地震地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (4): 802-820.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2024.04.003
张雅静1)( ), 李正芳1),*(
), 李正芳1),*( ), 周本刚1), 肖海波2)
), 周本刚1), 肖海波2)
收稿日期:2023-06-15
修回日期:2024-01-26
出版日期:2024-08-20
发布日期:2024-09-23
通讯作者:
李正芳
作者简介:张雅静, 女, 1999年生, 2024年于中国地震局地质研究所获构造地质学硕士学位, 主要研究方向为发震构造的判别及三维潜在震源模型的建立, E-mail: 2440410346@qq.com。
基金资助:
ZHANG Ya-jing1)( ), LI Zheng-fang1),*(
), LI Zheng-fang1),*( ), ZHOU Ben-gang1), XIAO Hai-bo2)
), ZHOU Ben-gang1), XIAO Hai-bo2)
Received:2023-06-15
Revised:2024-01-26
Online:2024-08-20
Published:2024-09-23
Contact:
LI Zheng-fang
摘要:
通过最新的浅部地震反射剖面和钻孔资料发现了大兴凸起东缘断裂全新世活动的证据, 这一发现改变了近几十年以来认为的其晚第四纪以来没有活动的结论, 对北京市地震灾害风险普查工作具有重要的应用价值, 同时也对大兴凸起东缘断裂最大潜在地震的震级上限评估提出了新的挑战。文中通过收集和整理多条地震浅层物探剖面和地震深反射剖面, 利用SKUA-GOCAD三维建模软件构建了大兴凸起东缘断裂的三维模型, 模拟了大兴凸起东缘断裂在三维空间中的展布情况, 揭示了该断裂的几何学特征及深浅构造关系。通过将大兴凸起东缘断裂和与其呈右阶排列的夏垫断裂进行构造类比, 对大兴凸起东缘断裂深、 浅部的构造特征进行了讨论, 认为大兴凸起东缘断裂是一条深浅共存的活动断裂, 并利用震级-破裂尺度经验关系式综合估计该断裂上可能诱发的最大潜在地震为7.5级。这一结论对首都圈南部地区开展震灾防治工作具有重要的科学指导意义。
张雅静, 李正芳, 周本刚, 肖海波. 大兴凸起东缘断裂的三维建模及其最大潜在地震评估[J]. 地震地质, 2024, 46(4): 802-820.
ZHANG Ya-jing, LI Zheng-fang, ZHOU Ben-gang, XIAO Hai-bo. 3D MODELING AND MAXIMUM POTENTIAL SEISMIC ASSESS-MENT OF THE EASTERN MARGIN FAULT OF DAXING UPLIFT[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2024, 46(4): 802-820.
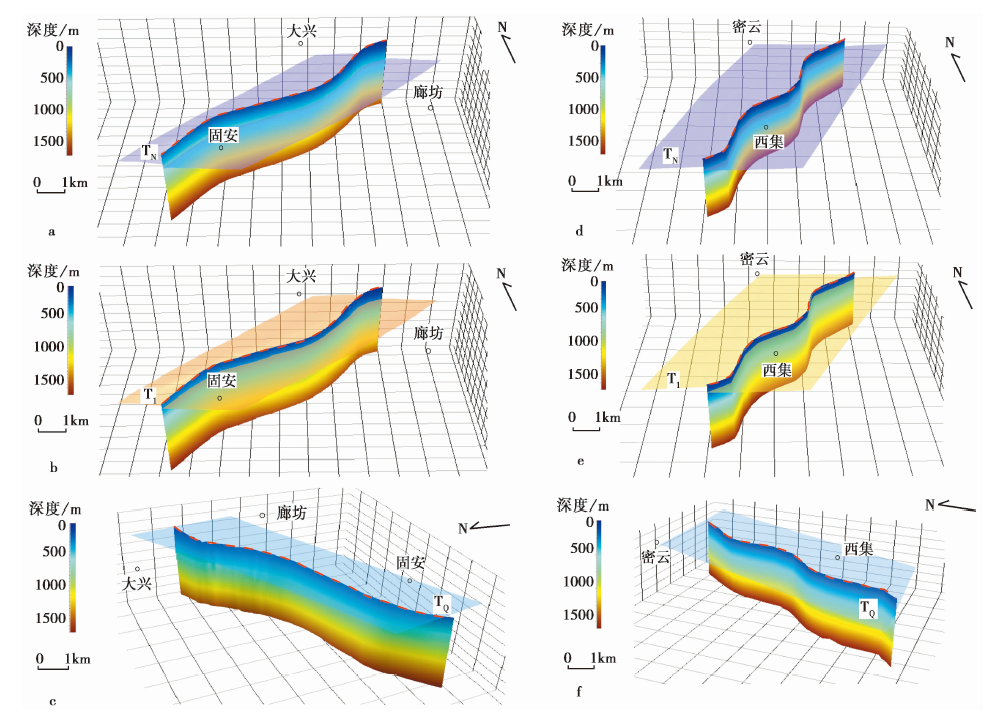
图 3 利用物探剖面构建大兴凸起东缘断裂(a—c)和夏垫断裂(d—f)的三维模型 该组图分别从不同视角展示了大兴凸起东缘断裂和夏垫断裂浅部(0~2km深度)在空间中的三维展布及切割和上覆地层情况。TQ第四系地层顶界; TN新近系地层顶界; T1第四系内部地层。图中H︰V=1︰15
Fig. 3 The 3D models of the eastern margin fault of Daxing uplift(a—c) and the Xiadian Fault(d—f) are constructed by using the shallow geophysical prospecting profile.
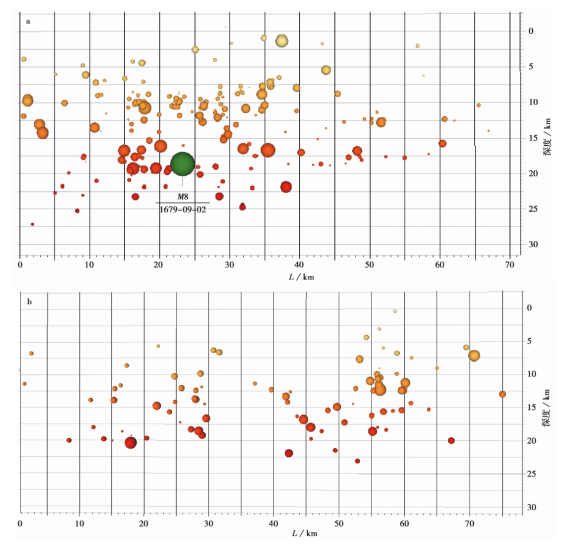
图 7 夏垫断裂(a)和大兴凸起东缘断裂(b)的小地震深度分布图
Fig. 7 Small earthquakes depth distribution map of the Xiadian Fault(a) and the eastern margin fault of Daxing uplift(b).
| [1] |
曹朋军, 夏方华, 李世斌, 等. 2021. 夏垫断裂东北段地震勘探资料研究[J]. 地震工程学报, 43(1): 56—62.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
邓梅, 沈军, 李西, 等. 2018. 夏垫断裂大胡庄探槽古地震事件分析[J]. 地震研究, 41(2): 293—301, 344.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
邓起东, 于贵华, 叶文华. 1992. 地震地表破裂参数与震级关系的研究 G//国家地震局地质研究所编. 活动断裂研究(2). 北京: 地震出版社:247—264.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 2002. 中国活动构造基本特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 32(12): 1020—1030, 1057.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
邓起东, 张裕明, 环文林, 等. 1980. 中国地震烈度区划图编制的原则和方法[J]. 地震学报, 2(1): 90—110.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
董瑞树, 冉洪流, 高铮. 1993. 中国大陆地震震级和地震活动断层长度的关系讨论[J]. 地震地质, 15(4): 395—400.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
高景华, 徐明才, 荣立新, 等. 2008. 利用地震剖面研究夏垫断裂西南段的活动性[J]. 地震地质, 30(2): 497—504.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
桂宝玲, 何登发, 闫福旺, 等. 2012. 大兴断层的三维几何学与运动学及其对廊固凹陷成因机制的约束[J]. 地学前缘, 19(5): 86—99.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
何付兵, 白凌燕, 王继明, 等. 2013. 夏垫断裂带深部构造特征与第四纪活动性讨论[J]. 地震地质, 35(3): 490—505. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2013.03.004.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
何付兵, 徐锡伟, 何振军, 等. 2020. 利用浅层地震反射剖面探测研究大兴断裂北段新近纪—第四纪的构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 42(4): 893—908. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.04.008.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
何正勤, 叶太兰, 丁志峰, 等. 2001. 城市活断层探测中的浅层地震勘探方法[J]. 国际地震动态, (3): 1—6.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
姬广军, 朱吉祥. 2019. 三维地质建模技术研究现状[J]. 科技风, (10): 109—110.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
江娃利, 侯治华, 肖振敏, 等. 2000. 北京平原夏垫断裂齐心庄探槽古地震事件分析[J]. 地震地质, 22(4): 413—422.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
李海君. 2002. 华北平原地表形变演化特征与影响因素分析研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 中国地震局工程力学研究所.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
李正芳, 李彦宝, 周本刚, 等. 2021. 北京平原大兴凸起东缘断裂全新世活动的新认识[J]. 地震地质, 43(6): 1671—1681. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.06.018.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
刘保金, 何宏林, 石金虎, 等. 2012. 太行山东缘汤阴地堑地壳结构和活动断裂探测[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(10): 3266—3276.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
刘保金, 胡平, 陈颙, 等. 2009. 北京平原西北部地壳浅部结构和隐伏活动断裂: 由地震反射剖面揭示[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(8): 2015—2025.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
刘保金, 张先康, 陈颙, 等. 2011. 三河-平谷8.0级地震区地壳结构和活动断裂研究: 利用单次覆盖深反射和浅层地震剖面[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(5): 1251—1259.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
刘保金, 张先康, 方盛明, 等. 2002. 城市活断层探测的高分辨率浅层地震数据采集技术[J]. 地震地质, 24(4): 524—532.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
刘先林, 唐正辉. 2016. 三维地质建模与数值模拟关键技术研究[J]. 西部交通科技, (5): 1—5, 9.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
龙锋, 闻学泽, 徐锡伟. 2006. 华北地区地震活断层的震级-破裂长度、 破裂面积的经验关系[J]. 地震地质, 28(4): 511—535.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
鲁人齐, 徐锡伟, 陈立春, 等. 2018. 2017 年8月8日九寨沟 MS7.0 地震构造与震区三维断层初始模型[J]. 地震地质, 40(1): 1—11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.01.001.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
马杏垣, 刘和甫, 王维襄, 等. 1983. 中国东部中、 新生代裂陷作用和伸展构造[J]. 地质学报, 57(1): 22—32.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
孟立朋, 彭远黔, 冉志杰, 等. 2019. 浅层人工地震探测揭示的夏垫断裂西南段特征[J]. 地震工程学报, 41(1): 155—161.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
牛琳琳. 2018. 京津冀地区现代构造应力场与孕震环境研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
潘懋, 方裕, 屈红刚. 2017. 三维地质建模若干基本问题探讨[J]. 地理与地理信息科学, 23(3): 1—5.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
彭白, 苏鹏, 鲁人齐, 等. 2022. 浅层人工地震和地质雷达在城市活动断层探测中的联合应用: 以鹤壁市汤东断裂为例[J]. 震灾防御技术, 17(2): 269—277.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
齐诚, 赵大鹏, 陈颙, 等. 2006. 首都圈地区地壳P波和S波三维速度结构及其与大地震的关系[J]. 地球物理学报, 49(3): 805—815.
|
|
|
|
| [29] |
冉勇康, 邓起东, 杨晓平, 等. 1997. 1679年三河-平谷8级地震发震断层的古地震及其重复间隔[J]. 地震地质, 19(3): 193—201.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
邵学钟, 张家茹, 章思亚, 等. 1993. 邢台地震区深部构造背景的地震转换波探测和研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 36(5): 609—620.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
万永魁, 沈军, 于晓辉, 等. 2014. 北京平原区夏垫活动断裂滑动速率及古地震复发间隔[J]. 防灾科技学院学报, 16(3): 38—45.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
王椿镛, 段永红, 吴庆举, 等. 2016. 华北强烈地震深部构造环境的探测与研究[J]. 地震学报, 38(4): 511—549.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
王椿镛, 王贵美, 林中洋, 等. 1993. 用深地震反射方法研究邢台地震区地壳细结构[J]. 地球物理学报, 36(4): 445—452.
|
|
|
|
| [34] |
王椿镛, 吴庆举, 段永红, 等. 2017. 华北地壳上地幔结构及其大地震深部构造成因[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 47(6): 684—719.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
王金艳, 鲁人齐, 张浩, 等. 2020. 郯庐断裂带江苏段新生界三维地质构造建模[J]. 地震学报, 42(2): 216—230.
|
|
|
|
| [36] |
王帅军, 王夫运, 张成科, 等. 2011. 北京及附近地区地壳速度结构与构造[J]. 华北地震科学, 29(2): 6—12.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
徐锡伟, 白鸾曦, 魏雷鸣, 等. 2019. 华北克拉通破坏区最新构造运动起始时间讨论[J]. 地球科学, 44(5): 1647—1660.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
薛林福, 李文庆, 张伟, 等. 2014. 分块区域三维地质建模方法[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 44(6): 2051—2058.
|
|
|
|
| [39] |
叶文华, 徐锡伟, 汪良谋. 1996. 中国西部强震的地表破裂规模与震级、 复发时问间隔关系的研究[J]. 地震地质, 18(1): 37—44.
|
|
|
|
| [40] |
殷娜, 李莹甄, 纪同娟, 等. 2021. 1679年三河-平谷8级地震地表破裂端部特征及其地质意义[J]. 地震工程学报, 43(6): 1288—1293, 1302.
|
|
|
|
| [41] |
于贵华, 徐锡伟, 柴炽章, 等. 2007. 利用活断层探测资料构建银川探测区地下三维结构模型[J]. 地震地质, 29(2): 320—329.
|
|
|
|
| [42] |
张先康, 赵金仁, 刘国华, 等. 2002. 三河-平谷8.0级大震区震源细结构的深地震反射探测研究[J]. 中国地震, 18(4): 326—336.
|
|
|
|
| [43] |
赵成彬, 刘保金, 姬计法, 等. 2013. 北京南部地壳精细结构深地震反射探测研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(4): 1168—l176.
|
|
|
|
| [44] |
赵红格, 刘池洋. 2002. 大兴断裂分段性研究[J]. 石油与天然气地质, 23(4): 368—371.
|
|
|
|
| [45] |
赵金仁, 张先康, 张成科, 等. 2004. 利用宽角反射/折射和深反射探测剖面揭示三河-平谷大震区深部结构特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 47(4): 646—653.
|
|
|
|
| [46] |
祝治平, 张建狮, 张成科, 等. 1999. 山西中南部壳幔结构的研究[J]. 地震学报, 21(1): 43—46, 48—50.
|
|
|
|
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [52] |
|
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
|
| [55] |
|
| [56] |
|
| [57] |
|
| [58] |
|
| [59] |
|
| [1] | 秦晶晶, 刘保金, 酆少英, 徐锡伟, 田一鸣, 朱国军, 左莹. 深地震反射剖面揭示沧县隆起和黄骅坳陷及邻区的地壳精细结构和构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 2024, 46(3): 608-626. |
| [2] | 田一鸣, 杨卓欣, 王志铄, 石金虎, 张扬, 谭雅丽, 张建志, 宋威, 季通宇. 新乡-商丘断裂封丘段浅部探测和第四纪活动性的初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 139-152. |
| [3] | 李倩, 宋前进, 酆少英, 姬计法, 段永红, 何银娟, 秦晶晶. 深地震反射剖面揭示的兰聊断裂带中南段深部特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 1029-1045. |
| [4] | 徐芳, 鲁人齐, 王帅, 江国焰, 龙锋, 王晓山, 苏鹏, 刘冠伸. 基于多元约束方法的2020年四川青白江MS5.1地震构造研究[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 220-237. |
| [5] | 李正芳, 李彦宝, 周本刚, 朱国军, 刘保金, 吴健. 北京平原大兴凸起东缘断裂全新世活动的新认识[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1671-1681. |
| [6] | 李正芳, 周本刚, 肖海波. 琉球-马尼拉海沟的构造背景及发震能力评估[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1381-1397. |
| [7] | 顾勤平, 许汉刚, 晏云翔, 赵启光, 李丽梅, 孟科, 杨浩, 王金艳, 蒋新, 马董伟. 郯庐断裂带新沂段地壳浅部结构和断裂活动性探测[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(4): 825-843. |
| [8] | 王浩然, 陈杰, 李涛, 李跃华, 张博譞. 北天山前陆盆地前缘西湖背斜带第四纪褶皱作用[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(4): 791-805. |
| [9] | 酆少英, 刘保金, 李倩, 袁洪克, 朱国军, 田一鸣, 王宏伟, 侯黎华, 邓小娟, 谭雅丽. 深地震反射剖面揭示的华北地块南缘地壳的精细结构[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(3): 581-594. |
| [10] | 田一鸣, 刘保金, 石金虎, 王晓谦, 酆少英, 李稳. 南阳盆地朱阳关-夏馆断裂的浅部特征及活动性[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(1): 87-96. |
| [11] | 刘保金, 曲国胜, 孙铭心, 刘亢, 赵成彬, 徐锡伟, 酆少英, 寇昆朋. 唐山地震区地壳结构和构造:深地震反射剖面结果[J]. 地震地质, 2011, 33(4): 901-912. |
| [12] | 刘保金, 杨晓平, 酆少英, 寇昆朋. 龙门山山前疑似汶川MS 8.0地震地表破裂的浅层地震反射调查[J]. 地震地质, 2008, 30(4): 906-916. |
| [13] | 马保起, 舒赛兵, 刘光勋. 山东半岛东北部新发现近EW向活断层[J]. 地震地质, 2004, 26(4): 638-644. |
| [14] | 周本刚, 冉勇康, 环文林, 冉洪流. 山东海阳断裂东石兰沟段晚更新世以来地表断错特征与最大潜在地震估计[J]. 地震地质, 2002, 24(2): 159-166. |
| [15] | 张裕明. 几个术语的含义及地震构造区最大潜在地震评价[J]. 地震地质, 1993, 15(4): 375-380. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||