地震地质 ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 235-245.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2025.01.014
祝意青1)( ), 赵云峰1,2,3),*(
), 赵云峰1,2,3),*( ), 隗寿春1), 张国庆1), 刘芳1)
), 隗寿春1), 张国庆1), 刘芳1)
收稿日期:2024-01-19
修回日期:2024-03-06
出版日期:2025-02-20
发布日期:2025-04-09
通讯作者:
赵云峰
作者简介:祝意青, 男, 1962年生, 研究员, 主要研究方向为重力学与地球动力学及地震预测, E-mail: zhuyiqing@163.com。
基金资助:
ZHU Yi-qing1)( ), ZHAO Yun-feng1,2,3),*(
), ZHAO Yun-feng1,2,3),*( ), WEI Shou-chun1), ZHANG Guo-qing1), LIU Fang1)
), WEI Shou-chun1), ZHANG Guo-qing1), LIU Fang1)
Received:2024-01-19
Revised:2024-03-06
Online:2025-02-20
Published:2025-04-09
Contact:
ZHAO Yun-feng
摘要:
2022年中国南北地震带先后发生青海门源 MS6.9 和四川泸定 MS6.8 地震, 2次地震均造成严重的财产损失, 后者还造成100多人伤亡与失联。这2次地震前, 中国地震局在南北地震带开展过多期地表重力观测, 观测到震中区域地表重力正、负变化交替出现, 呈现出的显著重力异常变化具有四象限分布特征。文中回顾了对这2次地震成功的中期预测和预测依据, 2次地震的实际震中与2022年度的预测地震危险区中心距离均≤56km, 尤其是2021年度对震中位置的精准判定, 实际震中与预测震中距离均≤10km。流动重力测量是探索地震预测的主要观测手段, 建立高密度的原子重力仪绝对重力观测网络或具有良好绝对重力控制的相对重力观测网络, 开展密集的强化监测, 有可能揭示高风险区震中附近的地下结构分布特征, 提取强震、大地震孕育过程中震源变化伴随的绝对重力变化信号, 发展其地震短临预测应用与研究。
祝意青, 赵云峰, 隗寿春, 张国庆, 刘芳. 2022年青海门源MS6.9和四川泸定MS6.8 地震震中的精准判定及思考[J]. 地震地质, 2025, 47(1): 235-245.
ZHU Yi-qing, ZHAO Yun-feng, WEI Shou-chun, ZHANG Guo-qing, LIU Fang. PRECISE JUDGMENT AND THINKING ON THE 2022 MENYUAN MS6.9 AND LUDING MS6.8 EPICENTERS[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2025, 47(1): 235-245.
| 地震 | 实际震中位置 | 2021年度预测震中及震级 | 2022年度预测震中及震级 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 门源MS6.9 | 37.77°N,101.26°E | (37.8°N,101.2°E),6级 | (37.5°N,101.8°E),6级 |
| 泸定MS6.8 | 29.59°N,02.08°E | (29.6°N,102.0°E),7级 | (29.2°N,102.0°E),7级 |
表1 门源 MS6.9 地震与泸定 MS6.8 地震预测情况
Table1 Prediction of the Menyuan MS6.9 earthquake and Luding MS6.8 earthquake
| 地震 | 实际震中位置 | 2021年度预测震中及震级 | 2022年度预测震中及震级 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 门源MS6.9 | 37.77°N,101.26°E | (37.8°N,101.2°E),6级 | (37.5°N,101.8°E),6级 |
| 泸定MS6.8 | 29.59°N,02.08°E | (29.6°N,102.0°E),7级 | (29.2°N,102.0°E),7级 |
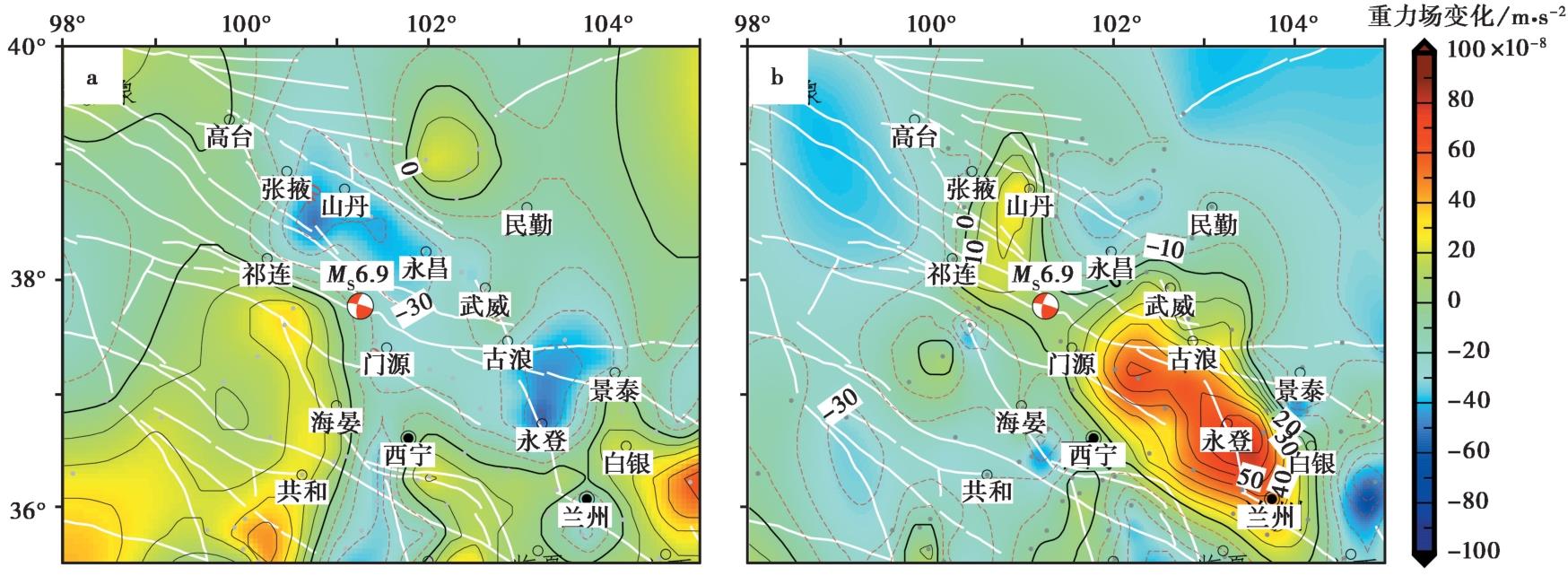
图1 门源 MS6.9 地震前区域重力场动态变化
Fig. 1 Dynamic change of the regional gravity field before the Mengyuan MS6.9 earthquake. a 2018-10—2020-10; b 2020-10—2021-07
| [1] |
郭树松, 祝意青, 徐云马, 等. 2021. 汶川地震亚失稳阶段的重力场变化研究[J]. 地震地质, 43(6): 1368—1380. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.06.002.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
江在森, 任金卫, 李志雄. 2005. 推进地震预测研究的战略对策问题[J]. 国际地震动态, 35(5): 168—173.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
江在森, 张希, 祝意青, 等. 2003. 昆仑山口西 MS8.1 地震前区域构造变形背景[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 163—172.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
马瑾. 2016. 从“是否存在有助于预报的地震先兆”说起[J]. 科学通报, 61(4-5): 409—414.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
马瑾, 郭彦双. 2014. 失稳前断层加速协同化的实验室证据和地震实例[J]. 地震地质, 36(3): 547—561. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.03.001.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
申重阳, 李辉, 孙少安, 等. 2009. 重力场动态变化与汶川 MS8.0 地震孕育过程[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(10): 2547—2557.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
申重阳, 邢乐林, 谈洪波, 等. 2012. 2010玉树 MS7.1 地震前后青藏高原东缘绝对重力变化[J]. 地球物理学进展, 27(6): 2348—2357.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
申重阳, 祝意青, 胡敏章, 等. 2020. 中国大陆重力场时变监测与强震预测[J]. 中国地震, 36(4): 729—743.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
石磊, 陈涛, 李永华. 2022. 利用重力异常分析2021年青海玛多 MS7.4 地震发震断层与结构特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 65(10): 3858—3870.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
石磊, 李永华, 张瑞青. 2021. 云南漾濞6.4级地震震源区及周边的重力均衡特征[J]. 地震地质, 43(5): 1140—1156. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.05.007.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
邢乐林, 李辉, 李建国, 等. 2016. 陆态网络绝对重力基准的建立及应用[J]. 测绘学报, 45(5): 538—543.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
易桂喜, 龙锋, 梁明剑, 等. 2023. 2022年9月5日四川泸定 MS6.8 地震序列发震构造[J]. 地球物理学报, 66(4): 1363—1384.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
袁道阳, 谢虹, 苏瑞欢, 等. 2023. 2022年1月8日青海门源 MS6.9 地震地表破裂带特征与发震机制[J]. 地球物理学报, 66(1): 229—244.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
张晶, 孙柏成. 2001. 张北 MS6.2 地震前重力异常及异常机制探讨[J]. 地震, 21(2): 75—78.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
赵云峰, 祝意青, 隗寿春, 等. 2023a. 2022年1月8日青海门源 MS6.9 地震前重力场动态变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 66(6): 2337—2351.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
赵云峰, 祝意青, 隗寿春, 等. 2023b. 基于重力数据的2022年青海门源 MS6.9 及四川泸定 MS6.8 地震预测[J]. 科学通报, 68(16): 2116—2123.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
祝意青, 付广裕, 梁伟锋, 等. 2015. 鲁甸 MS6.5、芦山 MS7.0、汶川 MS8.0 地震前区域重力场时变[J]. 地震地质, 37(1): 319—330. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.025.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
祝意青, 李铁明, 郝明, 等. 2016. 2016年青海门源 MS6.4 地震前重力变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 59(10): 3744—3752.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
祝意青, 梁伟锋, 徐云马. 2008. 重力资料对2008年汶川 MS8.0 地震的中期预测[J]. 国际地震动态, 38(7): 36—39.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
祝意青, 梁伟锋, 湛飞并, 等. 2012. 中国大陆重力场动态变化研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(3): 804—813.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
祝意青, 梁伟锋, 赵云峰, 等. 2017. 2017年四川九寨沟 MS7.0 地震前区域重力场变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(10): 4124—4131.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
祝意青, 刘芳, 张国庆, 等. 2022. 中国流动重力监测与地震预测[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 47(6): 820—829.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
祝意青, 申重阳, 张国庆, 等. 2018. 我国流动重力监测预报发展之再思考[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 38(5): 441—446.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
祝意青, 闻学泽, 孙和平, 等. 2013. 2013年四川芦山 MS7.0 地震前的重力变化[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(6): 1887—1894.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
祝意青, 徐云马, 吕弋培, 等. 2009. 龙门山断裂带重力变化与汶川8.0级地震关系研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(10): 2538—2546.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
祝意青, 张勇, 张国庆, 等. 2020. 21世纪以来青藏高原大震前重力变化[J]. 科学通报, 65(7): 622—632.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
|
| [28] |
|
| [29] |
|
| [30] |
|
| [1] | 李树鹏, 胡敏章, 祝意青, 郝洪涛, 殷海涛, 贾媛, 崔华伟, 陆汉鹏, 张刚, 王锋吉, 刘洪良. 2023年山东平原MS5.5地震前重力变化[J]. 地震地质, 2024, 46(5): 1172-1191. |
| [2] | 邱恒志, 马思远, 陈晓利. 2022年MS6.8泸定地震诱发滑坡中过剩地形的影响[J]. 地震地质, 2024, 46(4): 783-801. |
| [3] | 徐晶, 季灵运, 刘传金. 2022年泸定MS6.8地震震前区域变形背景及同震形变特征[J]. 地震地质, 2024, 46(3): 645-664. |
| [4] | 王嘉沛, 谈洪波, 李忠亚, 刘少明, 张毅, 郝洪涛, 胡敏章, 申重阳. 长宁地震前后重力变化和地壳垂直形变特征及其关系[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(4): 952-969. |
| [5] | 张文亮, 李营, 刘兆飞, 胡乐, 路畅, 陈志, 韩晓昆. 六盘山东麓断裂带土壤气体He浓度的空间分布特征及其与构造活动之间的关系[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(3): 753-771. |
| [6] | 王辽, 谢虹, 袁道阳, 李智敏, 薛善余, 苏瑞欢, 文亚猛, 苏琦. 结合野外考察的2022年门源MS6.9地震地表破裂带的高分七号影像特征[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 401-421. |
| [7] | 汪健, 张新林, 谈洪波, 胡敏章, 吴桂桔, 李忠亚, 张明辉. 木兰山重力基线场的初值测定及重力变化分析[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 553-569. |
| [8] | 朱治国, 祝意青, 王东振, 艾力夏提·玉山. 2020年伽师MS6.4地震重力与地壳形变综合分析[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 269-285. |
| [9] | 于书媛, 黄显良, 郑海刚, 李玲利, 骆佳骥, 丁娟, 范晓冉. 2022年门源MW6.7地震的同震破裂模型及应力研究[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 286-303. |
| [10] | 李昭, 付碧宏. 东昆仑断裂带玛沁-玛曲段晚第四纪构造活动特征的地貌响应定量研究[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1421-1447. |
| [11] | 郭树松, 祝意青, 徐云马, 刘芳, 赵云峰, 张国庆, 朱辉. 汶川地震前失稳过程的重力场观测证据[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1368-1380. |
| [12] | 汪健, 申重阳, 孙文科, 谈洪波, 胡敏章, 梁伟锋, 韩宇飞, 张新林, 吴桂桔, 王青华. 红河断裂带北、 中段近期重力变化及深部变形[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1537-1562. |
| [13] | 刘东, 郝洪涛, 王青华, 郑秋月, 黄江培. 2021年云南漾濞MS6.4地震前重力变化[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1157-1170. |
| [14] | 谈洪波, 王嘉沛, 杨光亮, 陈正松, 吴桂桔, 申重阳, 黄金水. 2021年玛多MS7.4地震的震后效应模拟[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 936-957. |
| [15] | 张新林, 汪健, 胡敏章, 王嘉沛, 李忠亚, 张毅. 2010-2020年云南及周缘绝对重力变化特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 972-983. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||