地震地质 ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 1041-1059.DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.05.001
• 云南漾濞6.4级地震与青海玛多7.4级地震研究专题 • 上一篇 下一篇
岳冲1,2)( ), 屈春燕1),*(
), 屈春燕1),*( ), 牛安福2), 赵德政1), 赵静2), 余怀忠2), 王亚丽2)
), 牛安福2), 赵德政1), 赵静2), 余怀忠2), 王亚丽2)
收稿日期:2021-06-17
修回日期:2021-08-13
出版日期:2021-10-20
发布日期:2021-12-06
通讯作者:
屈春燕
作者简介:岳冲, 男, 1989年生, 2015年于中国矿业大学(北京)获大地测量学与测量工程专业硕士学位, 助理研究员, 主要从事地壳形变监测及地球动力学研究工作, E-mail: dacongyue@126.com。
基金资助:
YUE Chong1,2)( ), QU Chun-yan1),*(
), QU Chun-yan1),*( ), NIU An-fu2), ZHAO De-zheng1), ZHAO Jing2), YU Huai-zhong2), WANG Ya-li2)
), NIU An-fu2), ZHAO De-zheng1), ZHAO Jing2), YU Huai-zhong2), WANG Ya-li2)
Received:2021-06-17
Revised:2021-08-13
Online:2021-10-20
Published:2021-12-06
Contact:
QU Chun-yan
摘要:
2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震的发震断层并不是传统意义上的巴颜喀拉块体北边界, 而是发生在巴颜喀拉块体内部一条与东昆仑断裂带主断裂近平行的次级断层上, 针对玛多地震对周边断层尤其是巴颜喀拉块体主边界造成的应力影响亟需开展研究工作。文中利用中国大陆岩石圈统一地震速度模型USTClitho1.0结果完成了研究区的岩石圈结构分层设置, 结合InSAR形变场及余震精定位结果反演得到玛多地震的同震滑动模型, 通过考虑更符合岩石圈实际变形过程的Burgers流变模型, 利用PSGRN/PSCMP程序计算得到玛多地震引起的震源区及周边断层的同震及震后黏弹性库仑应力变化。研究结果表明, 玛多 MS7.4 地震震源区同震库仑应力加载区除沿发震断层破裂面分布外, 在发震断层的西端、 东端分别有3处库仑应力变化正值区, 其中西端朝向发震断层的NW方向, 东端存在2处库仑应力加载区, 分别朝向发震断层的北部以及东部区域, 周边断层同震库仑应力变化正值段的分布与震源区库仑应力加载区的分布较为一致; 玛多地震引起的东昆仑断裂带近震源区段、 昆中断裂东段、 甘德南缘断裂西北段、 五道梁-长沙贡玛断裂中段的同震库仑应力变化均>0.01MPa, 且震后岩石圈黏弹性松弛作用使得上述断层的黏弹性库仑应力进一步增加, 未来应重点关注上述断层段的地震危险性。
中图分类号:
岳冲, 屈春燕, 牛安福, 赵德政, 赵静, 余怀忠, 王亚丽. 玛多MS7.4 地震对周边断层的应力影响分析[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1041-1059.
YUE Chong, QU Chun-yan, NIU An-fu, ZHAO De-zheng, ZHAO Jing, YU Huai-zhong, WANG Ya-li. ANALYSIS OF STRESS INFLUENCE OF QINGHAI MADUO MS7.4 EARTHQUAKE ON SURROUNDING FAULTS[J]. SEISMOLOGY AND EGOLOGY, 2021, 43(5): 1041-1059.
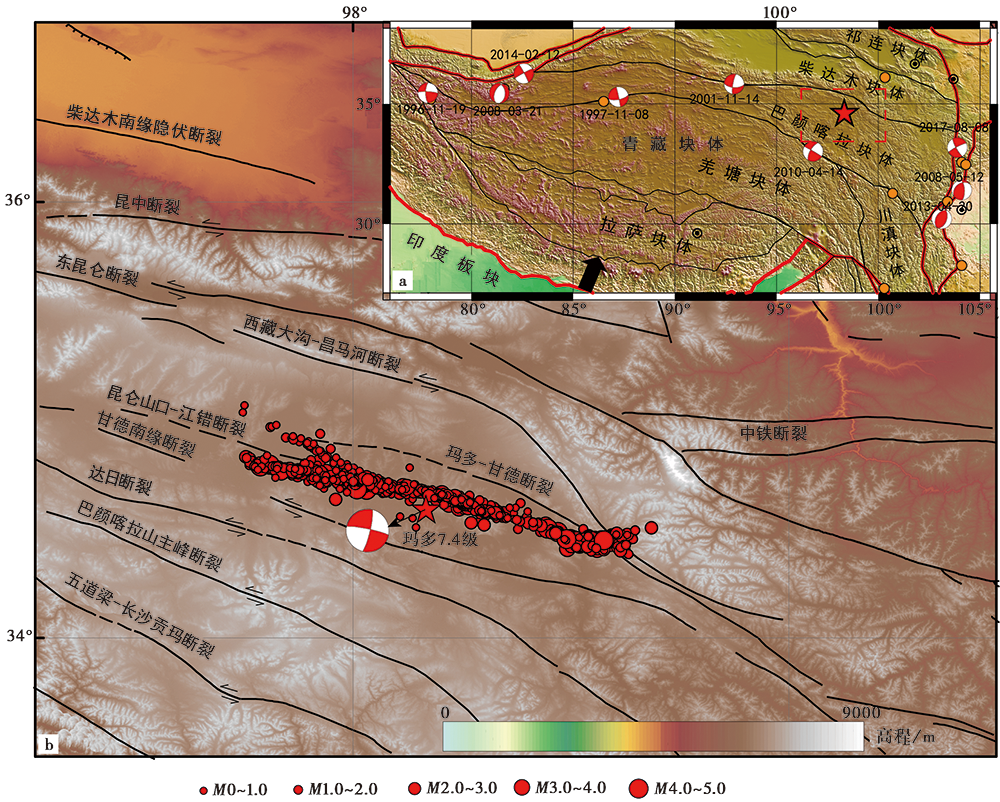
图 1 历史地震及玛多主、 余震分布图 a 巴颜喀拉块体自1970年以来MS>7.0历史地震的分布图(橙色圆点为1970年1月1日—1996年2月3日间的地震; 震源机制解为1996年2月4日—2021年5月21日间的地震; 红色五角星为2021年5月22日玛多地震的震中; 红色实线为一级块体边界, 黑色实线为二级块体边界, 黑色箭头为印度板块的推挤方向); b 玛多地震的主震、 余震分布图(截至2021年5月30日)
Fig. 1 Distribution map of historical earthquakes and Maduo main and aftershocks.
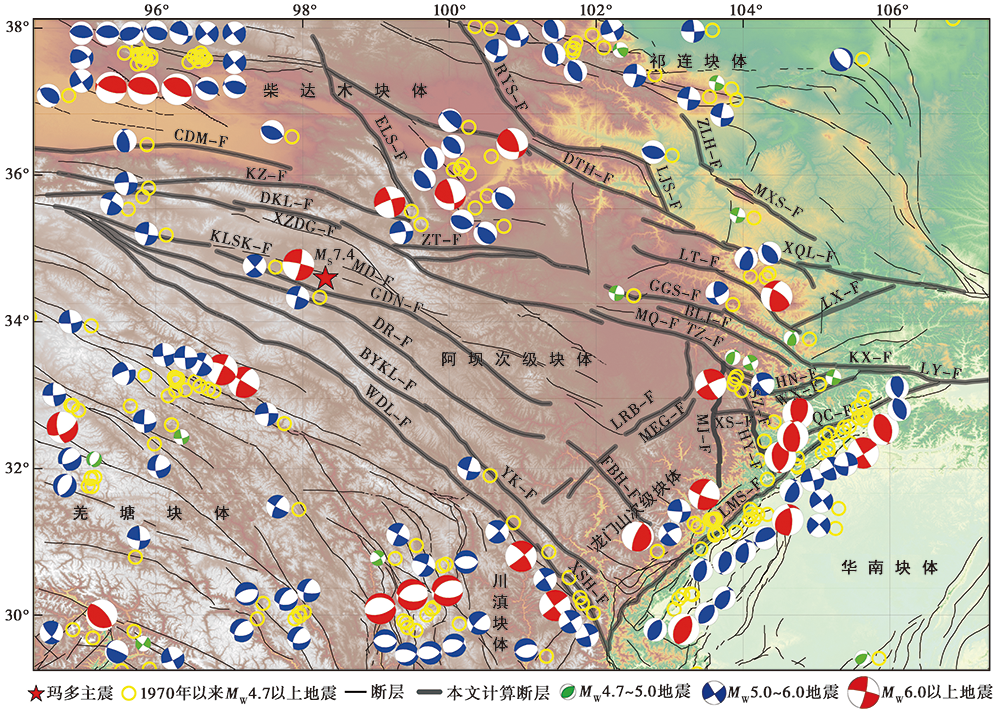
图 2 1970年以来MW>4.7历史地震及部分震源机制解分布图 KLSK-F 昆仑山口-江错断裂; MD-F 玛多-甘德断裂; XZDG-F 西藏大沟-昌马河断裂; DGN-F 甘德南缘断裂; YK-F 玉科断裂; DR-F 达日断裂; BRKL-F 巴颜喀拉主峰断裂; WDL-F 五道梁-长沙贡玛断裂; XSH-F 鲜水河断裂; LRB-F 龙日坝断裂; MEG-F 毛尔盖断裂; FBH-F 抚边河断裂; LMS 龙门山断裂; HY-F 虎牙断裂; SZ-F 树正断裂; MJ-F 岷江断裂; TZ-F 塔藏断裂; XS-F 雪山梁子断裂; DKL 东昆仑断裂; KZ-F 昆中断裂; CDM-F 柴达木南缘隐伏断裂; ZT-F 中铁断裂; MQ-F 玛曲断裂; BLJ-F 白龙江断裂; GGS-F 光盖山断裂; HN-F 哈南-稻畦子断裂; WX-F 文县断裂; QC-F 青川断裂; LY-F 略阳-勉县断裂; KX-F 康县-勉略断裂; LT-F 临潭-宕昌断裂; LX-F 礼县-罗家堡断裂; XQL-F 西秦岭北缘; ZLH-F 庄浪河断裂; DTH-F 倒淌河-临夏断裂; RYS-F 日月山断裂; LJS-F 拉脊山断裂; ELS-F 鄂拉山断裂; MXS-F马衔山断裂。圆圈为震源位置; 红色五角星为2021年5月22日玛多 MS7.4 地震的震中; 黑色实线为断层; 黑色加粗实线为本文计算断层; 震源机制解按震级大小分为绿色 MW4 ~5、 蓝色 MW5 ~6、 红色MW>6
Fig. 2 Distribution of historical earthquakes above MW4.7 and part of focal mechanism solutions since 1970.
| 序号 | 深度/km | VP/km·s-1 | VS/km·s-1 | ρ/kg·m-3 | ηk/Pa·s | ηm/Pa·s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 4.50 | 2.60 | 2 600 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 2 | 5 | 5.60 | 3.30 | 2 600 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 3 | 5 | 5.60 | 3.30 | 2 700 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 4 | 10 | 6.05 | 3.55 | 2 700 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 5 | 10 | 6.05 | 3.55 | 2 850 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 6 | 15 | 6.05 | 3.60 | 2 850 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 7 | 15 | 6.05 | 3.60 | 2 850 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 8 | 20 | 5.75 | 3.40 | 2 850 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 9 | 20 | 5.75 | 3.40 | 2 850 | 2.00×1019 | 2.00×1020 |
| 10 | 30 | 5.75 | 3.40 | 2 850 | 2.00×1019 | 2.00×1020 |
| 11 | 30 | 5.75 | 3.40 | 3 000 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 12 | 40 | 6.10 | 3.55 | 3 000 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 13 | 40 | 6.10 | 3.55 | 3 000 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 14 | 50 | 6.10 | 3.55 | 3 000 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 15 | 50 | 6.10 | 3.55 | 3 100 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 16 | 60 | 7.10 | 4.05 | 3 100 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 17 | 60 | 7.10 | 4.05 | 3 100 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 18 | 80 | 8.00 | 4.35 | 3 100 | 1.00×1020 | 1.00×1021 |
| 19 | 80 | 8.00 | 4.35 | 3 320 | 1.00×1020 | 1.00×1021 |
| 20 | 100 | 7.95 | 4.35 | 3 320 | 1.00×1020 | 1.00×1021 |
表1 岩石圈分层结构模型的参数
Table1 Parameters of the lithospheric layered structure model
| 序号 | 深度/km | VP/km·s-1 | VS/km·s-1 | ρ/kg·m-3 | ηk/Pa·s | ηm/Pa·s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | 4.50 | 2.60 | 2 600 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 2 | 5 | 5.60 | 3.30 | 2 600 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 3 | 5 | 5.60 | 3.30 | 2 700 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 4 | 10 | 6.05 | 3.55 | 2 700 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 5 | 10 | 6.05 | 3.55 | 2 850 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 6 | 15 | 6.05 | 3.60 | 2 850 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 7 | 15 | 6.05 | 3.60 | 2 850 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 8 | 20 | 5.75 | 3.40 | 2 850 | 1.00×1021 | 1.00×1022 |
| 9 | 20 | 5.75 | 3.40 | 2 850 | 2.00×1019 | 2.00×1020 |
| 10 | 30 | 5.75 | 3.40 | 2 850 | 2.00×1019 | 2.00×1020 |
| 11 | 30 | 5.75 | 3.40 | 3 000 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 12 | 40 | 6.10 | 3.55 | 3 000 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 13 | 40 | 6.10 | 3.55 | 3 000 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 14 | 50 | 6.10 | 3.55 | 3 000 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 15 | 50 | 6.10 | 3.55 | 3 100 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 16 | 60 | 7.10 | 4.05 | 3 100 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 17 | 60 | 7.10 | 4.05 | 3 100 | 6.30×1018 | 6.30×1019 |
| 18 | 80 | 8.00 | 4.35 | 3 100 | 1.00×1020 | 1.00×1021 |
| 19 | 80 | 8.00 | 4.35 | 3 320 | 1.00×1020 | 1.00×1021 |
| 20 | 100 | 7.95 | 4.35 | 3 320 | 1.00×1020 | 1.00×1021 |
| 断层名称 | 活动时代 | 断层性质 | 走向/(°) | 倾角/(°) | 滑动角/(°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘德南缘断裂(GDN-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 280~310 | 86 | 9 | |
| 玉科断裂(YK-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 285~315 | 86 | 9 | |
| 达日断裂(DR-F) | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 275~315 | 81 | 5 | |
| 巴颜喀拉主峰断裂(BRKL-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 300~325 | 72 | -3 | |
| 五道梁-长沙贡玛断裂(WDL-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 280~320 | 73 | -4 | |
| 鲜水河断裂(XSH-F) | 北段XSH1 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 310~325 | 73 | -4 |
| 中段XSH2 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 315~335 | 86 | 11 | |
| 南段XSH3 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 305~335 | 85 | -1 | |
| 龙日坝断裂(LRB-F) | 北段LRB1 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 165~180 | 75 | 0 |
| 中段LRQ | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 220~340 | 75 | 135 | |
| 南段LRB2 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 220~340 | 75 | 135 | |
| 毛尔盖断裂(MEG-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 200~235 | 60 | 90 | |
| 抚边河断裂(FBH-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 295~325 | 71 | 12 | |
| 龙门山断裂(LMS-F) | 北段LMS1 | 全新世 | 右旋走滑 | 215~235 | 84 | 178 |
| 中段LMS2 | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 220~235 | 68 | 63 | |
| 南段LMS3 | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 195~235 | 74 | 99 | |
| 虎牙断裂(HY-F) | 北段HY1 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 150 | 65 | 40 |
| 中段HY2 | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 155~175 | 60 | 90 | |
| 南段HY3 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 165 | 65 | 40 | |
| 树正断裂(SZ-F) | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 148 | 79 | -8 | |
| 岷江断裂(MJ-F) | 北段MJ1 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 1~15 | 65 | 45 |
| 中段MJ2 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 160~180 | 75 | 45 | |
| 南段MJ3 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 179 | 70 | 45 | |
| 塔藏断裂(TZ-F) | 西段TZ1 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 300~320 | 70 | 0 |
| 中段TZ2 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 280~305 | 70 | 45 | |
| 东段TZ3 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 100~120 | 55 | 45 | |
| 雪山梁子断裂(XS-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 265~285 | 65 | 90 | |
| 东昆仑断裂(DKL-F) | 西段 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 275~290 | 61 | -12 |
| 东段 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 275~320 | 83 | -20 | |
| 昆中断裂(KZ-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 265~295 | 88 | 29 | |
| 柴达木南缘隐伏断裂(CDM-F) | 更新世 | 逆冲 | 80~115 | 33 | 123 | |
| 中铁断裂(ZT-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 265~300 | 61 | -12 | |
| 玛曲断裂(MQ-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 290 | 80 | 45 | |
| 白龙江断裂(BLJ-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 290 | 75 | 45 | |
| 光盖山断裂(GGS-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 110 | 81 | -14 | |
| 哈南-稻畦子断裂(HN-F) | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 70 | 90 | 0 | |
| 文县断裂(WX-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 75 | 60 | 90 | |
| 青川断裂(QC-F) | 更新世 | 右旋走滑 | 245 | 70 | 180 | |
| 略阳-勉县断裂(LY-F) | 更新世 | 右旋走滑 | 245 | 70 | 180 | |
| 康县-勉略断裂(KX-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 280 | 75 | 20 | |
| 临潭-宕昌断裂(LT-F) | 更新世 | 逆冲 | 320 | 60 | 90 | |
| 礼县-罗家堡断裂(LX-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 65 | 70 | 0 | |
| 西秦岭北缘(XQL-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 275 | 65 | 45 | |
| 庄浪河断裂(ZLH-F) | 更新世 | 逆冲 | 150~170 | 60 | 80 | |
| 倒淌河-临夏断裂(DTH-F) | 更新世 | 逆冲 | 290~300 | 78 | 102 | |
| 日月山断裂(RYS-F) | 全新世 | 右旋走滑 | 135~155 | 80 | 180 | |
| 拉脊山断裂(LJS-F) | 更新世 | 逆断 | 270~330 | 50 | 90 | |
| 鄂拉山断裂(ELS-F) | 全新世 | 右旋走滑 | 300~340 | 80 | -170 | |
| 马衔山断裂(MXS-F) | 更新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 295~310 | 80 | 45 | |
表2 接收断层的主要参数
Table2 Main parameters of the receiving faults
| 断层名称 | 活动时代 | 断层性质 | 走向/(°) | 倾角/(°) | 滑动角/(°) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 甘德南缘断裂(GDN-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 280~310 | 86 | 9 | |
| 玉科断裂(YK-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 285~315 | 86 | 9 | |
| 达日断裂(DR-F) | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 275~315 | 81 | 5 | |
| 巴颜喀拉主峰断裂(BRKL-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 300~325 | 72 | -3 | |
| 五道梁-长沙贡玛断裂(WDL-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 280~320 | 73 | -4 | |
| 鲜水河断裂(XSH-F) | 北段XSH1 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 310~325 | 73 | -4 |
| 中段XSH2 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 315~335 | 86 | 11 | |
| 南段XSH3 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 305~335 | 85 | -1 | |
| 龙日坝断裂(LRB-F) | 北段LRB1 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 165~180 | 75 | 0 |
| 中段LRQ | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 220~340 | 75 | 135 | |
| 南段LRB2 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 220~340 | 75 | 135 | |
| 毛尔盖断裂(MEG-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 200~235 | 60 | 90 | |
| 抚边河断裂(FBH-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 295~325 | 71 | 12 | |
| 龙门山断裂(LMS-F) | 北段LMS1 | 全新世 | 右旋走滑 | 215~235 | 84 | 178 |
| 中段LMS2 | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 220~235 | 68 | 63 | |
| 南段LMS3 | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 195~235 | 74 | 99 | |
| 虎牙断裂(HY-F) | 北段HY1 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 150 | 65 | 40 |
| 中段HY2 | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 155~175 | 60 | 90 | |
| 南段HY3 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 165 | 65 | 40 | |
| 树正断裂(SZ-F) | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 148 | 79 | -8 | |
| 岷江断裂(MJ-F) | 北段MJ1 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 1~15 | 65 | 45 |
| 中段MJ2 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 160~180 | 75 | 45 | |
| 南段MJ3 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 179 | 70 | 45 | |
| 塔藏断裂(TZ-F) | 西段TZ1 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 300~320 | 70 | 0 |
| 中段TZ2 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 280~305 | 70 | 45 | |
| 东段TZ3 | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 100~120 | 55 | 45 | |
| 雪山梁子断裂(XS-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 265~285 | 65 | 90 | |
| 东昆仑断裂(DKL-F) | 西段 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 275~290 | 61 | -12 |
| 东段 | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 275~320 | 83 | -20 | |
| 昆中断裂(KZ-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 265~295 | 88 | 29 | |
| 柴达木南缘隐伏断裂(CDM-F) | 更新世 | 逆冲 | 80~115 | 33 | 123 | |
| 中铁断裂(ZT-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 265~300 | 61 | -12 | |
| 玛曲断裂(MQ-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 290 | 80 | 45 | |
| 白龙江断裂(BLJ-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 290 | 75 | 45 | |
| 光盖山断裂(GGS-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 110 | 81 | -14 | |
| 哈南-稻畦子断裂(HN-F) | 全新世 | 左旋走滑 | 70 | 90 | 0 | |
| 文县断裂(WX-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲 | 75 | 60 | 90 | |
| 青川断裂(QC-F) | 更新世 | 右旋走滑 | 245 | 70 | 180 | |
| 略阳-勉县断裂(LY-F) | 更新世 | 右旋走滑 | 245 | 70 | 180 | |
| 康县-勉略断裂(KX-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 280 | 75 | 20 | |
| 临潭-宕昌断裂(LT-F) | 更新世 | 逆冲 | 320 | 60 | 90 | |
| 礼县-罗家堡断裂(LX-F) | 更新世 | 左旋走滑 | 65 | 70 | 0 | |
| 西秦岭北缘(XQL-F) | 全新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 275 | 65 | 45 | |
| 庄浪河断裂(ZLH-F) | 更新世 | 逆冲 | 150~170 | 60 | 80 | |
| 倒淌河-临夏断裂(DTH-F) | 更新世 | 逆冲 | 290~300 | 78 | 102 | |
| 日月山断裂(RYS-F) | 全新世 | 右旋走滑 | 135~155 | 80 | 180 | |
| 拉脊山断裂(LJS-F) | 更新世 | 逆断 | 270~330 | 50 | 90 | |
| 鄂拉山断裂(ELS-F) | 全新世 | 右旋走滑 | 300~340 | 80 | -170 | |
| 马衔山断裂(MXS-F) | 更新世 | 逆冲兼走滑 | 295~310 | 80 | 45 | |
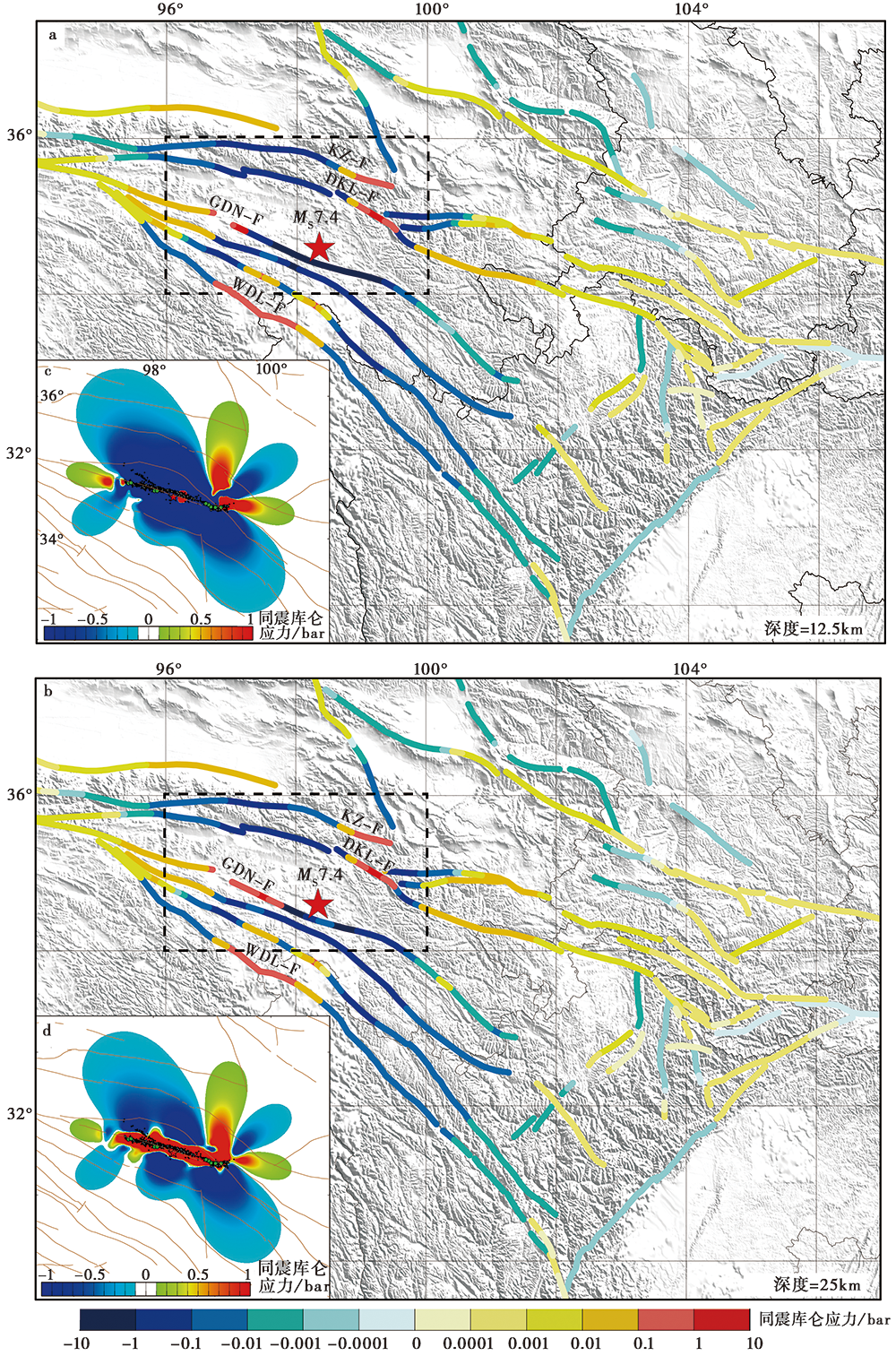
图 4 震源区及周边断层的同震库仑应力结果 a、 c分别为震源区及周边断层的结果, 计算深度为12.5km; b、 d分别为震源区及周边断层的结果,计算深度为25km。红色五角星为玛多主震的位置; 黑色虚线框为图c与图d所示区域; 有效摩擦系数取0.4
Fig. 4 Co-seismic Coulomb stress change in the source area and surrounding faults.
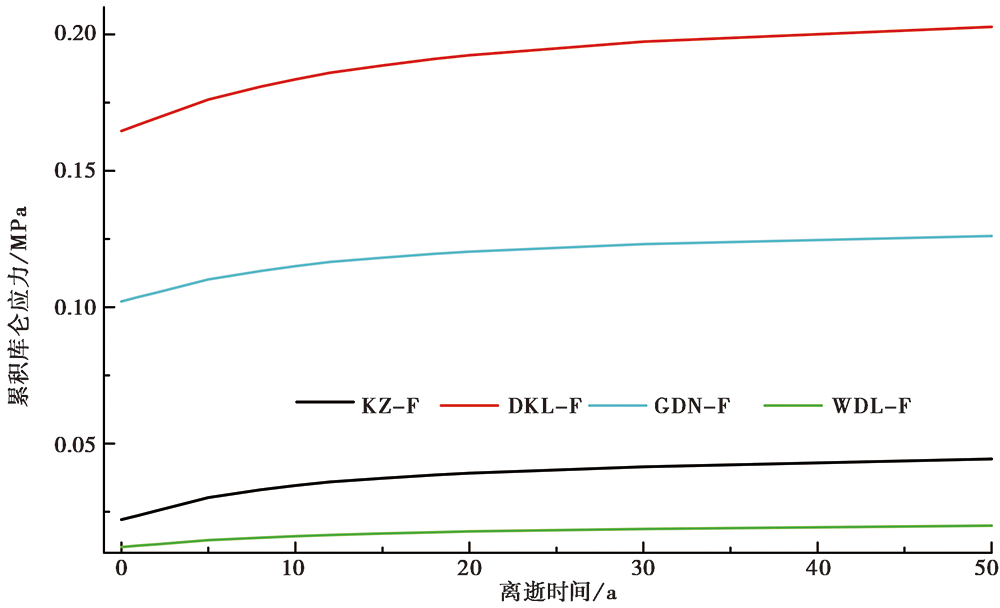
图 5 玛多震后50a间黏弹性库仑应力累积变化时序曲线图(μ'=0.4)
Fig.5 Time series curve of cumulative viscoelastic Coulomb stress change in 50 years after the Maduo(Qinghai)earthquake(μ'=0.4).
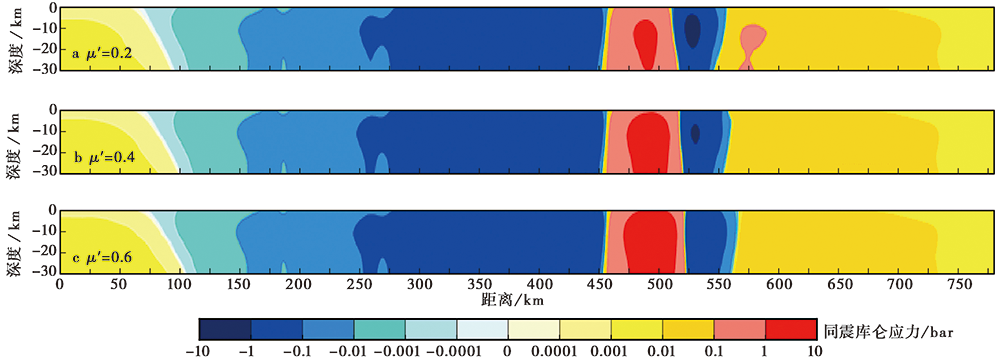
图 6 不同有效摩擦系数下东昆仑断裂带的同震库仑应力变化结果 a 有效摩擦系数为0.2; b 有效摩擦系数为0.4; c 有效摩擦系数为0.6
Fig. 6 Co-seismic Coulomb stress changes in the DKL-F under different effective friction coefficients.
| [1] | 程佳, 姚生海, 刘杰, 等. 2018. 2017年九寨沟地震所受历史地震黏弹性库仑应力作用及其后续对周边断层地震危险性的影响[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(5): 2133-2151. |
| CHENG Jia, YAO Sheng-hai, LIU Jie, et al. 2018. Viscoelastic Coulomb stress of historical earthquakes on the 2017 Jiuzhaigou earthquake and the subsequent influence on the seismic hazards of adjacent faults[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(5): 2133-2151. (in Chinese) | |
| [2] |
邓起东, 程绍平, 马冀, 等. 2014. 青藏高原地震活动特征及当前地震活动形势[J]. 地球物理学报, 57(7): 2025-2042. doi: 10.6038/cjg20140701.
DOI |
| DENG Qi-dong, CHENG Shao-ping, MA Ji, et al. 2014. Seismic activities and earthquake potential in the Tibetan plateau[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 57(7): 2025-2042. (in Chinese) | |
| [3] | 邓起东, 高翔, 陈桂华, 等. 2010. 青藏高原昆仑-汶川地震系列与巴颜喀喇断块的最新活动[J]. 地学前缘, 17(5): 163-178. |
| DENG Qi-dong, GAO Xiang, CHEN Gui-hua, et al. 2010. Recent tectonic activity of Bayankala fault-block and the Kunlun-Wenchuan earthquake series of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 17(5): 163-178. (in Chinese) | |
| [4] | 国家地震局震害防御司. 1995. 中国历史强震目录 [Z]. 北京: 地震出版社. |
| Department of Seismic Hazard Prevention, China Earthquake Administration. 1995. The Catalogue of Chinese Historical Strong Earthquakes [Z]. Seismological Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [5] |
华俊, 赵德政, 单新建, 等. 2021. 2021年青海玛多 MW7.3 地震InSAR的同震形变场、 断层滑动分布及其对周边区域的应力扰动[J]. 地震地质, 43(3): 677-691. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2021.03.013.
DOI |
| HUA Jun, ZHAO De-zheng, SHAN Xin-jian, et al. 2021. Coseismic deformation field, slip distribution and Coulomb stress disturbance of the 2021 MW7.3 Maduo earthquake using Sentinel-1 InSAR observations[J]. Seismology and Geology, 43(3): 677-691. (in Chinese) | |
| [6] |
雷兴林, 马胜利, 苏金蓉, 等. 2013. 汶川地震后中下地壳及上地幔的黏弹性效应引起的应力变化与芦山地震的发生机制[J]. 地震地质, 35(2): 411-422. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2013.02.019.
DOI |
| LEI Xing-lin, MA Sheng-li, SU Jin-rong, et al. 2013. Inelastic triggering of the 2013 MW6.6 Lushan earthquake by the 2008 MW7.9 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Seismology and Geology, 35(2): 411-422. (in Chinese) | |
| [7] |
梁明剑, 杨耀, 杜方, 等. 2020. 青海达日断裂中段晚第四纪活动性与1947年M7¾地震地表破裂带再研究[J]. 地震地质, 42(3): 703-714. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4967.2020.03.011.
DOI |
| LIANG Ming-jian, YANG Yao, DU Fang, et al. 2020. Late Quaternary activity of the central segment of the Dari Fault and restudy of the surface rupture zone of the 1947 M7¾ Dari earthquake, Qinghai Province[J]. Seismology and Geology, 42(3): 703-714. (in Chinese) | |
| [8] | 马保起, 苏刚, 侯治华, 等. 2005. 利用岷江阶地的变形估算龙门山断裂带中段晚第四纪滑动速率[J]. 地震地质, 27(2): 234-242. |
| MA Bao-qi, SU Gang, HOU Zhi-hua, et al. 2005. Late Quaternary slip rate in the central part of the Longmenshan fault zone from terrace deformation along the Minjiang River[J]. Seismology and Geology, 27(2): 234-242. (in Chinese) | |
| [9] | 任金卫, 王敏. 2005. GPS观测的2001年昆仑山口西 MS8.1 地震地壳变形[J]. 第四纪研究, 25(1): 34-44. |
| REN Jin-wei, WANG Min. 2005. GPS measured crustal deformation of the MS8.1 Kunlun earthquake on November 14th 2001 in Qinghai-Xizang plateau[J]. Quaternary Sciences, 25(1): 34-44. (in Chinese) | |
| [10] | 任俊杰, 徐锡伟, 张世民, 等. 2017. 东昆仑断裂带东端的构造转换与2017年九寨沟 MS7.0 地震孕震机制[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(10): 4027-4045. |
| REN Jun-jie, XU Xi-wei, ZHANG Shi-min, et al. 2017. Tectonic transformation at the eastern termination of the eastern Kunlun fault zone and seismogenic mechanism of the 8 August 2017 Jiuzhaigou MS70 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(10): 4027-4045. (in Chinese) | |
| [11] | 任天翔, 程惠红, 张贝, 等. 2018. 2001年昆仑山口西 MS8.1 地震对周围断层的应力影响数值分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 61(12): 4838-4850. |
| REN Tian-xiang, CHENG Hui-hong, ZHANG Bei, et al. 2018. Numerical study on the co-seismic stress changes of surrounding faults due to the MS8.1 earthquake, 2001, Kokoxili earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 61(12): 4838-4850. (in Chinese) | |
| [12] | 邵志刚, 傅容珊, 薛霆虓, 等. 2008. 震后短期和长期形变模拟: 以1960年智利 MW9.5 地震为例[J]. 地震学报, 30(4): 405-415. |
| SHAO Zhi-gang, FU Rong-shan, XUE Ting-xiao, et al. 2008. Modeling transient and long-term postseismic deformation: A case study of 1960 MW9.5 Chile earthquake[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 30(4): 405-415. (in Chinese) | |
| [13] | 沈正康, 万永革, 甘卫军, 等. 2003. 东昆仑活动断裂带大地震之间的黏弹性应力触发研究[J]. 地球物理学报, 46(6): 786-795. |
| SHEN Zheng-kang, WAN Yong-ge, GAN Wei-jun, et al. 2003. Viscoelastic triggering among lager earthquakes along the east Kunlun fault system[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 46(6): 786-795. (in Chinese) | |
| [14] | 石耀霖, 曹建玲. 2008. 中国大陆岩石圈等效黏滞系数的计算和讨论[J]. 地学前缘, 15(3): 82-95. |
|
SHI Yao-lin, CAO Jian-ling. 2008. Effective viscosity of China continental lithosphere[J]. Earth Science Frontiers, 15(3): 82-95. (in Chinese)
DOI URL |
|
| [15] | 石耀霖, 曹建玲. 2010. 库仑应力计算及应用过程中若干问题的讨论: 以汶川地震为例[J]. 地球物理学报, 53(1): 102-110. |
| SHI Yao-lin, CAO Jian-ling. 2010. Some aspects in static stress change calculation: Case study on Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 53(1): 102-110. (in Chinese) | |
| [16] | 万永革, 沈正康, 曾跃华, 等. 2007. 青藏高原东北部的库仑应力积累演化对大地震发生的影响[J]. 地震学报, 29(2): 115-129. |
| WAN Yong-ge, SHEN Zheng-kang, ZENG Yue-hua, et al. 2007. Evolution of cumulative Coulomb failure stress in northeastern Qinghai-Xizang(Tibetan)plateau and its effect on large earthquake occurrence[J]. Acta Seismologica Sinica, 29(2): 115-129. (in Chinese) | |
| [17] | 闻学泽. 2000. 四川西部鲜水河-安宁河-则木河断裂带的地震破裂分段特征[J]. 地震地质, 22(3): 239-249. |
| WEN Xue-ze. 2000. Character of rupture segmentation of the Xianshuihe-Anninghe-Zemuhe fault zone, western Sichuan[J]. Seismology and Geology, 22(3): 239-249. (in Chinese) | |
| [18] | 闻学泽, 杜方, 张培震, 等. 2011. 巴颜喀拉块体北和东边界大地震序列的关联性与2008年汶川地震[J]. 地球物理学报, 54(3): 706-716. |
| WEN Xue-ze, DU Fang, ZHANG Pei-zhen, et al. 2011. Correlation of major earthquake sequences on the northern and eastern boundaries of the Bayan Har block, and its relation to the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 54(3): 706-716. (in Chinese) | |
| [19] | 解朝娣, 朱元清, 雷兴林, 等. 2010. MS8.0 汶川地震产生的应力变化空间分布及其对地震活动性的影响[J]. 中国科学(D辑), 40(6): 688-698. |
| XIE Zhao-di, ZHU Yuan-qing, LEI Xing-lin, et al. 2010. Pattern of stress change and its effect on seismicity rate caused by MS8.0 Wenchuan earthquake[J]. Science of China(Ser D), 40(6): 688-698. (in Chinese) | |
| [20] | 熊仁伟, 任金卫, 张军龙, 等. 2010. 玛多-甘德断裂甘德段晚第四纪活动特征[J]. 地震, 30(4): 65-73. |
| XIONG Ren-wei, REN Jin-wei, ZHANG Jun-long, et al. 2010. Late Quaternary active characteristics of the Gande segment in the Maduo-Gande fault zone[J]. Earthquake, 30(4): 65-73. (in Chinese) | |
| [21] | 熊维, 谭凯, 刘刚, 等. 2015. 2015年尼泊尔 MW7.9 地震对青藏高原活动断裂同震、 震后应力影响[J]. 地球物理学报, 58(11): 4305-4316. |
| XIONG Wei, TAN Kai, LIU Gang, et al. 2015. Coseismic and postseismic Coulomb stress changes on the surrounding major faults caused by the 2015 Nepal MW7.9 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 58(11): 4305-4316. (in Chinese) | |
| [22] | 易桂喜, 龙锋, 梁明剑, 等. 2017. 2017年8月8日九寨沟M7.0地震及余震震源机制解与发震构造分析[J]. 地球物理学报, 60(10): 4083-4097. |
| YI Gui-xi, LONG Feng, LIANG Ming-jian, et al. 2017. Focal mechanism solution and seismogenic structure of the 8 August 2017 M70 Jiuzhaigou earthquake and its aftershocks, northern Sichuan[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 60(10): 4083-4097. (in Chinese) | |
| [23] | 詹艳, 梁明剑, 孙翔宇, 等. 2021. 2021年5月22日青海玛多 MS7.4 地震深部环境及发震构造模式[J]. 地球物理学报, 64(7): 2232-2252. |
| ZHAN Yan, LIANG Ming-jian, SUN Xiang-yu, et al. 2021. Deep structure and seismogenic pattern of the 2021.5.22 Maduo(Qinghai) MS7.4 earthquake[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 64(7): 2232-2252. (in Chinese) | |
| [24] | 郑文俊, 袁道阳, 何文贵, 等. 2013. 甘肃东南地区构造活动与2013年岷县-漳县 MS6.6 地震孕震机制[J]. 地球物理学报, 56(12): 4058-4071. |
| ZHENG Wen-jun, YUAN Dao-yang, HE Wen-gui, et al. 2013. Geometric pattern and active tectonics in southeastern Gansu Province: Discussion on seismogenic mechanism of the Minxian-Zhangxian MS6.6 earthquake on July 22, 2013[J]. Chinese Journal of Geophysics, 56(12): 4058-4071. (in Chinese) | |
| [25] | 中国地震局震害防御司. 1999. 中国近代地震目录(公元1912-1990年)[Z]. 北京: 中国科学技术出版社. |
| Department of Seismic Hazard Prevention, China Earthquake Administration. 1999. Catalogue of Recent Chinese Earthquakes(1912-1990, MS≥4.7)[Z]. China Science and Technology Press, Beijing. (in Chinese) | |
| [26] |
Ali S T, Freed A M, Calais E, et al. 2008. Coulomb stress evolution in northeastern Caribbean over the past 250 years due to coseismic, postseismic and interseismic deformation[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 174(3): 904-918.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
Allen C R, Luo Z L, Qian H, et al. 1991. Field study of a highly active fault zone: The Xianshuihe Fault of southwestern China[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 103(9): 1178-1199.
DOI URL |
| [28] | Cattin R, Avouac J P. 2000. Modeling mountain building and the seismic cycle in the Himalaya of Nepal[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 105(B6): 13389-13407. |
| [29] |
Cotton F, Coutant O. 1997. Dynamic stress variations due to shear faults in a plane-layered medium[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 128(3): 676-688.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
Diao F Q, Xiong X, Wang R J. 2010. Mechanisms of transient postseismic deformation following the 2001 MW7.8 Kunlun(China)earthquake[J]. Pure and Applied Geophysics, 168(5): 767-779. doi: 10.1007/s00024-010-0154-5.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
Freed A M. 2005. Earthquake triggering by static, dynamic, and postseismic stress transfer[J]. Annual Review of Earth and Planetary Sciences, 33(1): 335-367.
DOI URL |
| [32] | Freed A M, Lin J. 1998. Time-dependent changes in failure stress following thrust earthquakes[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 103(B10): 24393-24409. |
| [33] |
Freed A M, Lin J. 2001. Delayed triggering of the 1999 Hector Mine earthquake by viscoelastic stress transfer[J]. Nature, 411(6834): 180-183.
DOI URL |
| [34] | Gan W J, Zhang P Z, Shen Z K, et al. 2007. Present-day crustal motion within the Tibetan plateau inferred from GPS measurements[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 112(B8): B08416. |
| [35] |
Hetland E A, Hager B H. 2006. The effects of rheological layering on post-seismic deformation[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 166(1): 277-292.
DOI URL |
| [36] | Hilley G E, Bürgmann R, Zhang P Z, et al. 2005. Bayesian inference of plastosphere viscosities near the Kunlun Fault, northern Tibet[J]. Geophysical Research Letters, 32(1): L01302. |
| [37] | Huang J, Zhao D. 2006. High-resolution mantle tomography of China and surrounding regions[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 111(B9): B09305. |
| [38] | Johnson K M, Hilley G E, Burgmann R. 2007. Influence of lithosphere viscosity structure on estimates of fault slip rate in the Mojave region of the San Andreas fault system[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 112(B7): B07408. |
| [39] | Kilb D. 2003. A strong correlation between induced peak dynamic Coulomb stress change from the 1992 M 7.3 Landers, California, earthquake and the hypocenter of the 1999 M 7.1 Hector Mine, California, earthquake[J]. Journal of Geophysical Research: Solid Earth, 108(B1): ESE3-1-ESE3-7. |
| [40] | Kirby E, Harkins N, Wang E, et al. 2007. Slip rate gradients along the eastern Kunlun Fault[J]. Tectonics, 26(2): p. TC2010.1-TC2010.16. |
| [41] |
Kirby E, Whipple K X, Burchfiel B C, et al. 2000. Neotectonics of the Min Shan, China: Implications for mechanisms driving Quaternary deformation along the eastern margin of the Tibetan plateau[J]. Geological Society of America Bulletin, 112(3): 375-393.
DOI URL |
| [42] | Lay T, Wallace T C. 1995. Modern Global Seismology[M]. Academic Press. |
| [43] |
Liu Q Y, van der Hilst R D, Li Y, et al. 2014. Eastward expansion of the Tibetan plateau by crustal flow and strain partitioning across faults[J]. Nature Geoscience, 7(5): 361-365. doi: 10.1038/ngeo2130.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
Okada Y. 1985. Surface deformation due to shear and tensile faults in a half space[J]. Bulletin of the Seismological Society of America, 75(4): 1135-1154.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
Ren J J, Xu X W, Yeats R S, et al. 2013a. Millennial slip rates of the Tazang Fault, the eastern termination of Kunlun Fault: Implications for strain partitioning in eastern Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 608(1): 1180-1200. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.06.026.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
Ren J J, Xu X W, Yeats R S, et al. 2013b. Holocene paleoearthquakes of the Maoergai Fault, eastern Tibet[J]. Tectonophysics, 590(1): 121-135. doi: 10.1016/j.tecto.2013.01.017.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
Ren J J, Xu X W, Yeats R S, et al. 2013c. Latest Quaternary paleoseismology and slip rates of the Longriba fault zone, eastern Tibet: Implications for fault behavior and strain partitioning[J]. Tectonics, 32(2): 216-238. doi: 10.1002/tect.20029.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
Ryder I, Bürgmann R, Pollitz F. 2011. Lower crustal relaxation beneath the Tibetan plateau and Qaidam Basin following the 2001 Kokoxili earthquake[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 187(2): 613-630. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-246x.2011.05179.x.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
Wang R J, Lorenzo-Martin F, Roth F. 2006. PSGRN/PSCMP: A new code for calculating co- and post-seismic deformation, geoid and gravity changes based on the viscoelastic-gravitational dislocation theory[J]. Computers & Geosciences, 32(4): 527-541.
DOI URL |
| [50] | Wang R, Motagh M R, Walter T R. 2008. Inversion of slip distribution from co-seismic deformation data by a sensitivity based iterative fitting method[C]. EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 10: EGU2008-A-07971. |
| [51] |
Xin H L, Zhang H J, Min K, et al. 2018. High-resolution lithospheric velocity structure of continental China by double-difference seismic travel-time tomography[J]. Seismological Research Letters, 90(1): 229-241. doi: 10.1785/0220180209.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
Yao H J, Beghein C, van der Hilst R D. 2018. Surface wave array tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis-Ⅱ. Crustal and upper-mantle structure[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 173(1): 205-219.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
Yao H J, van der Hilst R D, de Hoop M V. 2006. Surface-wave array tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis-Ⅰ. Phase velocity maps[J]. Geophysical Journal International, 166(2): 732-744.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
Zhang H P, Liu S F, Yang N, et al. 2006. Geomorphic characteristics of the Minjiang drainage basin(eastern Tibetan plateau)and its tectonic implications: New insights from a digital elevation model study[J]. Island Arc, 15(2): 239-250.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
Zhang Z J, Yuan X H, Chen Y, et al. 2010. Seismic signature of the collision between the east Tibetan escape flow and the Sichuan Basin[J]. Earth and Planetary Science Letters, 292(3-4): 254-264. doi: 10.1016/j.pngl.2010.01.046.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 李经纬, 陈长云, 占伟, 武艳强. 青海玛多7.4级地震GNSS同震水平位移的快速获取[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1073-1084. |
| [2] | 姚生海, 盖海龙, 殷翔, 李鑫. 青海玛多MS7.4地震地表破裂带的基本特征和典型现象[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(5): 1060-1072. |
| [3] | 赵韬, 王莹, 马冀, 邵若潼, 徐一斐, 胡景. 2021年青海玛多7.4级地震序列重定位和震源机制特征[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(4): 790-805. |
| [4] | 王绍俊, 刘云华, 单新建, 屈春燕, 张国宏, 解朝娣, 赵德政, 范晓冉, 华俊, 梁诗明, 张克亮, 代成龙. 2021年云南漾濞MS6.4地震同震地表形变与断层滑动分布[J]. 地震地质, 2021, 43(3): 692-705. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||