地震地质 ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (2): 462-476.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2024.02.013
刘文玉1,4,5)( ), 程正璞2,3),*(
), 程正璞2,3),*( ), 年秀清4), 陈闫1), 胡钰铃4), 覃祖建4), 邵明正4)
), 年秀清4), 陈闫1), 胡钰铃4), 覃祖建4), 邵明正4)
收稿日期:2023-04-13
修回日期:2023-12-08
出版日期:2024-04-20
发布日期:2024-05-29
通讯作者:
*程正璞, 男, 1990年生, 现为中国科学技术大学地球和空间科学学院资源与环境专业在读博士研究生, 高级工程师, 主要从事地球物理研究及深部资源勘查相关工作, E-mail: 作者简介:刘文玉, 男, 1986年生, 2018年于中国科学院大学获矿床学、 岩石学和矿物学博士学位, 现为东华理工大学固体地球物理学专业讲师和吉林大学博士后, 研究方向为深部地质结构、 构造与矿产勘查, E-mail: Liujiahongsuv@sina.com。
基金资助:
LIU Wen-yu1,4,5)( ), CHENG Zheng-pu2,3),*(
), CHENG Zheng-pu2,3),*( ), NIAN Xiu-qing4), CHEN Yan1), HU Yu-ling4), QIN Zu-jian4), SHAO Ming-zheng4)
), NIAN Xiu-qing4), CHEN Yan1), HU Yu-ling4), QIN Zu-jian4), SHAO Ming-zheng4)
Received:2023-04-13
Revised:2023-12-08
Online:2024-04-20
Published:2024-05-29
摘要:
自2006年以来松原市乾安县与宁江区地震频发, 成为东北地震活动最为频繁的区域, 目前对两地的发震构造和地震成因的认识存在严重分歧, 制约了地震危险性评价与预防工作的开展。文中通过对区域重力数据进行非线性共轭梯度聚焦反演, 获得了松原震区的三维剩余密度结构, 结合石油井震资料, 获得了如下认识: 1)研究区的剩余密度异常呈高低相间的带状分布, 南部异常走向为NNW, 北部异常转变为NNE向, 该特征反映出乾安震区和宁江震区的深部孕震环境不同, 前者震源位于查干花高密度异常体内及其边缘, 后者震源位于松原低密度异常带中部, 指示两地震源位置的岩性不同; 2)两者的发震构造不相同, 前者受控于查干花断裂和乾安断裂, 后者受控于松原断裂和扶余北断裂; 3)地震的形成与区域应力, 基底结构, 深部气、 流体运移和长期油气开采等因素有关。长期注水采油破坏了地质结构和应力环境, 可能是重要的地震诱发因素。
刘文玉, 程正璞, 年秀清, 陈闫, 胡钰铃, 覃祖建, 邵明正. 基于三维剩余密度结构的松原地震成因[J]. 地震地质, 2024, 46(2): 462-476.
LIU Wen-yu, CHENG Zheng-pu, NIAN Xiu-qing, CHEN Yan, HU Yu-ling, QIN Zu-jian, SHAO Ming-zheng. GENESIS OF SONGYUAN EARTHQUAKES BASED ON 3D RESIDUAL DENSITY STRUCTURE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2024, 46(2): 462-476.
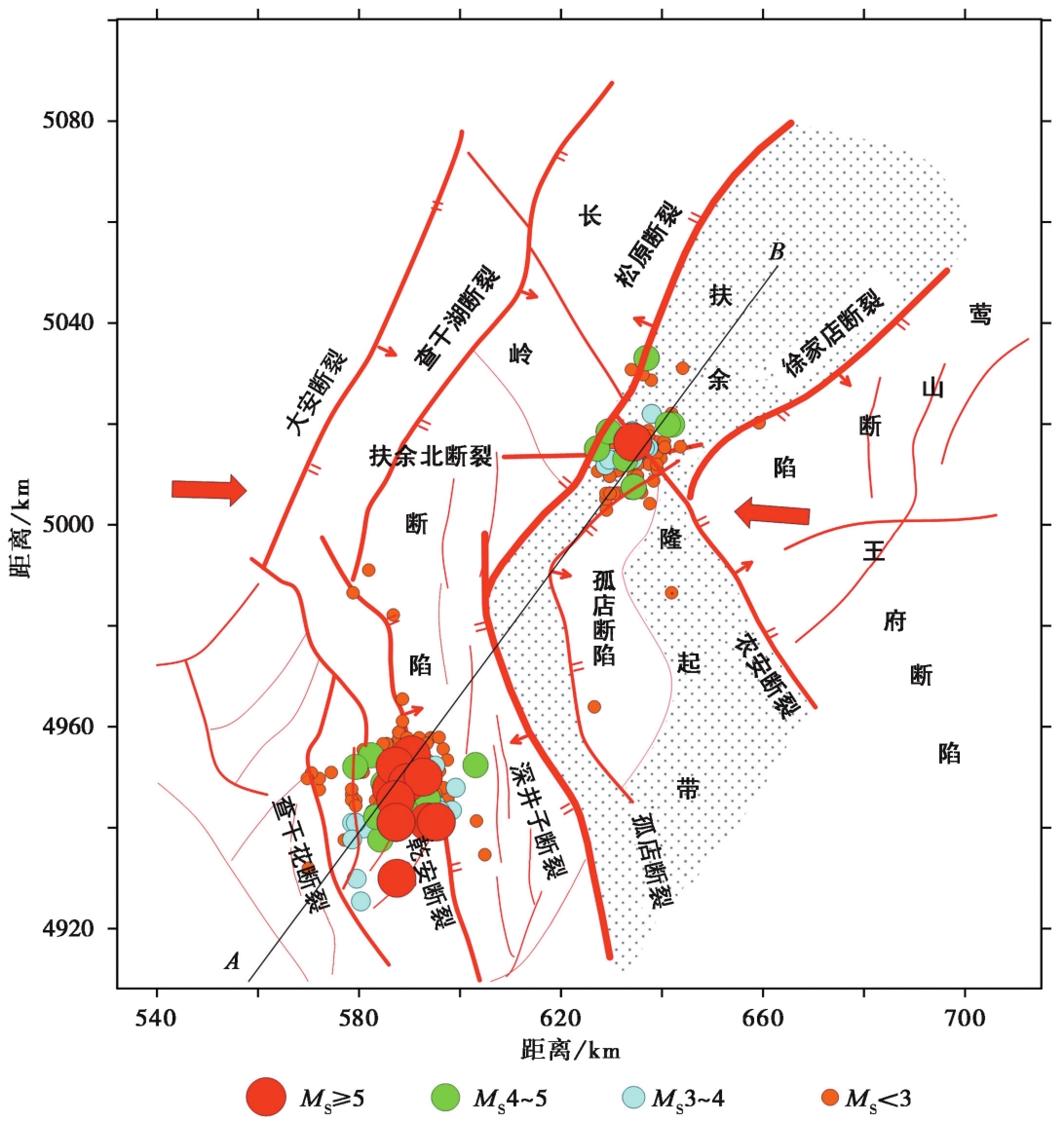
图6 研究区基底断裂构造的平面图(红色箭头为区域应力, 引自王斌, 2021)
Fig. 6 The basement fault structure in the study area(red indicates regional stress, cited from WANG Bin, 2021).
| [1] |
陈闯, 危自根, 李伟, 等. 2021. 2019-05-18松原 MS5.1 地震震源机制与地震参数分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 41(6): 584—588.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈闫. 2014. 重磁共轭梯度聚焦反演研究与应用[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 123.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
范婕. 2018. 长岭断陷龙凤山—东岭地区断-盖耦合控藏机制研究[D]. 青岛: 中国石油大学(华东): 153.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
符伟. 2019. 深反射剖面揭示的松辽盆地北部深部结构、 动力学背景与油气远景[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 113.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
高金哲, 李志伟, 包丰, 等. 2013. 2006年吉林乾安-前郭M5.0地震深度及其成因探讨[J]. 地球物理学进展, 28(5): 2328—2335.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
高立新, 戴勇, 王磊, 等. 2021. 现今中国东北地区地震活动特征与趋势探讨[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 41(5): 441—447, 453.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
韩江涛, 郭振宇, 刘文玉, 等. 2018. 松辽盆地岩石圈减薄的深部动力学过程[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(6): 2265—2279.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
姜伟, 李兆焱, 卢坤玉, 等. 2019. 5·28吉林松原地震液化特征初步分析[J]. 地震工程与工程振动, 39(3): 52—60.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
蒋雨函, 王子思, 刘佳琪, 等. 2023. 中国地震断裂带氢气观测研究现状[J]. 地震地质, 45(3): 622—637. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.03.002.
|
|
DOI |
|
| [10] |
李传友, 汪一鹏, 沈军, 等. 1999. 第二松花江断裂新活动性讨论[J]. 地震地质, 21(4): 351—360.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
李洪丽, 刘财, 田有, 等. 2021. 松原前郭地震区孕震构造的地震层析成像研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(5): 1597—1607.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [12] |
李君, 王勤彩. 2018. 2013年松原5级震群序列精定位、 震源机制解及发震构造特征[J]. 地震, 38(4): 62—73.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
李君, 王勤彩, 郑国栋, 等. 2019. 2018年5月松原 MS5.7 地震序列发震断层及应力场特征[J]. 地震学报, 41(2): 207—218.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
李平, 田兆阳, 薄景山, 等. 2019. 松原5.7级地震砂土液化研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 52(9): 91—99.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
李艳娥, 邢成起, 陈丽娟, 等. 2019. 2017—2018年吉林松原地震序列研究[J]. 地震学报, 41(4): 435—444.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
李永生, 赵谊, 李继业, 等. 2020. 2018年5月28日吉林松原 MS5.7 地震发震构造分析[J]. 地震学报, 42(1): 12—23.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
连鑫葆. 2021. 松原市区壳内电性结构及热源分析[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 61.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
梁姗姗, 徐志国, 张广伟, 等. 2019. 2019年吉林宁江 MS5.1 地震全矩张量反演及其发震机理初探[J]. 中国地震, 35(3): 488—498.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
刘爱华, 张伟, 龚飞, 等. 2018. 利用CAP方法分析吉林松原4.9级地震震源机制[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 39(6): 78—85.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
刘俊清. 2018. 吉林省西部地区典型地震活动研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 110.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
刘俊清, 刘财, 雷建设, 等. 2017. 2013年前郭 MS5.8 震群矩张量研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(9): 3418—3431.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [22] |
刘玉琢, 梁海庆, 刘建中. 1989. 我国东北地区新生代构造应力场的时空变化与地震活动[J]. 东北地震研究, 5(1): 17—24.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
吕晗. 2017. 扶余/松原-肇东断层南段地震危险性分析[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 70.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
卢燕红, 吴兆营, 丁广, 等. 2017. 吉林前郭5.8级震区上地壳速度结构[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 47(6): 1894—1903.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
盘晓东, 刘俊清, 贾若, 等. 2021. 2019年5月18日吉林松原宁江 MS5.1 地震总结[J]. 地震地磁观测与研究, 42(2): 147—148.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
盘晓东, 贾若, 康建红, 等. 2018. 2013年10月31日吉林前郭M5.8震群研究[J]. 国际地震动态, 4(472): 80—89.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
阮庆丰. 2022. 松原地区地震震群分布、 迁移和动力学机制研究[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 115.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
盛书中, 万永革, 王晓山, 等. 2017. 2013年吉林松原震群重定位及其发震构造[J]. 地学前缘, 24(2): 212—219.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [29] |
时应敏. 2012. 松辽盆地长岭断陷火山机构及天然气成藏特征研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质大学: 237.
|
|
|
|
| [30] |
唐裕, 翁爱华, 杨悦, 等. 2021. 松原地震与流体作用联系的大地电磁证据[J]. 中国科学(地球科学), 51(1): 134—149.
|
|
|
|
| [31] |
王斌. 2021. 松辽盆地现今应力环境研究[D]. 北京: 中国地质科学院: 251.
|
|
|
|
| [32] |
王亮, 李君, 顾强强, 等. 2015. 吉林松原5级震群的重新定位研究[J]. 防灾减灾学报, 31(1): 30—34.
|
|
|
|
| [33] |
王向腾, 李志伟, 邓居智, 等. 2021. 沉积盆地台网稀疏地区中等强度浅源地震起始深度测定: 以2013年前郭 MS5.8 和2016年Fairview MW5.1 地震序列为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(3): 851—863.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [34] |
尉洋, 沈军, 于晓辉, 等. 2016. 石油地震资料在隐伏活断层探测中的应用——以松原活断层探测为例[J]. 地震地质, 38(2): 423—433. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.02.015.
|
|
|
|
| [35] |
吴微微, 杨建思, 苏金蓉, 等. 2014. 2013年吉林前郭—乾安震源区中强地震矩张量反演与区域孕震环境研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(8): 2541—2554.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [36] |
向钰鉥. 2022. 松辽盆地中央古隆起带南部基岩风化壳型储层特征及油气成藏模式[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 121.
|
|
|
|
| [37] |
谢富仁, 张红艳, 崔效锋, 等. 2011. 中国大陆现代构造应力场与强震活动[J]. 国际地震动态, 385(1): 4—12.
|
|
|
|
| [38] |
薛林福, 祝铭, 李文庆, 等. 2018. 岩浆泡破裂引发地震的模式——以吉林松原2013年地震群为例[J]. 吉林大学学报(地球科学版), 48(6): 1865—1875.
|
|
|
|
| [39] |
杨宇, 雷建设, 张广伟, 等. 2019. 前郭 MS5.8 和松原 MS5.7 地震震源区地壳速度结构与孕震环境[J]. 地球物理学报, 62(11): 4259—4278.
DOI |
|
|
|
| [40] |
杨悦. 2019. 松原地震活跃区深部电性结构及其孕震机制[D]. 长春: 吉林大学: 121.
|
|
|
|
| [41] |
郁广程, 姚运生, 张丽芬, 等. 2020. 2013年吉林省松原地区MS≥5地震群成因研究[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 40(5): 534—539.
|
|
|
|
| [42] |
于晓辉. 2019. 松辽盆地东南部断裂构造活动性分析[D]. 北京: 中国地震局地质研究所: 105.
|
|
|
|
| [43] |
于晓辉, 沈军, 戴训也, 等. 2018. 生长地层揭示松原地区孤店断裂第四纪以来的构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 40(6): 1240—1253. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2018.06.004.
|
|
DOI |
|
| [44] |
张超群. 2014. 长岭断陷构造特征及其演化规律研究[D]. 大庆: 东北石油大学: 57.
|
|
|
|
| [45] |
DOI PMID |
| [46] |
DOI PMID |
| [47] |
|
| [48] |
|
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
|
| [51] |
|
| [1] | 王明亮, 张扬, 徐顺强, 徐志萍. 华北坳陷中南部深部结构大地电磁探测[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 536-552. |
| [2] | 冯向东, 岳秀霞, 王曰风, 王晓山, 刁桂苓, 张洪智, 程万正, 李悦, 冯志仁. 由向家坝水库震源机制探讨诱发地震的成因[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(2): 565-575. |
| [3] | 赵俊猛, 卢造勋, 姚长利, 黎益仕, 刘占坡. 准噶尔盆地基底断裂的重磁学研究[J]. 地震地质, 2008, 30(1): 132-143. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||