地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (5): 1112-1128.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.05.005
宋冬梅1)( ), 王慧1,2),*(
), 王慧1,2),*( ), 单新建3), 王斌1), 崔建勇1)
), 单新建3), 王斌1), 崔建勇1)
收稿日期:2022-04-06
修回日期:2022-08-10
出版日期:2023-10-20
发布日期:2023-11-23
通讯作者:
王慧, 女, 中国石油大学(华东)测绘科学与技术专业在读硕士研究生, 研究方向为遥感卫星重力场和热场的地震前兆, E-mail: 作者简介:宋冬梅, 女, 1973年生, 2003年于中国科学院沈阳应用生态研究所获理学博士学位, 教授, 主要研究方向为地震重力异常信息提取, E-mail: songdongmei@upc.edu.cn。
基金资助:
SONG Dong-mei1)( ), WANG Hui1,2),*(
), WANG Hui1,2),*( ), SHAN Xin-jian3), WANG Bin1), CUI Jian-yong1)
), SHAN Xin-jian3), WANG Bin1), CUI Jian-yong1)
Received:2022-04-06
Revised:2022-08-10
Online:2023-10-20
Published:2023-11-23
摘要:
地震作为最严重的地质灾害之一, 具有突发性和巨大的破坏性, 开展地震监测预警工作具有十分重要的意义。地表热红外辐射增强的现象是普遍存在的中强地震前兆, 目前已被作为地震监测预警与短临预报的重要参考信息。学者们对其产生的内在机理给出了多种解释。其中, 应力致热假说已被广泛接受, 并已在实验室的岩石力学加载实验中得到证实, 即岩石受力挤压时升温、 拉张时降温, 但这种地壳的挤压拉张运动和热辐射异常间的对应关系能否在野外条件下被观测到, 一直以来尚未有相关研究报道。为此, 文中采用GRACE重力和MODIS热红外2种卫星遥感数据, 以构造应力变化明显的大地震——汶川地震为时间节点开展应力致热假说的野外遥感验证研究。首先, 借助GRACE卫星反演得到的地壳质量密度进行与热红外辐射增温的比对分析; 然后, 分别采用基于最大切应变的重力异常提取方法和原地温度法获得重力异常和热异常, 并分别从时间尺度和空间尺度上检测震前重力异常和热异常的关联性, 对二者与构造断裂带的空间展布进行一致性分析, 得到以下结论: 1)应力致热假说在野外条件下能够被遥感手段验证。地壳的升温区(热偏移指数为正)与挤压区(地壳质量密度增加)、 降温区(热偏移指数为负)与拉张区(地壳质量密度减少)皆高度对应, 二者正、 负变化的一致性高达88.9%, 这为应力致热假说提供了野外观测证据。2)震前重力异常和热异常的时空变化具有较强的关联性。在时间域上, 重力异常和热异常具有较强的相关性, 主要表现为在震前3个月, 2种异常的强度同步出现了突增现象, 并同时达到最大值。在空间域上, 重力异常多出现在热偏移指数值的正、 负值交界处, 这表明重力异常和热异常的空间分布亦具有一定的关联性。此外, 2种异常多次呈现出沿断裂带分布的现象, 由此可知, 二者与构造活动皆密切相关。
宋冬梅, 王慧, 单新建, 王斌, 崔建勇. 基于汶川地震前重力场与热场关联性分析的应力致热假说的野外证明[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(5): 1112-1128.
SONG Dong-mei, WANG Hui, SHAN Xin-jian, WANG Bin, CUI Jian-yong. STRESS-INDUCED HEATING HYPOTHESIS BASED ON CORRELATION ANALYSIS OF GRAVITY AND THERMAL FIELDS BEFORE WENCHUAN EARTHQUAKE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(5): 1112-1128.
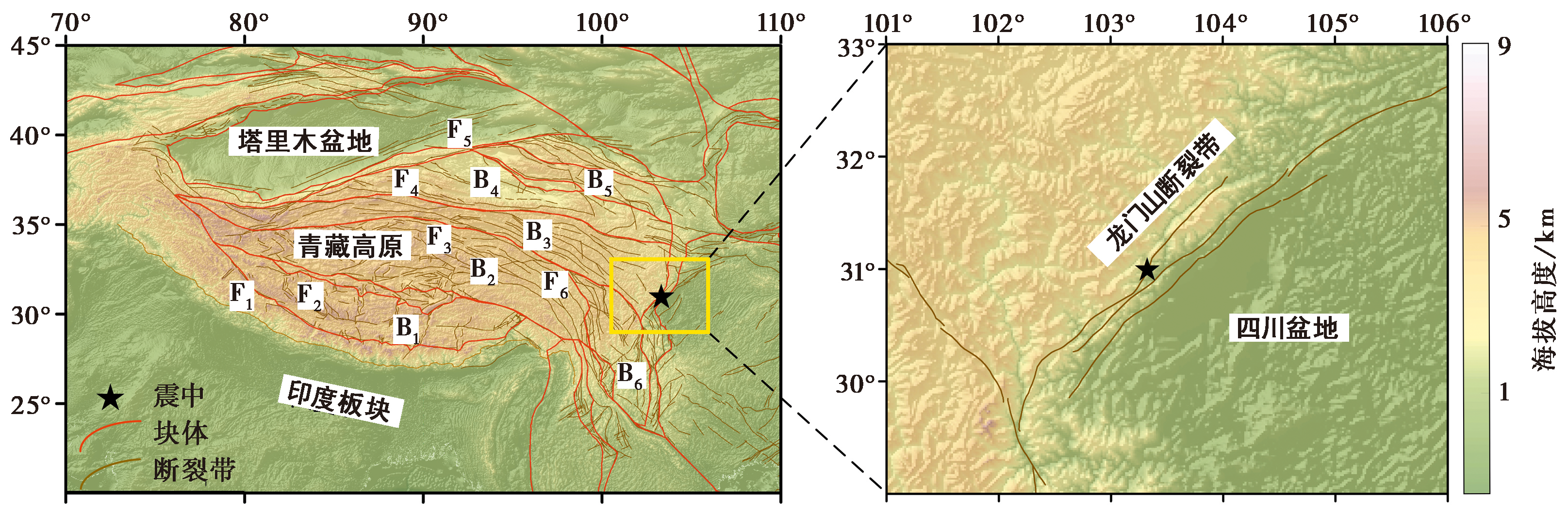
图1 龙门山断裂带(黄色矩形框内)在青藏高原上的位置 F1喜马拉雅主冲带; F2喀喇昆仑-嘉里断裂带; F3玛尼-玉树-鲜水河断裂带; F4昆仑-玛沁断裂带; F5阿尔金-海原断裂带; F6金沙江-红河断裂带。上述断裂带将青藏高原划分为6个不同的活动块体(Taylor et al., 2009), 分别是拉萨块体(B1)、 羌塘块体(B2)、 巴颜喀拉块体(B3)、 柴达木块体(B4)、 祁连块体(B5)和川滇块体(B6)
Fig. 1 The position of the Longmenshan fault zone(yellow rectangle)on the Tibetan plateau.
| 时期 | 分区 | 热偏移指数值KT | 地壳质量密度ρ/kg·m-2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KT>0 | ρ>0 | ||||
| 震前4~6个月 | 断裂带西侧 | 0.1 | 55.80% | 8.6 | 54.80% |
| 断裂带 | 0.1 | 61.70% | 16 | 71.60% | |
| 断裂带东侧 | 0.1 | 62.90% | 23.4 | 92.80% | |
| 震前1~3个月 | 断裂带西侧 | -0.3 | 21.90% | -29.8 | 3.90% |
| 断裂带 | 0.1 | 58.90% | 1 | 43.80% | |
| 断裂带东侧 | 0.2 | 67.50% | 36.1 | 79.10% | |
| 震前震后1个月 | 断裂带西侧 | 0.3 | 69.90% | -11.9 | 27.00% |
| 断裂带 | -0.1 | 44.30% | -20.2 | 31.60% | |
| 断裂带东侧 | -0.3 | 25.00% | -33 | 7.40% | |
| 热偏移指数均值和地壳质量密度均值的正负一致性: | 88.90% | ||||
| 热偏移指数均值与地壳质量密度均值的相关系数: | 0.7(P=0.03) | ||||
| 热偏移指数与地壳质量密度的正值占比的相关系数: | 0.8(P=0.02) | ||||
表1 汶川地震前龙门山断裂带区域的热偏移指数值KT和地壳质量密度的变化情况
Table 1 Variation of thermal offset index KT and crustal mass density in the Longmenshan fault zone before Wenchuan earthquake
| 时期 | 分区 | 热偏移指数值KT | 地壳质量密度ρ/kg·m-2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KT>0 | ρ>0 | ||||
| 震前4~6个月 | 断裂带西侧 | 0.1 | 55.80% | 8.6 | 54.80% |
| 断裂带 | 0.1 | 61.70% | 16 | 71.60% | |
| 断裂带东侧 | 0.1 | 62.90% | 23.4 | 92.80% | |
| 震前1~3个月 | 断裂带西侧 | -0.3 | 21.90% | -29.8 | 3.90% |
| 断裂带 | 0.1 | 58.90% | 1 | 43.80% | |
| 断裂带东侧 | 0.2 | 67.50% | 36.1 | 79.10% | |
| 震前震后1个月 | 断裂带西侧 | 0.3 | 69.90% | -11.9 | 27.00% |
| 断裂带 | -0.1 | 44.30% | -20.2 | 31.60% | |
| 断裂带东侧 | -0.3 | 25.00% | -33 | 7.40% | |
| 热偏移指数均值和地壳质量密度均值的正负一致性: | 88.90% | ||||
| 热偏移指数均值与地壳质量密度均值的相关系数: | 0.7(P=0.03) | ||||
| 热偏移指数与地壳质量密度的正值占比的相关系数: | 0.8(P=0.02) | ||||
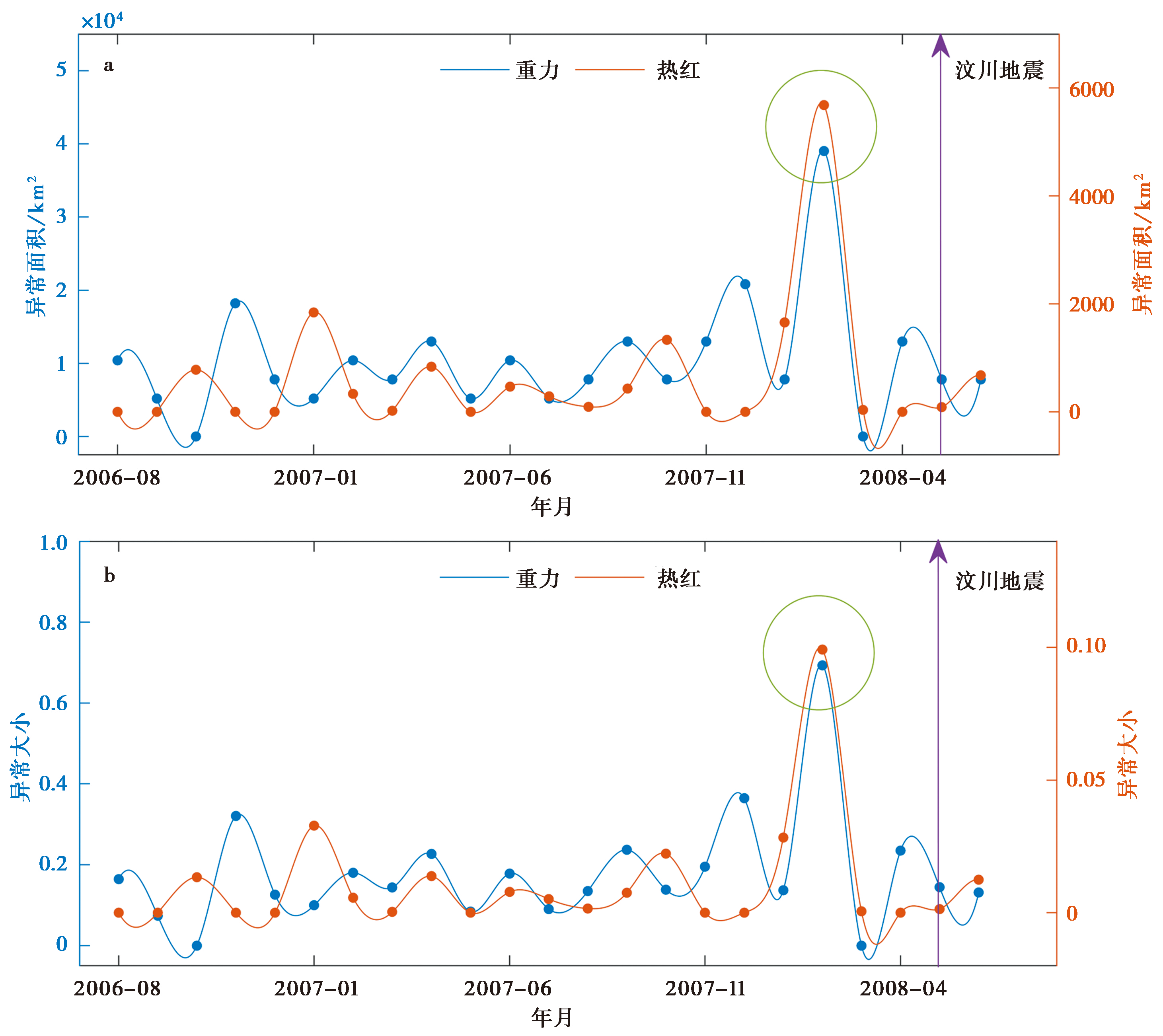
图4 汶川地震前龙门山断裂带区域的重力异常和热异常的异常强度变化情况 a 异常面积; b 异常大小
Fig. 4 The variation of gravity and thermal anomalies in the Longmenshan fault zone before the Wenchuan earthquake.
| 分析指标 | 异常面积 | 异常大小 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重力 | 热 | 重力 | 热 | |
| 显著异常出现时间 | 震前3个月 | 震前3个月 | 震前3个月 | 震前3个月 |
| 相关系数 | 0.64(P<0.01) | 0.66(P<0.01) | ||
表 2 重力异常和热异常的异常强度相关性
Table 2 Correlation of anomalous intensity between gravity anomaly and thermal anomaly
| 分析指标 | 异常面积 | 异常大小 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 重力 | 热 | 重力 | 热 | |
| 显著异常出现时间 | 震前3个月 | 震前3个月 | 震前3个月 | 震前3个月 |
| 相关系数 | 0.64(P<0.01) | 0.66(P<0.01) | ||
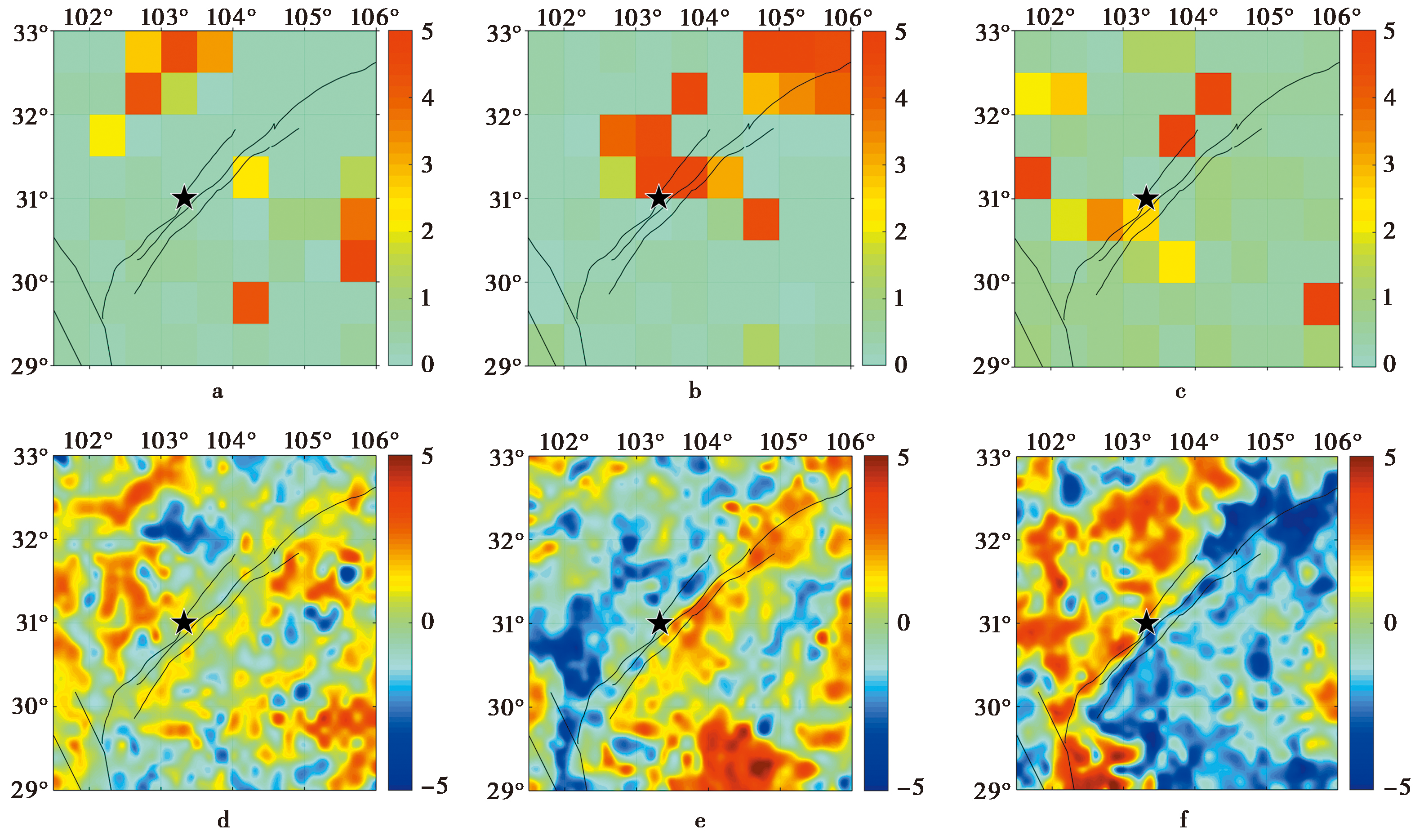
图5 龙门山断裂带上汶川地震震前半年偏移指数值KMSH和KT的时空变化结果 a—c KMSH 值分布; d—e KT值分布; 各行图幅从左至右分别表示: 震前4~6个月、 震前1~3个月和震前—震后1个月
Fig. 5 The spatio-temporal variation of the offset indexes KMSH and KT in six months before the Wenchuan earthquake on the Longmenshan fault zone.
| [1] |
陈顺云, 刘培洵, 陈立春, 等. 2020. 热测应力: 测震学证据[J]. 科学通报, 65(22): 2395—2405.
|
|
|
|
| [2] |
陈顺云, 马瑾, 刘培洵, 等. 2013. 利用Terra和Aqua卫星地表温度探索汶川地震同震热响应[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(11): 3788—3799.
|
|
|
|
| [3] |
李冲, 李建成, 黄瑞金, 等. 2015. 青藏高原东部地壳物质流变模型及汶川地震机理探讨[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 40(6): 810—815.
|
|
|
|
| [4] |
李光强. 2009. 时空异常探测理论与方法[D]. 长沙: 中南大学:1—142.
|
|
|
|
| [5] |
刘文宝, 孟庆岩, 张继超, 等. 2020. 基于偏度的地震热红外异常提取[J]. 地震地质, 42(6): 1509—1524. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.06.015.
|
|
|
|
| [6] |
刘玉国, 李欢, 郑涵, 等. 2022. 中国活动构造与地震及地质灾害的关系研究进展及展望[J]. 自然灾害学报, 31(1): 1—14.
|
|
|
|
| [7] |
钱庚, 冯蔚. 2021. 2020年全球地震灾害概要[J]. 地震科学进展, 51(7): 289—296.
|
|
|
|
| [8] |
强祖基, 孔令昌, 王弋平, 等. 1992. 地球放气、 热红外异常与地震活动[J]. 科学通报, 12(24): 53—56.
|
|
|
|
| [9] |
屈春燕, 单新建, 马瑾. 2007. 地震活动热红外异常的影响因素分析[J]. 地震研究, 30(2): 113—119.
|
|
|
|
| [10] |
瞿伟, 安东东, 张勤, 等. 2018. 智利 MW8.8 地震重力变化的GRACE观测与构造活动分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 38(6): 551—556.
|
|
|
|
| [11] |
任雅琼, 马瑾, 刘培洵, 等. 2016. 平直断层黏滑过程热场演化及失稳部位识别的实验研究[J]. 地震地质, 38(1): 65—76. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.01.005.
|
|
|
|
| [12] |
单新建, 屈春燕, 马瑾. 2005. 卫星热红外观测与发震断层不同段落交替活动特征分析[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 25(2): 58—62.
|
|
|
|
| [13] |
唐河, 孙文科. 2021. 黏弹地球地震变形理论研究进展和展望[J]. 地球与行星物理论评, 52(1): 11—26.
|
|
|
|
| [14] |
滕吉文, 马学英, 张雪梅, 等. 2017. 2015年尼泊尔 MS8.1 大地震孕育的深层过程与发生的动力学响应[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(1): 123—141.
|
|
|
|
| [15] |
王卫民, 赵连锋, 李娟, 等. 2008. 四川汶川8.0级地震震源过程[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(5): 1403—1410.
|
|
|
|
| [16] |
王武星, 顾国华, 陈石. 2014. 利用GRACE观测资料分析日本 MW9.0 地震前区域重力变化特征[J]. 地震地质, 36(2): 523—535. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.02.020.
|
|
|
|
| [17] |
吴立新, 刘善军, 吴育华, 等. 2004. 遥感-岩石力学(Ⅰ): 非连续组合断层破裂的热红外辐射规律及其构造地震前兆意义[J]. 岩石力学与工程学报, 23(1): 24—30.
|
|
|
|
| [18] |
许才军, 申文斌, 晁定波. 2006. 地球物理大地测量学原理与方法[M]. 武汉: 武汉大学出版社:193—209.
|
|
|
|
| [19] |
徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 叶建青, 等. 2008. 汶川 MS8.0 地震地表破裂带及其发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 30(3): 597—629.
|
|
|
|
| [20] |
张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等. 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12—20.
|
|
|
|
| [21] |
张璇, 张元生, 汤倩, 等. 2019. 2018年四川兴文5.7级地震及西昌5.1级地震震前红外前兆异常追踪[J]. 科学技术与工程, 19(29): 21—26.
|
|
|
|
| [22] |
张元生, 郭晓, 钟美娇, 等. 2010. 汶川地震卫星热红外亮温变化[J]. 科学通报, 55(10): 900—906.
|
|
|
|
| [23] |
祝意青, 申重阳, 刘芳, 等. 2020. 重力观测地震预测应用研究[J]. 中国地震, 36(4): 708—717.
|
|
|
|
| [24] |
祝意青, 申重阳, 张国庆, 等. 2018. 我国流动重力监测预报发展之再思考[J]. 大地测量与地球动力学, 38(5): 441—446.
|
|
|
|
| [25] |
邹正波, 李辉, 吴云龙, 等. 2016. 日本 MW9.0 地震震区及其周缘2002—2015年卫星重力变化时空特征[J]. 地震学报, 38(3): 417—428.
|
|
|
|
| [26] |
邹正波, 宋哲, 崔立鲁, 等. 2019. 重力卫星时变重力场条带误差加权平均滤波算法[J]. 科学技术与工程, 19(32): 52—57.
|
|
|
|
| [27] |
邹正波, 张毅, 谈洪波, 等. 2021. 利用重力卫星研究青海玛多及云南漾濞地震周边2002—2021年重力变化[J]. 地震地质, 43(4): 999—1012. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.04.017.
|
|
|
|
| [28] |
DOI URL |
| [29] |
DOI URL |
| [30] |
|
| [31] |
DOI URL |
| [32] |
DOI URL |
| [33] |
DOI URL |
| [34] |
DOI URL |
| [35] |
DOI |
| [36] |
|
| [37] |
|
| [38] |
DOI URL |
| [39] |
DOI URL |
| [40] |
DOI URL |
| [41] |
DOI |
| [42] |
DOI |
| [43] |
|
| [44] |
|
| [45] |
DOI URL |
| [46] |
DOI URL |
| [47] |
DOI URL |
| [48] |
DOI |
| [49] |
|
| [50] |
DOI URL |
| [51] |
DOI |
| [52] |
DOI URL |
| [53] |
|
| [54] |
DOI URL |
| [55] |
DOI URL |
| [56] |
DOI URL |
| [57] |
DOI URL |
| [58] |
DOI URL |
| [1] | 吴玮莹, 单新建, 屈春燕, 李新艳. 大地震震前热异常提取方法的对比研究--以2014年 MW6.9 于田地震为例[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1503-1520. |
| [2] | 徐志萍, 张扬, 杨利普, 徐顺强, 姜磊, 唐淋, 林吉焱. 河南省及邻区主要活动断裂的深部构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1521-1538. |
| [3] | 宋冬梅, 王慧, 单新建, 王斌, 崔建勇. 基于最大切应变的震前GRACE重力异常信息提取方法[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1539-1556. |
| [4] | 廖桂金, 叶东华, 邓志辉, 李翀, 唐国英, 胡伟明. 地震重力异常与地面沉降重力异常的特征分析[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 895-908. |
| [5] | 张国庆, 祝意青, 梁伟锋. 青藏高原东缘扶边河断裂周边地壳密度及垂向构造应力特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 578-589. |
| [6] | 王晓山, 万永革. 汶川地震前震中周围地壳应力场及应力方向集中的特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 363-377. |
| [7] | 叶轶佳, 谭锡斌, 钱黎. 通过河流剪切力获取河道侵蚀速率和基岩可蚀系数——以龙门山为例[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 115-129. |
| [8] | 郭树松, 祝意青, 徐云马, 刘芳, 赵云峰, 张国庆, 朱辉. 汶川地震前失稳过程的重力场观测证据[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(6): 1368-1380. |
| [9] | 吴桂桔, 于炳飞, 郝洪涛, 胡敏章, 谈洪波. 漾濞震区及周缘深部构造特征与发震构造[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 739-756. |
| [10] | 刘文宝, 孟庆岩, 张继超, 张颖, 卢显, 孟亚飞. 基于偏度的地震热红外异常提取[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(6): 1509-1524. |
| [11] | 兰剑, 陈晓利. 2008年MS8.0汶川地震诱发滑坡灾害在映秀地区的演化特征[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(1): 125-146. |
| [12] | 朱传华, 单新建, 张国宏, 焦中虎, 张迎峰, 李彦川, 乔鑫. 汶川地震热异常与构造应力关联的数值模拟[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(6): 1497-1510. |
| [13] | 宋冬梅, 向亮, 单新建, 尹京苑, 王斌, 崔建勇. 基于SVR模型的电离层TEC背景场构建方法[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(6): 1511-1528. |
| [14] | 汤井田, 杨磊, 任政勇, 胡双贵, 徐志敏. 龙门山断裂带卫星重力场特征及其发震机制[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(5): 1136-1154. |
| [15] | 付强, 刘天佑, 马龙, 杨宇山, 颜茂都. 基于小波变换和均衡重力异常的断裂识别——以柴达木盆地及周边地区为例[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(4): 960-978. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||