杉, 李文巧, 田勤俭, 等. 2019. 中条山北麓断裂解州段晚更新世滑动速率研究[J]. 地震, 39(4): 13-26. |
| GUO Chun-shan, LI Wen-qiao, TIAN Qin-jian, et al. 2019. Study on late Pleistocene slip rate of Haizhou section of North Zhongtiaoshan Faults[J]. Earthquake, 39(4): 13-26. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 胡小飞, 潘保田, Kirby E, 等. 2010. 河道陡峭指数所反映的祁连山北翼抬升速率的东西差异[J]. 科学通报, 55(23): 2329-2338. |
|
HU Xiao-fei, PAN Bao-tian, Kirby E, et al. 2010. Spatial differences in rock uplift rates inferred from channel steepness indices along the northern flank of the Qilian Mountain, northeast Tibetan plateau[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 55(23): 2329-2338.
DOI URL |
|
| [6] | 马冀. 2019. 1556年华县M8?级地震地表破裂与发震构造[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所. |
| MA Ji. 2019. Surface rupture and its seismogenic faults of 1556 Huaxian M8?earthquake[D]. Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] |
苗德雨, 李有利, 吕胜华, 等. 2014. 山西中条山北麓断裂夏县段新构造运动[J]. 地理研究, 33(4): 665-673.
DOI |
|
MIAO De-yu, LI You-li, LÜ Sheng-hua, et al. 2014. Neotectonic activity in Xiaxian segment of the north Zhongtiao Mountain fault zone, Shanxi[J]. Geographical Research, 33(4): 665-673. (in Chinese)
DOI |
|
| [8] | 司苏沛, 李有利, 吕胜华, 等. 2014. 山西中条山北麓断裂盐池段全新世古地震事件和滑动速率研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 44(9): 1958-1967. |
| SI Su-pei, LI You-li, LÜ Sheng-hua, et al. 2014. Holocene paleoseismic events and slip rate of Yanchi section of the north foot fault of Zhongtiao Mountain in Shanxi, China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 44(9): 1958-1967. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 田建梅, 李有利, 司苏沛, 等. 2013. 中条山北麓中段洪积扇上全新世断层陡坎的发现及其新构造意义[J]. 北京大学学报(自然科学版), 49(6): 986-992. |
| TIAN Jian-mei, LI You-li, SI Su-pei, et al. 2013. Discovery and neotectonic significance of fault scarps on alluvial fans in the middle of northern piedmont of the Zhongtiao Mountains[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Pekinensis, 49(6): 986-992. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 王一舟, 张会平, 郑德文, 等. 2016. 基岩河道河流水力侵蚀模型及其应用: 兼论青藏高原基岩河道研究的迫切性[J]. 第四纪研究, 36(4): 884-897. |
| WANG Yi-zhou, ZHANG Hui-ping, ZHENG De-wen, et al. 2016. Stream-power incision model and its implications: Discussion on the urgency of studying bedrock channel across the Tibetan plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 36(4): 884-897. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] |
徐伟, 杨源源, 袁兆德, 等. 2017. 华山山前断裂断错地貌及晚第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 39(3): 587-604. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.03.011.
DOI |
| XU Wei, YANG Yuan-yuan, YUAN Zhao-de, et al. 2017. Late Quaternary faulted landforms and fault activity of the Huashan piedmont fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(3): 587-604. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 杨源源, 高战武, 徐伟. 2012. 华山山前断裂中段晚第四纪活动的地貌表现及响应[J]. 震灾防御技术, 7(4): 335-347. |
| YANG Yuan-yuan, GAO Zhan-wu, XU Wei. 2012. Geomorphic expression and response of the activity along the middle section of Huashan front fault in the late Quaternary period[J]. Technology for Earthquake Disaster Prevention, 7(4): 335-347. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] |
England P, Molnar P. 1990. Surface uplift, uplift of rocks, and exhumation of rocks[J]. Geology, 18(12): 1173-1177.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
Flint J J. 1974. Stream gradient as a function of order, magnitude, and discharge[J]. Water Resources Research, 10(5): 969-973.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
Fox M, Goren L, May D A, et al. 2015. Inversion of fluvial channels for paleorock uplift rates in Taiwan[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 119(9): 1853-1875.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
Hijmans R J, Cameronse S E, Parra J L, et al. 2005. Very high resolution interpolated climate surfaces for global land areas[J]. International Journal of Climatology, 25(15): 1965-1978.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Howard A D, Kerby G. 1983. Channel changes in badlands[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 94(6): 739-752.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
Kirby E, Whipple K. 2001. Quantifying differential rock uplift rates via stream profile analysis[J]. Geology, 29(5): 415-418.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
Kirby E, Whipple K X. 2012. Expression of active tectonics in erosional landscapes[J]. Journal of Structural Geology, 44: 54-75.
DOI URL |
| [20] | Kirby E, Whipple K X, Tang W Q, et al. 2003. Distribution of active rock uplift along the eastern margin of the Tibetan plateau: Inferences from bedrock channel longitudinal profiles[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 108(B4): 2217. |
| [21] |
Li D P, Du J J, Ma Y S, et al. 2015. Active faults and dip slip rates along the northern margins of the Huashan Mountain and Weinan loess tableland in the southeastern Weihe Graben, central China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 114(1): 266-278.
DOI URL |
| [22] | Oskin M, Perg L, Blumentritt D, et al. 2007. Slip rate of the Calico Fault: Implications for geologic versus geodetic rate discrepancy in the eastern California shear zone[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 112(B7): B03402. |
| [23] |
Perron J T, Royden L. 2013. An integral approach to bedrock river profile analysis[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 38(6): 570-576.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Snyder N P, Whipple K X, Tucker G E, et al. 2003. Importance of a stochastic distribution of floods and erosion thresholds in the bedrock river incision problem[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 108(B2): 2117. |
| [25] | Stock J D, Montgomery D R. 1999. Geologic constraints on bedrock river incision using the stream power law[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 104(B3): 4983-4993. |
| [26] | Su P, He H L, Tan X B, et al. 2021. Initiation and evolution of the Shanxi rift system in North China: Evidence from low-temperature thermochronology in a plate reconstruction framework[J]. Tectonics, 40(3): e2020TC006298. |
| [27] |
Su Q, Wang X Y, Lu H Y, et al. 2020. Dynamic divide migration as a response to asymmetric uplift: An example from the Zhongtiao Shan, North China[J]. Remote Sensing, 12(24): 4188.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Whipple K X. 2001. Fluvial landscape response time: How plausible is steady-state denudation?[J]. American Journal of Science, 301(4-5): 313-325.
DOI URL |
| [29] | Whipple K X. 2004. Bedrock rivers and the geomorphology of active orogens[J]. Annual Review of Earth & Planetary Sciences, 32(1): 151-185. |
| [30] |
Whipple K X, Gasparini N M. 2014. Tectonic control of topography, rainfall patterns, and erosion during rapid post -12Ma uplift of the Bolivian Andes[J]. Lithosphere, 6(4): 251-268.
DOI URL |
| [31] | Whipple K X, Tucker G E. 1999. Dynamics of the stream-power river incision model: Implications for height limits of mountain ranges, landscape response timescales, and research needs[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 104(B8): 17661-17674. |
| [32] | Wobus C W, Tucker G E, Anderson R S. 2006. Self-formed bedrock channels[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 331(18): 273-274. |
| [33] |
Yang R, Willett S D, Goren L. 2015. In situ low-relief landscape formation as a result of river network disruption[J]. Nature, 520(7548): 526-529.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 徐伟, 刘志成, 袁兆德, 高战武, 杨源源. 华山山前河流地貌参数及其构造意义[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(6): 1316-1335. |
| [2] | 王怡然, 李有利, 闫冬冬, 吕胜华, 司苏沛. 中条山北麓断裂中南段全新世地震事件的初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(1): 1-12. |
| [3] | 邓万明. 青藏及邻区新生代火山活动及构造演化[J]. 地震地质, 2003, 25(s1): 51-61. |
| [4] | 王瑜, 李齐, 万景林, 李大明. 西藏南部地区南北向构造的形成及动力学探讨[J]. 地震地质, 2000, 22(s1): 117-. |
| [5] | 侯康明, 石亚缪, 张忻. 青藏高原北部NNW向构造活动方式及形成年代[J]. 地震地质, 1999, 21(2): 127-136. |
| [6] | 赵俊猛, 卢造勋. 辽河裂谷的深部构造与裂谷活动的侧向迁移[J]. 地震地质, 1998, 20(3): 225-233. |
| [7] | 程国良, 孙宇航, 孙青格, 王立红. 显生宙中国大地构造演化的古地磁研究[J]. 地震地质, 1995, 17(1): 69-78. |
| [8] | 陈社发, 邓起东, 赵小麟, C. J. L. Wilson P. Dirks, 罗志立, 刘树根. 龙门山中段推覆构造带及相关构造的演化历史和变形机制(二)[J]. 地震地质, 1994, 16(4): 413-421. |
| [9] | 程国良, 李永安, 李素玲, 李强, 张慧. 新疆准噶尔地块东北部晚古生代古地磁研究及构造含义[J]. 地震地质, 1993, 15(1): 32-44. |
| [10] | 彭建兵. 渭河断裂带的构造演化与地震活动[J]. 地震地质, 1992, 14(2): 113-120. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||