地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1648-1666.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.06.017
李传友1)( ), 孙凯1), 马骏1), 李俊杰1), 梁明剑2), 房立华3)
), 孙凯1), 马骏1), 李俊杰1), 梁明剑2), 房立华3)
收稿日期:2022-12-04
修回日期:2022-12-14
出版日期:2022-12-20
发布日期:2023-01-21
作者简介:李传友, 男, 1971年生, 研究员, 主要从事活动构造与古地震研究, E-mail: chuanyou@ies.ac.cn。
基金资助:
LI Chuan-you1)( ), SUN Kai1), MA Jun1), LI Jun-jie1), LIANG Ming-jian2), FANG Li-hua3)
), SUN Kai1), MA Jun1), LI Jun-jie1), LIANG Ming-jian2), FANG Li-hua3)
Received:2022-12-04
Revised:2022-12-14
Online:2022-12-20
Published:2023-01-21
摘要:
2022年9月5日12时52分, 川滇活动地块东边界的四川泸定地区发生6.8级强烈地震。在震中以北15km、 以南25km的范围内开展震后现场考察, 发现湾东村、 幸福村、 爱国村一带的磨西断裂沿线存在同震地表破裂迹象, 而在震中以北、 爱国村以南断裂通过的位置没有发育同震地表破裂。野外调查获得的同震地表破裂走向为320°~355°, 运动性质为左旋走滑, 位移量为20~30cm, 运动性质和走向与震源机制解获得的结果一致。深入分析认为, 本次四川泸定6.8级地震的同震地表破裂主要发育在泸定县磨西镇二台子以南-石棉县王岗坪乡爱国村之间, 长度为15.5km。根据野外地质调查结果, 并综合地震反演和形变观测已有结果等判定, 四川泸定6.8级地震的发震构造为鲜水河断裂的南东段, 即磨西断裂。结合余震分布时空演化特征分析进一步揭示, 以磨西断裂二台子-新民乡段为主震破裂段的运动导致了此次6.8级地震的发生, 并触发了震中以北的南门关-两河口段断裂的活动。泸定6.8级地震是一次主震破裂段发动、 其后全段参与的较为复杂的事件。
中图分类号:
李传友, 孙凯, 马骏, 李俊杰, 梁明剑, 房立华. 四川泸定6.8级地震--鲜水河断裂带磨西段局部发起、 全段参与的一次复杂事件[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1648-1666.
LI Chuan-you, SUN Kai, MA Jun, LI Jun-jie, LIANG Ming-jian, FANG Li-hua. THE 2022 M6.8 LUDING EARTHQUAKE: A COMPLICATED EVENT BY FAULTING OF THE MOXI SEGMENT OF THE XIANSHUIHE FAULT ZONE[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(6): 1648-1666.
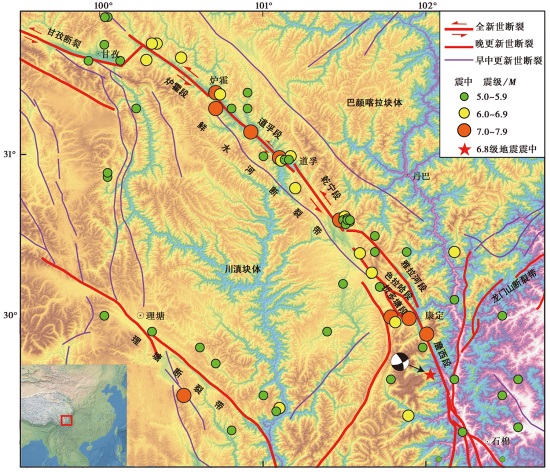
图 1 泸定6.8级地震的震中位置及其周边主要断裂构造 震源机制解据徐泰然等(2022), 红色五角星为泸定6.8级地震震中, 左下角图示断裂带的构造位置
Fig. 1 Map showing the location of the epicenter of the M6.8 Luding earthquake and major faults around the epicenter.
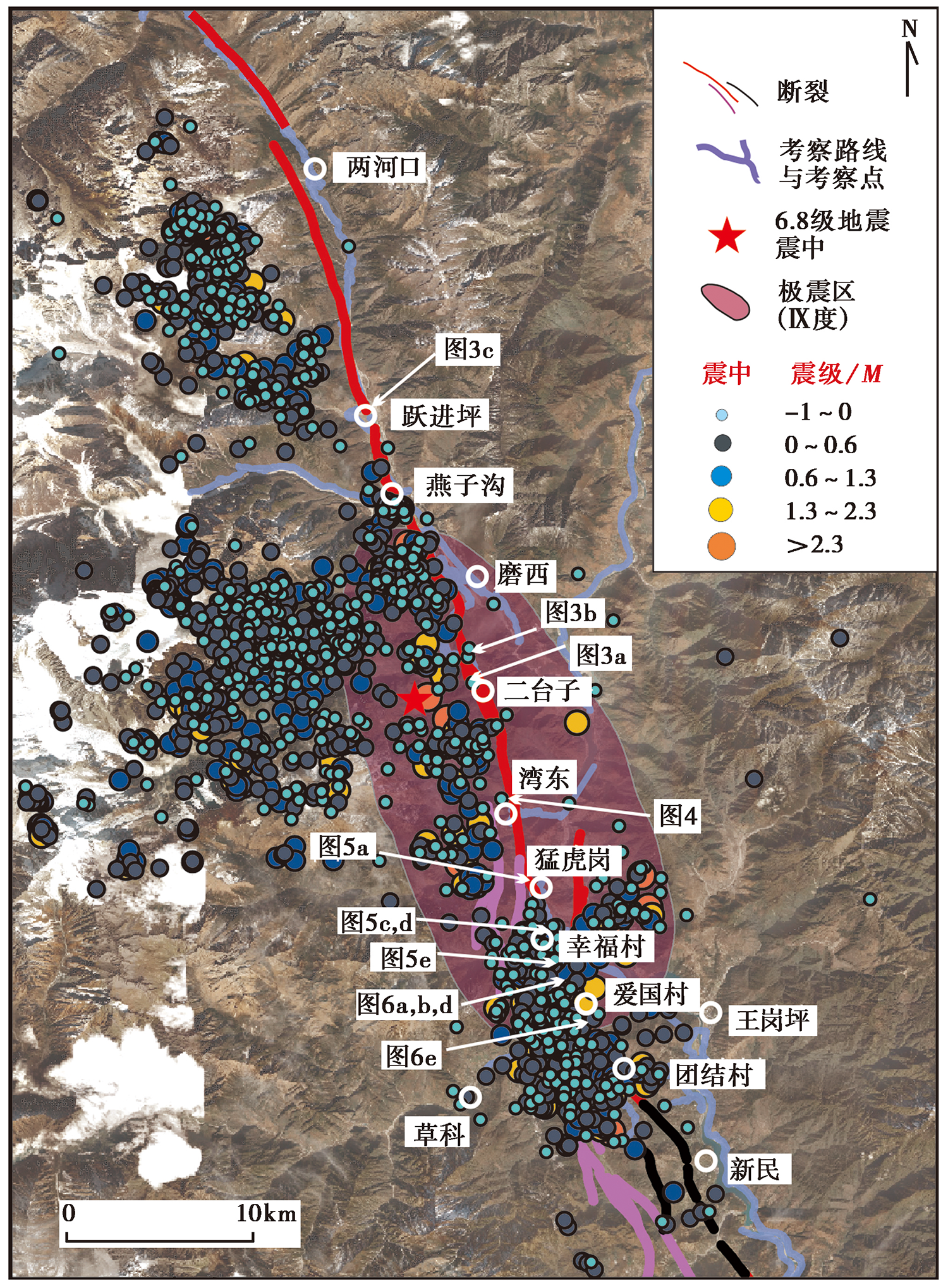
图 2 泸定地震现场考察点、 断裂展布与余震分布图 余震精定位数据截至2022年9月11日8时, 断裂迹线据陈桂华等(2018)
Fig. 2 Maps showing field observation sites, fault geometry and aftershock distribution.
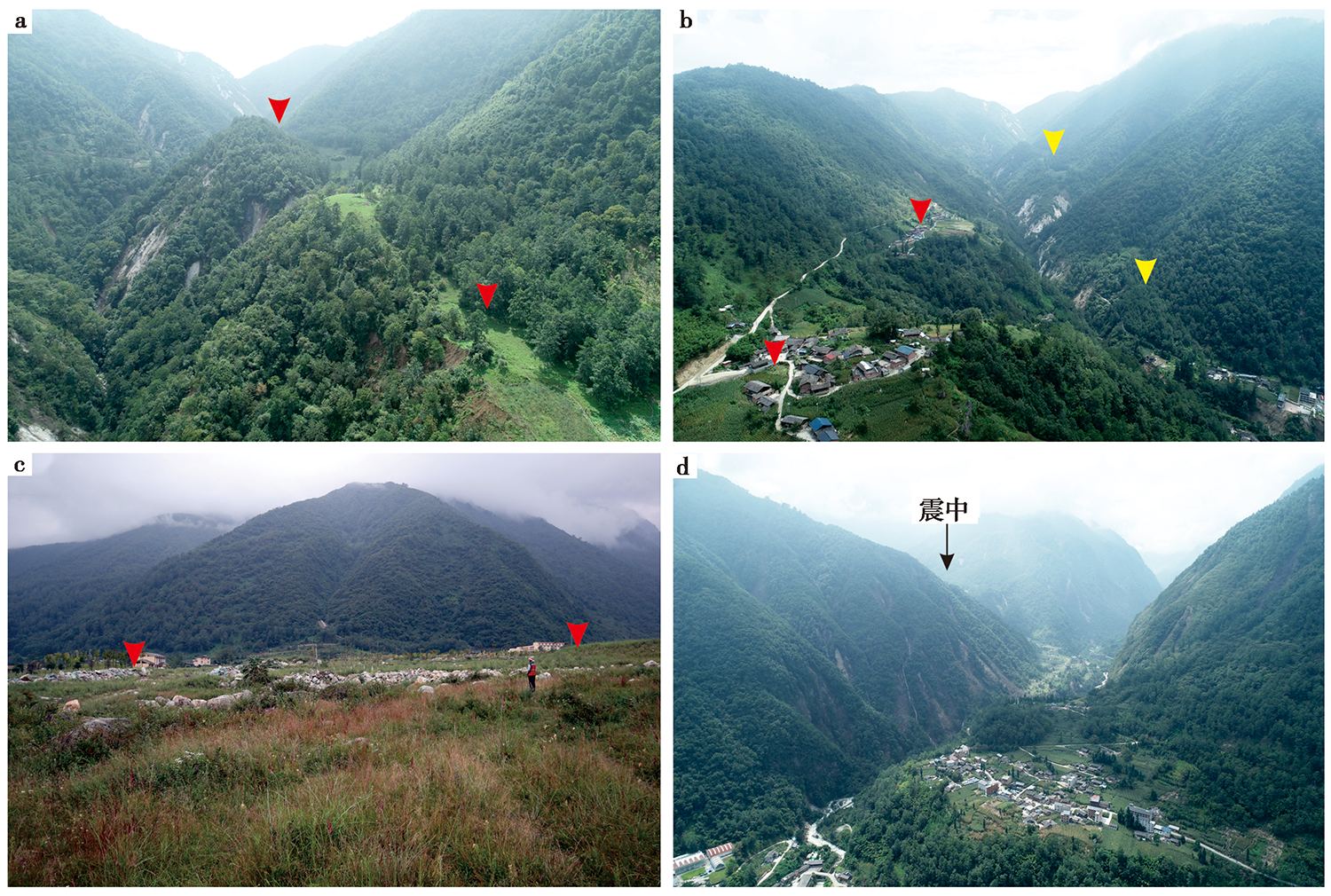
图 3 震中附近及以北磨西断裂沿线的震后地貌特征 a 海螺沟二台子附近的断裂槽谷地貌, 镜向SE; b 柏秧坪-二台子附近的断裂地貌, 断裂在此处右阶斜列, 镜向SE; c 跃进坪附近的NW向断裂陡坎, 镜向SW; d 海螺沟内震中附近的地貌, 镜向W。注意断裂地貌都没有显示同震地表破裂与变形,箭头指示断裂位置, 位置见图2
Fig. 3 Photographs showing fault expression and geomorphic features of the Moxi Fault along the section around and north of the epicenter.

图 4 湾东村一带的同震地表变形 a 湾东村北的NW向新鲜陡坎, 镜向SW; b 一系列滑坡形成的、 呈线性排列的三角面, 镜向NW; c 图a陡坎东南侧的坡面裂缝, 镜向SE; d 断裂坡折、 冲沟左旋地貌, 镜向SW; e 断裂沿线的同震滑坡与垮塌, 镜向W; f 湾东村内路面右阶斜列的裂缝, 镜向SE; g 断裂沿线的冲沟与山体左旋位错形成的闸门脊等地貌。红色箭头指示断裂和地表裂缝, 位置见图2
Fig. 4 Co-seismic deformation along the Moxi Fault around Wandong village.

图 5 猛虎岗-幸福村一带的地表同震变形 a 猛虎岗垭口同震滑坡与可能的地表破裂位置, 镜向W, 黄色箭头与红色虚线指示可能的破裂位置; b 猛虎岗南-幸福村间的同震地表变形与断裂地貌, 镜向SE; c 幸福村北公路边的同震地表破裂与变形, 镜向SE, 注意公路边缘被左旋位错约30cm; d 图c所处位置的断裂地貌, 镜向N; e 幸福村南断裂破碎带和同震滑坡地貌特征, 镜向SE; 箭头指示断裂, 位置见图2
Fig. 5 Co-seismic deformation along the Moxi Fault from the mountain pass of Menghugang to Xingfucun village.

图 6 爱国村一带的地表同震变形与磨西断裂沿线的地貌特征 a 爱国村北公路边的同震地表破裂与变形, 镜向SE; b 爱国村北河流阶地上的同震地表裂缝与断裂地貌, 镜向NW; c 潘家沟坪桥的同震左旋位移, 镜向N, 注意此处桥体2处发生左旋位错; d 图a、 b和c所处位置的断裂地貌, 镜向NW; e 爱国村附近断裂通过位置的地貌, 没有地表破裂与变形, 注意爱国村附近及以南无滑坡, 而爱国村北断裂沿线滑坡严重, 镜向NW。箭头指示断裂位置, 位置见图2
Fig. 6 Co-seismic deformation and geomorphic features along the Moxi Fault around Aiguo village.
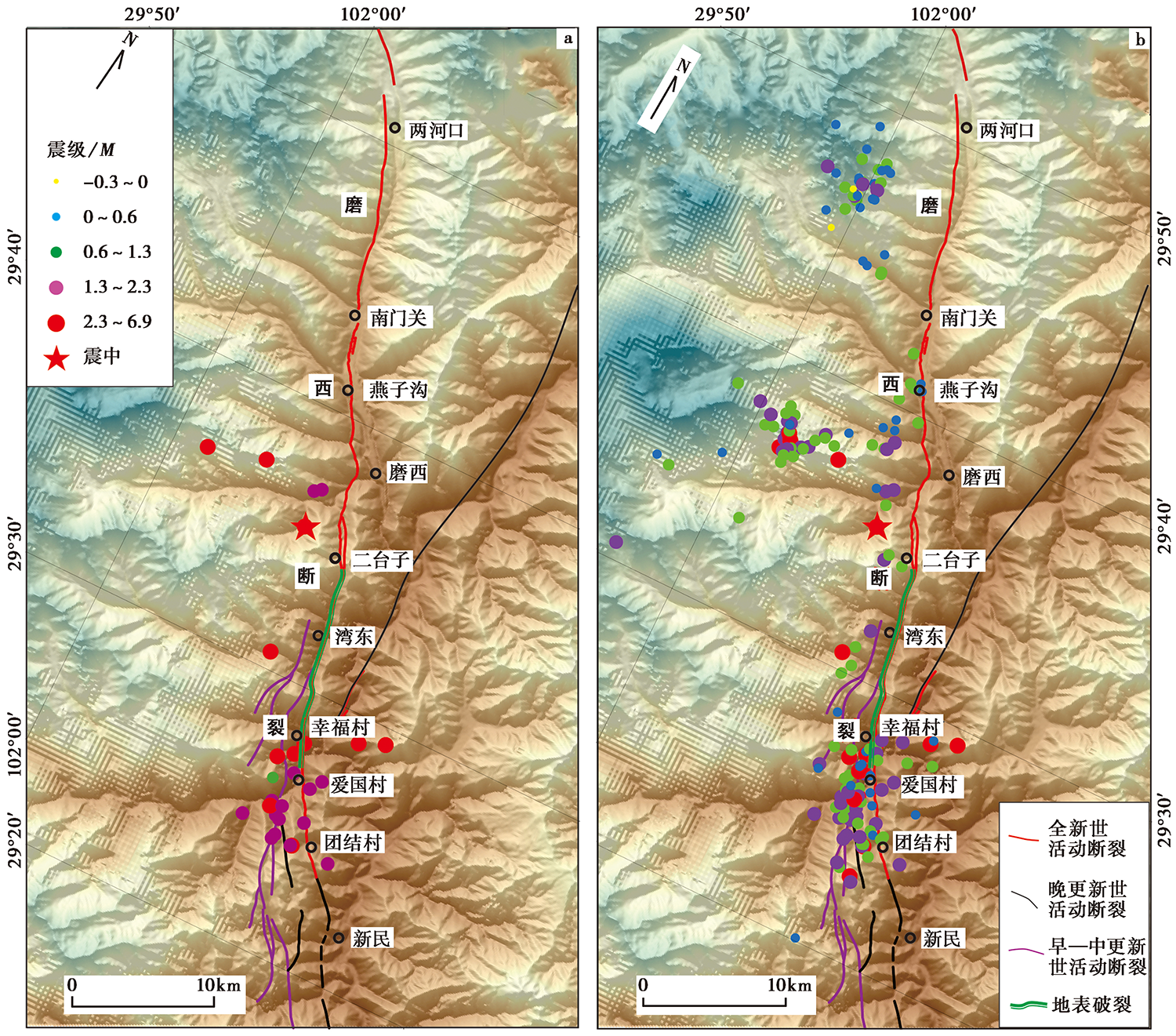
图 7 泸定6.8级地震余震分布的时-空变化特征 a 早期余震分布特征(2022年9月5日14:00以前); b 2022年9月5日19:15前的余震分布特征。 断裂迹线展布据陈桂华等(2018), 绿色粗线条指示主震破裂范围
Fig. 7 Spatio-temporal evolution of the aftershock distribution associated with the MS6.8 Luding earthquake.
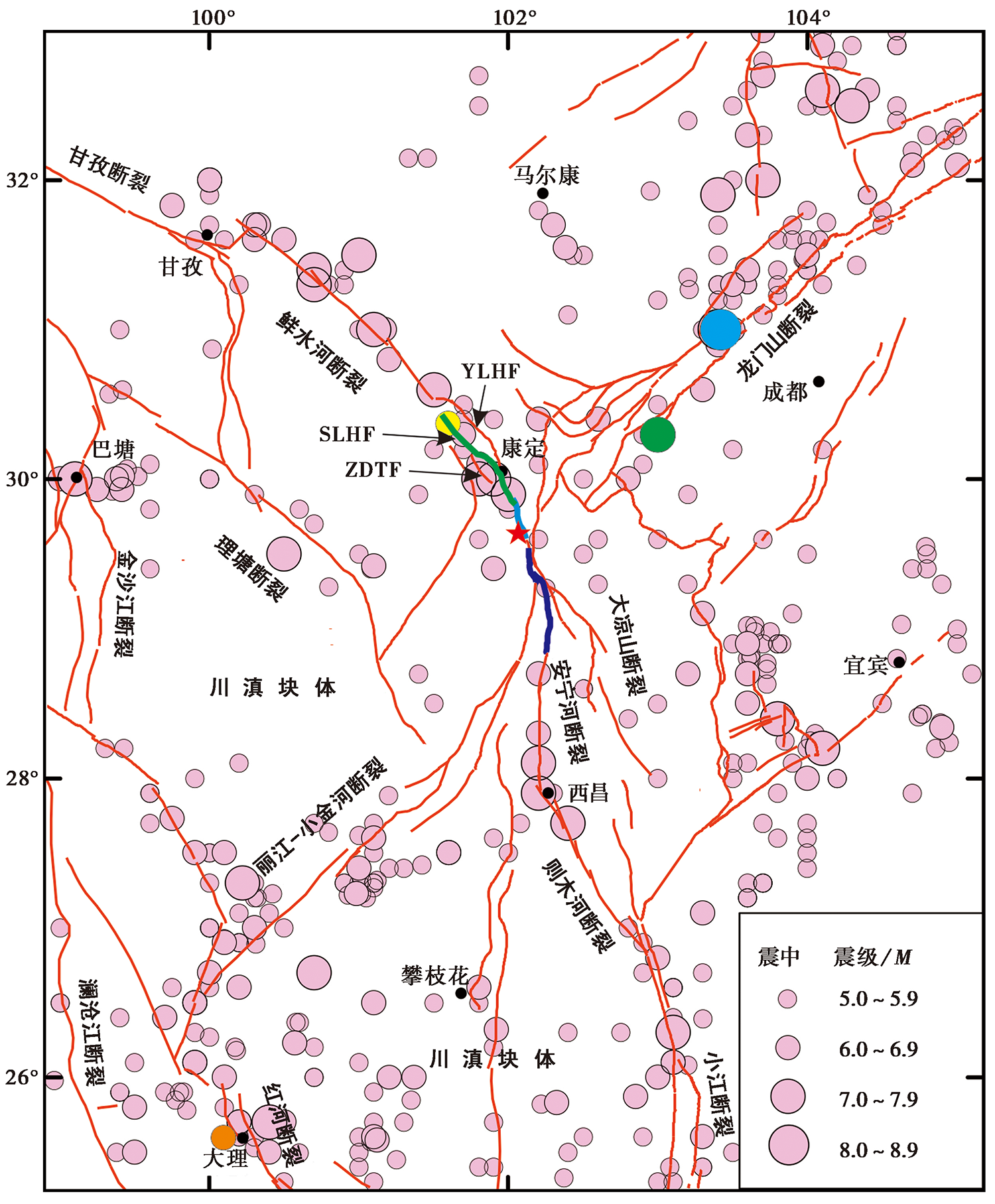
图 8 青藏高原东南缘的主要活动断裂与强震分布 图中浅蓝色线条为磨西断裂, 绿色线条为色拉哈断裂, 深蓝色线条为安宁河断裂北段; 蓝色、 绿色、 黄色、 橙色圆圈分别为2008年汶川M8.0、 2013年芦山M7.0、 2014年康定M6.3、 2021年漾濞M6.3地震的震中。ZDTF 折多塘断裂; SLHF 色拉哈断裂; YLHF 雅拉河断裂
Fig. 8 Major active faults and strong earthquakes(M≥5.0)on the eastern margin of Tibetan plateau.
| [1] | 陈博, 李振洪, 黄武彪, 等. 2022. 2022年四川泸定 MW6.6 地震诱发地质灾害空间分布及影响因素[J]. 地球科学与环境学报, 44(6): 971-985. |
| CHEN Bo, LI Zhen-hong, HUANG Wu-biao, et al. 2022. Spatial distribution and influencing factors of geohazards induced by the 2022 MW6.6 Luding(Sichuan, China)earthquake[J]. Journal of Earth Sciences and Environment, 44(6): 971-985. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 陈桂华, 安艳芬, 江国焰. 2018. 鲜水河活动断裂(雪门坎至石棉段)分布图(1:50 000)及说明书[M]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| CHEN Gui-hua, AN Yan-fen, JIANG Guo-yan. 2018. Map of the Xianshuihe Fault Zone and Descriptions (1:50 000)[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 陈桂华, 闵伟, 宋方敏, 等. 2011. 从1786年磨西地震看地震地表破裂带在不同地貌区的保存[J]. 地震地质, 33(4): 804-817. |
| CHEN Gui-hua, MIN Wei, SONG Fang-min, et al. 2011. Preservation of co-seismic surface rupture in different geomorphological settings from the study of the 1786 Moxi earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 33(4): 804-817. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 陈九辉, 刘启元, 李顺成, 等. 2009. 汶川 MS8.0 地震余震序列重新定位及其地震构造研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 52(2): 390-397. |
|
CHEN Jiu-hui, LIU Qi-yuan, LI Shun-cheng, et al. 2009. Seismotectonic study by relocation of the Wenchuan MS8.0 earthquake sequence[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 52(2): 390-397. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [5] | 邓起东, 张培震, 冉勇康, 等. 2002. 中国活动构造基本特征[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 32(12): 1020-1030. |
| DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Pei-zhen, RAN Yong-kang, et al. 2002. Basic characteristics of active tectonics in China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 32(12): 1020-1030. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] | 邓天岗, 龙德雄, 冯元保. 1986. 1786年四川康定地震[J]. 中国地震, 2(3): 98-99. |
| DENG Tian-gang, LONG De-xiong, FENG Yuan-bao. 1986. The 1786 Kangding earthquake in Sichuan[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 2(3): 98-99. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] | 范文纪. 1982. 贡嘎山的地质构造基础和冰川地貌特征[J]. 成都科技大学学报, (3): 19-33. |
| FAN Wen-ji. 1982. Geological structure foundation and glacial geomorphic characteristics of the Gongga Mountain[J]. Journal of Chengdu University of Science and Technology, (3): 19-33. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 房立华, 吴建平, 苏金蓉, 等. 2018. 四川九寨沟 MS7.0 地震主震及其余震序列精定位[J]. 科学通报, 63(7): 649-662. |
| FANG Li-hua, WU Jian-ping, SU Jin-rong, et al. 2018. Relocation of mainshock and aftershock sequence of the MS7.0 Sichuan Jiuzhaigou earthquake[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 63(7): 649-662. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 冯嘉辉, 陈立春, 王虎, 等. 2021. 大凉山断裂带北段石棉断裂的古地震[J]. 地震地质, 43(1): 53-71. |
| FENG Jia-hui, CHEN Li-chun, WANG Hu, et al. 2021. Paleoseismological study on the Shimian Fault in the northern section of the Daliangshan fault zone[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(1): 53-71. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 何宏林, 池田安隆, 何玉林, 等. 2008. 新生的大凉山断裂带--鲜水河-小江断裂系中段的截弯取直[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 38(5): 564-574. |
| HE Hong-lin, IKEDA Yasutaka, HE Yu-lin, et al. 2008. Newly generated Daliangshan fault zone: Shortcutting on the central section of Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang fault system[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 38(5): 564-574. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 李东雨, 陈立春, 梁明剑, 等. 2017. 鲜水河断裂带乾宁段古地震事件与大震复发行为[J]. 地震地质, 39(4): 623-643. |
| LI Dong-yu, CHEN Li-chun, LIANG Ming-jian, et al. 2017. Holocene paleoseismologic record and rupture behavior of large earthquake on the Xianshuihe Fault[J]. Seismology and Geology, 39(4): 623-643. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 李天袑, 杜其方, 游泽李, 等. 1997. 鲜水河活动断裂带及强震危险性评估[M]. 成都: 成都地图出版社:1-224. |
| LI Tian-shao, DU Qi-fang, YOU Ze-li, et al. 1997. The Xianshuihe Fault Zone and Risk Assessment of Strong Earthquake along It [M]. Chengdu Cartographic Publishing House, Chengdu: 1-224 (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 梁明剑, 陈立春, 冉勇康, 等. 2020. 鲜水河断裂带雅拉河段晚第四纪活动性[J]. 地震地质, 42(2): 513-525. |
| LIANG Ming-jian, CHEN Li-chun, RAN Yong-kang, et al. 2020. Late-Quaternary activity of the Yalahe Fault of the Xianshuihe fault zone, eastern margin of the Tibet plateau[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(2): 513-525. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 龙德雄, 邓天岗. 1990. 1786年康定地震形变特征的初步研究[J]. 地震研究, 13(1): 51-60. |
| LONG De-xiong, DENG Tian-gang. 1990. A preliminary study on the 1786 Kangding earthquake deformation characteristics[J]. Journal of Seismological Research, 13(1): 51-60. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 钱洪, Allen C R, 罗灼礼, 等. 1988. 全新世以来鲜水河断裂的活动特征[J]. 中国地震, 4(2): 9-18. |
| QIAN Hong, Allen C R, LUO Zhuo-li, et al. 1988. The active characteristics of the Xianshuihe Fault in Holocene[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 4(2): 9-18. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 冉勇康, 陈立春, 程建武, 等. 2008. 安宁河断裂冕宁以北晚第四纪地表变形与强震破裂行为[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 38(5): 543-554. |
| RAN Yong-kang, CHEN Li-chun, CHENG Jian-wu, et al. 2008. Late Quaternary surface deformation and rupture behavior of strong earthquake on the segment north of Mianning of the Anninghe Fault[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 38(5): 543-554. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 邵志刚, 马宏生, 张浪平, 等. 2013. 2010年玉树 MS7.1 地震同震破裂、 余震分布特征及其与构造的关系[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(11): 3800-3810. |
| SHAO Zhi-gang, MA Hong-sheng, ZHANG Lang-ping, et al. 2013. The characteristics of co-seismic slip and aftershocks distribution of the MS7.1 earthquake at Qinghai Yushu in 2010 and its relationship with tectonics[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(11): 3800-3810. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 四川省地震资料编辑组. 1980. 四川地震资料汇编[M]. 成都: 四川人民出版社. |
| Editorial Group for Earthquake Data of Sichuan Province. 1980. Collection of Earthquake Data of Sichuan Province[M]. Sichuan People’s Publishing House, Chengdu. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 唐荣昌, 韩渭滨. 1993. 四川活动断裂与地震[M]. 北京: 地震出版社, 附件: 12-20. |
| TANG Rong-chang, HAN Wei-bin. 1993. Active Faults and Earthquakes in Sichuan Province [M]. Seismological Press, Beijing: appendix: 12-20 (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 王碧泉, 王春珍. 1983. 余震序列的时空特征[J]. 地震学报, 5(4): 383-396. |
| WANG Bi-quan, WANG Chun-zhen. 1983. Temporal and spatial features of aftershock sequences[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 5(4): 383-396. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 王新民, 裴锡瑜. 1988. 对1786年康定-泸定磨西间7¾级地震的新认识[J]. 中国地震, 4(1): 110-117. |
| WANG Xin-min, PEI Xi-yu. 1988. Some new points of view on the 1786 earthquake(M=7¾)occurring in the area between Kangding and Moxi, Luding, Sichuan Province[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 4(1): 110-117. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 闻学泽. 2000. 四川西部鲜水河-安宁河-则木河断裂带的地震破裂分段特征[J]. 地震地质, 22(3): 239-249. |
| WEN Xue-ze. 2000. Character of rupture segmentation of the Xianshuihe-Anninghe-Zemuhe fault zone, western Sichuan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 22(3): 239-249. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 闻学泽, Allen C R, 罗灼礼, 等. 1989. 鲜水河全新世断裂带的分段性、 几何特征及其地震构造意义[J]. 地震学报, 11(4): 362-372. |
| WEN Xue-ze, Allen C R, LUO Zhuo-li, et al. 1989. Segmentation, geometric features, and their seismotectonic implications for the Holocene Xianshuihe fault zone[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 11(4): 362-372. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 闻学泽, 范军, 易桂喜, 等. 2008. 川西安宁河断裂上的地震空区[J]. 中国科学(D 辑), 38(7): 797-807. |
| WEN Xue-ze, FAN Jun, YI Gui-xi, et al. 2008. A seismic gap on the Anninghe Fault in western Sichuan, China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 38(7): 797-807. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 闻学泽, 徐锡伟, 郑荣章, 等. 2001. 磨西断裂的晚第四纪活动性与大地震复发间隔 [G]//卢演俦主编. 新构造与环境. 北京: 地震出版社: 255-266. |
| WEN Xue-ze, XU Xi-wei, ZHENG Rong-zhang, et al. 2001. Late Quaternary activity and large earthquake recurrence along the Moxi Fault [G]//LU Yan-chou(ed). The Neo-tectonics and Environment. Seismological Press, Beijing: 255-266 (in Chinese) | |
| [26] | 徐晶, 邵志刚, 刘静, 等. 2019. 川滇菱形块体东边界库仑应力演化及强震发生概率估算[J]. 地球物理学报, 62(11): 4189-4213. |
| XU Jing, SHAO Zhi-gang, LIU Jing, et al. 2019. Coulomb stress evolution and future earthquake probability along the eastern boundary of the Sichuan-Yunnan block[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 62(11): 4189-4213. (in Chinese) | |
| [27] | 徐泰然, 戴丹青, 杨志高, 等. 2022. 2022年9月5日四川泸定6.8级地震初步研究结果[J]. 中国地震, 38(3): 412-424. |
| XU Tai-ran, DAI Dan-qing, YANG Zhi-gao, et al. 2022. Preliminary study of emergency production and source parameters of the M6.8 earthquake on September 05, 2022 in Luding, Sichuan Province[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 38(3): 412-424. (in Chinese) | |
| [28] | 易桂喜, 龙锋, 闻学泽, 等. 2015. 2014年11月22日康定M6.3地震序列发震构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(4): 1205-1219. |
| YI Gui-xi, LONG Feng, WEN Xue-ze, et al. 2015. Seismological structure of the M6.3 Kangding earthquake sequence on 22 Nov. 2014, southwestern China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(4): 1205-1219. (in Chinese) | |
| [29] | 张广伟, 雷建设. 2013. 四川芦山7.0级强震及其余震序列重定位[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(5): 1764-1771. |
| ZHANG Guang-wei, LEI Jian-she. 2013. Relocation of Lushan, Sichuan strong earthquake(MS7.0) and its aftershocks[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(5): 1764-1771. (in Chinese) | |
| [30] | 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等. 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12-20. |
| ZHANG Pei-zhen, DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Guo-min, et al. 2003. Active tectonic blocks and strong earthquakes in the continent of China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 33(S1): 12-20. (in Chinese) | |
| [31] | 赵翠萍, 陈章立, 郑斯华. 2008. 1998-2003年伽师3次不同类型 MS6 地震震源破裂过程及短期内余震活动特征[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(4): 1093-1102. |
|
ZHAO Cui-ping, CHEN Zhang-li, ZHENG Si-hua. 2008. Source rupture process of 3 Jiashi MS6 events(1998-2003)and its correlation with the aftershock activity[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(4): 1093-1102. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [32] | 周荣军, 何玉林, 黄祖智, 等. 2001a. 鲜水河断裂带乾宁-康定段的滑动速率与强震复发间隔[J]. 地震学报, 23(3): 250-261. |
| ZHOU Rong-jun, HE Yu-lin, HUANG Zu-zhi, et al. 2001a. The slip rate and recurrence interval of strong earthquake on the Qianning-Kangding segment of the Xianshuihe fault zone[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 23(3): 250-261. (in Chinese) | |
| [33] | 周荣军, 何玉林, 杨涛, 等. 2001b. 鲜水河-安宁河断裂带磨西-冕宁段的滑动速率与强震位错[J]. 中国地震, 17(3): 253-262. |
| ZHOU Rong-jun, HE Yu-lin, YANG Tao, et al. 2001b. Slip rate and strong earthquake rupture on the Moxi-Mianning segment along the Xianshuihe-Anninghe fault zone[J]. Earthquake Research in China, 17(3): 253-262. (in Chinese) | |
| [34] | 周荣军, 雷建成, 黎小刚, 等. 2000. 晚第四纪以来大渡河断裂活动性的地质地貌判据 [C]//陈运泰主编. 中国地震学会第8次学术大会论文摘要集. 北京: 地震出版社: 54. |
| ZHOU Rong-jun, LEI Jian-cheng, LI Xiao-gang, et al. 2000. Geology and geomorphic evidence for activity of Daduhe Fault since late Quaternary [C]//CHEN Yun-tai(ed). Collection of Essays for the 8th Academic Conference of the Seismological Society of China. Seismological Press, Beijing: 54 (in Chinese) | |
| [35] | Allen C R, Luo Z L, Qian H, et al. 1991. Field study of a highly active fault zone: The Xianshuihe Fault of southwestern China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 13: 1178-1199. |
| [36] | Bai M, Chevalier M L, Leloup P H, et al. 2021. Spatial slip rate distribution along the SE Xianshuihe Fault, eastern Tibet, and earthquake hazard assessment[J]. Tectonics, 40(11): e2021TC006985. |
| [37] |
Burchfiel B C, Chen Z, Liu Y, et al. 1995. Tectonics of the Longmenshan and adjacent regions[J]. International Geology Review, 37(8): 661-735.
DOI URL |
| [38] | Das S, Henry C. 2003. Spatial relation between main earthquake slip and its aftershock distribution[J]. Reviews of Geophysics, 41(3): 1013. |
| [39] |
Gülen L, Pinar A, Kalafat D, et al. 2002. Surface fault breaks, aftershock distribution, and rupture process of the 17 August 1999 İzmit, Turkey, earthquake[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 92(1): 230-244.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Guo R M, Zheng Y, Tian W, et al. 2018. Locking status and earthquake potential hazard along the middle-south Xianshuihe Fault[J]. Remote Sensing, 10:2048. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs10122048.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
Harris R A. 1998. Introduction to special section: Stress triggers, stress shadows, and implications for seismic hazard[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 103(B10): 24347-24358.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Hu C Z, Yang P X, Liang P, et al. 2015. The Holocene paleoearthquakes on the 2014 Kangding MS6.3 earthquake faults[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin, 60(23): 2236-2244. |
| [43] |
Jiang G, Wen Y, Liu Y, et al. 2015. Joint analysis of the 2014 Kangding, southwest China, earthquake sequence with seismicity relocation and InSAR inversion[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 42: 3273-3281.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Li Y, Bürgmann R. 2021. Partial coupling and earthquake potential along the Xianshuihe Fault, China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 126(7): e2020JB021406. |
| [45] |
Liang M J, Chen L C, Ran Y K, 2020. Abnormal accelerating stress release behavior on the Luhuo segment of the Xianshuihe Fault, southeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau, during the past 3 000 years [J]. Frontiers in Earth Science, 8:274. doi: 10.3389/feart.2020.00274.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Molnar P, Deng Q D. 1984. Faulting associated with large earthquakes and the average rate of deformation in central and eastern Asia[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 89(B7): 6203-6227.
DOI URL |
| [47] | Ozawa S, Ando R. 2021. Mainshock and aftershock sequence simulation in geometrically complex fault zones[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 126(2): e2020JB020865. |
| [48] |
Qiao X, Zhou Y. 2021. Geodetic imaging of shallow creep along the Xianshuihe Fault and its frictional properties[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 567: 117001.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Toda S, Lin J, Meghraoui M, et al. 2008. 12 May 2008 M=7.9 Wenchuan, China, earthquake calculated to increase failure stress and seismicity rate on three major fault systems[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 35: L17305. doi: 10.1029/2008GL034903.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Wang E Q, Burchfiel B C, Royden L H, et al. 1998. Late Cenozoic Xianshuihe-Xiaojiang, Red River, and Dali fault systems of southwestern Sichuan and central Yunnan, China[R]. Geological Society of American, Special Paper, 327: 1-108. |
| [51] |
Wang H, Ran Y K, Chen L C, et al. 2017. Paleoearthquakes on the Anninghe and Zemuhe Fault along the southeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau and implications for fault rupture behavior at fault bends on strike-slip faults[J]. Tectonophysics, 721: 167-178.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Wang H, Ran Y K, Li Y B, et al. 2014. A 3 400-year-long paleoseismologic record of earthquakes on the southern segment of Anninghe Fault along the southeastern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 628: 206-217.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Wen X, Ma S, Xu X, et al. 2008. Historical pattern and behavior of earthquake ruptures along the eastern boundary of the Sichuan-Yunnan faulted-block, southwestern China[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 168(1-2): 16-36.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Yan B, Lin A M. 2017. Holocene activity and paleoseismicity of the Selaha Fault, southeastern segment of the strike-slip Xianshuihe fault zone, Tibetan plateau[J]. Tectonophysics, 694: 302-318.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Yukutake Y, Lio Y. 2017. Why do aftershocks occur?Relationship between mainshock rupture and aftershock sequence based on highly resolved hypocenter and focal mechanism distributions[J]. Earth, Planets and Space, 69:68. doi: 10.1186/s40623-017-0650-2.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王辽, 谢虹, 袁道阳, 李智敏, 薛善余, 苏瑞欢, 文亚猛, 苏琦. 结合野外考察的2022年门源MS6.9地震地表破裂带的高分七号影像特征[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 401-421. |
| [2] | 刘白云, 赵莉, 刘云云, 王文才, 张卫东. 2021年5月22日青海玛多M7.4地震余震重新定位与断层面参数拟合[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 500-516. |
| [3] | 赵德政, 屈春燕, 张桂芳, 龚文瑜, 单新建, 朱传华, 张国宏, 宋小刚. 基于InSAR技术的同震形变获取、地震应急监测和发震构造研究应用进展[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(2): 570-592. |
| [4] | 张珂, 王鑫, 杨红樱, 王玥, 徐岩, 李静. 2021年云南漾濞MS6.4地震序列特征及其发震构造分析[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 231-251. |
| [5] | 吴中海, 白玛多吉, 叶强, 韩帅, 史亚然, 尼玛次仁, 高扬. 西藏阿里阿鲁错地堑系的第四纪活动性、最新同震地表破裂及其地震地质意义[J]. 地震地质, 2023, 45(1): 67-91. |
| [6] | 李东臣, 任俊杰, 张志文, 刘亮. 基于高分辨率无人机影像的地震地表破裂半自动提取方法--以2021年MS7.4青海玛多地震为例[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(6): 1484-1502. |
| [7] | 张博譞, 郑文俊, 陈杰, 何骁慧, 李启雷, 张冬丽, 段磊, 陈干. 柴达木盆地北部2021年6月16日青海茫崖MS5.8地震发震构造分析[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(5): 1313-1332. |
| [8] | 姚生海, 盖海龙, 殷翔, 刘炜, 张加庆, 袁建新. 阿木尼克山山前地表破裂带与1962年6.8级地震关系的讨论[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 976-991. |
| [9] | 刘小利, 夏涛, 刘静, 姚文倩, 徐晶, 邓德贝尔, 韩龙飞, 贾治革, 邵延秀, 王焱, 乐子扬, 高天琪. 2021年青海玛多MW7.4地震分布式同震地表裂缝特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 461-483. |
| [10] | 韩龙飞, 刘静, 姚文倩, 王文鑫, 刘小利, 高云鹏, 邵延秀, 李金阳. 2021年玛多MW7.4地震震中区地表破裂的精细填图及阶区内的分布式破裂讨论[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 484-505. |
| [11] | 王文鑫, 邵延秀, 姚文倩, 刘静, 韩龙飞, 刘小利, 高云鹏, 王子君, 秦可心, 屠泓为. 基于摄影测量技术对玛多MW7.4地震地表破裂特征的快速提取及三维结构的室内重建[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 524-540. |
| [12] | 姚文倩, 王子君, 刘静, 刘小利, 韩龙飞, 邵延秀, 王文鑫, 徐晶, 秦可心, 高云鹏, 王焱, 李金阳, 曾宪阳. 2021年青海玛多MW7.4地震同震地表破裂长度的讨论[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 541-559. |
| [13] | 盖海龙, 李智敏, 姚生海, 李鑫. 2022年青海门源MS6.9地震地表破裂特征的初步调查研究[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 238-255. |
| [14] | 梁宽, 何仲太, 姜文亮, 李永生, 刘泽民. 2022年1月8日青海门源MS6.9地震的同震地表破裂特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 256-278. |
| [15] | 李占飞, 徐锡伟, 孟勇琦, 赵帅, 孙佳珺, 程佳, 李康, 康文君. 基于“吉林一号”高精度遥感数据研究华北地区最新构造变形样式——以夏垫断裂1679年三河-平谷地震地表破裂为例[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(1): 98-114. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||