地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (1): 115-129.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.01.008
收稿日期:2021-02-01
修回日期:2021-06-22
出版日期:2022-02-20
发布日期:2022-04-20
通讯作者:
谭锡斌
作者简介:叶轶佳, 女, 1996年生, 2021年于中国地震局地质研究所获构造地质专业硕士学位, 现为中国地震局地质研究所构造地质学专业在读博士研究生, 研究方向为构造地貌, E-mail: yeahrr96@qq.com。
基金资助:
YE Yi-jia( ), TAN Xi-bin*(
), TAN Xi-bin*( ), QIAN Li
), QIAN Li
Received:2021-02-01
Revised:2021-06-22
Online:2022-02-20
Published:2022-04-20
Contact:
TAN Xi-bin
摘要:
河流作为主要的地貌单元之一, 在经历构造活动、 气候变化、 海平面升降后, 会记录丰富的相关信息。基于河流剪切力模型, 可应用地貌参数对河流侵蚀速率进行计算。文中利用已有的龙门山地区沉积岩类和花岗岩类的河流剪切力与侵蚀速率之间的经验关系, 计算了沿河139个点的侵蚀速率。结果表明, 汶川-茂县断裂下盘的侵蚀速率为0.43mm/a, 双石-大川断裂上、 下盘的侵蚀速率分别为0.49mm/a和0.28mm/a。另外, 文中根据经验公式计算了每个观测点的可蚀系数(Erodibility), 揭示出: 1)断裂活动使沉积岩的可蚀系数增加了约3倍, 而花岗岩的可蚀系数增加了约1倍; 2)断裂活动对沉积岩的影响(距离断裂约2km范围内)明显比花岗岩(距离断裂约5km范围内)更集中。研究表明, 断层活动使可蚀系数明显增大(即断裂附近的岩石较破碎), 从而对区域地貌演化产生了重要影响。
中图分类号:
叶轶佳, 谭锡斌, 钱黎. 通过河流剪切力获取河道侵蚀速率和基岩可蚀系数——以龙门山为例[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 115-129.
YE Yi-jia, TAN Xi-bin, QIAN Li. QUANTIFYING EROSION RATE AND ROCK ERODIBILITY FROM FLUVIAL SHEAR STRESS:AN EXAMPLE FROM LONGMEN SHAN[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2022, 44(1): 115-129.
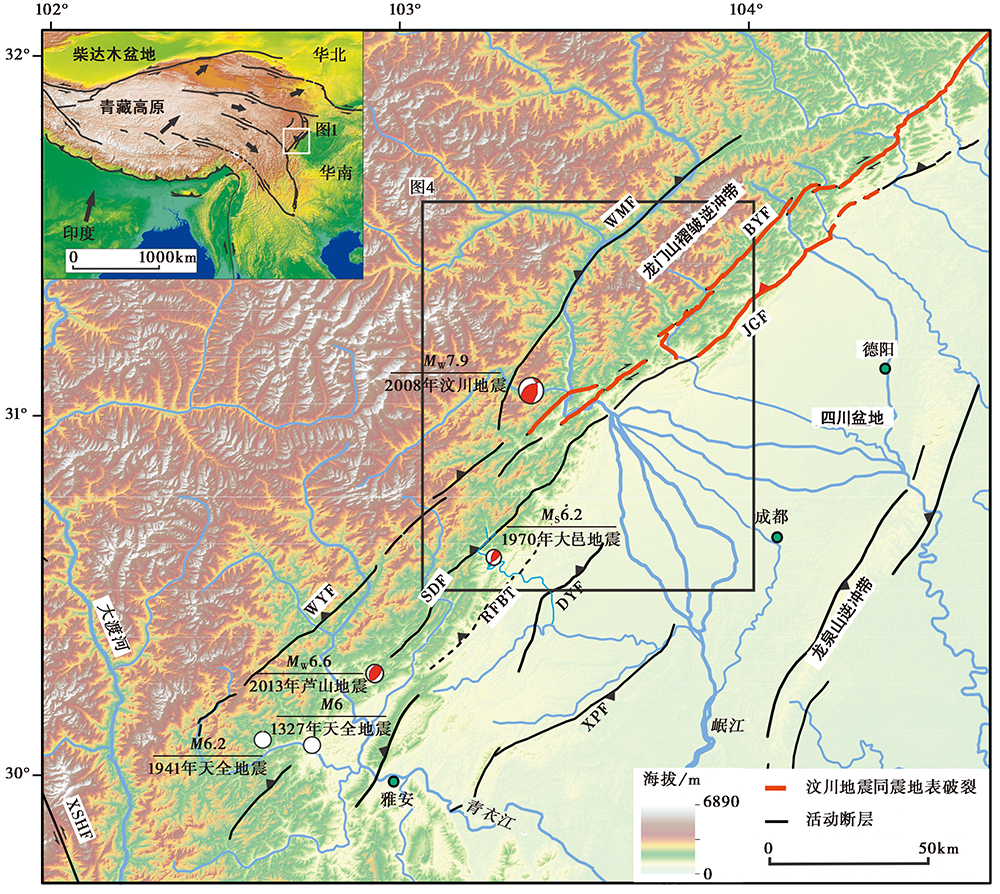
图 1 研究区地形及主要断裂分布图 黑色实线代表活动断层, 红色实线为2008年汶川地震同震地表破裂(徐锡伟等, 2008), 蓝色实线代表河流。WMF 汶川-茂县断裂; BYF 北川-映秀断裂; JGF 江油-灌县断裂; WYF 五龙-盐井断裂; SDF 双石-大川断裂; DYF 大邑断裂; XPF 熊坡断裂; XSHF 鲜水河断裂
Fig. 1 The topography of the study area and the distribution of main faults.
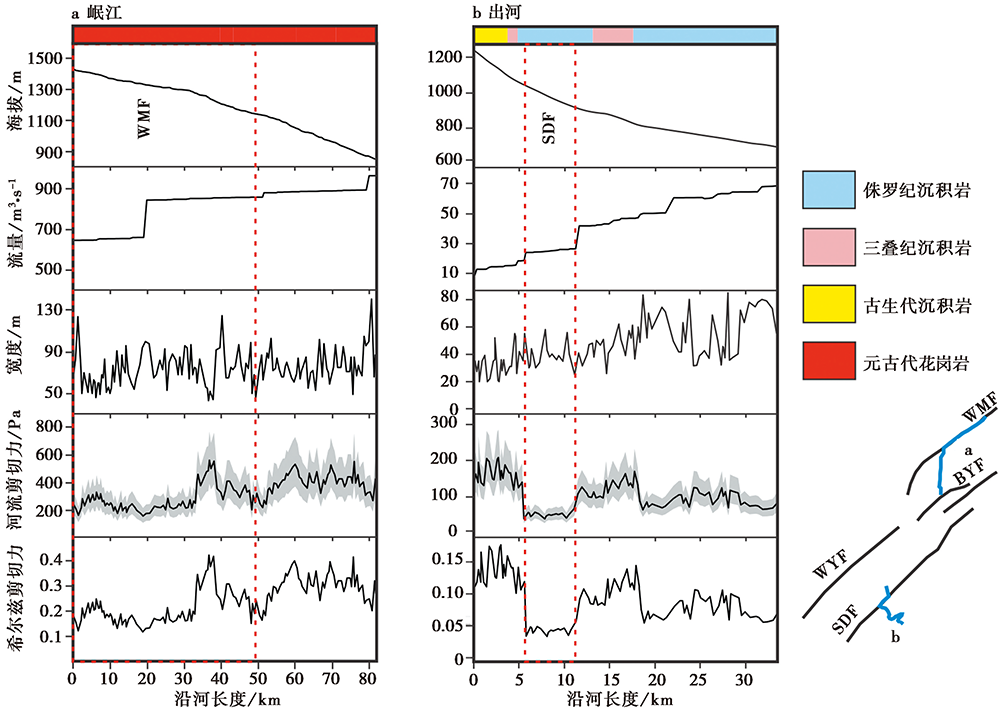
图 3 河流剪切力以及希尔兹力计算结果图 研究区2条河流的高程、 流量、 宽度、 河流剪切力及希尔兹力随沿河距离的变化图, 其中河流剪切力一栏中的灰色阴影部分代表了河流剪切力计算的不确定性; a 岷江; b 出河。红色虚线框是沿断裂流的河段。 右下角为河流和断层的索引图
Fig. 3 Shear stress and Shields stress calculation results.
| [1] | 邓起东, 陈社发, 赵小麟. 1994. 龙门山及其邻区的构造和地震活动及动力学[J]. 地震地质, 16(4): 389-403. |
| DENG Qi-dong, CHEN She-fa, ZHAO Xiao-lin. 1994. Tectonics, seismicity and dynamics of Longmenshan Mountains and its adjacent regions[J]. Seismology and Geology, 16(4): 389-403. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 梁明剑, 陈立春, 冉勇康, 等. 2016. 龙门山断裂南段天全段的新活动特征与1327年天全地震的关系[J]. 地震地质, 38(3): 546-559. |
| LIANG Ming-jian, CHEN Li-chun, RAN Yong-kang, et al. 2016. The discussion for the new activity of the Tianquan segment of Longmenshan fault zone and its relationship to the 1327 Tianquan earthquake, Sichuan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(3): 546-559. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 王一舟, 张会平, 郑德文, 等. 2016. 基岩河道河流水力侵蚀模型及其应用: 兼论青藏高原基岩河道研究的迫切性[J]. 第四纪研究, 36(4): 884-897. |
| WANG Yi-zhou, ZHANG Hui-ping, ZHENG De-wen, et al. 2016. Stream power incision model and its implications: Discussion on the urgency of studying bedrock channel across the Tibetan plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 36(4): 884-897. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 叶建青, 等. 2008. 汶川 MS8.0 地震地表破裂带及其发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 30(3): 594-629. |
| XU Xi-wei, WEN Xue-ze, YE Jian-qing, et al. 2008. The MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake surface ruptures and its seismogenic structure[J]. Seismology and Geology, 30(3): 594-629. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 徐锡伟, 陈桂华, 于贵华, 等. 2013. 芦山地震发震构造及其与汶川地震关系讨论[J]. 地学前缘, 20(3): 11-20. |
| XU Xi-wei, CHEN Gui-hua, YU Gui-hua, et al. 2013. Seismogenic structure of Lushan earthquake and its relationship with Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 20(3): 11-20. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 许志琴, 李化启, 侯立炜, 等. 2007. 青藏高原东缘龙门-锦屏造山带的崛起: 大型拆离断层和挤出机制[J]. 地质通报, 26(10): 1262-1276. |
| XU Zhi-qing, LI Hua-qi, HOU Li-wei, et al. 2007. Uplift of the Longmen-Jinping orogenic belt along the eastern margin of the Qinghai-Tibet plateau: Large-scale detachment faulting and extrusion mechanism[J]. Geological Bulletin of China, 26(10): 1262-1276. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 郑景云, 尹云鹤, 李炳元. 2010. 中国气候区划新方案[J]. 地理学报, 65(1): 3-12. |
| ZHENG Jing-yun, YIN Yun-he, LI Bing-yuan. 2010. A new scheme for climate regionalization in China[J]. Acta Geographica Sinica, 65(1): 3-12. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] |
Arne D, Worley B, Wilson C, et al. 1997. Differential exhumation in response to episodic thrusting along the eastern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 280(3-4): 239-256.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
Burchfiel B C, Chen Z, Liu Y, et al. 1995. Tectonics of the Longmen Shan and adjacent regions, central China[J]. International Geology Review, 37: 661-735.
DOI URL |
| [10] | Chang H H. 1992. Fluvial Processes in River Engineering[M]. Krieger Publishing Company, Melbourne, FL. |
| [11] |
Clark M K, Royden L H. 2000. Topographic ooze: Building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow[J]. Geology, 28(8): 703-706.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
Gallen S F, Clark M K, Godt J W. 2015. Coseismic landslides reveal near-surface rock strength in a high-relief, tectonically active setting[J]. Geology, 43(1): 11-14.
DOI URL |
| [13] | Godard V, Pik R, Lavé J, et al. 2009. Late Cenozoic evolution of the central Longmen Shan, eastern Tibet: Insight from(U-Th)/He thermochronometry[J]. Tectonics, 28(5). https://doi.org/10.1029/2008TC002407. |
| [14] |
Godard V, Lavé J, Carcaillet J, et al. 2010. Spatial distribution of denudation in eastern Tibet and regressive erosion of plateau margins[J]. Tectonophysics, 491(1-4): 253-274.
DOI URL |
| [15] | Hoek E, Brown E T. 1997. Practical estimates of rock mass strength[J]. International Journal of Rock Mechanics and Mining Sciences, 34(8): 1165-1186. |
| [16] |
Howard A D. 1994. A detachment-limited model of drainage basin evolution[J]. Water Resources Research, 30(7): 2261-2285.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
Howard A D, Kerby G. 1983. Channel changes in bad lands[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 94(6): 739-752.
DOI URL |
| [18] | Kirby E, Reiners P W, Krol M A, et al. 2002. Late Cenozoic evolution of the eastern margin of the Tibetan plateau: Inferences from40Ar/39Ar and(U-Th)/He thermochronology[J]. Tectonics, 21(1): 1-1-1-20. |
| [19] | Kirby E, Whipple K X, Tang W, et al. 2003. Distribution of active rock uplift along the eastern margin of the Tibetan plateau: Inferences from bedrock channel longitudinal profiles[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 108(B4). https://doi.org/10.1029/2001JB000861. |
| [20] |
Kirkpatrick H M, Moon S, Yin A, et al. 2021. Impact of fault damage on eastern Tibet topography[J]. Geology, 49(1): 30-34.
DOI URL |
| [21] | Lavé J, Avouac J P. 2001. Fluvial incision and tectonic uplift across the Himalayas of central Nepal[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 106(B11): 26561-26591. |
| [22] |
Liu Y D, Tan X B, Ye Y J, et al. 2020. Role of erosion in creating thrust recesses in a critical-taper wedge: An example from eastern Tibet[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 540:116270.
DOI URL |
| [23] | Ma Z F, Zhang H P, Wang Y Z, et al. 2020. Inversion of Dadu River bedrock channels for the late Cenozoic uplift history of the eastern Tibetan plateau[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 47(4): e2019GL086882. |
| [24] | Mezaki S, Yabiku M. 1984. Channel morphology of the Kali Gandaki and the Narayani rivers in central Nepal[J]. Journal of Nepal Geological Society, 4:161-176. |
| [25] | Molnar P, Anderson R S, Anderson S P. 2007. Tectonics, fracturing of rock, and erosion[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 112(F3). https://doi.org/10.1029/2005JF000433. |
| [26] |
Ouimet W B, Whipple K X, Granger D E. 2009. Beyond threshold hillslopes: Channel adjustment to base-level fall in tectonically active mountain ranges[J]. Geology, 37(7): 579-582.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Qin J, Huh Y, Edmond J M, et al. 2006. Chemical and physical weathering in the Min Jiang, a headwater tributary of the Yangtze River[J]. Chemical Geology, 227(1-2): 53-69.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
Royden L H, Burchfiel B C, King R W, et al. 1997. Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet[J]. Science, 276(5313): 788-790.
PMID |
| [29] |
Shen X M, Tian Y T, Zhang G H, et al. 2019. Late Miocene hinterland crustal shortening in the Longmen Shan thrust belt, the eastern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 124(11): 11972-11991.
DOI URL |
| [30] | Sklar L S, Dietrich W E. 2004. A mechanistic model for river incision into bedrock by saltating bed load[J]. Water Resources Research, 40(6). https://doi.org/10.1029/2003WR002496. |
| [31] |
Snyder N P, Whipple K X, Tucker G E, et al. 2000. Landscape response to tectonic forcing: DEM analysis of stream profiles in the Mendocino triple junction region, northern California[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 112(8): 1250-1263.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Stock J D, Montgomery D R, Collins B D, et al. 2005. Field measurements of incision rates following bedrock exposure: Implications for process controls on long profiles of valleys cut by rivers and debris flows[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 117(1-2): 174-194.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Stock J D, Montgomery D R. 1999. Geologic constraints on bedrock river incision using the stream power law[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 104(B3): 4983-4993. |
| [34] |
Sun M, Yin A, Yan D, et al. 2018. Role of pre-existing structures in controlling the Cenozoic tectonic evolution of the eastern Tibetan plateau: New insights from analogue experiments[J]. Earth and Planetary Scienc Letters, 491:207-215.
DOI URL |
| [35] | Tan X B, Liu Y D, Lee Y H, et al. 2019. Parallelism between the maximum exhumation belt and the Moho ramp along the eastern Tibetan plateau margin: Coincidence or consequence?[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 57:73-84. |
| [36] | Tan X B, Xu X W, Lee Y H, et al. 2017. Late Cenozoic thrusting of major faults along the central segment of Longmen Shan, eastern Tibet: Evidence from low-temperature thermochronology[J]. Tectonophysics, 712:145-155. |
| [37] |
Tan X B, Lee Y H, Chen W Y, et al. 2014. Exhumation history and faulting activity of the southern segment of the Longmen Shan, eastern Tibet[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 81:91-104.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
Tan X B, Yuan R M, Xu X W, et al. 2012. Complex surface rupturing and related formation mechanisms in the Xiaoyudong area for the 2008 MW7.9 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 58:132-142.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Tan X B, Yue H, Liu Y D, et al. 2018. Topographic loads modified by fluvial incision impact fault activity in the Longmenshan thrust belt, eastern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonics, 37(9): 3001-3017.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Tapponnier P, Xu Z Q, Roger F, et al. 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 294(5547): 1671-1677.
PMID |
| [41] |
Wang E, Kirby E, Furlong K P, et al. 2012. Two-phase growth of high topography in eastern Tibet during the Cenozoic[J]. Nature Geoscience, 5(9): 640-645.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Wang M M, Zhan Y, Lu R Q, et al. 2019. The seismogenic structure of the southern segment of the Longmen Shan thrust belt, eastern Tibetan plateau, SW China: A comprehensive analysis of surface geology and deep structure[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 179:11-20.
DOI URL |
| [43] | Wang W, Godard V, Liu Z J, et al. 2021. Tectonic controls on surface erosion rates in the Longmen Shan, eastern Tibet[J]. Tectonics, 40(3): e2020TC006445. |
| [44] |
Whipple K X. 2004. Bedrock rivers and the geomorphology of active orogens[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Science, 32:151-185.
DOI URL |
| [45] | Whipple K X, Tucker G E. 1999. Dynamics of the stream-power river incision model: Implications for height limits of mountain ranges, landscape response timescales, and research needs[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 104(B8): 17661-17674. |
| [46] |
Xu X W, Wen X, Yu G H, et al. 2009. Coseismic reverse- and oblique-slip surface faulting generated by the 2008 MW7.9 Wenchuan earthquake, China[J]. Geology, 37(6): 515-518.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Ye Y J, Tan X B, Liu Y D, et al. 2022. The impact of erosion on fault segmentation in thrust belts: Insights from thermochronology and fluvial shear stress analysis(southern Longmen Shan, eastern Tibet)[J]. Geomorphology, 397:108020.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Yin A. 2010. A special issue on the great 12 May 2008 Wenchuan earthquake(MW7.9): Observations and unanswered questions[J]. Tectonophysics, 491(1): 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Zhang H P, Kirby E, Pitlick J R, et al. 2017. Characterizing the transient geomorphic response to base-level fall in the northeastern Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Earth Surface, 122(2): 546-572.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
Zhang H P, Zhang P Z, Chanmpagnac J D, et al. 2014. Pleistocene drainage reorganization driven by the isostatic response to deep incision into the northeastern Tibetan plateau[J]. Geology, 42(4): 303-306.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
Zhou Y, Wu Z H, Sun Y J, et al. 2020. Constraints on late Cenozoic tectonics in the southern Longmen Shan: Evidence from low-temperature thermochronology[J]. International Geology Review, 63(13): 1619-1633.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 郭树松, 祝意青, 徐云马, 刘芳, 赵云峰, 张国庆, 朱辉. 汶川地震前失稳过程的重力场观测证据[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1368-1380. |
| [2] | 汤井田, 杨磊, 任政勇, 胡双贵, 徐志敏. 龙门山断裂带卫星重力场特征及其发震机制[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(5): 1136-1154. |
| [3] | 李振月, 万永革, 盛书中. 米亚罗断裂活动与汶川地震序列活动的关系[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(1): 72-83. |
| [4] | 江敏, 陈九辉, Yasuto Kuwahara, Reiken Matsushita. 利用小震震源机制解研究汶川地震后龙门山断裂带中段应力场时空演化[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(2): 310-322. |
| [5] | 刘洋, 何昌荣. 龙门山断层带浅钻花岗岩中断层泥的摩擦本构参数[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(5): 917-933. |
| [6] | 万永魁, 刘峡, 沈军, 王雷, 李妍. 汶川地震前龙门山及其周缘断裂形变运动与应力累积的数值模拟[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(4): 853-868. |
| [7] | 王旭光, 李传友, 吕丽星, 董金元. 龙门山后山断裂中段汶川-茂县断裂的晚第四纪活动性分析[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(3): 572-586. |
| [8] | 闫小兵, 李自红, 赵晋泉, 扈桂让, 郭瑾. 黄河壶口逆源速率及其与韩城断裂的关系[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(4): 911-921. |
| [9] | 梁明剑, 陈立春, 冉勇康, 王虎, 李东雨. 龙门山断裂南段天全段的新活动特征与1327年天全地震的关系[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(3): 546-559. |
| [10] | 苏鹏, 田勤俭, 梁朋, 李文巧, 王林. 基于青衣江变形河流阶地研究龙门山断裂带南段的构造活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(3): 523-545. |
| [11] | 彭淼, 姜枚, 谭捍东, 李庆庆, 张立树, 许乐红, 张福彬, 唐路特. 龙门山断裂带中北段的地壳电性结构及其动力学模型[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(1): 162-175. |
| [12] | 张雷, 何昌荣. 龙门山映秀-北川断裂平溪黑色断层泥中有机质成分分析及对断层摩擦滑动性质的影响[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(3): 896-906. |
| [13] | 马胜利, 姚路, 嶋本利彦, 東郷徹宏, 侯林锋, 王羽. 岩石高速摩擦实验的进展[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(3): 814-824. |
| [14] | 王立凤, 赵国泽, 詹艳, 陈小斌, 肖骑彬, 赵凌强, 王继军, 乔亮, 韩冰. 龙门山断裂带西南端地壳电性结构[J]. 地震地质, 2014, 36(2): 302-311. |
| [15] | 李传友, 徐锡伟, 甘卫军, 闻学泽, 郑文俊, 魏占玉, 许冲, 谭锡斌, 陈桂华, 梁明剑, 李新男. 四川省芦山MS7.0地震发震构造分析[J]. 地震地质, 2013, 35(3): 671-683. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||