地震地质 ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (2): 541-559.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2022.02.016
• 2021年玛多地震地表破裂机理研究专题文章 • 上一篇
姚文倩1)( ), 王子君1), 刘静1,2),*(
), 王子君1), 刘静1,2),*( ), 刘小利3), 韩龙飞1), 邵延秀1), 王文鑫1), 徐晶4), 秦可心1), 高云鹏1), 王焱1), 李金阳1), 曾宪阳2)
), 刘小利3), 韩龙飞1), 邵延秀1), 王文鑫1), 徐晶4), 秦可心1), 高云鹏1), 王焱1), 李金阳1), 曾宪阳2)
收稿日期:2022-01-25
修回日期:2022-03-01
出版日期:2022-04-20
发布日期:2022-06-14
通讯作者:
刘静
作者简介:姚文倩, 女, 1985年生, 2019年于中国地震局地质研究所获构造地质学博士学位, 讲师, 研究方向为活动构造及地震地质, E-mail: wenqian_08@163.com。
基金资助:
YAO Wen-qian1)( ), WANG Zi-jun1), LIU-ZENG Jing1,2),*(
), WANG Zi-jun1), LIU-ZENG Jing1,2),*( ), LIU Xiao-li3), HAN Long-fei1), SHAO Yan-xiu1), WANG Wen-xin1), XU Jing4), QIN Ke-xin1), GAO Yun-peng1), WANG Yan1), LI Jin-yang1), ZENG Xian-yang2)
), LIU Xiao-li3), HAN Long-fei1), SHAO Yan-xiu1), WANG Wen-xin1), XU Jing4), QIN Ke-xin1), GAO Yun-peng1), WANG Yan1), LI Jin-yang1), ZENG Xian-yang2)
Received:2022-01-25
Revised:2022-03-01
Online:2022-04-20
Published:2022-06-14
Contact:
LIU-ZENG Jing
摘要:
同震地表破裂长度是区域活动断裂最大震级估算以及区域未来地震潜力评估的重要参数之一。2021年5月22日在青海省果洛藏族自治州玛多县发生了 MW7.4 地震, 其触发的同震地表破裂沿东昆仑断裂东南分支延伸线上的江错断裂分布。文中基于震后2次大范围的野外调查, 结合无人机航拍影像和高精度地形数据的精细解译, 明确了此次地震的同震地表破裂自西往东可划分为鄂陵湖南段、 野马滩段、 黄河乡段和江错分支段, 最东端的地表破裂位置位于前人研究所确定的最东端以东2km以远, 破裂全长约158km。此外, 本研究在冬草阿隆湖以东的沙丘区域内发现了呈半圆弧形连续分布的地表破裂, 而破裂在沿走向SE的优云乡段的传播过程中所经过的大面积沙丘覆盖区域也存在零星的张剪性地表破裂和断层陡坎, 且陡坎的垂向位移可达30cm。对比已有的关于同震地表破裂长度的研究结果, 分析认为本研究与其他结果之间存在差异的主要原因在于: 1)本研究所得结果基于更广泛、 详实的野外调查和更大范围的高精度影像的精细解译; 2)分析过程中避免了阶区等段落几何复杂区两侧叠加段落的重复计算。结合巴颜喀拉块体周缘已有的强震震例, 均显示青藏高原地区同震地表破裂的长度较全球平均值偏大。
中图分类号:
姚文倩, 王子君, 刘静, 刘小利, 韩龙飞, 邵延秀, 王文鑫, 徐晶, 秦可心, 高云鹏, 王焱, 李金阳, 曾宪阳. 2021年青海玛多MW7.4地震同震地表破裂长度的讨论[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 541-559.
YAO Wen-qian, WANG Zi-jun, LIU-ZENG Jing, LIU Xiao-li, HAN Long-fei, SHAO Yan-xiu, WANG Wen-xin, XU Jing, QIN Ke-xin, GAO Yun-peng, WANG Yan, LI Jin-yang, ZENG Xian-yang. DISCUSSION ON COSEISMIC SURFACE RUPTURE LENGTH OF THE 2021 MW7.4 MADOI EARTHQUAKE, QINGHAI, CHINA[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND GEOLOGY, 2022, 44(2): 541-559.
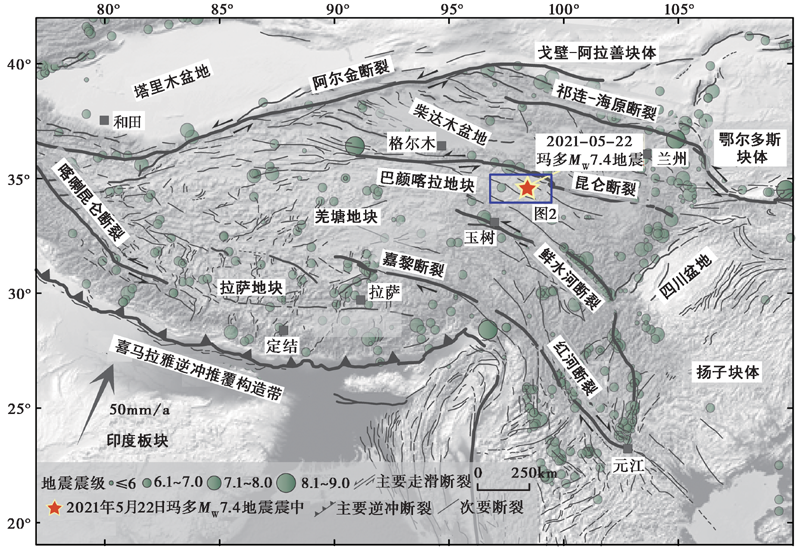
图 1 青藏高原的主要活动断裂及强震分布图 活动断裂修改自Tapponnier等(2001), 五角星指示2021年5月22日玛多 MW7.4 强震震中
Fig. 1 Distribution of major active faults and earthquakes of the Tibetan plateau.
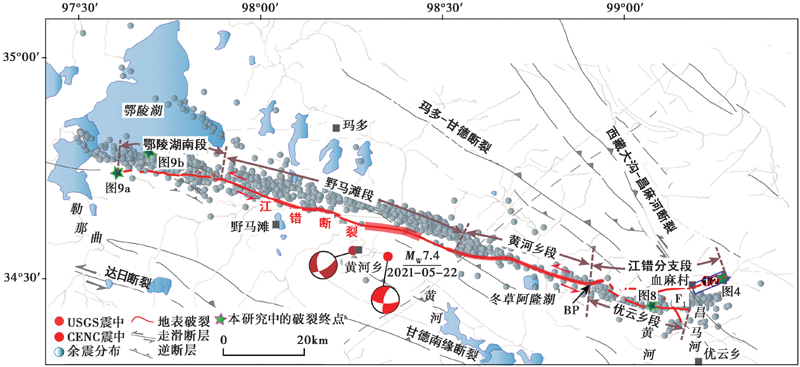
图 3 玛多 MS7.4 地震的地表破裂分段及区域活动断裂分布图 地表破裂的加粗位置为地表破裂的分散范围, BP指示地表破裂出现分支段的起点, 1号和2号点位分别为已有研究中的破裂东端点(潘家伟等, 2021; 李智敏等, 2021)
Fig. 3 Segmentation of coseismic surface rupture of the Madoi MW7.4 earthquake and distribution of active faults in the study area.
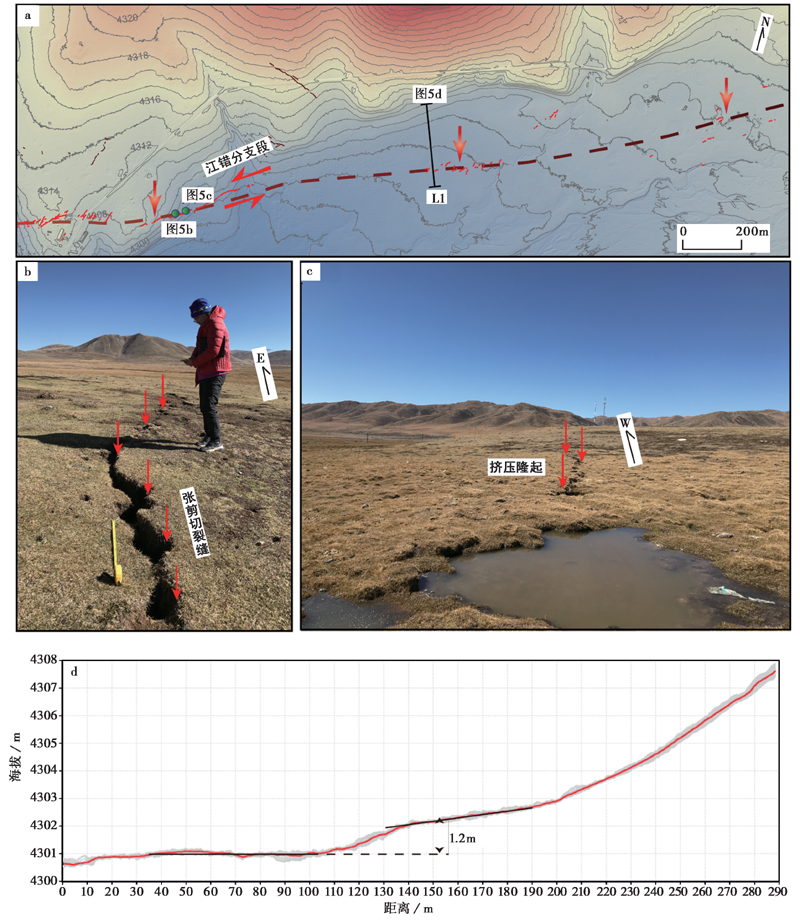
图 5 血麻村附近的同震地表破裂展布特征 a 地表破裂总体的几何形态展布特征; b 连续发育的张剪切裂缝; c 沿EW向连续分布的小型挤压鼓包, 至水洼处消失;d 垂直于江错分支段的高程剖面, 显示发育断层陡坎
Fig. 5 Characteristics of the coseismic surface ruptures near the Xuema village.
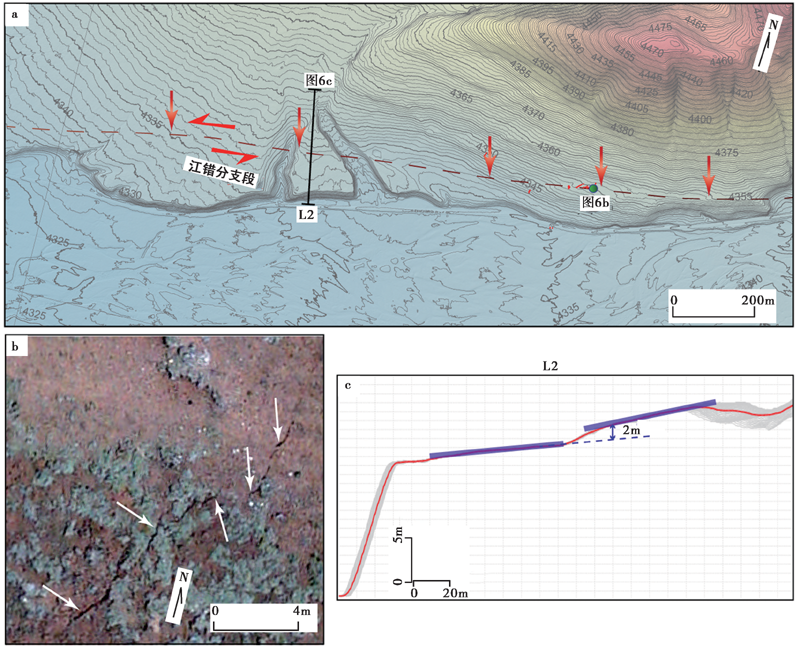
图 6 血麻村向E地表破裂零星分布的特征 a 地表破裂的总体几何形态展布特征; b 高精度数字正摄影像显示的右行雁列张裂隙分布; c 垂直于江错分支段的高程剖面, 显示断层陡坎发育
Fig. 6 Sparse distribution of the coseismic surface ruptures to the east of the Xuema village produced by Madoi earthquake.
| 序号 | 地表破裂长度/km | 量测方法 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 152.4 | 野外踏勘 | 潘佳伟等, 2021 |
| 2 | 160 | 野外踏勘 | 李智敏等, |
| 3 | 170 | 大地测量 | 王未来等, |
| 4 | 150 | 大地测量 | 赵韬等, |
| 5 | 180 | 大地测量 | 徐志国等, |
| 6 | 210 | 大地测量 | 华俊等, |
表1 玛多 MW7.4 地震同震地表破裂的长度统计
Table1 Length of the coseismic surface ruptures of the MW7.4 Madoi earthquake
| 序号 | 地表破裂长度/km | 量测方法 | 来源 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 152.4 | 野外踏勘 | 潘佳伟等, 2021 |
| 2 | 160 | 野外踏勘 | 李智敏等, |
| 3 | 170 | 大地测量 | 王未来等, |
| 4 | 150 | 大地测量 | 赵韬等, |
| 5 | 180 | 大地测量 | 徐志国等, |
| 6 | 210 | 大地测量 | 华俊等, |
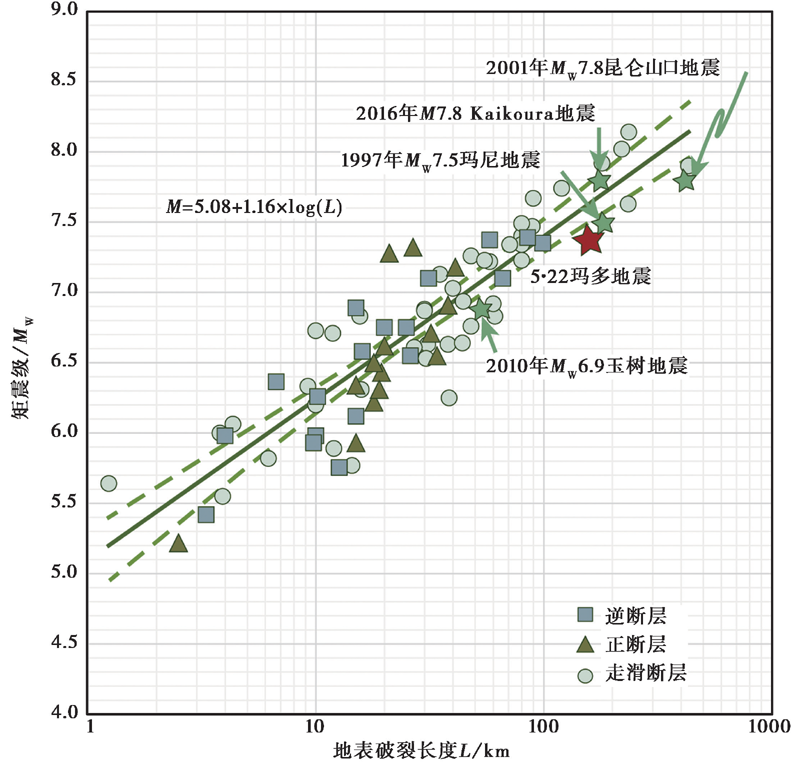
图 10 地表破裂长度及矩震级的经验关系图(修改自Well et al., 1994) 图中实线和虚线分别指示最佳和置信区间95%时地震震级和破裂长度的线性关系
Fig. 10 Regressions of moment magnitude versus surface rupture length(modified based on results of Well et al.,1994).
| [1] | 程丰, 李德威, Jerry B, 等. 2012. 玉树地震地表破裂特征及其破裂方式[J]. 大地构造与成矿学, 36(1): 69-75. |
| CHENG Feng, LI De-wei, Jerry B,et al. 2012. Characteristics and patterns of surface ruptures caused by the Yushu earthquake[J]. Geotectonica et Metallogenia, 36(1): 69-75. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] | 戴华光. 1983. 1947年青海达日$7\frac{3}{4}$级地震[J]. 西北地震学报, 5(3): 71-77. |
| DAI Hua-guang. 1983. On the Dari earthquake of 1947 in Qinghai Province[J]. Northwestern Seismological Journal, 5(3): 71-77. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 邓起东, 高翔, 陈桂华, 等. 2010. 青藏高原昆仑-汶川地震系列与巴颜喀喇断块的最新活动[J]. 地学前缘, 17(5): 163-178. |
| DENG Qi-dong, GAO Xiang, CHEN Gui-hua,et al. 2010. Recent tectonic activity of Bayankala fault-block and the Kunlun-Wenchuan earthquake series of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(5): 163-178. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 国家地震局阿尔金活动断裂带课题组. 1992. 阿尔金活动断裂带[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-319. |
| Research Group on Active Altun Fault Zone of State Seismological Bureau. 1992. The Altun Active Fault Zone[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing: 1-319. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] | 国家地震局震害防御司. 1995. 中国历史强震目录 [Z]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-514. |
| Department of Earthquake Disaster Prevention of State Seismological Bureau. 1995. The Catalogue of Historical Strong Earthquakes of China [Z]. Seismological Press, Beijing: 1-514. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] |
华俊, 赵德政, 单新建, 等. 2021. 2021年青海玛多 MW7.3 地震InSAR的同震形变场、 断层滑动分布及其对周边区域的应力扰动[J]. 地震地质, 43(3): 677-691. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4567.2021.03.013.
DOI |
| HUA Jun, ZHAO De-zheng, SHAN Xin-jian,et al. 2021. Coseismic deformation field, slip distribution and Coulomb stress disturbance of the 2021 MW7.3 Maduo earthquake using Sentinel-1 InSAR observations[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(3): 677-691. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] |
李智敏, 李文巧, 李涛, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震的发震构造和地表破裂初步调查[J]. 地震地质, 43(3): 722-737. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.03.016.
DOI |
| LI Zhi-min, LI Wen-qiao, LI Tao,et al. 2021. Seismogenic fault and coseismic surface deformation of the Maduo MS7.4 earthquake in Qinghai, China: A quick report[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(3): 722-737. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] |
梁明剑, 杨耀, 杜方, 等. 2020. 青海达日断裂中段晚第四纪活动性与1947年$M7\frac{3}{4}$地震地表破裂带再研究[J]. 地震地质, 42(3): 703-714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.03.011.
DOI |
| LIANG Ming-jian, YANG Yao, DU Fang,et al. 2020. Late Quaternary activity of the central segment of the Dari Fault and restudy of the surface rupture zone of the 1947 $M7\frac{3}{4}$Dari earthquake, Qinghai Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(3): 703-714. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] |
梁明剑, 周荣军, 闫亮, 等. 2014. 青海达日断裂中段构造活动与地貌发育的响应关系探讨[J]. 地震地质, 36(1): 28-38. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2014.02.003.
DOI |
| LIANG Ming-jian, ZHOU Rong-jun, YAN Liang,et al. 2014. The relationships between neotectonic activity of the middle segment of Dari Fault and its geomorphological response, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 36(1): 28-38. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 潘家伟, 白明坤, 李超, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震地表破裂带及发震构造[J]. 地质学报, 95(6): 1655-1670. |
| PAN Jia-wei, BAI Ming-kun, LI Chao,et al. 2021. Coseismic surface rupture and seismogenic structure of the 2021-05-22 Maduo(Qinghai) MS7.4 earthquake[J]. Acta Geologica Sinica, 95(6): 1655-1670. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 青海省地震局, 中国地震局地壳应力研究所. 1999. 东昆仑活动断裂带[M]. 北京: 地震出版社: 1-227. |
| Seismological Bureau of Qinghai Province,Institute of Crustal Dynamics, China Earthquake Administration. 1999. The Eastern Kunlun Active Fault Zone[M]. Seismological Press, Beijing: 1-227. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 孙鑫喆, 徐锡伟, 陈立春, 等. 2012. 2010年玉树地震地表破裂带典型破裂样式及其构造意义[J]. 地球物理学报, 55(1): 155-170. |
| SUN Xin-zhe, XU Xi-wei, CHEN Li-chun,et al. 2010. Surface rupture features of the 2010 Yushu earthquake and its tectonic implication[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 55(1): 155-170. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 王未来, 房立华, 吴建平, 等. 2021. 2021年青海玛多 MS7.4 地震序列精定位研究[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 51(7): 1193-1202. |
| WANG Wei-lai, FANG Li-hua, WU Jian-ping,et al. 2021. Aftershock sequence relocation of the 2021 MS7.4 Maduo earthquake, Qinghai, China[J]. Science China Earth Sciences, 51(7): 1193-1202. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 闻学泽. 2018. 巴颜喀拉块体东边界千年破裂历史与2008年汶川、 2013年芦山和2017年九寨沟地震[J]. 地震学报, 40(3): 255-267. |
| WEN Xue-ze. 2018. The 2008 Wenchuan, 2013 Lushan and 2017 Jiuzhaigou earthquakes, Sichuan, in the last more than one thousand years of rupture history of the eastern margin of the Bayan Har block[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 40(3): 255-267. (in Chinese) | |
| [15] | 徐锡伟, 陈文彬, 于贵华, 等. 2002. 2001年11月14日昆仑山库赛湖地震( MS8.1 )地表破裂带的基本特征[J]. 地震地质, 24(1): 1-13, 133-136. |
| XU Xi-wei, CHEN Wen-bin, YU Gui-hua,et al. 2002. Characteristic features of the surface ruptures of the Hoh Sai Hu(Kunlunshan)earthquake( MS8.1 ), northern Tibetan plateau, China[J]. Seismology and Geology, 24(1): 1-13, 133-136. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 徐志国, 梁姗姗, 张广伟, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震发震构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(8): 2657-2670. |
| XU Zhi-guo, LIANG Shan-shan, ZHANG Guang-wei,et al. 2021. Analysis of seismogenic structure of Madoi, Qinghai MS7.4 earthquake on May 22, 2021[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(8): 2657-2670. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 袁兆德, 刘静, 周游, 等. 2019. 阿尔金断裂中段乌尊硝尔段古地震记录与级联破裂行为[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 50(1): 50-65. |
| YUAN Zhao-de, LIU-ZENG Jing, ZHOU You,et al. 2019. Paleoseismologic record of earthquakes along the Wuzunxiaoer section of the Altyn Tagh Fault and its implication for cascade rupture behavior[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 50(1): 50-65. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 张军龙, 任金卫, 陈长云, 等. 2014. 东昆仑断裂带东部晚更新世以来活动特征及其大地构造意义[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 44(4): 654-667. |
| ZHANG Jun-long, REN Jin-wei, CHEN Chang-yun,et al. 2014. The Late Pleistocene activity of the eastern part of east Kunlun fault zone and its tectonic significance[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 44(4): 654-667. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 张培震, 邓起东, 张国民, 等. 2003. 中国大陆的强震活动与活动地块[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 33(S1): 12-20. |
| ZHANG Pei-zhen, DENG Qi-dong, ZHANG Guo-min,et al. 2003. Active tectonic blocks and strong earthquake in the continent of China[J]. Science in China(Ser D), 33(S1): 12-20. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 张培震, 徐锡伟, 闻学泽, 等. 2008. 2008年汶川8.0级地震发震断裂的滑动速率、 复发周期和构造成因[J]. 地球物理学报, 51(4): 1066-1073. |
| ZHANG Pei-zhen, XU Xi-wei, WEN Xu-ze,et al. 2008. Slip rates and recurrence intervals of the Longmen Shan active fault zone and tectonic implications for the mechanism of the May 12 Wenchuan earthquake, 2008, Sichuan, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 51(4): 1066-1073. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 赵韬, 王莹, 马冀, 等. 2021. 2021年青海玛多7.4级地震序列重定位和震源机制特征[J]. 地震地质, 43(4): 790-805. |
| ZHAO Tao, WANG Ying, MA Ji,et al. 2021. Relocation and focal mechanism solutions of the 2021 Maduo, Qinghai MS7.4 earthquake sequence[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(4): 790-805. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 中国地震局震害防御司. 1999. Seismology and Geology[z]. 北京, 中国科技出版社: 1-637. |
| Department of Earthquake Disaster Prevention of State Seismological Bureau. 1999. The Catalogue of Modern Earthquakes of China(1912-1990AD, MS≥4.7)[Z]. Science and Technology Press: Beijing: 1-637. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] |
Burchfiel B C, Chen Z L, Liu Y P,et al. 1995. Tectonics of the Longmen Shan and adjacent regions, central China[J]. International Geology Review, 37(8): 661-735.
DOI URL |
| [24] | Bonilla M G, Mark R K, Lienkaemper J J. 1984. Statistical relations among earthquake magnitude, surface rupture length, and surface fault displacement[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 74(6): 2379-2411. |
| [25] | Chen K, Avouac J P, Geng J,et al. 2022. The 2021 MW7.4 Madoi earthquake: An archetype bilateral slip-pulse rupture arrested at a splay fault[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 49(2): 1-9. |
| [26] |
Dietz L D, Ellsworth W L. 1990. The October 17, 1989, Loma Prieta, California, earthquake and its aftershocks: Geometry of the sequence from high-resolution locations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 17(9): 1417-1420.
DOI URL |
| [27] | Dietz L D, Ellsworth W L. 1997. Aftershocks of the Loma Prieta earthquake and their tectonic implications[J]. USGS Professional Paper: 1550( 4): D5-D47. |
| [28] | Fisher R, Dawson-Howe K, Fitzgibbon A,et al. 2005. Dictionary of Computer Vision and Image Processing[M]. John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken. |
| [29] |
Fonstad M A, Dietrich J T, Courville B C,et al. 2013. Topographic structure from motion: A new development in photogrammetric measurement[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 38(4): 421-430.
DOI URL |
| [30] | He L, Feng G, Wu X,et al. 2021. Coseismic and early postseismic slip models of the 2021 MW7.4 Maduo earthquake(western China)estimated by space-based geodetic data[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(24): 1-10. |
| [31] |
Hudnut K W, Brooks B A, Scharer K,et al. 2020. Airborne Lidar and electro-optical imagery along surface ruptures of the 2019 Ridgecrest earthquake sequence, southern California[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 91(4): 2096-2107.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
Klinger Y, Xu X W, Tapponnier P,et al. 2005. High-resolution satellite imagery mapping of the surface rupture and slip distribution of the MW7.8, 14 November 2001 Kokoxili earthquake, Kunlun Fault, northern Tibet, China[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 95(5): 1970-1987.
DOI URL |
| [33] | Kanamori H, Anderson D L. 1975. Theoretical basis of some empirical relations in seismology[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 65(5): 1073-1095. |
| [34] | Jin Z, Fialko Y. 2021. Coseismic and early postseismic deformation due to the 2021 M7.4 Maduo(China)earthquake[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(21): 1-10. |
| [35] |
Johnson K, Nissen E, Saripalli S,et al. 2014. Rapid mapping of ultrafine fault zone topography with structure from motion[J]. Geosphere, 10(5): 969-986.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
Li C, Pang J, Zhang Z. 2012. Characteristics, geometry, and segmentation of the surface rupture associated with the 14 April 2010 Yushu earthquake, eastern Tibet, China[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 102(4): 1618-1638.
DOI URL |
| [37] | Molnar P, Stock J M. 2009. Slowing of India's convergence with Eurasia since 20Ma and its implications for Tibetan mantle dynamics[J]. Tectonics, 28(3): 1-11. |
| [38] |
Oskin M E, Arrowsmith J R, Corona A H,et al. 2012. Near-field deformation from the El Mayor-Cucapah earthquake revealed by differential LiDAR[J]. Science, 335(6069): 702-705.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Le Dain A Y,et al. 1982. Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: New insights from simple experiments with plasticine[J]. Geology, 10(12): 611-616.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
Tapponnier P, Xu Z Q, Roger F,et al. 2001. Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibet Plateau[J]. Science, 294(5547): 1671-1677.
PMID |
| [41] |
Ren Z K, Zhang Z Q. 2019. Structural analysis of the 1997 MW7.5 Manyi earthquake and the kinematics of the Manyi Fault, central Tibetan plateau[J]. Journal of Asian Earth Sciences, 179: 149-164.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
Stirling M, Gerstenberger M, Litchfield N,et al. 2008. Seismic hazard of the Canterbury region, New Zealand: New earthquake source model and methodology[J]. Bulletin of the New Zealand Society for Earthquake Engineering, 41(2): 51-67.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
van der Woerd J, Tapponnier P, Ryerson F J,et al. 2002. Uniform postglacial slip-rate along the central 600km of the Kunlun Fault(Tibet), from 26Al, 10Be, and 14C dating of riser offsets, and climatic origin of the regional morphology[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 148(3): 356-388.
DOI URL |
| [44] | Wells D L, Coppersmith K J. 1994. New empirical relationships among magnitude, rupture length, rupture width, rupture area, and surface displacement[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 84(4): 974-1002. |
| [45] |
Wen X Z, Ma S L, Xu X W,et al. 2008. Historical pattern and behavior of earthquake ruptures along the eastern boundary of the Sichuan-Yunnan faulted-block, southwestern China[J]. Physics of the Earth and Planetary Interiors, 168(1-2): 16-36.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Wesnousky S G. 2008. Displacement and geometrical characteristics of earthquake surface ruptures: Issues and implications for seismic-hazard analysis and the process of earthquake rupture[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 98(4): 1609-1632.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Westoby M J, Brasington J, Glasser N F,et al. 2012. Structure-from-Motion photogrammetry: A low cost, effective tool for geoscience applications[J]. Geomorphology, 179: 300-314.
DOI URL |
| [48] | Xu X, Yu G, Klinger Y,et al. 2006. Reevaluation of surface rupture parameters and faulting segmentation of the 2001 Kunlunshan earthquake( MW7.8 ), northern Tibetan plateau, China[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research, 111(B5): 1-16. |
| [49] | Zhao D, Qu C, Chen H,et al. 2021. Tectonic and geometric control on fault kinematics of the 2021 MW7.3 Maduo(China)earthquake inferred from interseismic, coseismic, and postseismic InSAR observations[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 48(18): 1-12. |
| [1] | 邓文泽, 刘杰, 杨志高, 孙丽, 张雪梅. 青海玛多MS7.4地震震源破裂过程反演结果的初步分析[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(4): 1059-1070. |
| [2] | 魏延坤, 陈晓利. 不同地震滑坡危险性评价方法的适用性探讨——以玛多MS7.4地震为例[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(3): 590-603. |
| [3] | 刘小利, 夏涛, 刘静, 姚文倩, 徐晶, 邓德贝尔, 韩龙飞, 贾治革, 邵延秀, 王焱, 乐子扬, 高天琪. 2021年青海玛多MW7.4地震分布式同震地表裂缝特征[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 461-483. |
| [4] | 韩龙飞, 刘静, 姚文倩, 王文鑫, 刘小利, 高云鹏, 邵延秀, 李金阳. 2021年玛多MW7.4地震震中区地表破裂的精细填图及阶区内的分布式破裂讨论[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 484-505. |
| [5] | 邵延秀, 刘静, 高云鹏, 王文鑫, 姚文倩, 韩龙飞, 刘志军, 邹小波, 王焱, 李云帅, 刘璐. 同震地表破裂的位移测量与弥散变形分析——以2021年青海玛多MW7.4地震为例[J]. 地震地质, 2022, 44(2): 506-523. |
| [6] | 谈洪波, 王嘉沛, 杨光亮, 陈正松, 吴桂桔, 申重阳, 黄金水. 2021年玛多MS7.4地震的震后效应模拟[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 936-957. |
| [7] | 华俊, 赵德政, 单新建, 屈春燕, 张迎峰, 龚文瑜, 王振杰, 李成龙, 李彦川, 赵磊, 陈晗, 范晓冉, 王绍俊. 2021年青海玛多MW7.3地震InSAR的同震形变场、断层滑动分布及其对周边区域的应力扰动[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(3): 677-691. |
| [8] | 李智敏, 李文巧, 李涛, 徐岳仁, 苏鹏, 郭鹏, 孙浩越, 哈广浩, 陈桂华, 袁兆德, 李忠武, 李鑫, 杨理臣, 马震, 姚生海, 熊仁伟, 张彦博, 盖海龙, 殷翔, 徐玮阳, 董金元. 2021年5月22日青海玛多MS7.4地震的发震构造和地表破裂初步调查[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(3): 722-737. |
| [9] | 祁玉萍, 龙锋, 林圣杰, 肖本夫, 赵小艳, 王培玲, 冯建刚. 南北地震带中段及周边中强地震序列类型的特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(1): 177-196. |
| [10] | 谢卓娟, 李山有, 吕悦军, 徐伟进, 张愉玲, 刘雯歆. 中国海域及邻区统一地震目录及其完整性分析[J]. 地震地质, 2020, 42(4): 993-1019. |
| [11] | 吴果, 周庆, 冉洪流. 震级-频度关系中b值的极大似然法估计及其影响因素分析[J]. 地震地质, 2019, 41(1): 21-43. |
| [12] | 徐锡伟, 吴熙彦, 于贵华, 谭锡斌, 李康. 中国大陆高震级地震危险区判定的地震地质学标志及其应用[J]. 地震地质, 2017, 39(2): 219-275. |
| [13] | 吴微微, 苏金蓉, 魏娅玲, 吴朋, 李俊, 孙玮. 四川地区介质衰减、场地响应与震级测定的讨论[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(4): 1005-1018. |
| [14] | 吴富峣, 冉勇康, 陈立春, 李安. 东天山三条地震地表破裂带的展布及其与两次历史地震的关系[J]. 地震地质, 2016, 38(1): 77-90. |
| [15] | 唐茂云, 刘静, 邵延秀, 王鹏, 袁兆德. 中小震级事件产生地表破裂的震例分析[J]. 地震地质, 2015, 37(4): 1193-1214. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||