地震地质 ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 338-354.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2023.02.003
赵朋1,2)( ), 李军辉1), 陶月潮1), 疏鹏1),*(
), 李军辉1), 陶月潮1), 疏鹏1),*( ), 方震1,3)
), 方震1,3)
修回日期:2022-07-15
出版日期:2023-04-20
发布日期:2023-05-18
通讯作者:
*疏鹏, 男, 1989年生, 工程师, 主要研究方向为活动构造, E-mail: 作者简介:赵朋, 男, 1982年生, 2009年于中国地震局地质研究所获构造地质学专业硕士学位, 高级工程师, 研究方向为地震地质、地震预测, E-mail: zp20131688@163.com。
基金资助:
ZHAO Peng1,2)( ), LI Jun-hui1), TAO Yue-chao1), SHU Peng1),*(
), LI Jun-hui1), TAO Yue-chao1), SHU Peng1),*( ), FANG Zhen1,3)
), FANG Zhen1,3)
Revised:2022-07-15
Online:2023-04-20
Published:2023-05-18
摘要:
郯庐断裂带苏皖交界段处于断裂中段与南段的过渡区, 断层新活动较为复杂。近几年的研究成果显示, 在淮河南侧浮山、紫阳一带断层晚第四纪仍有较强活动, 该断层向S至女山湖的活动情况如何、晚第四纪活动是否延伸至女山湖, 是值得关注的问题。在明光女山湖北侧六谷堆村东开挖的地质探槽揭示了宽2~4m的断层变形带, 带内沿断层卷入多个棕黄色黏土团; 断层的新活动错动了上覆晚更新世黏土层, 断层面延伸至地表呈“通天”状, 地层年代数据表明其最新活动时代至少为晚更新世晚期; 断层面发育的擦痕及阶步显示断层经历过逆右旋活动。以上成果表明, 郯庐断裂带东支最为活动的断层晚第四纪的活动向S延伸至明光女山湖。泗洪-明光是郯庐断裂带中-南段的构造“节点”, 多个断层剖面存在楔状土、正断、黏土团等现象, 显示以逆走滑为主要运动方式的断层在地表局部存在丰富的伴生现象, 而产生这些现象的原因可能与断层在不同时、空所受的区域复杂应力及其变化有关。
中图分类号:
赵朋, 李军辉, 陶月潮, 疏鹏, 方震. 郯庐断裂带女山湖北侧探槽的新活动现象及讨论[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 338-354.
ZHAO Peng, LI Jun-hui, TAO Yue-chao, SHU Peng, FANG Zhen. NEW ACTIVITY PHENOMENA REVEALED BY TRENCH ON THE NORTH SIDE OF NÜSHAN LAKE IN THE TANLU FAULT ZONE AND DISCUSSION[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2023, 45(2): 338-354.
| 编号 | 采样位置 | 测量方法 | 环境剂量率/Gy·ka-1 | 年龄/ka |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGD1-1 | 南壁f2黏土团 | SMAR | 3.74±0.24 | 52.97±8.75 |
| LGD1-3 | 南壁U3层下部 | SMAR | 3.51±0.22 | 22.19±2.4 |
| LGD1-6 | 南壁U2层上部 | SMAR | 3.63±0.24 | 50.92±4.65 |
| LGD1-2-3 | 南壁U2层上部 | SMAR | 3.52±0.23 | 51.87±5.3 |
| LGD1-8 | 北壁U2层上部 | SMAR | 3.56±0.24 | 53.3±6.41 |
| LGD1-9 | 北壁f1黏土团 | SMAR | 4.25±0.28 | 52.09±6.98 |
| LGD1-10 | 北壁U3层下部 | SMAR | 4.08±0.27 | 27.12±2.26 |
表1 六谷堆探槽光释光(OSL)样品的测年结果
Table1 OSL sample dating results of Liugudui trench
| 编号 | 采样位置 | 测量方法 | 环境剂量率/Gy·ka-1 | 年龄/ka |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| LGD1-1 | 南壁f2黏土团 | SMAR | 3.74±0.24 | 52.97±8.75 |
| LGD1-3 | 南壁U3层下部 | SMAR | 3.51±0.22 | 22.19±2.4 |
| LGD1-6 | 南壁U2层上部 | SMAR | 3.63±0.24 | 50.92±4.65 |
| LGD1-2-3 | 南壁U2层上部 | SMAR | 3.52±0.23 | 51.87±5.3 |
| LGD1-8 | 北壁U2层上部 | SMAR | 3.56±0.24 | 53.3±6.41 |
| LGD1-9 | 北壁f1黏土团 | SMAR | 4.25±0.28 | 52.09±6.98 |
| LGD1-10 | 北壁U3层下部 | SMAR | 4.08±0.27 | 27.12±2.26 |
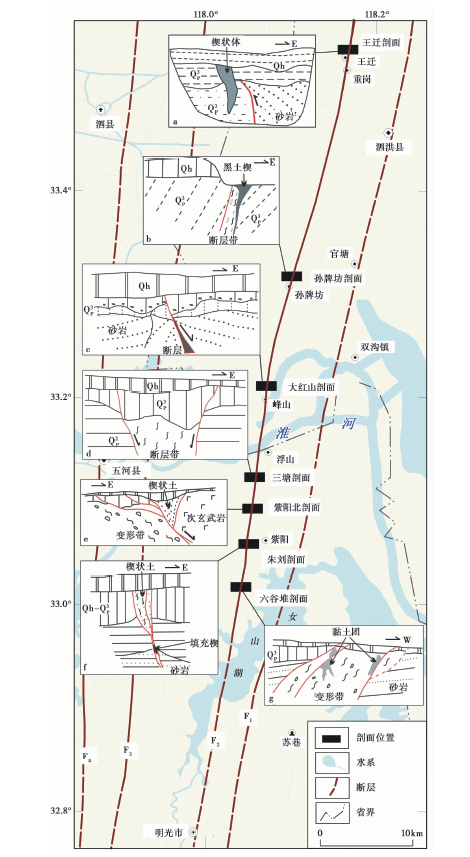
图12 郯庐带泗洪-明光段断层活动现象剖面 F1藕塘-清水涧断裂; F2池河-西山驿断裂; F3桑涧-广寒桥断裂; F4乌云山-合肥断裂
Fig. 12 Profiles of fault activity phenomena in Sihong-Mingguang section of Tanlu fault zone.
| [1] |
曹筠, 冉勇康, 许汉刚, 等. 2015. 宿迁城市活动断层探测多方法技术运用的典型案例[J]. 地震地质, 37(2): 430-439. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.02.007.
DOI |
| CAO Jun, RAN Yong-kang, XU Han-gang, et al. 2015. Typical case analysis on application of multi-method detection technique to active fault exploration in Suqian City[J]. Seismology and Geology, 37(2): 430-439. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 晁洪太, 李家灵, 崔昭文, 等. 1994. 郯庐断裂带中段全新世活断层的几何结构与分段 G∥国家地震局地质研究所编. 活动断裂研究(3). 北京: 地震出版社. |
| CHAO Hong-tai, LI Jia-ling, CUI Zhao-wen, et al. 1994. Geometry and segmentation of the Quaternary fault in the middle segment of the Tanlu fault zone [G]∥Institute of Geology, SSB(ed).Research of Active Fault (3). Seismological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 晁洪太, 李家灵, 崔昭文, 等. 1997. 郯庐断裂带潍坊-嘉山段全新世活断层的活动方式与发震模式[J]. 地震研究, 20(2): 218-226. |
| CHAO Hang-tai, LI Jia-ling, CUI Zhao-wen, et al. 1997. Mode of motion of the Holocene fault in Weifang-Jiashan segment of the Tanlu fault zone and earthquake-generating model[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 20(2): 218-226. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 方仲景, 丁梦林, 计凤桔, 等. 1980. 郯城-庐江断裂带地质活动的地质分析[J]. 地震地质, 2(4): 39-46. |
| FANG Zhong-jing, DING Meng-lin, JI Feng-ju, et al. 1980. Geological analysis of the seismicity in the Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone, East China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 2(4): 39-46. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 方仲景, 计凤桔, 向宏发, 等. 1976. 郯庐带中段第四纪断裂活动特征与地震地质条件述评[J]. 地质科学, 4: 354-366. |
| FANG Zhong-jing, JI Feng-ju, XIANG Hong-fa, et al. 1976. The characteristics of Quaternary movements along the middle segment of the old Tancheng-Lujiang fracture-zone and their seismogeologic conditions[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 4:354-366. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 高维明, 郑朗荪. 1991. 郯庐断裂带的活断层分段与潜在震源区的划分[J]. 中国地震, 7(1): 87-91. |
| GAO Wei-ming, ZHENG Lang-sun. 1991. Active fault segmentation and the identification of potential seismic zones along the Taulu Fault[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 7(1): 87-91. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 国家地震局地质研究所. 1987. 郯庐断裂[M]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| Institute of Geology, China Earthquake Administration. 1987. The Tanlu Fault Zone[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 何宏林, 宋方敏, 李传友, 等. 2004. 郯庐断裂带莒县胡家孟晏地震破裂带的发现[J]. 地震地质, 26(4): 630-637. |
| HE Hong-lin, SONG Fang-min, LI Chuan-you, et al. 2004. Hujiamengyan surface rupture in Juxian County, Shandong Province: A new discovery on the Tanlu fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 26(4): 630-637. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 侯明金, 朱光, Jacques M, 等. 2007. 郯庐断裂带(安徽段)及邻区的动力学分析与区域构造演化[J]. 地质科学, 42(4): 362-381. |
| HOU Ming-jin, ZHU Guang, Jacques M, et al. 2007. Analyzing on geodynamics and regional tectonic evolution of the Tan-Lu fault zone(Anhui segment)and its environs[J]. Chinese Journal of Geology, 42(4): 362-381. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] |
计昊旻, 李安, 张世民. 2021. 基于冲沟右旋水平位错的安丘-莒县断裂地震特征位移分析[J]. 地震地质, 43(3): 471-487. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.03.001.
DOI |
| JI Hao-min, LI An, ZHANG Shi-min. 2021. Analysis on the seismic characteristic displacement of Anqiu-Juxian Fault based on dextral horizontal dislocation of gully[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(3): 471-487. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 李家灵, 晁洪太, 崔昭文, 等. 1991. 郯庐断裂带郯城-新沂段活断层研究 G∥国家地震局地质研究所编. 活动断裂研究(1). 北京: 地震出版社: 164-173. |
| LI Jia-ling, CHAO Hong-tai, CUI Zhao-wen, et al. 1991. Researches on the active fault of the Tancheng-Xinyi segment of the Tanlu Fault [G]∥Institute of Geology, SSB(ed). Research of Active Fault (1).Seismological Press, Beijing: 164-173. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 李家灵, 晁洪太, 崔昭文, 等. 1994. 1668年郯城8.5级地震断层及其破裂机制[J]. 地震地质, 16(3): 229-237. |
| LI Jia-ling, CHAO Hong-tai, CUI Zhao-wen, et al. 1994. Seismic fault of the 1668 Tancheng earthquake(M=8.5) and its fracture mechanism[J]. Seismology and Geology, 16(3): 229-237. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 李腊月, 李玉江, 张风霜, 等. 2020. 郯庐断裂带中南段闭锁特征与地震危险性分析[J]. 地质学报, 94(2): 467-479. |
|
LI La-yue, LI Yu-jiang, ZHANG Feng-shuang, et al. 2020. Fault blocking characteristics and seismic hazard analysis in the middle and southern segments of the Tanlu fault zone[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 94(2): 467-479. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [14] | 李起彤. 1994. 郯庐断裂带江苏段全新世活动新证据 [G]∥中国地震学会地震地质专业委员会编. 中国活动断层研究. 北京: 地震出版社: 140-145. |
| LI Qi-tong. 1994. New evidence for the Holocene movement along the Jiangsu segment of the Tancheng-Lujiang Fault zone [G]∥Committee on Seismogeology, Seismological Society of China(ed). Research of Active Faults in China. Seismological Press, Beijing: 140-145. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] |
闵伟, 焦德成, 周本刚, 等. 2011. 依兰-伊通断裂全新世活动的新发现及其意义[J]. 地震地质, 33(1): 141-150. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2011.01.014.
DOI |
| MIN Wei, JIAO De-cheng, ZHOU Ben-gang, et al. 2011. The significance of discovery on Holocene activity on the Yilan-Yitong Fault in Northeast China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 33(1): 141-150. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] |
秦晶晶, 刘保金, 王志才, 等. 2022. 利用地震反射剖面探测研究安丘-莒县断裂板泉段的浅部构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 44(2): 349-362. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.02.005.
DOI |
| QIN Jing-jing, LIU Bao-jin, WANG Zhi-cai, et al. 2022. Research on shallow structural characteristics in the Banquan segment of Anqiu-Juxian fault zone based on shallow seismic reflection profiling[J]. Seismology and Geology, 44(2): 349-362. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] |
沈小七, 姚大全, 郑海刚, 等. 2015. 郯庐断裂带重岗山-王迁段晚更新世以来的活动习性[J]. 地震地质, 37(1): 139-148. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.01.011.
DOI |
| SHEN Xiao-qi, YAO Da-quan, ZHENG Hai-gang, et al. 2015. The research on activity behavior of Chonggangshan-Wangqian segment of Tan-Lu fault zone since late Pleistocene[J]. Seismology and Geology, 37(1): 139-148. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 宋方敏, 杨晓平, 何宏林, 等. 2005. 山东安丘-莒县断裂小店子-茅埠段新活动及其定量研究[J]. 地震地质, 27(2): 200-211. |
| SONG Fang-min, YANG Xiao-ping, HE Hong-lin, et al. 2005. Quantitative analysis of recent activity of the Xiaodianzi-Maobu segment of the Anqiu-Juxian Fault, Shandong Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 27(2): 200-211. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] |
孙业君, 黄耘, 刘泽民, 等. 2021. 郯庐断裂带苏鲁皖段及邻区构造应力场特征及其动力学意义[J]. 地震地质, 43(5): 1188-1207. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.05.010.
DOI |
| SUN Ye-jun, HUANG Yun, LIU Ze-min, et al. 2021. Characteristics of tectonic stress field and dynamic significance in the Shandong-Jiangsu-Anhui segment of Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone and its adjacent areas[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(5): 1188-1207. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 汤有标, 姚大全. 1990. 郯庐断裂带赤山段晚更新世以来的活动性[J]. 中国地震, 6(2): 63-69. |
| TANG You-biao, YAO Da-quan. 1990. Activity since late Pleistocene on Chishan segment of the Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 6(2): 63-69. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 王志才, 贾荣光, 孙昭民, 等. 2005. 沂沭断裂带安丘-莒县断裂安丘-朱里段几何结构与活动特征[J]. 地震地质, 27(2): 212-220. |
| WANG Zhi-cai, JIA Rong-guang, SUN Zhao-min, et al. 2005. Geometry and activity of the Anqiu-Zhuli segment of the Anqiu-Juxian Fault in the Yishu fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 27(2): 212-220. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] |
杨源源, 赵朋, 郑海刚, 等. 2017. 郯庐断裂带安徽紫阳山段发现全新世活动证据[J]. 地震地质, 39(4): 644-655. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.04.002.
DOI |
| YANG Yuan-yuan, ZHAO Peng, ZHENG Hai-gang, et al. 2017. Evidence of Holocene activity discovered in Anhui Ziyangshan segment of Tanlu fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(4): 644-655. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] |
余中元, 张培震, 闵伟, 等. 2016. 依兰-伊通断裂带尚志段晚全新世以来的强震复发间隔: 来自古地震与历史文献的约束[J]. 地震地质, 38(4): 844-861. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2016.04.004.
DOI |
| YU Zhong-yuan, ZHANG Pei-zhen, MIN Wei, et al. 2016. Late Holocene average recurrence interval of great earthquakes of Shangzhi part of the Yilan-Yitong fault zone, NE China: Constraints from paleo-earthquakes and historical written records[J]. Seismology and Geology, 38(4): 844-861. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 翟炳松, 侍继成, 杨一冲. 1992. 郯庐断裂带泗洪段全新世活动性初步研究[J]. 地震, (5): 61-64. |
| ZHAI Bing-song, SHI Ji-cheng, YANG Yi-chong. 1992. Preliminary research on recent activity along Sihong segment of Tan-Lu fault zone[J]. Earthquake, (5): 61-64. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] |
张鹏, 李丽梅, 冉勇康, 等. 2015. 郯庐断裂带安丘-莒县断裂江苏段晚第四纪活动特征研究[J]. 地震地质, 37(4): 1162-1176. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2015.04.018.
DOI |
| ZHANG Peng, LI Li-mei, RAN Yong-kang, et al. 2015. Research on characteristics of late Quaternary activity of the Jiangsu segment of Anqiu-Juxian Fault in the TanLu fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 37(4): 1162-1176. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] |
张鹏, 张媛媛, 李丽梅, 等. 2019. 郯庐断裂带安丘-莒县断裂江苏段全新世活动的新证据[J]. 地震地质, 41(3): 576-586. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2019.03.003.
DOI |
| ZHANG Peng, ZHANG Yuan-yuan, LI Li-mei, et al. 2019. New evidences of Holocene activity in the Jiangsu segment of Anqiu-Juxian Fault of the Tanlu fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 41(3): 576-586. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] |
赵朋, 姚大全, 杨源源, 等. 2017. 郯庐断裂带安徽浮山段晚第四纪以来活动新发现[J]. 地震地质, 39(5): 889-903. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.05.002.
DOI |
| ZHAO Peng, YAO Da-quan, YANG Yuan-yuan, et al. 2017. A new discovery of activity of Fushan section of the Tan-Lu fault zone in the late Quaternary[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(5): 889-903. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] |
赵朋, 姚大全, 郑海刚, 等. 2018. 郯庐断裂带安徽明光段紫阳山探槽及其意义[J]. 中国地震, 34(4): 642-651. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2017.03.008.
DOI |
| ZHAO Peng, YAO Da-quan, ZHENG Hai-gang, et al. 2018. The Ziyang Hill trenches in the Anhui Mingguang section of the Tan-Lu fault zone and their significance[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 34(4): 642-651. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] |
朱艾斓, 徐锡伟, 王鹏, 等. 2018. 以精定位背景地震活动与震源机制解研究郯庐断裂带中南段现今活动习性[J]. 地学前缘, 25(1): 218-226.
DOI |
| ZHU Ai-lan, XU Xi-wei, WANG Peng, et al. 2018. The present activity of the central and southern segments of the Tancheng-Lujiang fault zone evidenced from relocated microseismicity and focal mechanisms[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 25(1): 218-226. (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | Min W, Liu Y G, Jiao D C, et al. 2013. Evidence for Holocene activity of the Yilan-Yitong Fault, northeastern section of the Tan-Lu fault zone in Northeast China[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 67-68: 207-216. |
| [31] |
Wang Z C, Deng Q D, Du X S, et al. 2006. Active fault survey on the Tanlu fault zone in Laizhou Bay[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 19(5): 530-541.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 郑海刚, 姚大全, 赵朋, 杨源源, 黄金水. 郯庐断裂带赤山段全新世新活动的特征[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 127-138. |
| [2] | 杨源源, 李鹏飞, 路硕, 疏鹏, 潘浩波, 方良好, 郑海刚, 赵朋, 郑颖平, 姚大全. 郯庐断裂带中段F5断裂淮河-女山湖段的古地震与垂直滑动速率[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1365-1383. |
| [3] | 秦晶晶, 刘保金, 王志才, 酆少英, 邓小娟, 花鑫升, 李倩. 利用地震反射剖面探测研究安丘-莒县断裂板泉段的浅部构造特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 349-362. |
| [4] | 孙业君, 黄耘, 刘泽民, 郑建常, 江昊琳, 李婷婷, 叶青, 方韬. 郯庐断裂带鲁苏皖段及邻区构造应力场特征及其动力学意义[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1188-1207. |
| [5] | 常祖峰, 常昊, 李鉴林, 毛泽斌, 臧阳. 维西-乔后断裂全新世活动与古地震[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 881-898. |
| [6] | 计昊旻, 李安, 张世民. 基于冲沟右旋水平位错的安丘-莒县断裂地震特征位移分析[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(3): 471-487. |
| [7] | 顾勤平, 康清清, 张鹏, 孟科, 吴珊珊, 李正楷, 王俊菲, 黄群, 蒋新, 李大虎. 郯庐断裂带中南段及邻区Rayleigh波相速度与方位各向异性[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(5): 1129-1152. |
| [8] | 魏勇, 许强, 董秀军, 郭鹏, 李松林, 李骅锦. 近景摄影测量在探槽地质信息获取中的应用——以泾阳南塬庙店4#滑坡为例[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(5): 1240-1254. |
| [9] | 顾勤平, 许汉刚, 晏云翔, 赵启光, 李丽梅, 孟科, 杨浩, 王金艳, 蒋新, 马董伟. 郯庐断裂带新沂段地壳浅部结构和断裂活动性探测[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(4): 825-843. |
| [10] | 章鑫, 杜学彬. 郯庐断裂带南段对近地表大地电流的分异性[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(4): 909-922. |
| [11] | 郑颖平, 杨晓平, 疏鹏, 路硕, 方良好, 石金虎, 黄雄南, 刘春茹. 合肥盆地中郯庐断裂带西支乌云山-合肥断裂最新活动特征[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(1): 50-64. |
| [12] | 张继红, 赵国泽, 董泽义, 王立凤, 韩冰, 王庆林, 唐廷梅, 王梅. 郯庐断裂带安丘、莒县电磁台地壳电性结构研究[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(5): 1239-1253. |
| [13] | 张鹏, 张媛媛, 李丽梅, 蒋新, 孟科. 郯庐断裂带安丘-莒县断裂江苏段全新世活动的新证据[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(3): 576-586. |
| [14] | 李西, 冉勇康, 吴富峣, 马兴全, 张彦琪, 曹筠. 小江断裂带西支晚第四纪强震破裂特征[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(6): 1179-1203. |
| [15] | 庞炜, 张波, 何文贵, 吴明. 金塔南山断裂中东段古地震特征初步研究[J]. 地震地质, 2018, 40(4): 801-817. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||